
- Introduction to Production Management
- Definition and Key Concepts
- Importance of Production Management
- Objectives and Goals
- Production Planning and Control
- Types of Production Systems
- Resource and Inventory Management
- Quality Control and Assurance
- Process Optimization Techniques
- Tools and Software Used
- Career Opportunities in the Field
- Conclusion
Introduction to Production Management
Production management is a process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling operations related to the production of goods or services. It is centered on the effective utilization of resources like raw materials, labor, and machinery to produce high-quality goods on time. Its aim is to maximize the production process, minimize waste, and effectively meet customer demands. In present-day competitive business practices, effective production management is crucial to being cost-effective, keeping product quality intact, and delivering customer satisfaction. PMP Training is a mix of strategic planning, operational implementation, and continuous refinement to make the production process smoother. Companies ‘ practical application of production management techniques can help increase productivity, cut costs, and achieve competitiveness.
Definition and Key Concepts
Production management is all about coordinating production activities to meet organizational objectives. Production management includes several major concepts that describe its purpose and scope:
- Production Planning: Part of production planning is determining what to make, how much to make, and when to make it. Planning leads to optimum resource utilization and on-time delivery.
- Resource Management: Proper utilization of What is Agile , labor, and machinery is vital to prevent congestion and smooth functioning.
- Quality Control: Ensuring product standards by having regular inspections and taking corrective actions.
- Inventory Management: Maintaining inventory levels optimized to prevent overproduction and shortages.
- Process Optimization: Optimizing workflows to minimize waste, maximize efficiency, and maximize productivity.
- Cost Efficiency: Keeping production processes cost-effective while ensuring product quality.
- Optimal Resource Utilization: Labor, materials, and machinery must be utilized effectively to increase productivity.
- Cost Minimization: Minimize the cost of production by reducing waste and optimizing the process.
- Quality Consistency: Maintaining consistent product quality by following the quality standards and regulations.
- Timely Delivery: Products must be produced and delivered on time to meet customer requirements.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Modifying production processes to adapt to shifting market needs.
- Customer Satisfaction: Providing high-quality products that meet or surpass customer requirements.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously improving production processes to increase efficiency and quality.
- Batch Production: In this production system, a definite number of products are manufactured in batches. Operations Management is prevalent in food processing and pharmaceuticals.
- Mass production : It is the large-scale production of standardized goods, such as nonstopronics, on an assembly line.
- Continuous Production: Continuous production is applied to high-volume items, e.g., chemicals, oil, or electricity.
- Lean Production: This aims to eliminate waste while optimizing efficiency. It employs methods such as Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing and value stream mapping.
- Quality Control (QC): Stages of Team Development entails checking and testing products at several points of the production process. It ensures that faulty products are detected and rectified before customer delivery.
- Quality Assurance (QA): This aims to avoid defects by applying standard processes and best practices across production. It encompasses frequent audits, training, and ongoing improvement.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Combine production, inventory, and financial activities. Examples: SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics.
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): It offer real-time monitoring and control of production operations. Examples include Siemens Opcenter and Rockwell Automation.
- Inventory Management Tools: Monitors stock levels and reorders automatically. Examples: Zoho Inventory, QuickBooks.
- Quality Management Software (QMS): Controls quality processes and compliance. Examples: ETQ, MasterControl.
- Production Manager: Managing the complete production process.
- Operations Manager: Managing business activities daily.
- Quality Assurance Manager: Maintaining the quality standards of the product.
- Supply Chain Manager: Managing procurement and logistics.
By following and applying these concepts, companies can maintain consistent production quality, minimize inefficiencies, and respond effectively to market needs.
Gain in-depth knowledge of PMP by joining this PMP Certification Training now.
Importance of Production Management
Production management is essential to the success of any manufacturing or service-based company. Its importance can be seen in several important areas: First, it increases operational resource use by maximizing resource utilization, minimizing downtime, and rationalizing processes. This results in increased productivity and reduced production costs. Second, good production management guarantees quality consistency, vital for customer satisfaction and reputation. By having quality control, companies can minimize defects and provide dependable products. In addition, production management assists in controlling costs by reducing waste, maximizing the use of resources, and eliminating unnecessary costs. Project Management Tools also facilitates timely delivery, avoiding production delays and satisfying customers. Furthermore, it gives companies a competitive edge by allowing them to produce quality products efficiently and at low costs, placing them ahead in the market.
