
- Introduction to Azure Site Recovery
- Benefits of Azure Site Recovery
- Site Recovery Setup and Configuration
- Supported Replication Scenarios
- Azure Site Recovery for Disaster Recovery
- Cost Management for Azure Site Recovery
- Best Practices for Azure Site Recovery
- Conclusion
Introduction to Azure Site Recovery
Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a disaster recovery service provided by Microsoft Azure. It helps organizations protect their workloads by replicating on-premises machines (or Azure virtual machines) to Azure or other secondary locations. In the event of a disaster or failure at the primary location, ASR enables businesses to quickly failover to the replicated environment, ensuring minimal downtime and business continuity. Azure Site Recovery automates the replication, failover, and failback processes for virtual machines (VMs), physical servers, and applications, a critical feature that is comprehensively covered in Microsoft Azure Training, helping professionals understand how to streamline disaster recovery and ensure business continuity. It is designed to help businesses set up and manage disaster recovery without the need for extensive infrastructure or costly investment in secondary data centers.
To Explore Azure in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Azure Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Benefits of Azure Site Recovery
Azure Site Recovery offers several benefits to organizations looking to implement disaster recovery (DR) plans and ensure business continuity. Azure Site Recovery eliminates the need for a secondary data center by leveraging Azure’s cloud infrastructure. This can significantly reduce the costs associated with maintaining on-premises disaster recovery infrastructure. ASR ensures that critical applications and services remain available even during local or regional outages. It helps minimize downtime by quickly failing over to the replicated environment. Site Recovery can be easily configured through the Azure portal, and it supports a wide range of source environments (e.g., on-premises Hyper-V, VMware, and Azure VMs), demonstrating key Applications of Cloud Computing in disaster recovery and business continuity across diverse IT infrastructures. It automates most aspects of disaster recovery, simplifying the management process. ASR scales automatically to match your workloads, meaning you can easily replicate a large number of machines or applications without manual intervention.
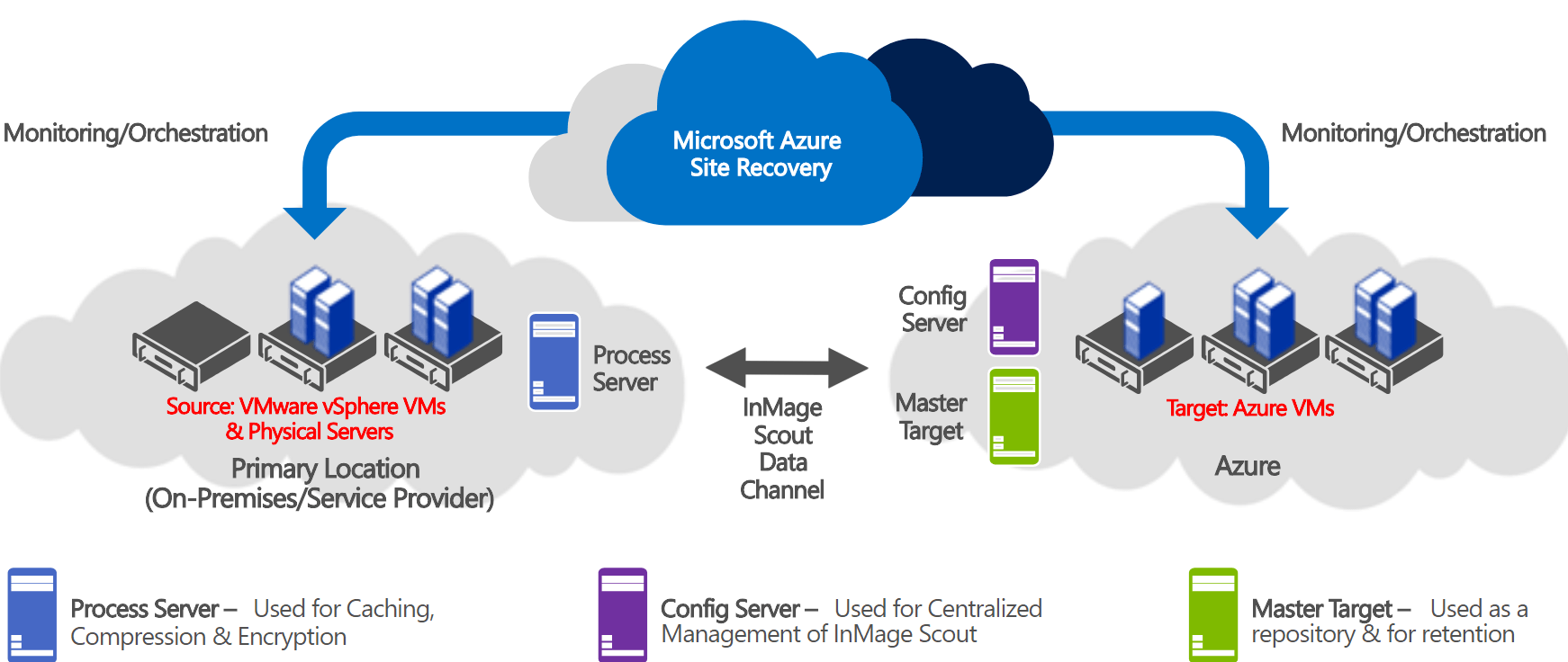
Azure Site Recovery supports hybrid environments, where businesses may have workloads across on-premises and cloud environments, enabling seamless replication and failover between the two. Site Recovery allows organizations to test their disaster recovery plan by performing non-disruptive test failovers. This helps ensure that the failover process will work as expected when needed. Site Recovery integrates with other Azure services like Azure Backup and Azure Automation, providing a comprehensive solution for backup, replication, and disaster recovery.
