
- Introduction
- What are Cyber Threats?
- Types of Cybersecurity Threats
- Emerging Cyber Threats
- Sources of Cybersecurity Threats
- Why is it necessary to protect from Cyber Threats?
- Best Practices for Cyber Protection
- Conclusion
Introduction
Cybersecurity has evolved from being a niche issue to now becoming a general requirement in today’s digitally-first world, from personal gadgets to massive enterprise systems, cloud computing infrastructures, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Almost every industry is connected due to the exponential growth of the Internet and digital technology. Devastating outcomes can result from cyberattacks, ranging from loss of personal information to extensive disruptions in vital infrastructure. The growing sophistication, frequency, and scope of cyberattacks seem to have synchronized with the development of digital systems. Cyber Security Training Courses are essential in addressing this challenge, equipping individuals and organizations with the knowledge and skills to defend against these evolving threats. Cyberattacks on financial systems, vital infrastructure such as hospitals and power grids, sensitive personal information, and the very foundation of democratic processes by hacking, data security, or the dissemination of disinformation are currently all possible.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
What are Cyber Threats?
Cyber threats, in simple terms, refer to any possible malevolent acts or assaults that pose a threat to compromise either the availability, confidentiality, or integrity of computer networks, devices, data security, or systems. That is, cyber threats take different forms and can be executed by different players, including nation-state hackers, disgruntled workers, and cybercriminals, among others. Cipher Encryption plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive data from these threats by ensuring secure communication and data storage.
Cyber threats mainly target the exploitation of weaknesses in a system to achieve nefarious goals, such as stealing confidential data, sabotaging commercial activities, leading to losses, or damaging the brand name of an organization. Internal as well as external cyber threats are present and vary in terms of complexity and cyber protection. Knowing these threats is essential for creating effective cybersecurity strategies and techniques to protect digital assets from getting ruined.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats are malicious activities that seek to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to networks, computer systems, and private information. There can be so many forms and sources for such dangers. The following are the most common types of cybersecurity risks:
- Malware: Malicious software, or malware, is the term used in cyber security for a threat in a form that harms or gains unauthorized access to a computer system. Such types of threats include ransomware, Trojan horses, worms, and viruses. It spreads through various means, including software downloads, rogue websites, and contaminated email attachments.
- Viruses: Malicious programs that can multiply and even transmit from one device to another are viruses. Once on your devices, viruses can change files, steal data, and even hijack the whole device. Reconnaissance in Cyber Security often involves gathering information about potential targets, which can include identifying vulnerable systems for viruses to exploit.
- Worms: Worms differ from the viruses, though they are more or less similar. This is because they are capable of spreading without human interaction. They are known to slow down your devices, create network congestion, and make them vulnerable to other internet threats.
- Trojans: Trojan horses are malicious applications that come as software disguising themselves to be trusted applications. When you unknowingly download a trojan, it can open backdoors in your system, which gives hackers direct access to your device.
- Ransomware: The most destructive forms of malware are the various types of ransomware, which work by encrypting files or locking users out of their systems once the malware has infected the victim’s device or network. Only by paying the attacker a ransom and sometimes these ransom payments are paid in cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, will the attacker unlock the machine or decrypt the data. Individuals, large corporations, government institutions, and other critical infrastructure are all victims of ransomware attacks. Such attacks can lead to significant outages, financial loss, and data breaches.
- Phishing: Another type of cybersecurity threat is phishing, where hackers attempt to deceive victims into revealing sensitive information such as credit card numbers or passwords. A sense of urgency or importance is usually added to the message in question, nudging the recipient to act instantly by sharing such information or clicking on a link.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Man-in-the-middle attacks arise when hackers secretly capture communications between two parties, such as a user and a website. Therefore, if hackers can intercept private data or even change the conversation for the hacker’s needs, man-in-the-middle attacks pose a particularly grave danger in terms of online shopping and banking.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: A hacker that floods a site or network with traffic is performing a denial-of-service attack, which makes it unavailable to legitimate users. Their services may be impaired or organizations financially ruined by such hackers. The toughest fight will be distributed denial-of-service attacks since they try to flood the targeted resource from multiple sources.
- SQL Injection: A cyber threat that has been known for a long time is SQL injection, where attackers inject harmful code into a website’s database, allowing them access to and control private data. This leads to identity theft, data security, and website vandalism. By using appropriate security measures and frequently updating software, this form of attack can be partially prevented.
- Social Engineering: Social engineering is a practice where hackers deceive people into providing them with private information or performing activities that compromise security. Strict data security procedures and awareness training are essential to prevent social engineering attacks.
