
- What is Quality Control?
- The Importance of Quality Control in Modern Industries
- The Process of Quality Control
- Benefits of Implementing Quality Control
- Challenges in Quality Control
- Key Tools and Techniques in Quality Control
- Quality Control Careers: Roles and Responsibilities
- Conclusion
What is Quality Control?
Quality Control (QC) is a systematic approach to ensuring products or services meet predefined specifications and remain free from defects or inconsistencies, involving continuous monitoring, inspections, and testing across every production stage from raw materials to final output—to maintain consistent standards. It assures customers that what they receive is reliable, safe, and uniform in quality. In professional development fields like PMP Training, understanding QC principles is crucial for managing project quality effectively. Unlike Quality Assurance (QA), which focuses on preventing issues by refining processes, QC zeroes in on detecting and fixing defects after they occur, ensuring problems are resolved quickly to uphold product quality and customer satisfaction. By emphasizing defect detection, correction, and continuous oversight, QC helps reduce waste, cut costs, boost operational efficiency, and build lasting consumer trust.
The Importance of Quality Control in Modern Industries
Quality Control plays a fundamental role in today’s competitive business landscape. As industries evolve and customer expectations rise, ensuring the highest standards of quality has become increasingly vital for businesses. Quality Control is important because it directly impacts customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and overall operational efficiency. In industries such as automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and electronics, a defect or malfunction can lead to severe consequences, including safety hazards, product recalls, and legal liabilities. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, QC ensures that medicines meet safety and efficacy standards before they are sold to the public.
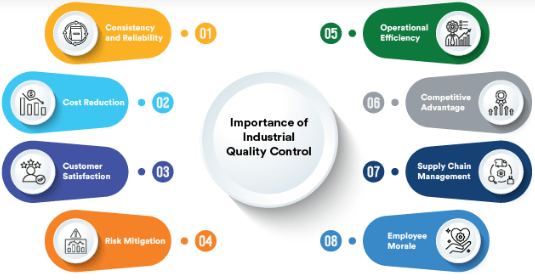
In the tech industry, QC ensures that software products are free from bugs and vulnerabilities. Quality Control also helps organizations identify inefficiencies in their production processes, which can lead to cost savings and improved productivity. By preventing defective products from reaching the market, companies can avoid costly recalls, penalties, and damage to their brand reputation.
To Earn Your Project Management Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Project Management Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Project Management Training Today!
The Process of Quality Control
The QC process varies depending on the industry and the nature of the product or service being offered, but it generally follows a few key steps:
- Defining Standards: The first step is to establish clear quality standards and specifications that the product or service must meet. These standards are based on industry regulations, customer expectations, and internal benchmarks.
- Inspection and Testing: Products or services are tested or inspected at different stages of production to identify any defects. This can involve visual inspections, manual testing, or automated systems that check for defects in real-time.
- Data Collection: The results of these inspections are documented and analyzed to determine if the product is within acceptable quality limits. Statistical tools may be used to interpret the data.
- Corrective Actions: If defects are found, corrective measures are taken to resolve the issue. This might involve reworking the product, adjusting production processes, or making design changes.
- Final Review: Once the corrective actions have been implemented, a final review of the product ensures that it meets all quality standards before it is released to the customer.
Benefits of Implementing Quality Control
Implementing effective Quality Control practices brings a wide range of benefits to both organizations and their customers:
- Consistency and Reliability: QC ensures that products are consistent in quality, which builds customer trust and loyalty. A customer who knows they can rely on a product or service will likely return for future purchases.
- Reduced Costs: By identifying defects early in the production process, QC helps to minimize the costs associated with rework, scrap, and product recalls. Quality Control also helps identify inefficiencies that may be costing the company more than necessary.
- Customer Satisfaction: High-quality products lead to greater customer satisfaction. When customers are pleased with the performance and durability of a product, it enhances the reputation of the brand and encourages repeat business.
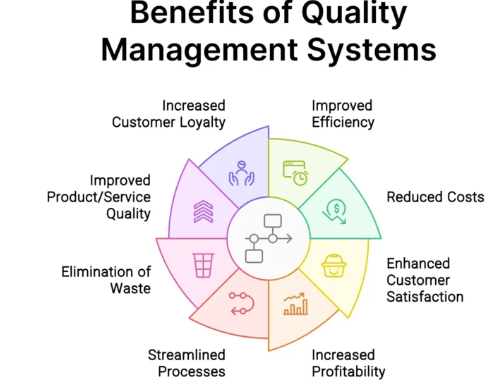
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Many industries have strict regulations regarding the quality and safety of products. Effective QC ensures compliance with these standards, avoiding legal penalties and protecting the company’s reputation.
