
Critical Path Method Tutorial | How to use CPM for project management
Last updated on 04th Feb 2022, Blog, Tutorials
- Introduction
- The Critical Path Method
- Different guidelines to consider
- Key Steps in Critical Path Method
- Benefits of Critical Path Method
- The Critical Path Method has four key components…
- Conclusion
- Assignments expected to finish the undertaking
- Conditions between assignments
- The length expected to finish an action
- Assignments expected to finish the venture
- Conditions between undertakings
- The term expected to finish an action
- Occasions are addressed by a circle and will happen toward the beginning and end of an action. Occasion 1 is the tail occasion and Event 2 is the head occasion. On account of our model, the occasions are 1, 2,3,4, 5, and 6. Thinking about, hubs 1 and 2, and the association between them, 1 will be alluded to as the tail occasion, and 2 will be alluded to as the head occasion.
- Additionally, for 2 and 3, 2 is the tail occasion, and 3 is the head occasion.
- A fake movement addresses a connection between two occasions. On account of the model underneath us, the dabbed line addresses a connection between hubs 4 and 3.
- The action between these hubs won’t have any worth.
- The organization ought to have a remarkable beginning and finishing hub. On account of our model, occasion 1 addresses a one of a kind beginning Step and 6 addresses the novel fruition hub
- No action can be addressed by in excess of a solitary bend (the line with a bolt interfacing the occasions) in the organization
- No two exercises can have a similar beginning and finishing hub. Presently, we should discuss the course of the Critical Path Method with a model.
- You can utilize the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to distinguish the exercises engaged with the task. This is the primary contribution for the basic way strategy.
- In movement particular, just the more significant level exercises are chosen for basic way technique.
- Whenever nitty gritty exercises are utilized, the basic way technique might turn out to be too complicated to even consider overseeing and keep up with.
- Which assignments should occur before this undertaking occurs.
- Which errands ought to be finished simultaneously as this assignment.
- Which errands ought to happen following this undertaking.
- When the movement arrangement is accurately distinguished, the organization graph can be drawn (allude to the example chart above).
- Albeit the early outlines were drawn on paper, there are various programs, like Primavera, for this reason these days.
- This could be an immediate contribution from the WBS based assessment sheet. The majority of the organizations utilize 3-point assessment technique or COCOMO based (work focuses based) assessment strategies for errands assessment.
- You can involve such assessment data for this progression of the cycle.
- Earliest beginning time (ES) – The earliest time an action can begin once the past ward exercises are finished.
- Earliest completion time (EF) – ES + movement term.
- Most recent completion time (LF) – The most recent time a movement can complete without deferring the undertaking.
- Most recent beginning time (LS) – LF – movement term.
- The float time for a movement is the time between the earliest (ES) and the most recent (LS) start time or between the earliest.
- During the float time, a movement can be postponed without deferring the undertaking finish date.
- The basic way is the longest way of the organization outline. The exercises in the basic way affect the cutoff time of the task. On the off chance that a movement of this way is postponed, the venture will be deferred.
- On the off chance that assuming the venture the executives needs to speed up the undertaking, the times for basic way exercises ought to be diminished.
- Basic way graph is a live relic. Hence, this outline ought to be refreshed with genuine qualities once the undertaking is finished.
- This gives more reasonable figure for the cutoff time and the venture the executives can know whether they are on target in regards to the expectations.
- Offers a visual portrayal of the venture exercises.
- Presents an opportunity to do the jobs and the general venture.
- Following of basic exercises.
- Assist you with distinguishing the exercises that should be finished on schedule to finish the entire venture on schedule.
- Show you which assignments can be postponed and for how long without affecting the general undertaking plan.
- Work out the base measure of time it will take to finish the venture.
- Let you know the earliest and most recent dates every movement can begin on to keep up with the timetable.
