
- Introduction to Cloud Computing and IoT
- How Cloud Computing Supports IoT Devices
- Role of Edge Computing in IoT and Cloud
- IoT Data Storage in Cloud Platforms
- Security Challenges in Cloud-Based IoT
- Cloud-Based IoT Application Development
- Serverless Computing and IoT
- Role of AI and Big Data in IoT Cloud Computing
- Future of Cloud Computing in IoT
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cloud Computing and IoT
Cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) are two transformative technologies that are revolutionizing industries across the globe. Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more over the internet. It provides flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, making it an ideal platform for managing and processing large volumes of data. On the other hand, IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices that collect, exchange, and process data through the internet, a concept often explored in-depth in a Cloud Computing course. These devices range from smart home appliances to industrial machinery, wearable health devices, and connected cars. The combination of cloud computing and IoT has led to the development of more intelligent, data-driven applications that can process and analyze large amounts of data in real-time. This synergy between cloud computing and IoT enables businesses and individuals to harness the power of data collected from a wide range of devices, ensuring efficiency, scalability, and continuous innovation.
Excited to Obtaining Your Cloud Computing Certificate? View The Cloud Computing Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
How Cloud Computing Supports IoT Devices
Cloud computing is essential in enabling the full potential of IoT by providing scalable infrastructure and services for IoT devices. Here are some ways in which cloud computing supports IoT:
- Data Processing and Analytics: IoT devices generate large amounts of data, and cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure to store, process, and analyze this data in real time. Cloud platforms offer powerful computing power and storage capabilities, ensuring that IoT data can be effectively managed and analyzed.
- Storage: Cloud platforms, such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Computing, offer scalable storage solutions to accommodate the massive data generated by IoT devices. Cloud storage ensures that data is stored securely and can be accessed easily from any location.
- Scalability: IoT networks often require the ability to scale up or down based on demand. Cloud services provide the flexibility to scale resources in real time, ensuring that devices can be added or removed from the network without any disruption.
- Centralized Management: Cloud-based IoT platforms provide centralized management for IoT devices. This allows businesses to monitor, manage, and update their devices remotely without requiring direct interaction with each individual device.
- Cost Efficiency: With cloud computing, businesses don’t need to invest heavily in on-premise infrastructure. Instead, they pay for the computing resources they actually use, making it a cost-effective solution for managing IoT systems.
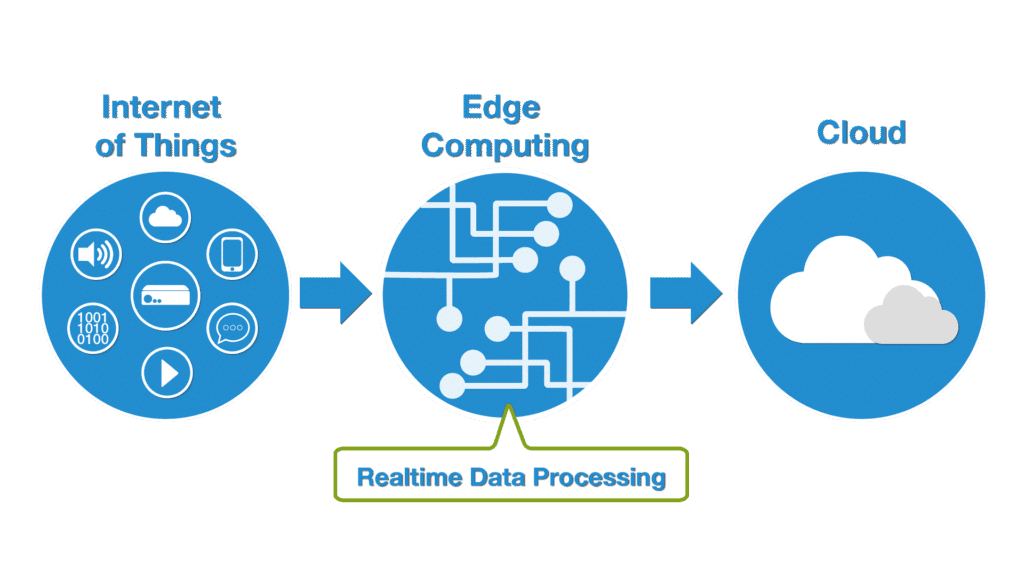
Role of Edge Computing in IoT and Cloud
While cloud computing plays a critical role in managing and processing IoT data, edge computing is equally important for reducing latency and improving the performance of IoT systems. Edge computing involves processing data closer to where it is generated, such as on the device or a nearby gateway, instead of sending it to a centralized cloud. This approach reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, lowers latency, and enables real-time decision-making. By processing data locally, edge computing helps reduce latency, which is crucial for time-sensitive Internet of Things like autonomous vehicles or industrial automation, where even a small delay can have significant consequences. It also improves bandwidth efficiency by reducing the volume of data sent to the cloud, making it ideal for remote or bandwidth-constrained environments. Additionally, edge computing facilitates real-time decision-making, essential for applications like predictive maintenance or smart grid management, where immediate actions are needed based on IoT data. Furthermore, by processing sensitive data locally, edge computing enhances privacy and security, minimizing exposure to potential breaches by avoiding unnecessary transmission of data to the cloud.
