
- Introduction
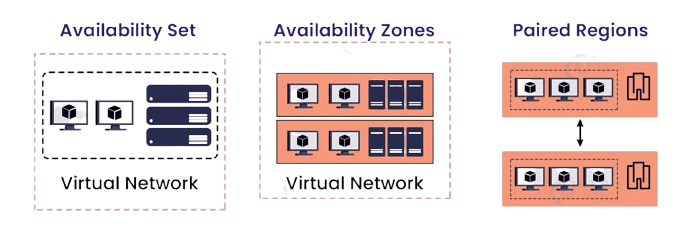
- What is an Availability Set?
- What is an Availability Zone?
- Key Differences Between Availability Sets and Zones
- How Availability Sets Ensure High Availability
- Benefits of Using Availability Zones
- Configuring Availability Sets and Zones in Azure
- Best Practices for High Availability in Azure
- Conclusion
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, ensuring high availability and business continuity is crucial for any cloud-based application. Azure, Microsoft’s cloud computing platform, offers several solutions to help organizations achieve this goal, including Availability Sets and Availability Zones. Both of these features are designed to enhance the resilience of your applications by reducing downtime caused by hardware failures, maintenance events, or even entire data center outages, which is a key focus of Microsoft Azure Training to help professionals build highly available and fault-tolerant applications in the cloud. However, each has its own unique characteristics and use cases. In this article, we will explore the key differences between Availability Sets and Availability Zones, how they ensure high availability, and best practices for configuring and utilizing these options in Azure. Whether you’re looking to safeguard your applications within a single data center or across multiple geographically separated locations, understanding these Azure offerings is essential for building robust, fault-tolerant systems.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Azure? Sign Up For Our Azure Training Today!
What is an Availability Set?
An Availability Set in Azure is a logical grouping of virtual machines (VMs) that are deployed across multiple isolated hardware resources within an Azure data center. The purpose of an Availability Set is to ensure high availability by distributing VMs across different fault domains and update domains.
- Fault Domains: Represent physical hardware failure boundaries. VMs in different fault domains are spread across different racks of physical hardware to avoid simultaneous failures due to hardware issues, much like how the Red Hat Certification Path equips professionals to manage and troubleshoot system failures in Linux-based environments effectively.
- Update Domains: Represent software update boundaries. VMs in different update domains are rebooted at different times during planned maintenance or software updates, ensuring that not all VMs are affected simultaneously.
- High Availability: By deploying resources (e.g., VMs, storage) across multiple Availability Zones, you ensure that your application can withstand failures of a single data center or zone, offering better reliability and availability, which is a key advantage discussed in the comparison of Public Cloud vs Private Cloud for determining the right cloud infrastructure based on your reliability and availability needs.
- Low Latency: Availability Zones within a region are connected via low-latency, high-throughput networking, making them ideal for critical applications requiring high availability.
- Fault Isolation: Availability Zones provide fault isolation by distributing resources across separate physical data centers within a region. If one zone experiences a failure (e.g., power outage, network failure), other zones in the same region remain unaffected, ensuring application availability.
- Disaster Recovery: By deploying resources across multiple Availability Zones, you ensure that your application remains operational even in the event of a complete failure in one zone, which is a key consideration in What is Cloud Computing Technology with SalesForce Integration, as it ensures business continuity and seamless service delivery across integrated cloud platforms.
- Low-Latency Communication: Availability Zones in the same region are connected via high-throughput, low-latency networking. This ensures that applications can still interact with resources in different zones with minimal performance degradation.
- Geographically Redundant Storage: Azure services like Azure Storage and Azure SQL Database can replicate data across Availability Zones for automatic failover, ensuring high availability of your data.
- Scalability: With Availability Zones, you can scale your application across multiple isolated zones, providing enhanced scalability and load distribution while maintaining high availability.