- Basic Path Analysis
- Float Determination
- Promising beginning and Early Finish Calculation
- Poor Start and Late Finish Calculation
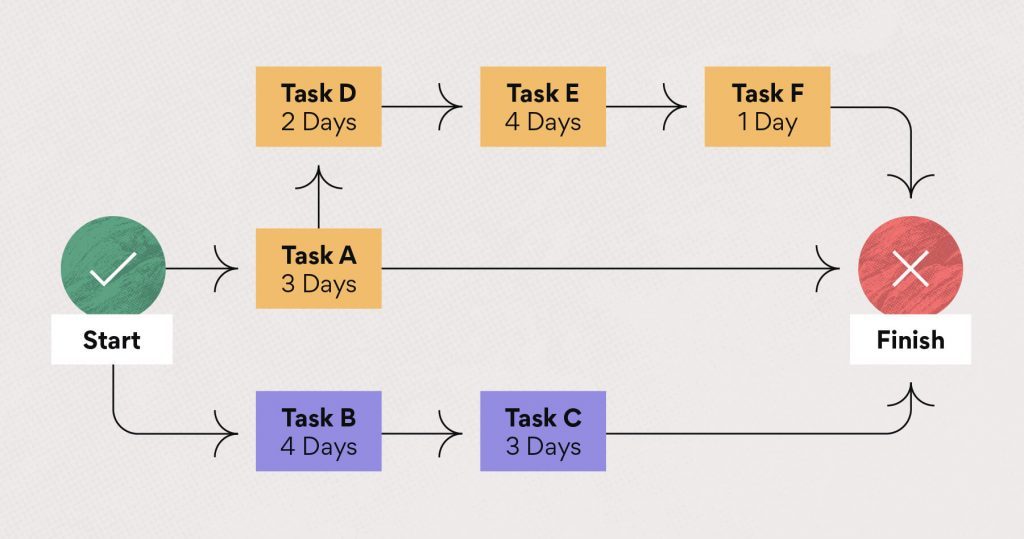
- The basic way is the succession of exercises with the longest term. A deferral in any of these exercises will bring about a postponement for the entire venture. The following are some basic way guides to assist you with understanding the key components…
- The span of every action is recorded over every hub in the outline. For every way, add the span of every hub to decide it’s complete term. The basic way is the one with the longest span.
- There are three ways through this task.
- Utilize Critical Path Analysis to track down your Critical Path
- The Critical Path Method incorporates a strategy called the Forward Pass which is utilized to decide the earliest date an action can begin and the earliest date it can wrap up.
- These dates are substantial as long as all earlier exercises in that way begun their earliest beginning date and didn’t slip.
- Beginning with the basic way, the Early Start (ES) of the primary movement is one. The Early Finish (EF) of an action is its ES in addition to its span less one.
- Utilizing our previous model, Activity 2 is the principal action on the basic way: ES = 1, EF = 1 + 5 – 1 = 5.
- You then, at that point, move to the following action in the way, for this situation Activity 3. Its ES is the past movement’s EF + 1. Movement 3 ES = 5 + 1 = 6. Its EF is determined equivalent to previously: EF = 6 + 7 – 1 = 12.
- Assuming that an action has more than one ancestor, to compute its ES you will utilize the movement with the most recent EF.
- Basic way recognizable proof is expected for any venture arranging Step. This gives the venture the board the right consummation date of the general undertaking and the adaptability to drift exercises.
- A basic way chart ought to be continually refreshed with real data when the undertaking advances to refine the action length/project term forecasts.
Introduction :-
In the event that you have been into project the board, I’m certain you have effectively heard the term ‘basic way strategy.’On the off chance that you are new to the subject, it is ideal to begin with understanding the ‘basic way’ and afterward continue on to the ‘basic way strategy.’
Basic way is the successive exercises from start to the furthest limit of an undertaking. Albeit many undertakings have just a single basic way, a few tasks might have more than one basic ways relying upon the stream rationale utilized in the venture. Assuming that there is a postponement in any of the exercises under the basic way, there will be a deferral of the task expectations.
The majority of the times, assuming such deferral is happened, project speed increase or re-sequencing is done to accomplish the cutoff times.Basic way technique depends on numerical estimations and it is utilized for booking project exercises. This strategy was first presented in 1950s as a joint endeavor between Remington Rand Corporation and DuPont Corporation.
The underlying basic way strategy was utilized for overseeing plant upkeep projects. Albeit the first strategy was produced for development work, this technique can be utilized for any task where there are associated exercises.In the basic way technique, the basic exercises of a program or a task are recognized. These are the exercises that straightforwardly affect the culmination date of the venture.
