
- Introduction to Cybercrime
- Types of Cybercrime
- How Cybercrime Works
- Implications of Cybercrime
- Preventive Measures and Cybersecurity Best Practices
- The Role of Law Enforcement in Combatting Cybercrime
- Emerging Trends in Cybercrime
- The Future of Cybercrime and Cybersecurity
- Conclusion
Cybercrime is a growing concern in today’s digital landscape, making it essential to identify, assess, and mitigate potential threats to systems, applications, and networks. Understanding cyber risks, vulnerabilities, and attack methods helps individuals and organizations implement effective security strategies before breaches occur. Cyber Security Training Courses play a vital role in equipping individuals with the knowledge needed to identify and mitigate potential threats. This article will explore the impact of cybercrime, its significance, and preventive measures. We will also examine common cyber threats, best security practices, and tools to strengthen defenses against online attacks. By staying informed and proactive, businesses and individuals can safeguard sensitive data and reduce the risk of cyber threats in an increasingly connected world.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Introduction to Cybercrime
Cybercrime refers to illegal activities conducted through the Internet or digital technologies. With the increasing reliance on the Internet for both personal and business activities, cybercrime has grown significantly. These crimes can range from hacking and data breaches to more sophisticated attacks like cyber espionage and cyber terrorism. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, or human behavior to achieve their goals, such as stealing sensitive data, financial gain, or causing harm. One form of cybercrime that has grown in prevalence is Cyberstalking, where individuals use digital platforms to harass or threaten others. As technology advances, cybercriminals continue to develop more sophisticated tactics, targeting individuals, businesses, and even governments. They exploit system vulnerabilities, weak security practices, and human errors to gain unauthorized access. The consequences of cybercrime can be devastating, leading to financial losses, data theft, and reputational damage. Strengthening cybersecurity measures is essential to combat these growing threats.
Types of Cybercrime
Cybercrime comes in various forms, each targeting different aspects of digital security. The most common types include:
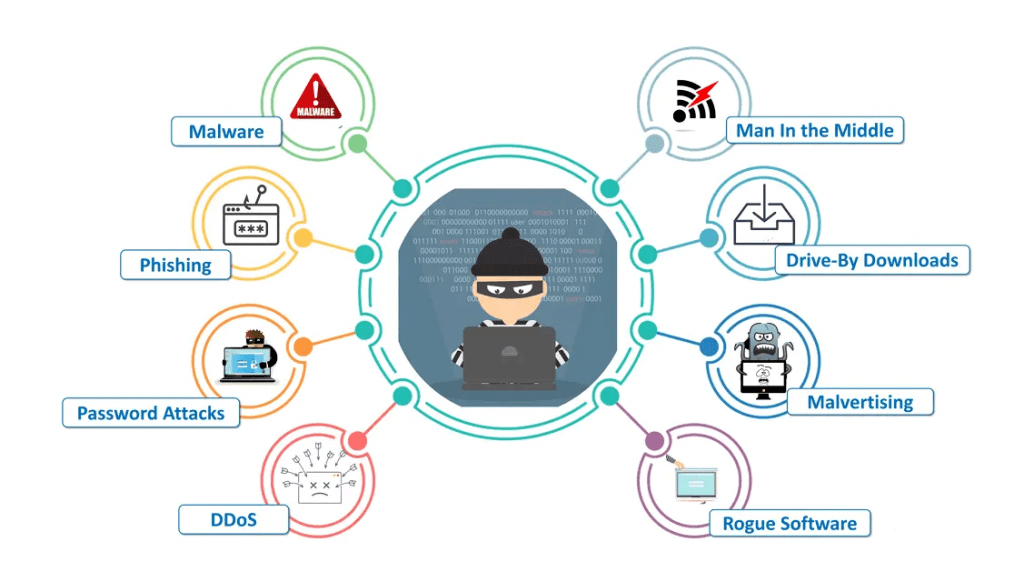
- Hacking and Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to networks or systems to steal sensitive information, such as personal data, corporate secrets, or government records, is often facilitated by Phishing Attacks, where cybercriminals deceive individuals into providing confidential information through fraudulent emails or websites.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Techniques used to deceive individuals into disclosing confidential information, such as passwords or credit card details, often through fraudulent emails, websites, or phone calls.
