
- Introduction to Information Security and Cybersecurity
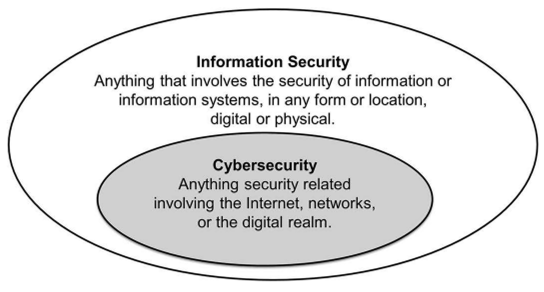
- Definition of Information Security
- Definition of Cybersecurity
- Key Differences Between Information Security and Cybersecurity
- Focus Areas of Information Security
- Focus Areas of Cybersecurity
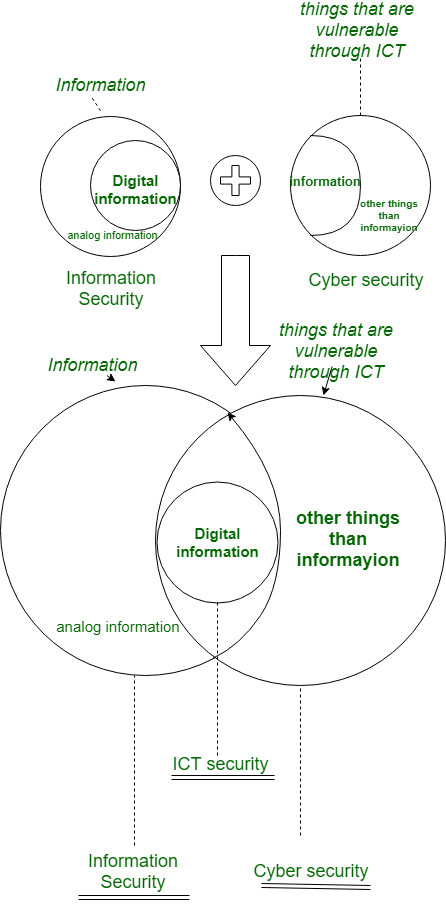
- Overlap Between Information Security and Cybersecurity
- Importance of Both in Modern Organizations
- Challenges in Information Security and Cybersecurity
- Conclusion
Introduction to Information Security and Cybersecurity
With the increased reliance on digital systems and the Internet, information security and cybersecurity have become inevitable. As Cybersecurity Training Courses organizations continue to digitize their operations, cyber threats increase, making it crucial to integrate both into organizational frameworks. The consequences of inadequate protection can range from reputational damage to financial losses, regulatory penalties, and loss of customer trust.
Are you curious to know more about Cybersecurity ? Take advantage of our comprehensive online Cyber Security Online Training .
Definition of Information Security
- Internal Threats vs. External: Information security entails protecting both internal and external threats, including employees, from unauthorized or intentional misuse. Cybersecurity addresses external risks like hacking but is concerned with fewer internal risks when it impacts digital systems.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Both information security and cybersecurity support disaster recovery planning, but information security generally involves more broad-ranging data recovery, using tape backups and redundant systems, whereas cybersecurity focuses more on securing data in a cyberattack.
- Preventive vs. Reactive: Information security practices tend to be more preventative, focusing on policies, procedures, and controls before a data breach occurs. Cybersecurity, while also preventive, often focuses more on rapid responses to ongoing cyberattacks and vulnerabilities.
- Protection against cybercrime: the threat of organizations by Cyber Awareness is growing in strength and sophistication and is often organized with a financial motivation. Efforts for information security and cybersecurity must be made in this regard.
- Customer Trust and Reputation: The damage caused to reputation, legal consequences, and customer trust are associated with data breaches and cyberattacks. Data and systems protection helps organizations maintain credibility and customer confidence.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations must comply with laws and regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA. They must implement strong information security and cybersecurity practices to avoid penalties. Failure to comply may result in legal ramifications and financial loss.
- Digital Transformation: As organizations shift towards more digital and cloud-based operations, ensuring robust information security and cybersecurity measures becomes critical to protecting sensitive data from evolving threats.
Governance and Compliance: Information security refers to protecting information and ensuring compliance with a myriad of data protection laws, regulations, and industry standards, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS. Organizations must set governance frameworks in place to better manage data security.
Data Classification: An important part of information security is classifying data as public, confidential, or restricted and applying security controls to this classified data.
