
- Introduction to Cybersecurity Vulnerability
- Types of Cybersecurity Vulnerability
- Identifying and Assessing Vulnerability
- Common Cybersecurity Vulnerability
- Impact of Vulnerability on Organizations
- Best Practices for Vulnerability Management
- Future of Vulnerability Management in Cybersecurity
- Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Vulnerability
- Conclusion
Vulnerability in cybersecurity refers to weaknesses or flaws in systems, networks, or applications that can be exploited by cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access, disrupt operations, or steal sensitive data. These vulnerabilities can arise from software bugs, misconfigurations, outdated systems, or human error. Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities is crucial in safeguarding against cyberattacks such as data breaches, ransomware, and Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks through Cyber Security Training Courses. Effective vulnerability management involves regular assessments, timely patching, security audits, and continuous monitoring to detect and mitigate risks. As cyber threats evolve, proactive measures and updated security protocols are essential to maintain strong defenses and protect valuable assets.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Introduction to Cybersecurity Vulnerability
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities are weaknesses or flaws in a system that malicious actors can exploit to gain unauthorized access or cause harm. These vulnerabilities exist in software, hardware, or an organization’s overall security infrastructure. In today’s digital world, cybersecurity vulnerabilities are a serious concern for businesses, governments, and individuals. The growing sophistication of cyberattacks makes it crucial for organizations to identify, address, and manage these vulnerabilities effectively, especially through fields like Cybersecurity and Data Science. Understanding these vulnerabilities is the first step in protecting critical data and assets from cyber threats. The types of vulnerabilities range from software bugs and misconfigurations to human errors and inadequate security policies. Once identified, vulnerabilities can be mitigated or eliminated through various security measures such as patching, secure coding practices, and enhanced network defenses.
Types of Cybersecurity Vulnerability
Software vulnerability are flaws or bugs in software applications or operating systems that can be exploited. Examples include buffer overflows, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS). These vulnerabilities are usually the result of coding errors or design flaws.
- Hardware-related vulnerability : Weak points in hardware, such as the CPU, memory chip, or network devices themselves, which hackers can manipulate. Examples are Spectre and Meltdown, which are vulnerabilities within modern processors, often discovered during Reconnaissance in Cyber Security.
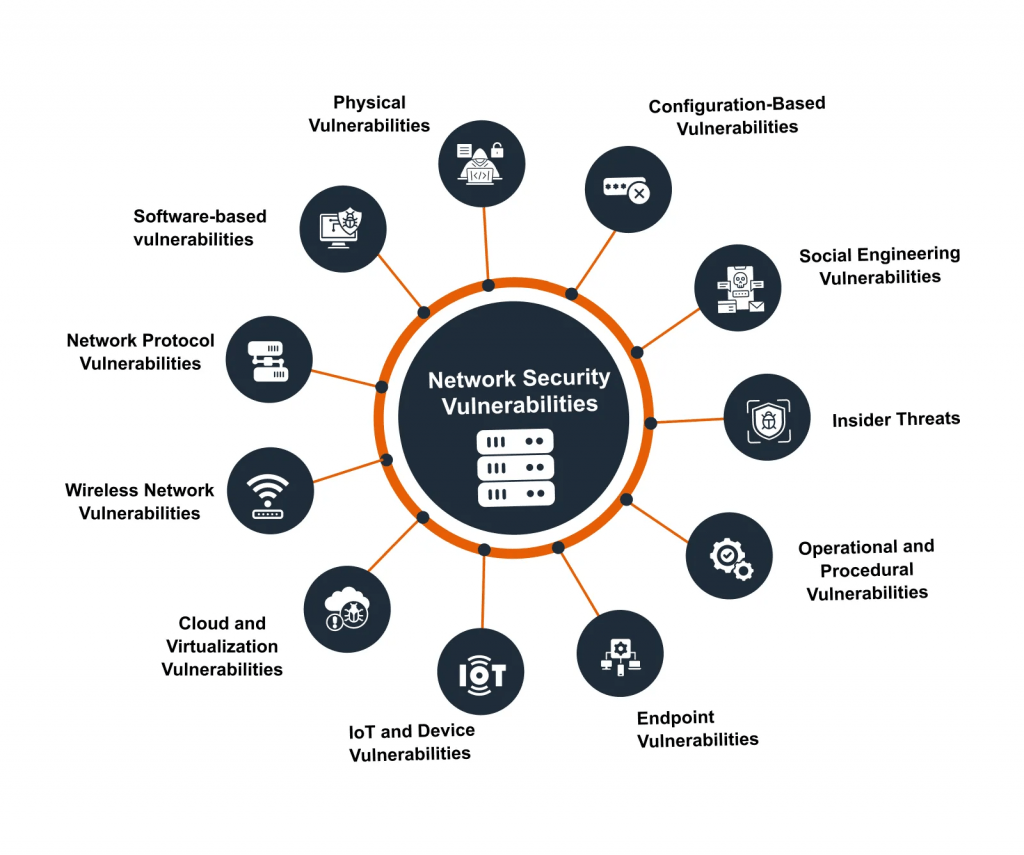
- Network-related vulnerabilities: These include weaknesses in infrastructure within a network, such as non-secured communication protocols, misconfigured firewalls, weak encryption, and so many more. Through network vulnerabilities, the attacker can intercept traffic as well as unauthorized access to systems. Configuration vulnerability occur when systems or applications are not configured correctly. For example, misconfigured cloud storage permissions or default admin passwords can open doors for attackers.
