
- Introduction to Network Securitys
- Types of Network Security Threats
- Firewall Tools and Their Functions
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
- Encryption Tools for Secure Communication
- Vulnerability Scanning Tools
- Future Trends in Network Security Solutions
- Conclusion
Introduction to Network Security
Network security refers to the combination of technologies, processes, and policies that are put in place to safeguard the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of computer networks and data. In today’s hyper connected digital world, data breaches and cyber threats are a constant concern. Every business, from startups to global enterprises, depends heavily on digital infrastructure, which makes protecting networks more critical than ever. Network security encompasses a wide range of Cyber Security Training Courses , including hardware and software solutions, administrative controls, access management systems, and routine security monitoring. Whether it’s protecting data while in transit or ensuring endpoints are not compromised, network security acts as the foundational defense mechanism of an organization’s IT ecosystem. Security tools are integral to a solid cyber threats infrastructure. They automate processes, offer visibility into potential threats, and provide a mechanism to respond rapidly to security incidents. Without proper tools, even the most robust policies may fall short in detecting or mitigating attacks. Modern network security tools play multiple roles. web applications help organizations monitor traffic, detect unauthorized access, prevent data leakage, and ensure compliance with regulatory mandates like GDPR or HIPAA. These tools are essential not only for preventing attacks but also for performing forensic analysis after a breach, thereby strengthening the overall defense system.
Types of Network Security Threats
- Threats to network security are evolving, both in volume and complexity. Understanding these threats is the first step in choosing the right tools to defend against them.
- Malware, such as viruses, ransomware, spyware, and worms, infiltrates systems to steal data, damage files, or disrupt operations. Phishing attacks trick users into providing sensitive information like passwords or banking details by pretending to be trustworthy entities.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks flood networks or systems with traffic, causing legitimate services to become inaccessible.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks occur when hackers secretly intercept or alter communication between two parties. SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) exploit vulnerabilities in web applications to Vulnerability Scanning unauthorized access to databases.
- Each threat requires specific tools and Database Security to effectively mitigate its impact. Selecting the right tools depends on various factors, including an organization’s size, industry, infrastructure, and risk tolerance. One of the first considerations should be scalability—tools must be capable of growing with the organization’s needs.
- The solution should also offer real-time detection and response capabilities, ensuring immediate action in case of a breach.Ease of integration is another major factor; tools should work seamlessly with existing systems and workflows.
- Support for regulatory compliance and centralized management dashboards are crucial for visibility and control. Lastly, vendor reputation, technical support, and update frequency can significantly affect the overall effectiveness of the tool.
To become a certified cyber security, have a look at our Cyber Security Online Training right now.
Firewall Tools and Their Functions
Firewalls act as the first line of defense by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic. They can be hardware-based, software-based, or both. Traditional firewalls filter traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols, while Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs) include features like deep packet inspection, web applications, and threat intelligence. Popular firewall tools include pfSense, Cisco ASA, Fortinet FortiGate, and CheckPoint Firewalls. Network Topology tools help block unauthorized access, prevent data leaks, and can be configured to match specific policies. Modern firewalls also integrate with SIEM platforms to provide comprehensive threat analysis.
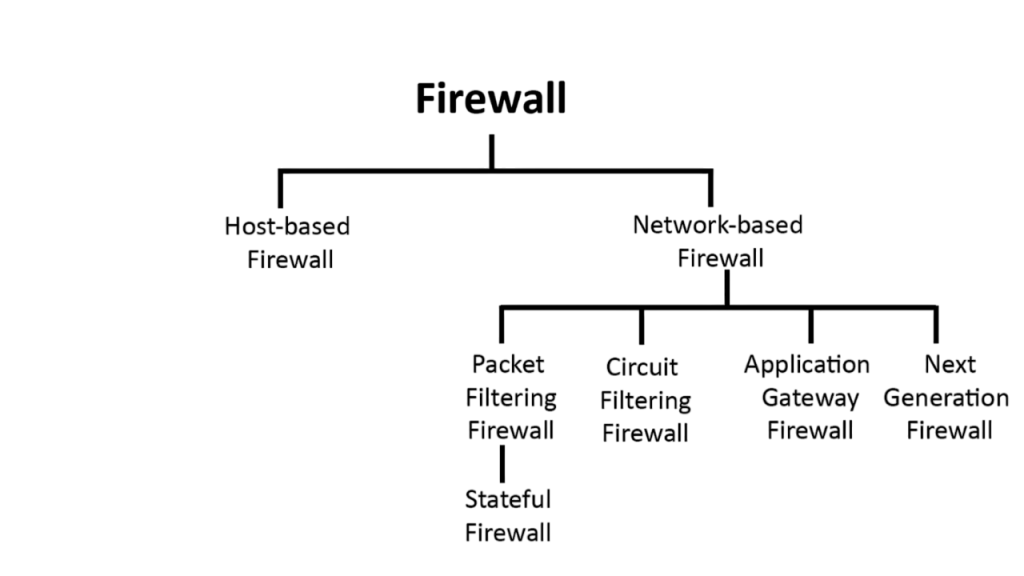
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): NGFWs often include IPS to detect and block sophisticated attacks in real time.