- Hackers: Hackers try security breaches and exploit vulnerabilities in a computer system or network through a host of strategies and approaches. Mostly, hackers do this for personal gain, making money, political activism, and sometimes even to retaliate and stalk. Hackers can indeed invent new risks for the fun of the challenge or to brag about within the hacking community.
- Nation-states: Nation-state cyberattacks place a shocking amount of time and money to gain an advantage for their purposes, including intelligence gathering, espionage, theft, and disruption of military power. They will stop at nothing to achieve their strategic objectives, as evidenced by attacks on software supply chains and efforts to exfiltrate intellectual property data on vaccinations. As a recent study sponsored by HP Inc. recently reported, some governments use tactics that organized crime groups use online.
- Criminal Groups: For financial advantage, criminal organizations mostly aim to infiltrate networks or systems. They use malware, spam, spyware, and phishing to commit different frauds, thefts, and extortions. Whitelisting can help mitigate these threats by allowing only trusted applications and processes to run, preventing malicious software from infiltrating systems.
- Terrorist Groups: Terrorists aim to destroy, infiltrate, or take advantage of vital infrastructure using cyberattacks to endanger national security, interfere with the economy, compromise military hardware, or result in a large number of casualties.
- Malicious Insiders: Insiders are an entity who are legally authorized to access an organization’s assets and make wrongful use of them for their financial or personal gain. They may include contractors, employees, other business acquaintances, or outside vendors.In many countries, there is a blurred line between criminal organizations and national intelligence. Most cyberespionage is performed by criminals. Additionally, the “dark web,” an increasingly popular underground marketplace among criminals, is where much of the cyber threat exchange occurs. It is here that hackers buy and sell ransomware, malware, stolen credentials to compromised networks, and other illegal goods and services.
- Passwords must contain numbers, capital and small case letters, and special characters. Using personal details like birth dates, usernames, or email addresses would make it very easy for cybercriminals to hack into your system.
- Never use easily guessable common words prone to “dictionary attacks.” The passphrase is the new word for authentication. It is more secure and more extended than the normal passwords.
- Using a separate password for each different account will make disclosure impossible. And it will protect your other accounts in case one of them gets exposed. Besides, password management tools are great choices for creating and saving strong passwords and adding another layer to security.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Emerging Cyber Threats
The digital world is always evolving, and so do the cybersecurity threats. One has to be very vigilant about these new threats in cyber security also, and to be prepared and to counter the situation even better in the longer run. Since the year 2020, the biggest hurdle that businesses along with IT organizations have faced is the pandemic. This period has seen a surge in cyber threats, and the threats have also become more evolved. Cyber Security Training Courses are crucial in helping individuals and organizations stay ahead of these advanced threats by providing the necessary skills to detect and mitigate them effectively.The pandemic situation will likely be used by cybercriminals as a motivation for phishing and social engineering attacks. Besides this, the pandemic forcing employees in all countries to work from home and conduct their businesses on the internet has created a myriad of unsecured entry points for hackers. Cloud Breaches Companies are shifting to the cloud to ensure business continuity through remote working, and increasingly, cybercriminals are targeting the cloud. The most common sources of cyberattacks and cybercrime include cloud misconfigurations, vulnerable cloud apps, and incomplete data deletion as sources of cloud-based security risks. IoT Attacks IoT devices and applications are being deployed in large numbers by major world organizations. This increased connectivity has brought in its wake new challenges in terms of security, thereby placing them at risk. Devices can be taken over by cyber crooks who use vulnerabilities as a means of breaching networks.
Sources of Cybersecurity Threats
Many things can cause cyber threats. Threat actors and their motivations need to be known to protect one’s self from a cyberattack. Here are some of the areas where cyber dangers may arise:
Are You Considering Pursuing a Cybersecurity Master’s Degree? Enroll For Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Why is it necessary to protect from Cyber Threats?
Every organization is exposed to cybersecurity dangers, which are not always under the direct supervision and control of IT security teams. With greater and greater interconnectedness (IoT), outsourcing, and the growing use of cloud services and technologies, there are more cybersecurity attack vectors than ever before.Increased importance of cyber security risk management, vendor risk management, and third-party risk management is required to reduce third-party data breaches since third-party and fourth-party risks are also growing. Cyber Media plays a critical role in raising awareness about these risks and keeping both organizations and the public informed about the latest threats and security measures. Business executives unknowingly make riskier choices every day. Information security needs to be an organization-wide effort and cannot be left to the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) alone.
Best Practices for Cyber Protection
For digital assets to be safeguarded, cybersecurity best practices are key. These excellent practices may also help make workers better augment the overall security posture and lower the likelihood of cyber incidents.