Site Recovery Setup and Configuration
Setting up Azure Site Recovery involves configuring replication, defining recovery plans, and setting up failover mechanisms. Here’s an overview of the steps for setting up ASR:
- Prepare Source Environment:On-premises Environment: Install the Azure Site Recovery Provider on your on-premises machines (VMware, Hyper-V, or physical servers).
- Azure Environment: Ensure your Azure subscription is ready, and you have sufficient resources like storage and networking configurations.
- Create a Recovery Vault: A Recovery Services Vault is a storage entity that holds the configurations and data related to your disaster recovery setup. This vault manages your backup and replication data, playing a crucial role in the Content Delivery Networks by ensuring data is securely replicated and easily accessible for disaster recovery scenarios.
- Configure Replication:Choose the type of replication based on your source environment (e.g., VMware, Hyper-V, or Azure VM). Set up replication for each machine or application that you want to protect. For VMware and Hyper-V, install the Site Recovery provider, configure replication, and associate the virtual machines with the Recovery Vault.
- Define Recovery Plans:A recovery plan specifies the sequence in which virtual machines or applications will fail. Define failover priorities and groupings to automate recovery and minimize manual intervention.
- Test Failover:After replication is set up, perform a test failover to ensure that your workloads will fail over as expected. This will not impact production, as it’s a non-disruptive test.
- Perform Failover and Failback:In case of a disaster, you can initiate a failover to Azure. Once the primary site is restored, you can initiate a failback to move workloads back to their original location.
- Automated Failover:In the event of an outage or failure at the primary site, Site Recovery can automatically failover workloads to the secondary location (e.g., Azure) without manual intervention. This minimizes downtime and ensures business continuity.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO):Site Recovery provides a near-zero RPO by continuously replicating data from the primary site to the secondary location, a concept thoroughly explored in Microsoft Azure Training, where professionals learn to implement and manage disaster recovery solutions efficiently. This ensures that data loss is minimized in the event of a disaster.
- Failback:After a disaster, once the primary infrastructure is restored, Site Recovery allows for a failback to return workloads to the original environment.
- Multi-Tier Application Recovery:ASR allows you to set up recovery plans that sequence the failover of multiple applications or services in the correct order. This ensures that dependent services (e.g., databases, web servers) are recovered together, ensuring application functionality.
- Replication Costs: You are charged for the storage used for replicated data, as well as the data transfer between your on-premises machines or Azure VMs and Azure.
- Compute Costs: During failover, the VMs running in Azure incur compute costs based on the resources they consume (e.g., CPU, memory), which highlights the differences between Containers Vs Virtual Machines, where containers generally offer more cost efficiency and flexibility compared to VMs by sharing the host system’s OS rather than running separate OS instances. Azure provides cost estimation tools to help calculate these expenses.
- Storage Costs: Azure Site Recovery uses Azure Storage to store replicated data. Storage costs depend on the type and size of storage used (e.g., Standard or Premium).
- Network Costs: There may also be data transfer costs associated with replicating data to Azure or between regions, particularly if large amounts of data are being replicated.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Azure Training Today!
