
A ServiceNow Administrator manages the configuration and upkeep of ServiceNow platforms, focusing on IT Service Management (ITSM). Responsibilities include customizing workflows, overseeing user access, and optimizing system performance to improve operational efficiency. This role is pivotal in ensuring smooth service delivery, aligning IT services with organizational goals through effective administration and ongoing enhancement of ServiceNow capabilities.
1. What is the Tool for Service Now?
Ans:
ServiceNow provides a cloud-based platform and suite of applications designed to automate IT service management (ITSM), business processes, and operations. It offers tools for incident management, change management, problem management, and more. Because of the platform’s significant degree of adaptability, businesses can customize it to meet their requirements. ServiceNow also includes modules for IT operations management (ITOM) and IT business management (ITBM).
2. What is the CMDB baseline?
Ans:
A CMDB baseline in ServiceNow is a snapshot of the Configuration Management Database (CMDB) at a particular point in time. It captures the state of configuration items (CIs) and their relationships, helping track changes, analyze trends, and maintain data integrity. Baselines are used for comparison purposes, enabling IT teams to identify deviations and ensure consistency. They are crucial for auditing and compliance purposes. Regularly creating baselines helps maintain accurate and reliable CMDB data.
3. What is an “Application” in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- An “Application” in ServiceNow refers to a set of related modules, features, and components that provide specific functionalities.
- Applications are designed to address various business needs, such as IT service management, HR service delivery, and customer service management.
- Each application includes tables, scripts, workflows, and user interfaces tailored to its purpose.
- Applications can be customized and extended to meet unique organizational requirements. ServiceNow’s App Store offers pre-built applications for different use cases.
4. Which tasks and responsibilities are the responsibility of the ServiceNow Administrator?
Ans:
- The ServiceNow platform must be managed and configured by a ServiceNow Administrator.
- Duties include user and group management, instance maintenance, and implementing workflows.
- Administrators also handle system updates, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues.
- They ensure data integrity, security, and compliance with organizational policies. They also customize forms, fields, and reports.
5. What does the term “coalesce” mean?
Ans:
In ServiceNow, “coalesce” refers to a setting used during data imports to determine if existing records should be updated or new records should be created. When a field is set to merge, the system uses it as a unique key to find matching records. Should a match be discovered, the current record is updated; if not, a new record is created. This is crucial for maintaining data consistency and avoiding duplicates. Coalescing helps in accurate data integration from external sources. It simplifies data management and ensures up-to-date information.
6. How do UI policies work?
Ans:
UI policies in ServiceNow dynamically change the behavior of fields on a form based on specific conditions. They can show, hide, and make fields read-only or mandatory without writing code. UI policies are defined using conditions and actions in the ServiceNow interface. They enhance user experience by guiding users through form completion. These policies are client-side scripts that execute as the user interacts with the form. They help enforce data entry standards and improve data quality.
7. Explain the difference between Client Script and Business Rule.
Ans:
| Feature | Client Script | Business Rule |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Context | Executes on the client-side (browser) | Executes on the server-side (ServiceNow server) |
| Trigger Events | Triggers on form load, field change, or submit | Triggers on database actions (before or after) |
| Functionality | Used for client-side validation and UI behavior | Implements server-side logic and data manipulation |
| Scope | Affects individual forms and UI actions | Applies globally across records or tables |
| Performance | Lightweight and responsive | Heavier, impacting server processing |
