
- Introduction
- What is Data Classification?
- Why is Data Classification Important?
- Types of Data Classification
- The Data Classification Process
- Best Practices for Data Classification
- Conclusion
- Enhanced Security: This means one would know the kind of data and the security controls that need to be applied. For example, sensitive personal information (PII) is better protected than public data.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Many industries regulate how particular types of data should be treated, especially when it comes to Risk Threat and Vulnerability management.The proper classification ensures organizations comply and mitigate legal risks.
- Improved Data Management: By knowing the categories of data, organizations can manage their data more streamlined, making it easier to store, retrieve, and archive information.
- Resource Allocation: Data classification helps organizations prioritize resources for data protection and management efforts by first focusing on the most critical data.
- Facilitating Data Governance: A strong scheme of data classification is crucial for data governance and helps facilitate it by allowing organizations to develop policies and procedures regarding data usage and management.
- Public Data is information: That is openly available for anyone to access and share. This includes marketing materials, press releases, and publicly available research. Such data is typically meant for broad dissemination and does not require any special permissions for use. Examples are company product catalogues or publicly shared industry reports.
- Internal Data: Data intended for use within the organization only and not to be shared publicly. It includes internal emails, memos, reports, or employee data like HR records, which can be exposed through techniques like Google Dorking. This type of data helps in the daily functioning of the organization but should remain confidential within the company. It is not meant for external distribution.
- Confidential Data: Sensitive information whose unauthorized disclosure could harm individuals or the organization. Examples include customer personal details, financial records, proprietary business strategies, or contracts. This data requires special handling and is typically protected by confidentiality agreements. Sharing it without proper consent could lead to legal or reputational risks.
- Restricted Data: Highly sensitive, tightly controlled, and only accessible to authorized individuals. This includes personal health information, classified government data, and other critical national cyber security threats information. Strict regulations and laws usually govern access to protect privacy and cyber threats. Unauthorized access to this information could have catastrophic repercussions.
- Critical Data: Data essential for the organization’s core operations, where loss or corruption would have severe consequences. Examples include production data, system configurations, or financial transaction records. Its integrity is vital to avoid operational disruption or legal issues.
- Non-Critical Data: While valuable, information is optional for day-to-day operations. This could include historical data, non-essential reports, or archived files. Loss of non-critical data may be inconvenient but typically does not directly impact business continuity.
- Regulated Data: Information subject to legal and compliance requirements, such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI), and payment card data. Laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS govern this type of data. It must be handled with strict security measures to avoid legal and financial penalties.
- Non-Regulated Data: Data that does not fall under specific legal or regulatory obligations but still requires proper management and protection. This may include general business data, internal communications, or operational records. While not legally mandated, improper handling can still lead to risks like loss of business value or internal inefficiencies.
Introduction
Data, undoubtedly, is one of the most precious things an organization can own, especially in the digitized world that is prevalent today. Such a digitized world creates and stores loads of information daily; hence, effective management is important for data’s efficient operation, compliance, and network security, as highlighted by Cyber Media. Data classification is one of the vital steps involved in managing data. In this article, we shall discuss what data classification is and why it matters, various data classifications, and the processes and best practices followed in data classification for smooth implementation.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Data classification? Sign Up For Our Cyber Security Online Training Today!
What is Data Classification?
Data classification is the process of separating data into categories that are easier to manage, access, and protect. Sorting data based on their sensitivity, importance, or impact in case of non-authoritative access can allow firms to implement proper safety measures and ensure regulation compliance. Cyber Security Training Courses leads to appropriate data handling during its life cycle from creation to deletion.
Why is Data Classification Important?
