
- Introduction to Operations Management
- The Role of Operations Management in Business
- Key Functions of Operations Management
- The Importance of Operations Management in Business Success
- Key Skills Required for Effective Operations Management
- Operations Management Models and Frameworks
- Challenges in Operations Management
- The Role of Technology in Operations Management
- Best Practices in Operations Management
- Conclusion
Introduction to Operations Management
In the competitive world of business, efficiency is key to success. Whether a company is manufacturing products, providing services, or operating in any other industry, smooth and effective operations are crucial to meeting customer expectations, maximizing profitability, and achieving long-term growth. This is where Operations Management (OM) comes into play. It involves managing the processes that transform inputs—like raw materials, labor, and capital into finished products or services. As a multidisciplinary field combining engineering, management, and strategy, it often aligns closely with Project Management Training to ensure efficient project execution and operational success. It involves overseeing production processes, supply chains, quality control, and more, to ensure businesses operate efficiently and effectively. In this guide, we’ll dive deeper into the meaning of Operations Management, its importance in business, its key functions, the challenges faced by professionals in the field, and the best practices you can implement to optimize your operations for success.
The Role of Operations Management in Business
Operations Management (OM) plays a central role in ensuring that a company runs smoothly. While the focus of marketing, sales, and finance may be on external factors such as customer acquisition or financial health, OM focuses on internal processes that directly impact how products and services are delivered. The role of operations management can be summed up as ensuring that the resources available to a business (including labor, technology, and materials) are used efficiently to create value—an essential concept for those looking to Learn Project Management tools and improve organizational effectiveness. Efficient operations lead to reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, better product quality, and a competitive edge in the market. The field of OM is applicable across industries, from manufacturing to service-based businesses. Regardless of the sector, operations management involves optimizing processes, managing resources, and ensuring the continuous delivery of high-quality products and services to customers.
Would You Like to Know More About Project Management? Sign Up For Our Project Management Course Training Now!
Key Functions of Operations Management
Operations management is a broad field with several critical functions. Below are some of the most important aspects of OM:
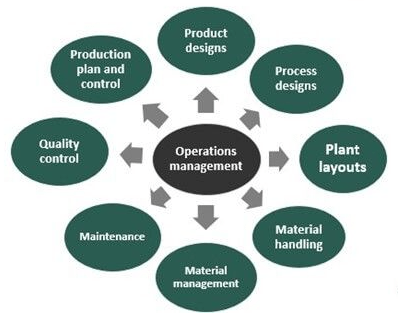
Product Design and DevelopmentA crucial function of operations management is ensuring that the products being developed meet customer needs and can be efficiently produced at scale. Operations managers work with product development teams to ensure that products are designed in ways that streamline manufacturing and minimize costs. This includes decisions on materials, features, and manufacturability. Efficient product design not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces waste and improves cost-efficiency in production.
Process ManagementAt the heart of operations management is process management, which is the design, execution, monitoring, and optimization of processes involved in creating a product or service. Process management ensures that workflows are streamlined, bottlenecks are minimized, and operations are consistently running at peak efficiency. Operations managers focus on standardizing processes, eliminating waste, and improving productivity. This could involve automation, refining the sequence of steps, or applying Agile principles and improving the use of technology to make production smoother and faster.
Supply Chain ManagementSupply chain management (SCM) refers to the coordination of all activities involved in obtaining materials, manufacturing products, and delivering them to customers. This includes sourcing raw materials, managing relationships with suppliers, and overseeing logistics. Operations managers play a crucial role in SCM by selecting reliable suppliers, negotiating contracts, managing inventory levels, and ensuring the timely delivery of products. Effective supply chain management ensures that products are available when needed, which is critical to maintaining customer satisfaction and minimizing delays.
Quality Control and ImprovementQuality is a top priority in operations management. Operations managers are responsible for maintaining the standards of the products and services delivered. This involves implementing quality control processes, which can include regular inspections, testing, and audits to ensure that the products meet the required specifications. Additionally, continuous improvement techniques like Lean, Six Sigma, and Kaizen are often employed to refine operations and eliminate inefficiencies, ensuring that quality does not slip over time.
Inventory ManagementInventory management is a core responsibility of operations management. It involves maintaining the right amount of raw materials, work-in-progress goods, and finished products to meet demand without overstocking or running out of items. Poor inventory management can lead to either waste and increased costs or missed sales due to shortages. Operations managers use techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory and economic order quantity (EOQ) to balance supply and demand, reduce holding costs, and improve cash flow.
The Importance of Operations Management in Business Success
Operations management is integral to the success of any business for several reasons, including its role in aligning processes with the Product Roadmap to ensure efficient execution and delivery.
- Cost Efficiency: Effective operations reduce costs through better resource management, streamlined processes, and waste reduction. Businesses that can control operational costs while maintaining quality have a competitive edge in pricing.