The Critical Path Method :-
CPM or the Critical Path Method is a calculation utilized in project the board that is utilized to plan project exercises. The basic way alludes to the longest stretch of the exercises, and a proportion of them beginning to end.
With the assistance of CPM, we’ll have the option to make a model that empowers you to decide the accompanying:
Presently, before we can begin with CPM or Critical Path Method, we’ll need to comprehend two significant ideas which are Events and Activities. To assist with understanding them better, how about we examine the organization graph (which is likewise the result) of the cycle.
CPM or the Critical Path Method is a calculation utilized in project the executives that is utilized to plan project exercises. The basic way alludes to the longest stretch of the exercises, and a proportion of them beginning to end. With the assistance of CPM, we’ll have the option to make a model that empowers you to decide the accompanying:
Presently, before we can get everything rolling with CPM or Critical Path Method, we’ll need to comprehend two significant ideas which are Events and Activities. To assist with understanding them better, we should examine the organization chart (which is additionally the result) of the interaction.
This result addresses the absolute most significant pieces of the interaction: Events and Activities.
Event :
Activity :
Different guidelines to consider :-
Key Steps in Critical Path Method :-
How about we view how basic way strategy is utilized by and by. The most common way of involving basic way technique in project arranging Step has six Steps.
Step 1: Activity detail :
Step 2: Activity arrangement foundation :
In this progression, the right action grouping is laid out. For that, you really want to pose three inquiries for each assignment of your rundown.
Step 3: Network graph :
Step 4: Estimates for every movement :
Step 5: Identification of the basic way :
For this, you want to decide four boundaries of every action of the organization.
Step 6: Critical way outline to show project advances :
Benefits of Critical Path Method :-
Following are benefits of basic way techniques:
The Critical Path Method (CPM) can assist you with keeping your ventures on target.Basic way timetables will…
The Critical Path Method has four key components… :-
Basic Path Analysis :
Float Determination :
Whenever you’ve distinguished the basic way for the undertaking, you can decide the float for every movement. Float is how much time a movement can slip before it makes your task be deferred. Float is at times alluded to as slack.Sorting out the float utilizing the Critical Path Method is genuinely simple. You will begin with the exercises on the basic way. Every one of those exercises has a float of nothing. Assuming any of those exercises slips, the venture will be deferred.
Then, at that point, you follow the following longest way. Take away it’s term from the span of the basic way. That is the float for every one of the exercises on that way.You will keep doing likewise for each resulting longest way until every exercises float not entirely set in stone. Assuming an action is on two ways, it’s float will be founded on the more extended way that it has a place with.
Utilizing the basic way graph from the past area, Activities 2, 3, and 4 are on the basic way so they have a float of nothing. The following longest way is Activities 1, 3, and 4. Since Activities 3 and 4 are likewise on the basic way, their float will stay as nothing.
For any excess exercises, for this situation Activity 1, the float will be the span of the basic way less the length of this way. 14 – 12 = 2. So Activity 1 has a float of 2.The following longest way is Activities 2 and 5. Action 2 is on the basic way so it will have a float of nothing. Action 5 has a float of 14 – 9, which is 5. So as long as Activity 5 doesn’t slip over 5 days, it won’t create a setback to the venture.
Promising beginning and Early Finish Calculation :
Poor Start and Late Finish Calculation :
The Backward Pass is a Critical Path Method techique you can use to decide the most recent date a movement can begin and the most recent date it can complete before it defers the task.Once more you’ll begin with the basic way, yet this time you’l start from the last action in the way. The Late Finish (LF) for the last movement in each way is equivalent to the last action’s EF in the basic way.
The Late Start (LS) is the LF – term + 1.In our model, Activity 4 is the keep going movement on the basic way. Its LF is equivalent to its EF, which is 14. To ascertain the LS, take away its term from its LF and add one. LS = 14 – 2 + 1 = 13.
You then, at that point, continue on to the following movement in the way. Its not entirely set in stone by taking away one from the past action’s LS. In our model, the following Activity in the basic way is Activity 3. Its LF is equivalent to Activity 4 LS – 1. Action 3 LF = 13 – 1 = 12. It’s LS is determined equivalent to before by taking away its length from the LF and adding one. Action 3 LS = 12 – 7 + 1 = 6.