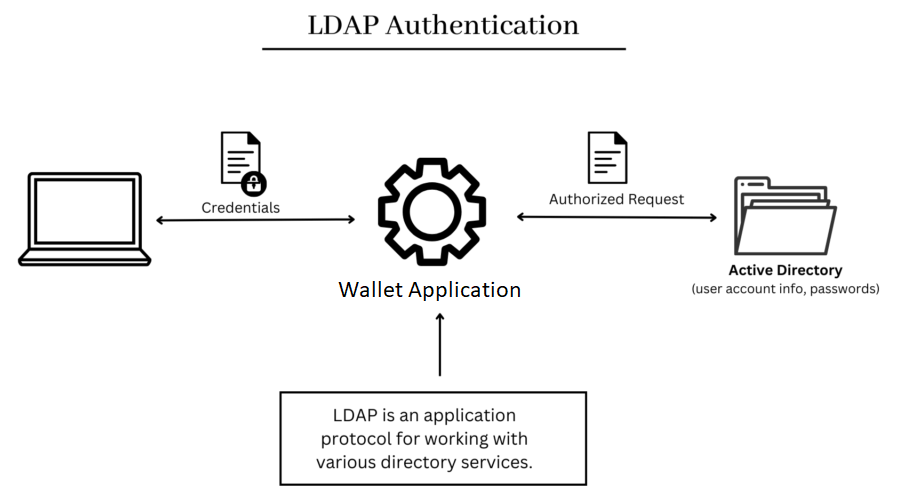
8. What is Integration with LDAP?
Ans:
- Integration with LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) in ServiceNow allows for the synchronization of user data from an LDAP directory into ServiceNow.
- This facilitates single sign-on (SSO) and ensures that user information is consistent and up-to-date.
- LDAP integration helps automate user provisioning and de-provisioning processes.
- It enhances security by centralizing authentication and access control. The integration is configured through the ServiceNow LDAP integration module.
9. What does the acronym CMDB stand for, and what does it do?
Ans:
CMDB stands for Configuration Management Database. It is a repository that stores information about configuration items (CIs) and their relationships within an IT environment. The CMDB helps organizations manage and control their IT assets, services, and infrastructure. It supports ITIL processes such as change management, incident management, and problem management. By providing a single source of truth, the CMDB improves decision-making and service delivery. It is crucial for maintaining IT service continuity and compliance.
10. What is a policy for data?
Ans:
A data policy in ServiceNow is a rule that enforces data integrity by ensuring data entered into the system meets specific criteria. Data policies apply to all data operations, including imports, updates, and form submissions. They can make fields mandatory, set default values, or enforce data formats. Data policies help maintain the consistency and accuracy of the data across the platform. They are similar to UI policies but apply to server-side operations. Their primary purpose is to ensure data quality and compliance.
11. Describe ACL.
Ans:
- ACL (Access Control List) in ServiceNow defines security rules that control user access to data.
- It consists of permissions that specify what operations (read, write, create, delete) users can perform on specific tables, fields, and records.
- ACL rules are evaluated top-down, meaning the most specific rule is applied first.
- ACLs enhance data security by restricting access based on user roles and conditions. They also ensure data integrity and privacy by only allowing authorized users to interact with certain data.
12. What does “impersonating a user” mean, and how does it help?
Ans:
- An administrator can temporarily take over the identity of another user in ServiceNow by impersonating them, all without having to log out.
- This feature helps troubleshoot by replicating the user’s exact permissions and experiences.
- It aids in debugging user-specific issues, ensuring accurate problem resolution. Impersonation is also used to verify that security configurations are correctly applied to different roles.
- It ensures that changes made by admins function as intended for various users. The impersonation process maintains audit logs for security and transparency.
13. What are the dictionary overrides in ServiceNow?
Ans:
Dictionary overrides in ServiceNow allow administrators to customize field properties for a specific extended table without altering the parent table’s dictionary entry. They enable field-level control and flexibility in child tables. Overrides can modify attributes like default value, mandatory status, read-only status, and choice list. This feature supports the inheritance model by ensuring specific requirements of extended tables are met. It helps maintain the consistency and relevance of data fields across different table extensions.
14. What exactly is a viewpoint?
Ans:
In ServiceNow, a viewpoint refers to a specific perspective or angle from which data and processes are analyzed and presented. It allows users to focus on relevant information tailored to their roles or needs. Viewpoints can be configured through dashboards, reports, and filtered views to provide actionable insights. They help in simplifying data interpretation by highlighting critical metrics and trends. Viewpoints enhance decision-making by providing targeted information.
15. Explain Business Rules.
Ans:
- Business Rules in ServiceNow are server-side scripts that execute automatically when specific conditions are met.
- They are employed in the implementation of business logic, process automation, and data consistency enforcement.
