
- A Supply Chain Management: What Is It?
- Types of supply chain
- How Do Attacks on the Supply Chain Operate?
- Well-known Supply Chain Attacks
- How can supply chain attacks be spotted?
- How Can Supply Chain Attacks Be Prevented?
- Conclusion
Cybersecurity has become an important issue for organizations as digital transformation changes the shape of business operations. As organizations rely increasingly on a network of third-party vendors, suppliers, and service providers, the vulnerability in these interconnected relationships may pose a significant risk. A compromised vendor or a software update can be a backdoor entry for cybercriminals, leading to data breaches, operational disruption, and financial loss. The Solar Winds attack and the Kaseya ransomware incident highlight that the requirement for good cybersecurity in supply chains is now at an emergency level of supply chain management.
Enroll Supply Chain In ACTE’S Cyber Security Course If You Want To Become An Expert In The Field And Have A Prosperous Career.
A Supply Chain Management: What Is It?
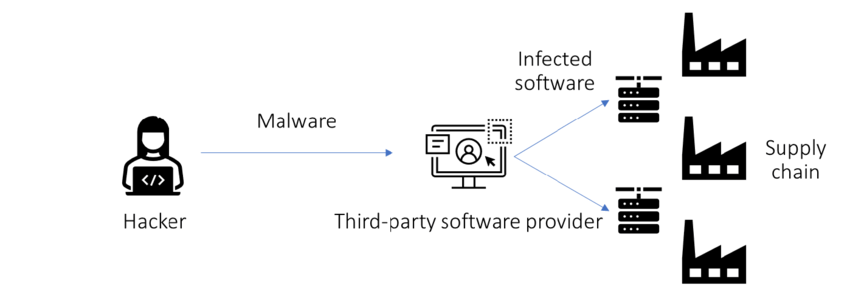
Cyberattacks that target the software manufacturing process, or the network of suppliers and vendors who supply the hardware and software components that go into modern technology goods, are known as supply chain attacks. The software chain of custody, a collection of suppliers and vendors that supply the hardware and software components that go into modern technology goods, is the target of a supply chain attack of Two-Factor Authentication
The attacker enters the supply chain through an upstream vendor or supplier and introduces spyware or an entry point into the hardware or software they offer. As the attack spreads downstream, all suppliers and vendors who depend on the affected component may then have their products infected. Attacks on the supply chain can have disastrous effects and jeopardize the security of several businesses and people. They are predicted to become more frequent as technological items become more intricate and linked.
Types of supply chain
- Software Supply Chain: This deals with the development and distribution of software products, like operating systems, applications, and libraries. Hazards Injection of malicious code, compromised updates, and third-party library vulnerabilities.
- Hardware Supply Chain: It refers to the design, production, and distribution of hardware components in physical form, such as computers, servers, and IoT devices. Hazards Tampering with the manufacturing process, fake or counterfeit components, and firmware vulnerability.
- Service Supply Chain: The third-party services that help to facilitate or enable business operations, such as cloud services, managed services, and advisory services. Threats of credential theft, insecure APIs, and data breaches.
- Data Supply Chain: In most cases, data flows through collections to processes, and then storage may involve the involvement of third-party service providers of data as well as other services for analytical services. Risks include leakages and compromised management that breach their respective compliance.
- Cloud Supply Chain: This encompasses the use of a service and or product distribution under a cloud Computing structure and or platform or infrastructure, as infrastructure, as service, software, as services. Risks: Incorrect configuration of cloud settings, vulnerabilities of shared resources, and dependency on third-party cloud service providers.
- Telecommunications Supply Chain:This involves hardware and software in a telecommunications network, including routers, switches, and mobile networks. It involves Risks such as the vulnerabilities of the network equipment, the interception of Database as it travels over the telecommunication network, and insider attacks.
- Third-Party Integration Supply Chain:Third-party software and services integrations, including payment processors, CRM systems, and APIs. Risks Poorly secured integrations, API vulnerabilities, and supply chain dependency risks.
Become An Expert In Supply Chain . Enroll In This Cyber Security Course Now To Acquire The Knowledge You Need.
How Do Attacks on the Supply Chain Operate?
- Initial compromise: By exploiting a flaw in their systems or using social engineering tactics, the attacker obtains access to a vendor or upstream provider in the software supply chain management .
- Insertion of harmful code: After gaining access to the supplier’s systems, the attacker introduces a backdoor or malicious code into the hardware or software components they supply.
- Distribution: Every vendor and supplier that depends on the compromised component receives it downstream. The backdoor or malicious malware could be concealed in components or software upgrades that appear authentic.
- Activation: After activating the malicious code or backdoor, the attacker gains access to all information. This ultimately enables them to use the compromised component or obtain access to the systems of every enterprise linked to the targeted system.
- Data theft or other malicious activities: Once the attacker has access to the target systems, they can carry out various destructive tasks, such as conducting espionage, launching ransomware attacks, or stealing confidential information.
- Difficult detection: Because the initial source of compromise may be remote from the attack’s final target, these attacks can be challenging to identify. Furthermore, the backdoor or malicious code might be constructed to avoid being discovered by software.
Leverage Supply Chain To Unlock The Future! Enroll In The Master Of A Cyber Security Program At ACTE Right Way.