- Human vulnerability : Many vulnerabilities result from human error, such as weak passwords, phishing attacks, or improper handling of sensitive data. Social engineering techniques often exploit human vulnerabilities, tricking individuals into revealing confidential information.
Identifying and Assessing Vulnerability
Identification and assessment of vulnerability are important processes in cybersecurity management. The first step includes finding possible weaknesses that attackers might use. This process is completed through various tools and techniques, including. Automated software, such as Nessus, Qualys, and OpenVAS, can scan systems for known vulnerabilities and weaknesses. This process involves ethical hackers simulating real-world attacks on systems, applications, and networks to find security flaws. In software development, source code reviews can identify weak points for potential flaws, security bugs, and vulnerabilities before the actual bug occurs. Periodic security audits and risk assessments enable organizations to check on the effectiveness of their security posture. Once vulnerabilities are discovered, organizations evaluate their severity and risk. The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a common tool for rating vulnerabilities based on exploitability, impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
To Earn Your Cyber Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Common Cybersecurity Vulnerability
One of the most common vulnerabilities is using simple, easily guessable passwords. Attackers use brute-force attacks to gain access to accounts or systems protected by weak passwords.
- Old Software: Using old software or applications that have not received security patches with the latest security updates is another serious weakness. Cybercriminals continuously scan for unpatched systems to exploit known vulnerabilities.
- Unencrypted Communication: The transfer of sensitive information over unsecured channels, such as HTTP rather than HTTPS, exposes the data to interception by attackers. Without proper encryption, businesses and individuals are at risk of suffering data breaches.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing is one of the most successful social engineering attacks. Attackers trick people into clicking harmful links or downloading malware-laden attachments. Lack of Proper Security Setting: Many cloud services, apps, or devices are accessed with default or inappropriate security settings, such as open ports, active services, or exposed admin credentials that make it easy for them to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Malware and Ransomware: Malicious software, such as viruses, Trojan horses, and ransomware, can exploit system vulnerabilities to gain access, steal data, or hold systems hostage for ransom, which is why Cyber Security Training Courses are essential for prevention and mitigation.
- Insider Threats: Employees or insiders with access to sensitive information or systems may intentionally or unintentionally create security gaps. The former includes malicious actions like data theft, while the latter includes accidental mistakes such as sending confidential information to the wrong person.
Impact of Vulnerability on Organizations
The influence of vulnerabilities can be strongly dependent on the type of weakness and the importance level of the system being damaged. Some of the severe effects include. Data breaches and cyberattacks result in direct economic loss, legal fines, and costs related to remediation and recovery, often caused by malicious tools like a Keylogger. Cyber incidents can severely damage an organization’s reputation and erode customer trust and loyalty. Legal and Regulatory Consequences Failure to secure sensitive data results in penalties under various regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. vulnerability can lead to the theft of sensitive intellectual property, giving attackers access to trade secrets or proprietary technologies. Operational Disruption Exploited vulnerabilities can cause service disruptions, downtime, or system failures, impacting productivity and business continuity.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Best Practices for Vulnerability Management
Effective vulnerability management is crucial to minimizing risks and securing systems. Here are some best practices:
- Scanning and Penetration Testing: The ongoing scanning and testing of systems help discover new vulnerabilities and remediate them without delay. Patch Management involves ensuring that software, hardware, and systems are kept up to date with the latest security patches to close known vulnerabilities.
- Risk-Based Prioritization: Not all vulnerabilities are the same. Instead, patch and remediation efforts should be prioritized based on their potential impact and exploitability.
- Security Training: Inform employees about phishing attempts, secure password usage, and effective security practices to minimize the chances of human error vulnerabilities.
- Incidence Response Planning: Organizations should have a clear and well-performing incident response plan ready to respond quickly upon detecting vulnerability exploitation.