- Identity Theft: The act of stealing someone’s personal information, such as Social Security numbers or bank account details, to commit fraud or other illegal activities.
- Cyberbullying and Online Harassment: Using digital platforms to harass, intimidate, or bully others. It may include spreading rumors, sending abusive messages, or sharing harmful content.
- Ransomware and Malware Attacks: These are malicious software that locks files or encryption data and demands payment to release it. These can also include spyware, viruses, and worms that infect systems to steal or destroy information.
- Cyber Espionage and Cyberterrorism: The use of hacking and digital tools to spy on or sabotage government, military, or corporate organizations for political or ideological purposes.
- Economic Impact: Cybercrime causes billions of dollars in losses annually. This includes direct financial losses from fraud, theft, and disruption, as well as the costs associated with recovering from a cyber attack (e.g., ransom payments, legal fees, and system repairs).
- Legal and Ethical Implications: Cybercrime is illegal, and individuals or groups caught engaging in it can face severe legal consequences, including imprisonment and hefty fines. It also raises ethical concerns about privacy, trust, and the safety of digital spaces.
- Impact on Personal Privacy: Personal data breaches can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and emotional distress for individuals. Victims may suffer from the misuse of their details in illegal activities.
- Impact on Businesses and Organizations: Cyber attacks may cause businesses to experience financial losses, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. Cybercrime can also lead to operational disruptions, intellectual property theft, and exposure of sensitive business data.
- National Security Threats: Cybercrime can also pose a significant threat to national security. Cybercriminals target government agencies, critical infrastructure, and military organizations, which can lead to espionage, sabotage, and Cyber attacks on public safety systems.
- Agencies: Many countries have dedicated cybercrime units and Cyberterrorism laws such as the FBI’s Cyber Division, Europol’s European Cybercrime Centre (EC3), and INTERPOL. These agencies cooperate to track and capture cybercriminals involved in serious crimes like hacking, fraud, and terrorism.
- Global Collaboration: Since cybercrime often transcends borders, international cooperation between law enforcement agencies is vital for effective prosecution. Organizations like the Council of Europe’s Cybercrime Convention facilitate this collaboration.
- Legal Frameworks: Cybercrime laws vary by jurisdiction, but common legislation includes anti-hacking laws, data protection regulations, and cyberterrorism laws. These legal frameworks provide guidelines for prosecuting offenders and protecting digital spaces.
- Increased Automation: The future of cybercrime will likely see more automated attacks using bots and AI, making it harder to detect and prevent cyberattacks. To counter such threats, techniques like Cyclic Redundancy Check can be used to detect changes or errors in data, helping to ensure data integrity and identify potential attacks.
- Cybersecurity Advancements: As a response, cybersecurity technologies will continue to evolve. Quantum encryption, AI-powered threat detection, and blockchain-based security are some innovations that may help combat future threats.
- The Need for Continuous Awareness: Cybersecurity will require continuous adaptation to new threats. To combat emerging risks, professionals in the field will need to stay updated with the latest trends, tools, and techniques.
- Rise of Deepfake Threats: Deepfake technology is expected to be used more frequently for fraud, misinformation, and identity theft, making digital verification increasingly crucial.
- Growth in Zero-Trust Security Models: Organizations will adopt zero-trust frameworks, requiring continuous authentication and strict access controls to minimize risks.
- Stronger Regulatory Measures: Governments worldwide will enforce stricter data protection laws and cybersecurity regulations to address evolving cyber threats and enhance global security efforts.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
How Cybercrime Works
Cybercriminals often use sophisticated tools and techniques to carry out their attacks. These can include common techniques such as social engineering, malware deployment, denial-of-service attacks, software vulnerabilities, and weak security practices. Tools Used by Cybercriminals Cybercriminals use a range of tools, such as hacking software (e.g., Metasploit, Cain & Abel), viruses, keyloggers, botnets, and phishing kits to execute their attacks. These tools help them gain unauthorized access, gather data, and exploit weaknesses in systems. Attack Vectors: Cybercriminals exploit several attack vectors, such as email attachments, malicious links, unsecured Wi-Fi networks, and outdated software systems to gain unauthorized access to systems. One common threat is a Man in the Middle Attack, where attackers intercept and manipulate communication between two parties without their knowledge. Cybercriminals continuously refine their tactics to bypass security measures and exploit vulnerabilities. They often target individuals, businesses, and government institutions to steal sensitive data or cause disruptions. The financial and reputational damage from such attacks can be severe, impacting millions worldwide. Organizations must implement robust cybersecurity strategies, including regular software updates, employee training, and multi-layered security measures. Proactive threat detection and incident response plans are crucial in minimizing risks. Strengthening global cybersecurity efforts is essential to combat the growing threat of cybercrime.