Use Strong Passwords:First, among the lines of defense, stronger passwords increase security. On the other hand, weak passwords enable cybercrime to access sensitive assets unauthorizedly.
Tips that IT professionals should follow when creating strong passwords include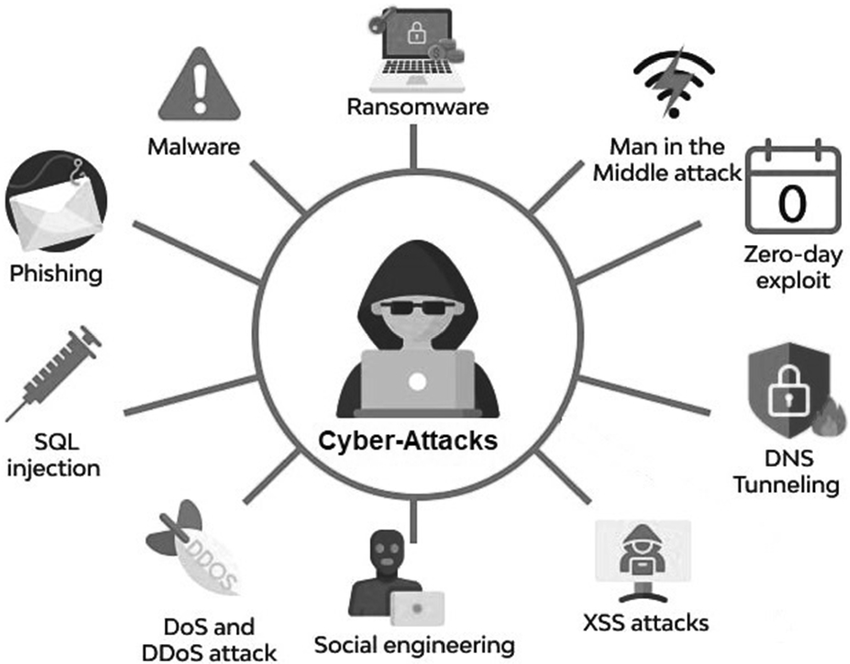
Multi-factor authentication is the process of using at least two different factors for verifying during account login. In addition, the implementation of MFA provides additional security. Even though you suffer password theft, your password is exposed, and still, MFA keeps you safe from cybercriminals. Web Security is strengthened with MFA by adding an extra layer of protection, ensuring that even if attackers gain access to login credentials, they cannot easily breach systems. MFA authentication has 3 main classes of methods: password or pin, badge or smartphone, and fingerprint or face recognition. MFA enables IT professionals to enhance IAM policies. In most cases, the MFA factor is the combination of a username-password and a one-time password (OTP) code sent to mail or mobile phones restricted to a limited time.
Keep Your Software Up to Date:Keeping the software updated is important for identifying security flaws and taking action against vulnerabilities to reduce attack surfaces. It would mean that IT professionals must update all software with the latest security patches because cyber thieves could use the vulnerability in outdated software. Patch management helps produce more output with less cost and increases compliance with standards and regulations.
Be Aware of Social Engineering Attacks:Be Alert to Social Engineering Attacks is one of the most important calls to action in the current technological world. Social engineering attacks describe the manipulation and exploitation of human nature to gain access to sensitive information. Social engineering cybercrime exploits psychology and “human hacking” rather than any hacking of a technical nature.
Backup Your Data:Backup your data is important in recovering data from different failures, including human errors as well as computer or network system failures, natural disasters, or cybercrime. Regular backups can reduce data failures and ensure business continuity. There are three types of data backup. The first is a full backup, a full copy of all files. The second is incremental backup, copying files that differ from the previous document.
Want to Learn About Cyber Security? Explore Our Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Conclusion
With the rapid evolution of the digital landscape, cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly complex and frequent. Cyberattacks against individual, business, and government targets, multiplied by the tens of thousands, leave no one in the dark about becoming the next target. Cyber Security Training Courses are becoming increasingly essential to prepare individuals and organizations to recognize and respond effectively to these growing threats. Ransomware, phishing, and even APTs targeting insiders are a mix of threats that involve both individuals and organizations. Bottom line: cybersecurity is a process that requires vigilance, change, data security, and collaboration. Maintaining strategies for proactive defense, informing the culture of cyber protection, and building a culture of security can highly reduce the risks caused by cyber threats for both individuals and organizations. However, as the art of cybercrime advances along with its complexity, new cyber tactics are developed, and hence, the resultant cybersecurity practices evolve to protect not only the systems but also the data against the backdrop of the threat landscape.