IoT Data Storage in Cloud Platforms
As IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, cloud platforms provide an efficient, scalable, and secure solution for storing this data. Cloud storage enables organizations to store IoT data without the need for physical hardware. The key storage options for IoT data include:
- Object Storage: Services like Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage are ideal for storing large amounts of unstructured data generated by IoT devices. These platforms offer scalability and durability, ensuring that IoT data is stored securely and can be accessed easily.
- Data Lakes: Cloud-based data lakes, such as AWS Lake Formation or Azure Data Lake, allow businesses to store massive amounts of raw data in its native format.AWS Data Lake are particularly useful for IoT environments that need to process and analyze data from diverse sources.
- Database Storage: IoT systems often require relational or NoSQL databases to store structured or semi-structured data. AWS RDS, Azure SQL Database, and Google Cloud Spanner are commonly used to store IoT data in a more structured format.
- Time-Series Databases: IoT data is often generated at regular intervals, making it ideal for time-series databases. Services like AWS Timestream, InfluxDB, and TimescaleDB are optimized for storing and querying time-stamped data generated by IoT devices.
- IoT Frameworks and Platforms: AWS IoT, Azure IoT Hub, and Google Cloud IoT Core are popular frameworks for building and managing IoT applications. These platforms offer features like device provisioning, messaging, and data ingestion, which are essential for IoT applications.
- Data Processing: Cloud platforms offer services for processing IoT data in real-time or batch mode. AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions allow developers to create serverless applications that respond to events from IoT devices.
- Data Analytics and Visualization: Cloud services like Amazon Kinesis, Azure Stream Analytics, and Google BigQuery help developers process, analyze, and visualize IoT data. These services enable real-time data analytics, which is crucial for applications like predictive maintenance or smart city management.
- Integration with Other Services: Cloud-based IoT applications can be easily integrated with other cloud services, such as machine learning, AI, and big data analytics, to enhance their capabilities.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical IoT data and applying machine learning algorithms, cloud-based IoT systems can predict when equipment will fail and schedule maintenance proactively, reducing downtime.
- Anomaly Detection: AI algorithms can analyze real-time IoT data to detect abnormal behavior or performance patterns, triggering alerts or automated actions.
- Data Insights: Big data platforms like Aws Redshift, Azure Synapse, and Google BigQuery enable the analysis of massive volumes of IoT data to uncover patterns, trends, and insights that can inform business decisions.
- Optimization: AI models can be used to optimize IoT system performance, such as adjusting sensor parameters or improving resource allocation based on real-time data.
- Increased Adoption of Edge and Fog Computing: As IoT devices generate more data, the need for edge and fog computing will increase, enabling faster decision-making and reducing reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: More IoT applications will leverage AI and machine learning for predictive analytics, automation, and real-time decision-making.
- 5G and IoT Integration: The advent of 5G will enable ultra-fast connectivity, allowing for more efficient and real-time data exchange between IoT devices and cloud platforms.