Supported Replication Scenarios
Azure Site Recovery supports a variety of replication scenarios, allowing you to protect a wide range of workloads. Replicate on-premises virtual machines (VMware or Hyper-V) and physical servers to Azure for disaster recovery. This is the most common use case where businesses replicate their workloads to the cloud for failover. For businesses already running workloads in Azure, ASR can replicate VMs from one Azure region to another. This is ideal for protecting against regional outages and ensuring high availability across Azure regions. ASR supports VMware-to-VMware replication, where you can replicate VMware virtual machines from one on-premises VMware infrastructure to another VMware infrastructure in Azure. Azure Site Recovery also supports Hyper-V-to-Hyper-V replication, enabling organizations to replicate Hyper-V virtual machines from an on-premises Hyper-V environment to Azure or another Hyper-V host, similar to how AWS VPC enables secure, isolated network environments in the cloud for various replication and disaster recovery scenarios. For physical servers, you can replicate the workloads to Azure, allowing businesses with physical infrastructure to move to the cloud for disaster recovery purposes. ASR also supports cross-platform replication, allowing VMware VMs to be replicated to Hyper-V and vice versa, enabling flexibility in heterogeneous environments. Azure Site Recovery (ASR) also enables organizations to replicate their workloads between different cloud environments, offering flexibility for businesses using multiple cloud providers. Additionally, it supports the replication of critical applications, such as databases and web servers, to ensure they remain operational during a disaster. With ASR, businesses can automate the failover and failback process, significantly reducing manual intervention during a disaster recovery event. The service provides a simple and intuitive recovery plan setup, helping ensure that recovery procedures are both efficient and consistent. Furthermore, ASR’s ability to continuously monitor and report replication health allows organizations to stay informed and make necessary adjustments to their disaster recovery strategy.
Azure Site Recovery for Disaster Recovery
Azure Site Recovery is an essential tool for disaster recovery (DR). It helps businesses ensure that their mission-critical applications and services remain available even in the face of significant disruptions such as hardware failure, network outages, or natural disasters.
Key features of ASR for disaster recovery:
Considering Pursuing a Cloud Computing Master’s Degree? Enroll For Cloud Computing Masters Course Today!
Cost Management for Azure Site Recovery
While Azure Site Recovery provides excellent disaster recovery capabilities, it’s important to manage and optimize costs. The main costs associated with ASR include:
To manage costs effectively, you can optimize replication settings, such as adjusting the frequency of replication or enabling compression for data storage.
Best Practices for Azure Site Recovery
Regularly test your disaster recovery plan using Site Recovery’s test failover capabilities. This ensures that your recovery plan is effective and that your team is familiar with the failover process. Set up Azure Monitor to track the health and status of your disaster recovery plan. Use Azure Alerts to notify you of any issues or failures in the replication process. Focus on replicating the most critical workloads first, such as databases, application servers, and web services. This ensures that mission-critical services are always available during a disaster. Define and document clear recovery plans that specify the order of failover for different applications and services. This helps maintain business continuity even in complex environments, similar to the concepts discussed in the Introduction To Docker Networking, where efficient network configurations are crucial for ensuring seamless communication and uptime in containerized applications across diverse environments.
Regularly review your replication settings and storage costs. Consider using Azure Blob Storage for cost-effective storage of replication data and adjust replication frequency to balance performance and cost. Automate the failover process to ensure faster recovery times during a disaster. Set up automated scripts or integration with Azure Automation to streamline the recovery process. Ensure that your disaster recovery plan is aligned with your business continuity strategy by regularly updating and refining it to address any changes in your environment. Leverage Azure Site Recovery’s built-in integration with Azure Backup for a comprehensive data protection solution. In addition, perform frequent drills with your team to ensure smooth execution during a real disaster scenario. Utilize Azure’s Cost Management tools to track and optimize expenses related to Site Recovery and avoid unexpected charges. Finally, establish a communication plan to ensure your team and stakeholders are promptly informed during a failover or recovery event.
Want to Learn About Cloud Computing? Explore Our Azure Interview Questions And Answers Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Conclusion
Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a powerful and cost-effective disaster recovery solution that enables businesses to ensure continuity and minimize downtime in the face of disasters. By automating replication, failover, and failback processes, ASR makes it easier to protect critical workloads across on-premises, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments. The service provides several benefits, such as reducing the need for expensive secondary data centers, ensuring high availability, and allowing for seamless recovery across various platforms and environments. Moreover, it supports different replication scenarios like on-premises to Azure, Azure to Azure, and cross-platform replication, making it highly adaptable for various IT infrastructures. This flexibility is a key aspect covered in Microsoft Azure Training, which equips professionals with the skills to manage and optimize such diverse replication strategies effectively. While it offers robust disaster recovery capabilities, managing costs effectively and following best practices is essential for maximizing the value of ASR. By regularly testing your disaster recovery plan, monitoring performance, prioritizing critical workloads, and automating recovery processes, you can ensure that your organization is always prepared for potential disruptions. In conclusion, Azure Site Recovery is a critical component of an organization’s disaster recovery strategy, helping businesses recover quickly, ensure business continuity, and optimize costs all within a flexible and scalable cloud environment.