To Explore Data classification in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Types of Data Classification
Data classification can be classified in several ways. Here are some common classifications:
1. Based on Sensitivity
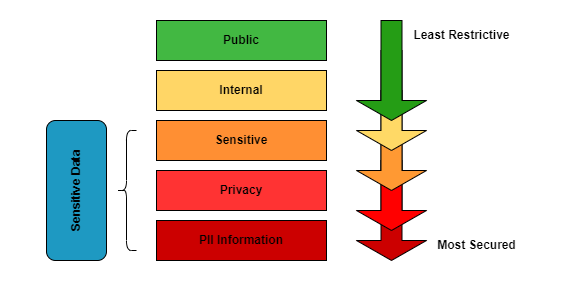
2. Based on Importance
3. According to Regulatory Requirements
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cybersecurity? Enroll in the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
The Data Classification Process
1. Identify Sources of Data
Identify all data sources. This includes databases, file systems, applications, cloud storage, and all other forms of information. Knowing where the data resides has to be established to start the classification process. Knowing where all data sources are will better enable a data sensitivity appraisal and suitable security measures to be implemented.
2. Determine your classification criteria
The classification criteria should define how a record will be classified with respect to its sensitivity level, importance, or even both, while considering factors like Network Penetration Testing to assess potential vulnerabilities. However, depending on the level of regulation compliance requirement, other relevant considerations could include consulting cross-functional stakeholders like IT stakeholders, legal and compliance, and operations.
3. Classify Data
Once the criteria are established, it then starts classifying a process. It may even be done manually, otherwise by some automated tools for scanning and classification with particular predefined rules. All of these data should have appropriate labelling according to their type of classification.
4. Security Controls
After classification, appropriate security controls are applied according to the classification level. For example, confidential data could be secured through encryption, access controls, and regular audits. However, public data may not necessarily require any special protection.
5. Employee Training
Educate employees on a classification scheme and how best to handle data based on its classification. Continuous training shows that proper data security and compliance are essential. Adding real-life cases and case studies to training can make best practices easier to understand and remember.
6. Review and Update
Cyber Security Training Courses is an ongoing process. Regularly review and update the classification scheme to ensure the data remains relevant to growth, regulations, and business changes. Engaging stakeholders can provide helpful feedback so the classification continues representing the organizations’ objectives.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Best Practices for Data Classification
1. Policy Establishment
Develop clear data classification policies. These policies will state clearly the criteria for classification, the responsibilities of the employee, and the procedures applied to each classification level. Make these policies available to all staff members. Maintain regular communication with the different updates and reinforcement of policies through training sessions to ensure continued compliance and awareness.
2. Employ Automated Tools
Leverage automation using data classification tools to enhance data security. Tools used in this process facilitate the identification, categorization, and management of data more streamlined and efficiently, therefore limiting the potential for errors through human oversight. Finally, automation enables real-time monitoring and adjustments, allowing data to remain well-classified as it matures.
3. Interdepartmental Collaboration
Involvement of different departments in the classification process, which may involve IT, legal, compliance, and business units, is crucial to prevent security risks such as Keylogger attacks that could compromise sensitive information. Collaboration ensures that all views are considered and the classification scheme aligns with organizational goals.
4. Monitoring Access and Usage
These need monitoring tools that monitor the levels of access to classified information. They are effective when tracking unauthorized access, such as data not treated in line with prescribed rules and regulations. Conduct of an audit on these monitoring machines helps increase security even more. It will determine other loopholes and show where one still needs to achieve compliance with the data governance policy.
5. Conduct Regular Audits
Regular classified data audits should be conducted and must adhere to the guidelines of internal policies and regulatory bodies. In this way, audits will depict weaknesses of the classification process that can immediately be corrected. A schedule for conducting these audits encourages the organization to embrace accountability and continuous improvement.
6. Be on Top of Regulatory Changes
Keep abreast of evolving regulations and industry best practices. As the law and compliance evolve, so should your data classification policy. You can find good information on emerging trends and best practices in data governance by attending industry forums and consulting with legal experts.
Conclusion
Data classification is part and parcel of effective data management and security. Understanding data types, implementing a solid data classification process, and implementing best practices help an organization better secure its information assets in aws certification. Data will continue to grow and become increasingly complex; therefore, proactive Cyber Security Training Courses strategies can enhance data security, improve compliance, streamline data management, and aid in informed business decision-making. Applied in most organizations today, regardless of size, data classification prevents businesses from misusing and mismanaging data while instilling the value of good stewardship among its users.