- Customer Satisfaction: Operations management ensures that customers receive high-quality products or services on time. Meeting customer expectations is key to building loyalty and retaining business.
- Increased Profitability: By optimizing processes, reducing waste, and improving the quality of products, OM helps improve the bottom line. Companies with strong operations can achieve economies of scale and deliver higher profit margins.
- Sustainability: Operations managers are increasingly focused on making processes environmentally sustainable. From reducing energy consumption to eliminating waste, OM can help businesses achieve sustainability goals that are important to customers and stakeholders.
- Leadership and Decision-Making: An operations manager must be able to make informed, timely decisions that drive efficiency and productivity, even in high-pressure situations.
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze data, identify trends, and use insights to improve operations is crucial.
- Project Management: OM professionals must manage multiple projects, allocate resources, and meet deadlines, requiring strong organizational and time-management skills.
- Process Optimization: Operations managers need to identify inefficiencies and create solutions that streamline processes.
- Communication: Effective communication, often reinforced through Project Management Training, is essential for coordinating with teams, suppliers, and stakeholders to keep operations running smoothly.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: External factors such as natural disasters or geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains, leading to delays and increased costs.
- Technology Integration: Adopting and integrating new technologies can be costly and complex.
- Maintaining Quality Control: As businesses scale, maintaining consistent product quality can become more challenging, requiring continuous attention and improvement.
- Global Competition: Companies face increasing competition from both local and global markets, requiring efficient operations to stay ahead.
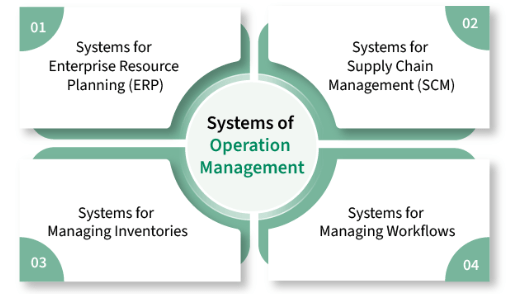
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems: These systems integrate various functions like finance, human resources, and supply chain management into one cohesive system.
- Automation and Robotics: Automation of repetitive tasks can free up human resources for higher-value work.
- Data Analytics: Real-time data collection and analysis can help make informed decisions and predict trends, reducing risks and optimizing operations.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: Regularly review processes and strive for continuous improvement through feedback, innovation, and adopting new technologies.
- Leverage Technology: Implement ERP systems and automation tools to streamline processes and improve efficiency.
- Adopt Lean Principles: Reduce waste and enhance value by applying lean management principles.
- Empower Employees: Foster a culture of collaboration and empowerment, where employees are encouraged to contribute ideas for improving operations.
Interested in Obtaining Your Project Management Certificate? View The Project Management Course Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Key Skills Required for Effective Operations Management
To succeed in operations management, professionals must possess a diverse set of skills that encompass leadership, technical knowledge, and problem-solving capabilities. Below are some of the key skills for an effective operations manager:
Operations Management Models and Frameworks
Various models and frameworks have been developed to help businesses optimize their operations. Some of the most popular include Lean Management, Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM), and the Scaled Agile Framework. These methodologies support organizations in improving efficiency, reducing waste, and delivering consistent value across teams and processes. Lean Management focuses on reducing waste and maximizing value by streamlining processes and promoting continuous improvement. Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at reducing defects in products or services through statistical analysis, ultimately improving quality and consistency. Total Quality Management (TQM) takes a holistic, organization-wide approach to achieving long-term success through customer satisfaction. It involves every employee in the process of continuous improvement to ensure that customer expectations are consistently met or exceeded.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Project Management by Enrolling in Our Project Management Masters Course.
Challenges in Operations Management
While operations management can lead to increased efficiency and profitability, it’s not without challenges. Some common issues include:
The Role of Technology in Operations Management
Technology plays a crucial role in modern operations management. From automation tools to data analytics and supply chain software, technology can significantly improve operational efficiency. A Project Manager often leverages these technologies to streamline workflows, coordinate teams, and ensure that operational goals are met effectively. Key technologies include:
Go Through These Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Best Practices in Operations Management
To maximize the effectiveness of operations management, companies can adopt several best practices:
Conclusion
Operations management is a cornerstone of business efficiency. It involves a variety of functions, from process optimization to inventory management, all aimed at creating value for customers while minimizing costs and inefficiencies. Integrating skills from areas like Project Management Training further enhances an organization’s ability to plan, execute, and improve operational workflows effectively. Whether in manufacturing, services, or any other industry, operations management helps businesses deliver high-quality products or services efficiently and cost-effectively. By focusing on continuous improvement, leveraging technology, and maintaining a clear strategic vision, businesses can gain a competitive advantage and achieve long-term success. Operations management is not just about managing processes; it’s about creating a sustainable foundation for growth and efficiency in today’s dynamic business environment.