- Improved Efficiency: Continuous monitoring and improvements to the production process ensure that businesses run more smoothly. QC helps identify bottlenecks and areas where resources are being wasted, allowing for greater efficiency and optimization.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC uses statistical methods to monitor and control a process. By tracking product measurements, SPC helps detect trends that may indicate a potential problem.
- Control Charts: These are graphical representations of data points over time, helping to identify variations in the process and distinguish between normal fluctuations and abnormal deviations.
- Six Sigma: This methodology seeks to reduce defects and improve processes by analyzing data, identifying root causes, and implementing improvements. Six Sigma aims for a defect rate of fewer than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
- Fishbone Diagram: Also known as an Ishikawa or cause-and-effect diagram, this tool helps identify potential causes of problems within a process. It is commonly used during root cause analysis.
- Pareto Analysis: This tool helps prioritize issues by identifying the most significant problems that will have the greatest impact on quality. It is based on the Pareto Principle, which suggests that 80% of problems are caused by 20% of the factors.
- Quality Control Inspector: QC inspectors are responsible for examining products to ensure they meet quality standards. They conduct tests, document findings, and report defects.
- Quality Control Manager: QC managers oversee the QC process, ensuring that quality standards are adhered to across the production process. They manage teams of inspectors, develop quality control plans, and work closely with other departments to implement improvements.
- Quality Assurance Engineer: QA engineers focus on designing and implementing quality assurance processes. They work on the prevention side of quality, creating systems to prevent defects from occurring.
- Process Improvement Specialist: These professionals are responsible for identifying inefficiencies in production and implementing solutions to improve processes. They often use methodologies like Six Sigma or Lean to optimize operations.
- Compliance Officer: QC compliance officers ensure that products meet all regulatory requirements and industry standards. They monitor processes and conduct audits to verify compliance.
- Testing and Validation Engineer: These professionals design and execute tests to ensure that products perform as expected. They often work in fields like software development or manufacturing, ensuring products are safe and effective.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Project Management? Sign Up For Our Project Management Training Today!
Challenges in Quality Control
While Quality Control offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges that companies must navigate. One major hurdle is the high cost of implementing a comprehensive QC system, especially for small businesses. Expenses related to staff training, purchasing testing equipment, and maintaining quality management systems can add up quickly, making it difficult for smaller companies to keep up. Another challenge is the subjectivity in inspection. Despite the integration of automated tools, many aspects of QC still rely on human judgment, particularly in visual inspections where the criteria for defects may not always be clearly defined. Additionally, the QC process can be time-consuming, particularly in industries with complex production systems. Frequent inspections and testing can slow down production, which can be especially challenging in fast-paced sectors like automotive or technology. Balancing quality with speed is another challenge companies face, as achieving high standards of quality can sometimes conflict with tight deadlines. Finally, global supply chains add a layer of complexity. Sourcing materials and components from various parts of the world means companies must manage different production standards, labor quality, and material consistency, all of which can impact the final product’s quality.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Project Management? Enroll in the Project Management Masters Course Today!
Key Tools and Techniques in Quality Control
Several tools and techniques are commonly used in Quality Control to help detect, measure, and improve product quality:
Want to Learn About Project Management? Explore Our Project Management Interview Questions & Answer Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Quality Control Careers: Roles and Responsibilities
Conclusion
Quality Control will continue to evolve as technology advances and customer expectations rise. Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are already playing significant roles in improving QC processes, from real-time monitoring to predictive maintenance. Additionally, as industries move towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices, QC will play an important role in ensuring that new standards for sustainability are met. For individuals considering a career in Quality Control, the field offers diverse opportunities in both traditional manufacturing sectors and emerging industries like tech and pharmaceuticals. As companies increasingly recognize the importance of quality, the demand for skilled QC professionals is expected to grow, making it an exciting and rewarding field to pursue. In conclusion, Quality Control remains a vital component of any business that produces goods or services. Its ability to enhance customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and improve operational efficiency ensures that it will continue to be a key focus for companies around the world.