- Use of security frameworks: Organizations that apply a structured approach to vulnerability management, using standards such as NIST, CIS, and ISO 27001, are best positioned to reduce the occurrences.
Future of Vulnerability Management in Cybersecurity
The future of vulnerability management will likely encompass the integration of advanced technologies and practices, such as. Automated Vulnerability Detection: The increased use of AI and machine learning will enhance detection capabilities faster and with greater accuracy, complementing security measures like Two-Factor Authentication. Continuous Security Monitoring Organizations will begin to shift toward continuous monitoring of their IT environments to enable real-time detection and response to vulnerabilities. Cloud Security As more organizations move to the cloud, the future of vulnerability management will focus on securing cloud-based infrastructure and applications. Security by Design Building security into the development process and embracing DevSecOps will become standard practice, helping to prevent vulnerabilities from being introduced in the first place.
Emerging Trends in Cybersecurity Vulnerability
The cybersecurity landscape is in constant flux, and so are the vulnerabilities organizations face. Emerging trends include the following:
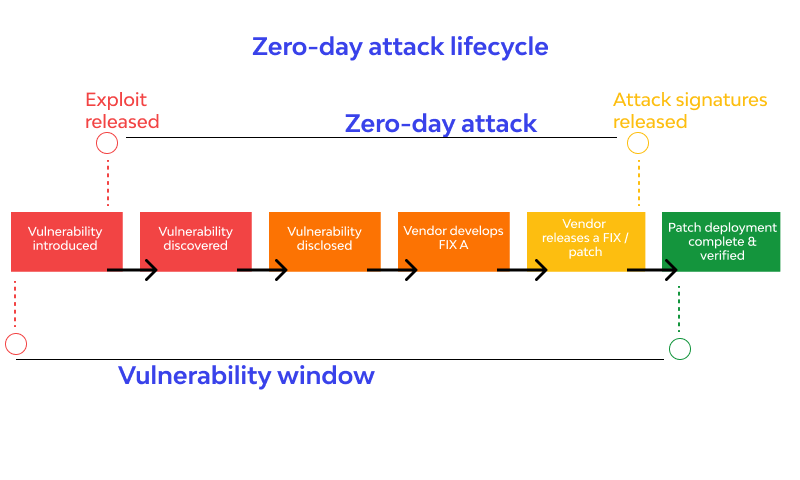
- Zero-Day vulnerability : Zero-day vulnerabilities refer to unknown vulnerabilities for vendors. Although there has been no patch release yet, attackers use these vulnerabilities before they are discovered or resolved.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Cybercriminals exploit the weaknesses of third-party vendors or software providers, using them as an entry point into an organization’s network through the supply chain.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service: Ransomware as a service (RaaS) has become more prevalent; it enables those with limited technical expertise to conduct ransomware attacks by providing access to malicious tools for hire.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI is becoming more widely adopted to strengthen security measures. On the other hand, hackers are using it to identify unknown vulnerabilities or even automate attacks.
- IoT vulnerability : More connected devices mean that attackers will soon find vulnerabilities in IoT devices, highlighting the importance of robust Database Security to protect sensitive data.
- Case Studies of Notable Cybersecurity vulnerability : Many notable cybersecurity vulnerabilities have received significant media attention recently.
- Equifax Data Breach (2017): A vulnerability in Apache Struts, the widely used web application framework, allowed the data of 147 million Americans to be stolen.
- Heartbleed Bug (2014): A flaw in the OpenSSL encryption library could be used to access passwords, encryption keys, and private information on servers running vulnerable versions of OpenSSL.
- WannaCry Ransomware Attack (2017): The WannaCry ransomware attacked a hole in the Windows SMB protocol. Its effects have already reached hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide, creating serious disruption in many infrastructures.
- SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack (2020 ): Attackers manipulated the software updates of the leading IT management company SolarWinds, gaining access to both government agencies and private companies.
Want to Learn About Cyber Security? Explore Our Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities are an evolving threat present in all types of organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises. As technology advances and digital systems become more interconnected, the attack surface for cybercriminals continues to grow, making it essential to remain vigilant against potential vulnerabilities. Identifying, assessing, and managing vulnerabilities is a critical aspect of any Cyber Security Training Courses strategy. It is not just about detecting weaknesses but also implementing effective mitigation techniques to minimize risks and protect sensitive data. An organization can significantly reduce its exposure to cyber threats by following industry best practices, such as regular vulnerability assessments, patch management, and security audits. A proactive approach to cybersecurity involves continuous monitoring of networks and systems, ensuring that vulnerabilities are detected and remediated as soon as possible.