- # az vm create –name MyVM –resource-group MyResourceGroup –availability-set MyAvailabilitySet –image UbuntuLTS
- # az vm create –name MyVM –resource-group MyResourceGroup –zone 1 –image UbuntuLTS
- Distribute Resources Across Multiple Availability Zones: For maximum fault tolerance and resilience, deploy critical resources (e.g., VMs, databases, load balancers) across multiple Availability Zones within the same region.
- Use Load Balancers for Traffic Distribution: Utilize Azure Load Balancer or Azure Application Gateway to distribute traffic evenly across VMs in different Availability Zones or Availability Sets. This helps prevent overloading a single resource and ensures high availability.
- Implement Autoscaling: Enable Azure Autoscale to automatically adjust the number of VM instances based on demand. Autoscaling can help your application handle traffic spikes while maintaining availability and performance.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Use Azure Backup to regularly back up your data and Azure Site Recovery to replicate workloads to a secondary region for disaster recovery, essential practices covered in Microsoft Azure Training to ensure data protection and business continuity in the cloud. This ensures business continuity in case of a region-wide outage.
- Monitor Health and Performance: Use Azure Monitor and Azure Application Insights to monitor the health and performance of your applications and resources. Set up alerts for resource failures or performance degradation to take action before they affect your application.
- Consider Geo-Redundancy: For mission-critical applications, consider replicating data and resources across multiple regions (geo-redundancy) to ensure your application remains available even in the event of a regional outage.
By using Availability Sets, you ensure that your application remains available even during hardware failures or maintenance events.
What is an Availability Zone?
An Availability Zone (AZ) in Azure is a physically separate data center within an Azure region that is designed to be isolated from other Availability Zones. Each zone has independent power, cooling, and networking, ensuring that a failure in one zone does not affect the others.
Interested in Obtaining Your Azure Certificate? View The Azure Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Azure Availability Zones are available in selected regions and offer an extra layer of redundancy by distributing your application across physically separated data centers.
Key Differences Between Availability Sets and Zones
| Feature | Availability Set | Availability Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A logical grouping of VMs across fault and update domains within a single Azure data center. | Physically separate data centers within an Azure region. |
| Scope | Ensures availability within a single data center (region). | Provides isolation and high availability across multiple data centers in a region. |
| Fault Domains | VMs are distributed across fault domains to protect against hardware failures, similar to how Kubernetes vs Docker Swarm compares the distribution and management of containerized applications across nodes to ensure high availability and fault tolerance. | Each Availability Zone is a separate data center with independent power, cooling, and networking. |
| Update Domains | VMs are placed in update domains to stagger maintenance and updates. | Not applicable, as each Availability Zone is independent and unaffected by maintenance in other zones. |
| Use Case | Suitable for ensuring high availability within a single data center. | Ideal for disaster recovery, fault tolerance, and high availability across geographically separated data centers. |
| Cost | Less expensive compared to Availability Zones, as resources are within the same region. | More expensive due to cross-zone redundancy and isolation. |
How Availability Sets Ensure High Availability
Availability Sets ensure high availability by distributing virtual machines (VMs) across fault domains and update domains. Fault domains represent physical hardware boundaries, such as separate racks within a data center. This means that if one rack experiences a failure, like a power or hardware issue, only the VMs within that fault domain are impacted, while those in other domains remain operational. On the other hand, update domains manage planned maintenance and updates by staggering the reboot of VMs, ensuring that not all VMs are taken down at once, a concept that is thoroughly covered in Microsoft Azure Training to help professionals manage high availability and minimize downtime during updates. This approach minimizes downtime during updates and ensures continuous application availability.