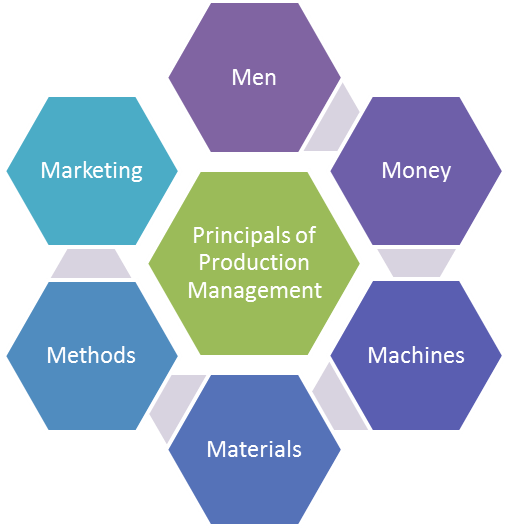
Objectives and Goals of Production Management
The main goals of production management are efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. The main goals are:
Through these aims, companies can enhance their operational performance, Visualizing Project Timelines , and improve their market position.
Start your journey in PMP by enrolling in this PMP Certification Training .
Production Planning and Control
Production planning and control (PPC) is one of the most critical functions of production management that ensures organized and efficient operations. PPC has two main components, Production Planning Identifying the production schedule, resource allocation, and workflow. It encompasses Forecasting Predicting future demand to plan production quantities precisely. Scheduling Identifying the time frame for different production activities. Resource Allocation Allocating the required labor, materials, and equipment to the production process. Production Control the monitoring and controlling of the production process to ensure it’s in line with the plan. PMP Training entails Monitoring Monitoring production progress and detecting deviations from the schedule. Adjustments Updating changes to correct problems or delays in real-time. Quality Assurance Taking measures to keep product quality intact during production. Effective management of PPC can enable businesses to improve efficiency, reduce delays, and provide consistent product quality.
Types of Production Systems
There are different production systems, each of which is intended to serve particular business requirements and production objectives. The principal types are, Job Production is the production of tailor-made products or small lots, usually based on individual customer specifications. Examples are bespoke furniture and handcrafted jewelry.
The choice of an effective production system depends on the nature of the business, product type, and production objectives.
Enhance your knowledge in PMP. Join this PMP Master Program Training Course today!
Resource and Inventory Management
Practical resource and inventory management are vital for trouble-free production activities. Resource Management is the efficient use of labor, machines, and materials. Proper labor distribution, equipment upkeep, and material handling ensure timeliness in production and lower costs. Inventory Management Maintaining optimum stock levels ensures that production is not interrupted due to material shortages. Business Agility also avoids overproduction and unnecessary inventory, which may result in wastage. Methods like Just-in-Time (JIT) and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) are used for effective management of inventory. Optimizing resource and inventory management makes businesses waste-free, saves costs, and increases productivity.
Quality Control and Assurance
High product quality is a fundamental goal of production management. Quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) are integral parts:
By incorporating QC and QA in production processes, companies can provide consistent, high-quality products and minimize the chances of recalls or customer complaints.
Preparing for PMP interviews? Visit our blog for the best PMP Interview Questions and Answers!
Process Optimization Techniques
To improve efficiency and lower costs, companies apply different process optimization techniques, such as, Lean Manufacturing aims to reduce waste while keeping productivity intact. Methods such as Kanban and 5S assist in streamlining processes. Six Sigma A fact-based methodology to minimize defects and enhance product quality using the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improverol) approach. Total Quality Management (TQM) organization involves a strategy for ongoing quality improvement that engages all employees. Continuous Improvement (Kaizen) Phases of Project Management , small changes to improve productivity and efficiency. Using these methods enables companies to attain operational excellence and increase customer satisfaction.
Tools and Software Utilized in Production Management
Technology has a critical role to play in contemporary production management. Widely employed tools and software are:
With these tools, companies can enhance accuracy, simplify operations, and make informed decisions.
Career Opportunities in Production Management
Lean manufacturing certifications, Six Sigma, and project management certifications broaden career opportunities for this role.
Conclusion
Production management is critical for companies to maximize efficiency, PMP Training , and produce high-quality products. Proper resource management, quality control practices, and process improvement can improve productivity and customer satisfaction. With the appropriate tools, strategies, and technologies, production management leads to business success in the current competitive environment.