- Business Rules can run on database operations like insert, update, delete, or query.
- They consist of four types: Display, Before, After, and Async. These rules ensure data integrity and streamline workflow automation.
16. What are metrics in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- Metrics in ServiceNow are quantitative measures used to track and assess the performance of processes and services.
- They help in evaluating efficiency, quality, and compliance with service level agreements (SLAs).
- Various KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), such as resolution time, incident count, and customer satisfaction, can have metrics defined.
- They are essential for continuous improvement, as they identify areas that need enhancement.
17. What is BSM Map?
Ans:
A BSM (Business Service Management) Map in ServiceNow visualizes the relationships and dependencies between business services and the underlying IT infrastructure. It helps in understanding the impact of IT components on business services. BSM Maps are used for impact analysis, troubleshooting, and service dependency tracking. They provide a graphical representation of how services interact with applications, servers, and databases. BSM Maps enhance visibility into service health and performance.
18. What Is a Recorded Glide?
Ans:
A Recorded Glide in ServiceNow refers to the GlideRecord API, which allows for querying and interacting with the database from server-side scripts. CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) actions are carried out on records using it. GlideRecord provides methods to query tables, retrieve data, and manipulate records programmatically. It supports server-side scripting to automate processes and enforce business logic. GlideRecord is fundamental for developing and customizing applications within ServiceNow.
19. What does an import set entail?
Ans:
- An import set in ServiceNow is a tool used to import data from external sources into ServiceNow tables.
- It allows for data transformation and mapping before the data is inserted into the target tables.
- Import sets support a variety of data formats, such as CSV, Excel, and XML. They integrate data from different systems into ServiceNow.
- Import sets provide a staging area for data cleansing and transformation. They ensure accurate and efficient data migration and integration.
20. Describe a transform map.
Ans:
- In ServiceNow, a transform map specifies the link between fields in an import set and fields in the target table.
- It specifies how data should be mapped, transformed, and loaded during an import process.
- Transform maps support data transformation rules, scripting, and field mapping.
- They ensure that data from import sets is accurately inserted into the appropriate fields of the target table. Transform maps facilitate data normalization and consistency.
21. How does the ServiceNow IT Service Management module function?
Ans:
The ServiceNow IT Service Management (ITSM) module optimizes IT processes and enhances service delivery. It integrates incident, problem, change, and request management within a single platform. Users can log issues, track their progress, and receive timely resolutions. ITSM includes automated workflows and notifications to boost efficiency. It offers a unified system for IT operations, ensuring consistency and compliance.
22. What is the purpose of ServiceNow workflows?
Ans:
ServiceNow workflows automate business processes to improve efficiency and consistency. They define a series of steps for tasks like approvals, notifications, and record updates. Workflows make ensuring the right people do the right tasks in the correct order. They can be combined with other ServiceNow modules and customized to meet specific company needs. Workflows that are automated eliminate errors and require less manual labor. They provide transparency and traceability for business processes.
23. What is the process for creating a Service Catalog in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To create a Service Catalog in ServiceNow, navigate to “Service Catalog” in the application navigator.
- Click on “Create New” to define the catalog item. Enter details like name, category, description, and pricing.
- Configure fulfillment workflows and approvals if necessary. Set visibility rules and user access permissions.
- Publish the catalog item, making it available for users to request services through the Service Portal.
24. What is an Update Set in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- An Update Set in ServiceNow is a collection of customizations and changes made to the platform.
- It tracks modifications such as scripts, forms, and configurations. Update Sets are used to transfer changes between instances, such as from development to production.
- They ensure consistency and support version control. Each Update Set captures a snapshot of changes, simplifying their application elsewhere. It’s crucial for managing changes in a structured and controlled way.
25. Explain the use of ServiceNow’s Incident Management module.
Ans:
ServiceNow’s Incident Management module helps quickly restore normal service operations after disruptions. It manages the lifecycle of incidents from identification to resolution. Users report incidents, and the system assigns them to the appropriate teams. Incident Management includes prioritization, categorization, and escalation features. It ensures timely resolutions through workflows and automation. The module also provides metrics and reports to monitor incident trends and performance.