- Application Awareness: Firewalls can identify and control applications regardless of port or protocol used.
- User Identity Integration: Modern firewalls can enforce rules based on user roles and identities by integrating with directory services like Cybersecurity Training Courses or Active Directory.
- VPN Support: Firewalls often support secure remote access through VPNs, protecting data in transit.
- Cloud Compatibility: Many firewall solutions now offer cloud-based deployments to protect virtualized environments and hybrid infrastructures.
- Automated Updates: NGFWs frequently update their threat intelligence databases automatically to stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Firewalls: Fortinet FortiGate, Cisco ASA, pfSense
- IDS/IPS: Snort, Suricata, Cisco Firepower
- Antivirus: Bitdefender, Norton, ESET
- Encryption: VeraCrypt, OpenSSL, NordLayer
- Vulnerability Scanners: Nessus, OpenVAS
- SIEM: Splunk, IBM QRadar, Microsoft Sentinel
- Vulnerability Scanning assess systems and networks for potential weaknesses that attackers could exploit. These tools identify misconfigurations, outdated software, and known vulnerabilities, providing remediation guidance.
- Common tools include Nessus, OpenVAS, and QualysGuard. Scanners should be used regularly to ensure that new vulnerabilities introduced by software updates or network changes are promptly identified and addressed.
- These tools are essential for both internal security Cyberwarfare and compliance certifications.SIEM tools collect, analyze, and correlate security event data from across the network to provide real-time insights and alerts.
- They are central to threat detection and response strategies. SIEM solutions provide a unified view of an organization’s security posture and help investigate incidents faster.
- Examples include Splunk, IBM QRadar, LogRhythm, and Microsoft Sentinel. Modern SIEMs also use machine learning to detect anomalies and provide predictive insights, making them a valuable tool for security analysts and SOC teams.
- As technology continues to advance, so do the threats. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are increasingly used in security tools to detect and respond to threats in real time. AI-driven tools can analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and respond to threats faster than human teams.
- Another growing trend is Zero Trust Architecture, where no user or device is automatically trusted, even inside the network perimeter. Tools supporting zero trust are gaining momentum as businesses embrace cloud and hybrid environments. Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is also on the rise.
- Encryption Tools unifies threat detection across multiple layers (network, endpoints, servers, and cloud) into one platform. Additionally, as quantum computing emerges, the need for post-quantum cryptography is becoming evident to prepare for future decryption capabilities.
- Cloud-native security tools are also in high demand, as organizations migrate to platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. These tools offer scalability, integration, and centralized control that on-premise tools often lack.
To learn about different Cybersecurity techniques, sign up for our Cyber Security Online Training right now!
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
IDS and IPS tools monitor network traffic for signs of suspicious activity. While IDS tools detect and alert administrators about potential threats, IPS tools go a step further by actively blocking or preventing them. These systems rely on signature-based detection, which matches known attack patterns, and anomaly-based detection, which identifies unusual network Hacking Tools and Software. Tools like Snort, Suricata, and Cisco Firepower offer robust intrusion detection and prevention capabilities. When integrated with other tools, IDS/IPS systems form a critical layer of proactive defense against complex threats.
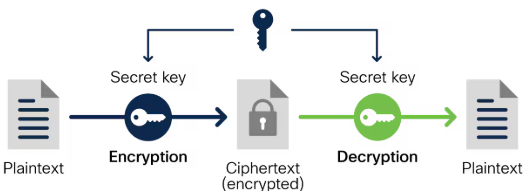
Encryption Tools for Secure Communication
Encryption is essential for protecting data both at rest and in transit. Network Security Solutions transforms data into unreadable code, making it accessible only to those with the correct decryption key. Encryption tools are critical for securing emails, files, databases, and network communications. Popular tools include VeraCrypt, OpenSSL, and Application Security for data encryption. SSL/TLS protocols, implemented through tools like Let’s Encrypt and Cloudflare, secure web applications communications. VPN services such as NordLayer, Perimeter 81, and Cisco AnyConnect encrypt all internet traffic, making them vital for remote workers.
Some of the most widely adopted and reliable tools include:
These tools are selected based on factors like performance, ease of use, threat intelligence capabilities, customer support, and integration options. Organizations typically use a combination of cyber threats tools to ensure layered protection.
Transform Your Career with Cyber Security Knowledge Enroll in ACTE’s Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Preparing for Cyber Security job interviews? Check out our Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers now!
Future Trends in Network Security Solutions
Conclusion
Network Security Solutions is not a one-time investment but a continuous process of evaluation, improvement, and adaptation. With cyber threats growing in sophistication, organizations must be equipped with the right mix of security tools to protect their digital assets. From basic Firewall Tools to Cybersecurity Training AI-powered SIEM systems, each tool plays a unique role in defending against network-based threats. Understanding the functions, capabilities, and use cases of these tools enables businesses to make informed decisions and build robust cybersecurity infrastructures. Looking ahead, the integration of AI, automation, and cloud-based security solutions will define the next era of network protection. Organizations that invest in proactive security measures today will be better positioned to defend against the cyber challenges of tomorrow.