Implications of Cybercrime
The consequences of cybercrime can be far-reaching, affecting individuals, businesses and entire nations:
Preventive Measures and Cybersecurity Best Practices
To protect against cybercrime, individuals and organizations must adopt preventive measures,Regularly updating software, using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and being cautious of unsolicited emails or messages. Businesses should implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and employee cybersecurity training. Additionally, conducting regular security audits and penetration tests can help identify and address vulnerabilities. Cyber Security Training Courses are also crucial in educating employees on compliance with these laws. Governments worldwide have enacted laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Cybersecurity Act to protect citizens and businesses from cybercrime. International collaboration is also essential to combat cross-border cyber threats. Cybercrime continues to evolve, making continuous monitoring and adaptation crucial. Companies should invest in advanced threat intelligence solutions to detect and prevent cyberattacks. Secure cloud computing practices, including data encryption and access control, help protect sensitive information. Encouraging cybersecurity awareness at all levels ensures a proactive approach to digital security. Multi-layered defense strategies significantly reduce the risk of breaches and data theft. Strong partnerships between the public and private sectors further enhance global cybersecurity resilience.
The Role of Law Enforcement in Combating Cybercrime
Law enforcement agencies play a crucial role in investigating and prosecuting cybercriminals:
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Emerging Trends in Cybercrime
As technology evolves, so do the tactics used by cybercriminals. Some emerging trends include, AI in Cybercrime. Cybercriminals are increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to automate Cyber attacks, make phishing schemes more convincing, and crack passwords more efficiently. Cloud Security and New Threats: As more organizations move to cloud-based services, cybercriminals are targeting vulnerabilities in cloud security, exploiting misconfigurations and weak access controls to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. One such tactic they use is Spoofing, where attackers impersonate trusted sources to deceive users into revealing confidential information or granting access to cloud systems.
The rise of cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, has facilitated anonymous ransom payments in ransomware attacks, making it more difficult for law enforcement to trace and shut down cybercriminal operations. The Internet of Things (IoT) has also become a growing target, with attackers exploiting insecure smart devices to launch large-scale attacks. Deepfake technology is being weaponized for fraud, misinformation, and identity theft. Cybercriminals are increasingly focusing on supply chain attacks, compromising vendors to infiltrate multiple organizations. Phishing techniques are evolving, using AI to create highly personalized and deceptive messages. The rise of 5G networks introduces new security challenges, increasing the attack surface for cyber threats. Businesses and governments must adopt proactive cybersecurity strategies to stay ahead of these emerging risks. Strengthening international collaboration is crucial in combating advanced cybercrime tactics.
The Future of Cybercrime and Cybersecurity
As the digital world continues to grow, so will the sophistication of cybercrime:
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Cybercrime is an ever-growing threat in our digital world. As technology evolves, so do cybercriminals’ tactics. To effectively combat this threat, individuals, businesses, and governments must stay vigilant and adopt the latest cybersecurity practices and technologies. Building a culture of awareness and continuous learning in the cybersecurity domain is critical to safeguarding our digital future. Cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities in systems and networks. Cyber Security Training Courses are essential in helping individuals stay updated on the latest threats and best practices to defend against these evolving attacks. Organizations must invest in proactive security measures such as AI-driven threat detection and zero-trust frameworks. Regular security training for employees can help prevent phishing attacks and social engineering scams. Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication are essential for protecting sensitive data. Governments and regulatory bodies must enforce strict cybersecurity laws to hold attackers accountable. Collaboration between the public and private sectors is crucial to developing innovative strategies for tackling emerging cyber threats.