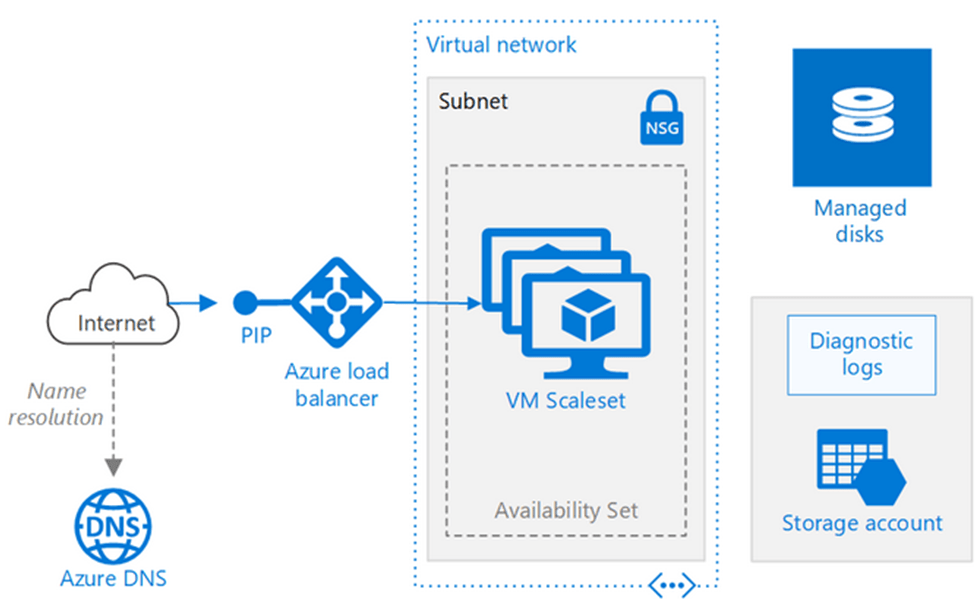
By leveraging both fault and update domains, Availability Sets reduce the risk of simultaneous failures, helping to keep applications running smoothly during both unplanned outages and scheduled maintenance.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cloud Computing? Enroll in the Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
Benefits of Using Availability Zones
Using Availability Zones in Azure provides several benefits for ensuring high availability and disaster recovery:
Configuring Availability Sets and Zones in Azure
Configuring Availability Sets: When creating a virtual machine (VM) in Azure, you can place it into an Availability Set to distribute it across fault and update domains. Here’s how you can do it:
Using Azure Portal: Go to the Virtual Machines section and click on Add to create a new VM. In the Availability options section, choose Availability Set. Create a new Availability Set, or select an existing one to place your VM in.
Using Azure CLI:Using ARM Templates: You can define Availability Sets in Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates to automate the deployment of VMs with high availability, similar to how AWS Reinvent Reinforces the Growth of Cloud Computing, promoting innovations and strategies for enhancing cloud infrastructure and ensuring availability across AWS environments.
Configuring Availability Zones: To deploy resources across multiple Availability Zones, you can select an Availability Zone when creating the resource (e.g., VM, Load Balancer, Storage Account). Availability Zones are supported in select Azure regions.
Using Azure Portal: When creating a resource, select the Availability Zone option to choose which zone the resource should be placed in. You can select multiple zones for redundancy.
Using Azure CLI:Using ARM Templates: You can specify the zones in ARM templates to deploy resources across multiple Availability Zones.
Are You Preparing for Azure Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Azure Interview Questions And Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Best Practices for High Availability in Azure
To ensure high availability of applications and services in Azure, follow these best practices:Conclusion
In conclusion, both Availability Sets and Availability Zones play a vital role in ensuring the high availability and resilience of your applications in Azure. While Availability Sets are ideal for safeguarding workloads within a single data center by distributing resources across fault and update domains, Availability Zones provide even greater fault tolerance by leveraging physically separate data centers within a region. Understanding when and how to use each of these options is essential for building robust, scalable, and reliable cloud applications. By following best practices such as distributing resources across multiple zones, using load balancers, and implementing autoscaling, you can ensure your applications remain operational even in the face of failures or maintenance events. Ultimately, selecting the right combination of Availability Sets and Zones based on your specific needs will help you achieve the high availability and disaster recovery objectives critical to maintaining business continuity in the cloud.