Physical Security: Information security encompasses physical controls, too, including the protection of servers and workstations and physical site access control to limit access.
Definition of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from digital attacks, theft, or damage. This involves implementing various measures and technologies designed to safeguard information from unauthorized access, breaches, and other cyber threats, such as viruses, Malware Analysis, and hackers. Cybersecurity is critical for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data in an increasingly interconnected digital world.
Focus on Cyber Threats: Cybersecurity aims to defend against all types of digital attacks that target online systems, networks, and devices. The field includes defense against various kinds of malware (viruses, worms, Trojans) and cyberattacks like DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service).
Protecting Critical Infrastructure: Cybersecurity is an essential tool to safeguard critical infrastructures like financial systems, power grids, and government networks. Cyberattacks may have severe impacts on services, loss of finance, and risks to national security.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Cybersecurity also deals with advanced persistent Cybersecurity Threats Protection , where attackers penetrate a system, remain undetected for a long time, and extract valuable information.
Become an expert in cyber security. Enroll in this Cyber Security Online Training now to acquire the knowledge you need.
Key Differences Between Information Security and Cybersecurity
Focus Areas of Information Security
The use of DLP (Data Loss Prevention)techniques and systems by information security professionals to prevent unauthorized sharing, transfer, or loss of sensitive data.Data should be encrypted in both storage and transmission and is a key area of information security to protect against unauthorized access in Cybersecurity Training Courses . Access Control Information security also deals with administering access controls and limiting certain information to authorized access by only those individuals due to role-based access or multifactor authentication. Security Auditing and Monitoring is critical as it relates to monitoring systems; therefore, one has to audit access logs when necessary to identify any possible information security breach and verify if security policies are being implemented.
Focus Areas of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity experts collect, analyze, and respond to threat intelligence for one to remain in front of cyberattacks. They monitor emerging attack patterns, hacker tactics, and possible vulnerabilities. Malware Analysis is a Part of cybersecurity is analyzing different types of malware, such as ransomware, spyware, and trojans, to understand how they work, how to prevent them, and how to mitigate their effects. Penetration testing (pen testing)is a routine conducted by cybersecurity experts. It simulates attacks on systems to find vulnerabilities that a hacker might exploit. Zero-trust security models that do not trust any entity by default, whether it is inside or outside the network, have become a primary focus area of cybersecurity against threats from within and outside.
Transform Your Career with Cyber Security Knowledge Enroll in ACTE’s Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Overlap Between Information Security and Cybersecurity
Security Controls: Both information security and cybersecurity apply security controls to minimize risks. For instance, firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) can monitor and block unauthorized access.
Incident Response: When a security breach occurs, both practices need to be involved. Information security concerns data-related breaches, whereas cybersecurity concerns the technical approach to addressing and countering a cyber breach.
Security Policies and Awareness: Information Network Security Keys and cybersecurity professionals develop security policies, train staff, and educate them on the necessity of following security practices.
Encryption: While it is mostly related to cybersecurity, encryption also plays a significant role in information security, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality while being stored, transmitted, or processed.
Importance of Both in Modern Organizations
Get interview-ready with our collection of Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers Questions.
Challenges in Information Security and Cybersecurity
Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated. They employ methods such as social engineering, spear phishing, and advanced malware to exploit weaknesses. Both fields must constantly update their defenses to keep up with these threats. Employees, whether by action or mistake, are among the biggest sources of vulnerability. Therefore, it is a continuous challenge for information security and cybersecurity teams to improve insider threats and reduce human error through continuous training.As companies incorporate new technologies, such as Internet of Things, AI, and cloud computing, the complexity of integrating security measures for those technologies becomes significant. Both domains must be aware of new attack surfaces that come along with innovation.Many organizations struggle with limited security budgets. Prioritizing investments and justifying the costs of robust security measures against the potential financial and reputational damage of a breach remains a significant challenge.
Conclusion
Information security and cybersecurity are two different things that serve as the most important need in today’s highly connected world and data-driven world. Although their scope and focus areas are different, they must collectively provide holistic protection to organizations. Organizations will thus be able to protect their digital data and infrastructures by targeting the physical threats as well, enhancing the level of user awareness, introducing recent security measures, and staying a step ahead of Cybersecurity Training. Continuous partnership, investment into security, and adaptation to emerging risks are key features of a secure and resilient digital environment.