- Enhanced Security: As IoT ecosystems expand, there will be a greater focus on securing IoT devices, data transmission, and cloud platforms.
Ready to Earn Your Cloud Computing Certificate? View The Cloud Computing Course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Security Challenges in Cloud-Based IoT
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits for IoT, it also introduces several security challenges due to the large number of devices, data privacy concerns, and the potential for cyberattacks. One of the key challenges is device security, as IoT devices are often vulnerable to cyberattacks due to weak authentication methods, outdated firmware, and insecure communication channels. Ensuring that these devices are secure is crucial to protect the entire IoT ecosystem. Data privacy is another concern, as IoT devices collect sensitive information such as location and personal health data, which must be protected from unauthorized access. Cloud platforms must implement robust encryption and access controls to safeguard this data. Additionally, cloud security is essential, as the cloud infrastructure that stores IoT data must be secured from external threats by using proper network segmentation and encryption both at rest and in transit, topics that are typically covered in a Cloud Computing Course. Managing authentication and access control is equally critical to prevent unauthorized users from gaining control of devices or stealing sensitive data, with methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA) being highly recommended. Lastly, vulnerability management is vital; regular security updates, patching, and vulnerability assessments should be conducted to protect IoT devices and cloud services from emerging threats.
Interested in Pursuing Cloud Computing Master’s Program? Enroll For Cloud Computing Master Course Today!
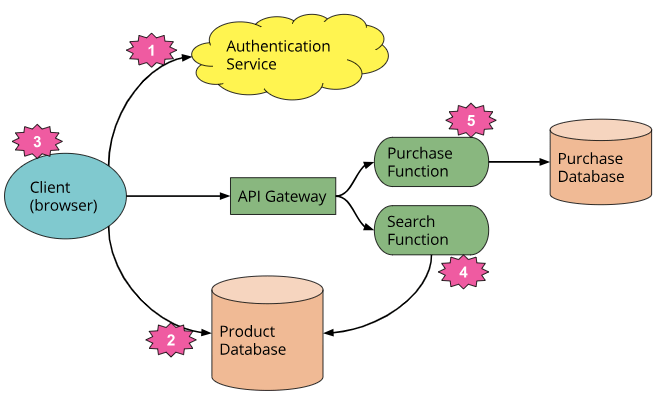
Cloud-Based IoT Application Development
Cloud computing provides developers with the tools and services needed to build scalable, efficient, and secure IoT applications. Key components of cloud-based IoT application development include:
Serverless Computing and IoT
Serverless computing allows developers to build and run applications without managing servers. This model is particularly useful for IoT applications because it abstracts the underlying infrastructure, enabling developers to focus on writing code and delivering functionality. Serverless computing offers several advantages for IoT applications, making it an attractive option for developers. It provides cost efficiency by allowing developers to pay only for the resources they use, which is particularly beneficial for IoT applications with variable workloads. Additionally, serverless platforms automatically scale based on the number of requests or events, accommodating the fluctuating demands of IoT devices. This scalability ensures seamless performance, regardless of the load. Moreover, Serverless Computing is often used in event-driven architectures, where cloud functions are triggered by specific events, such as IoT devices sending data or detecting faults. Popular services like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions further enhance the appeal of serverless computing, simplifying the development and management of cloud-based IoT applications.
Role of AI and Big Data in IoT Cloud Computing
The integration of AI and Big Data with cloud-based IoT systems has opened up new possibilities for intelligent decision-making and predictive analytics. Here’s how AI and big data enhance IoT:
Preparing for Your Cloud Computing Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions & Answer
Future of Cloud Computing in IoT
Conclusion
The combination of cloud computing and IoT is transforming industries by enabling scalable, data-driven applications. Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure and tools needed to manage IoT data, while edge computing helps reduce latency and bandwidth requirements. The integration of AI, big data, and serverless computing, concepts often covered in a Cloud Computing course, further enhances the capabilities of IoT. As IoT continues to evolve, the role of cloud computing will remain central to the development of smart, connected systems, offering new opportunities for innovation and optimization across a range of industries.