Well-known Supply Chain Attacks
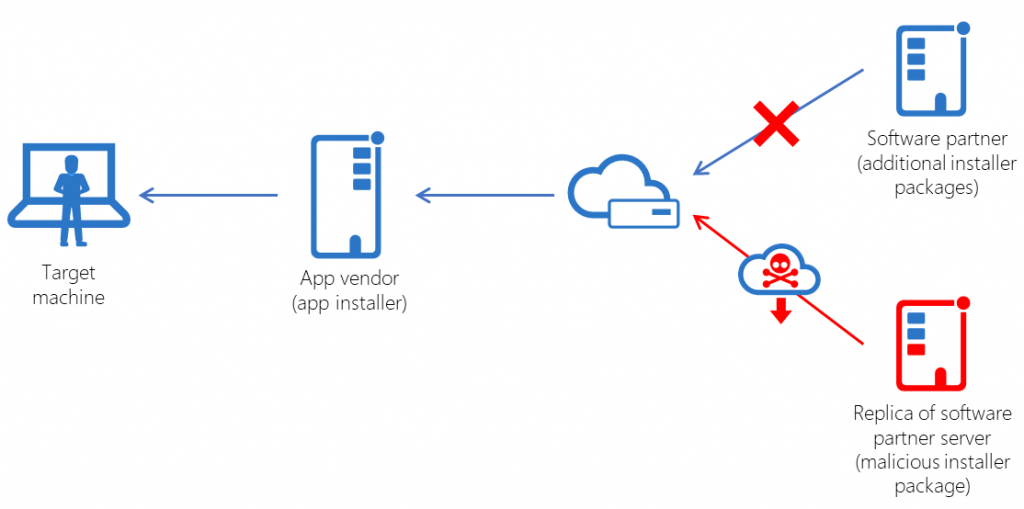
SolarWinds 2020 was the point of inflexion in the supply chain Cyber Awareness with the breach at SolarWinds in which hackers had inserted malware with the name “SUNBURST” in SolarWinds’ Orion software platform. The customers went on to update the software that opened thousands of doorways, from government organizations in the U.S. to massive business organizations worldwide for backdoors to attackers. This highlights the vulnerability of third-party software and needs better validation and monitoring mechanisms. Target In 2013, cybercriminals penetrated the system of Target using a compromised vendor supplying HVAC services. Using those stolen credentials, attackers continued to penetrate the network of Target and installed malware that helped steal 40 million credit card numbers and 70 million records of personal information. Due to this incident, the need for stringent vendor management practices was highly emphasized. Kaseya VSA In July 2021, the attackers targeted Kaseya’s VSA software, which managed service providers use to deploy ransomware to several organizations. Approximately 1,500 companies around the world were affected. This attack proved that one vulnerable vendor can spread harm across wide ranges.
How can supply chain attacks be spotted?
- Check for abnormal behaviour within the system or networks. These activities range from trying something out of the norm, which seems quite peculiar, to an unexpected movement of data or a recently made account without an acceptable permit.
- Vendor Risk Analysis Perform third-party analysis or assessments on periodic vendor partners or third-party people based on their Web Application Security postures. Recognize a modification of the security postures of any breach occurring around the organization.
- Software Integrity Checks Make checksums or hash verification on software updates and installations so no unauthorized changes have been made.
- Threat Intelligence Update threat intelligence feeds for information on the latest emerging supply chain threats and known vulnerabilities in commonly used software or hardware.
- Code should be reviewed regularly, especially with open-source components, where malicious changes or vulnerabilities might be introduced by third-party code. Logging and Monitoring: Use granular logging to discover what has been accessed and modified in critical systems. Response Plan.
- Develop and test your organization’s supply chain-specific incident response plans at least once yearly to ensure timely detection and response. User Training and awareness. Educate employees about the risks and indicators of supply chain attacks, such as phishing attempts against suppliers.
Prepare For Your Supply Chain Interview With Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Interview Questions Bank. Get Started Now!
How Can Supply Chain Attacks Be Prevented?
- Perform Due diligence: Before working with a new vendor or supplier, it is essential to perform due diligence to ensure that they have strong Web Security procedures in place. This could mean reviewing their security policies, conducting vulnerability analyses, and completing background investigations.
- Supply Chain Monitoring: Ongoing supply chain monitoring is necessary to identify and address supply chain attacks. This can involve monitoring for anomalous activity, regularly evaluating vulnerabilities, and establishing a strong incident response plan.
- Perform Frequent Vulnerability Assessments: Frequent vulnerability assessments can help locate and resolve supply chain weaknesses before attackers can exploit them. Program for Employee Training: Employee training is essential to stopping supply chain attacks of any kind. Workers must be aware of these situations and how to spot and report questionable activities.
- Use Software Integrity Checks: Ensure proper control over integrity verification for all software downloads and installations.Check with checksums, cryptographic signatures, or hash verifications to ensure that the software component has not been tampered with and actually comes from the authorized source.
- Incident Response Plans: Design a comprehensive incident response plan focused on supply chain attacks. Action: Provide identification, response, and recovery procedures from supply chain incidents. Make the roles and responsibilities clear.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a constituent part of a robust cybersecurity approach in today’s very connected digital world. Organizations increasingly rely on third-party vendors and providers, and vulnerabilities can follow the relationships with potentially disastrous consequences. Several high-profile incidents over the years have demonstrated how single breaches in the supply chain might compromise sensitive data, damage operations, and seriously damage reputations in supply chain management.This means that adequate risk mitigation requires proactive moves by organizations, such as extensive risk assessments, rigorous practices in vendor management, and more comprehensive security protocols. All these, coupled with the appropriate culture of security awareness at the employee level and adequate communication with vendors, help organizations better identify and react to threats.