26. What steps are involved in performing an upgrade in ServiceNow?
Ans:
To perform an upgrade in ServiceNow, first review the release notes for new features and changes. Back up your instance and ensure you have a current update set. Navigate to “System Diagnostics” and select “Upgrade Center.” Follow the prompts to download and apply the upgrade package. Thoroughly test the instance post-upgrade to identify any issues. Use the “Upgrade History” module to track progress and resolve conflicts.
27. What is a GlideRecord in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- A GlideRecord is a JavaScript class in ServiceNow used for database operations.
- It enables developers to work with tables in CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) fashion.
- GlideRecord provides methods to query, insert, update, and delete records programmatically.
- It simplifies interaction with the ServiceNow database using script logic.
- Developers use GlideRecord in server-side scripts like Business Rules and Script Includes. It’s a powerful tool for manipulating data within the platform.
28. What methods are used to manage user roles in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To manage user roles in ServiceNow, navigate to “User Administration” in the application navigator. In order to view and change user records, select “Users.”
- Users can be assigned roles by adding them to the relevant list named “Roles.” Use “Groups” to manage roles for multiple users collectively.
- Ensure roles align with users’ responsibilities and access requirements.
- Regularly review and update roles to maintain security and compliance.
29. What defines a ServiceNow plugin, and what is the procedure for installing one?
Ans:
A ServiceNow plugin is an add-on that extends the platform’s functionality. Plugins provide additional features and integrations that are not available in the base system. To install a plugin, navigate to “System Applications” and select “All Available Applications.” After finding the required plugin, select “Install.” Follow the installation prompts and review any needed configurations. Ensure compatibility with your instance version before installation.
30. What is the process for making a custom application in ServiceNow?
Ans:
To create a custom application in ServiceNow: Use the “Application Studio” module. Start by defining the application scope and basic properties. Create new tables and fields as needed for your application’s data model. Develop forms, lists, and UI components for user interaction. Implement business logic using scripts, workflows, and automation. Before putting the application into production, Utilize source control and Update Sets to manage application changes.
31. What is the purpose of ServiceNow’s Knowledge Management module?
Ans:
- ServiceNow’s Knowledge Management module is designed to capture, store, and share information within an organization.
- Users can create and manage knowledge articles, making it easy to find solutions to common problems.
- It supports multiple knowledge bases with controlled access, ensuring the right people have the correct information.
- The module enhances efficiency by reducing the need for repetitive inquiries.
32. What are the steps to configure email notifications in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To set up email notifications in ServiceNow, go to “System Notification” and choose “Email.”
- Create a new notification by setting conditions for when it should be sent. Define the recipients, subject, and message content, using variables to include dynamic information.
- Test the notification to ensure it functions correctly. Save and activate the notification to start sending emails. This ensures timely communication based on specific triggers.
33. What is the significance of Business Services in ServiceNow?
Ans:
Business Services in ServiceNow represent essential services provided to customers or internal teams. They depict the connections and dependencies between business procedures and IT components. This understanding helps manage service impacts and prioritize IT tasks. Business Services are crucial for decision-making and aligning IT efforts with business goals. They also play a key role in monitoring performance and ensuring service levels are met.
34. Explain the concept of Scoped Applications in ServiceNow.
Ans:
Scoped Applications in ServiceNow are self-contained apps with their namespaces, preventing conflicts and enhancing data security. Each scoped app includes its tables, scripts, and modules, separated from other applications. This modular design facilitates easier development, testing, and deployment. Scoped Applications are ideal for custom solutions and third-party integrations. They provide better control over access and permissions and can be shared via the ServiceNow Store.
35. How are reports built and maintained in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To create a report in ServiceNow, go to the “Reports” application and click “Create New.”
- Select the report type and data source, then configure the layout, filters, and visualization options.
- Save the report and set sharing permissions. Use the “Reports” dashboard to manage and schedule reports.
- Regularly review and update reports to ensure they meet evolving business needs. This process provides valuable insights and supports data-driven decisions.
36. What does a ServiceNow Script Include?
Ans:
- A ServiceNow Script Include is a reusable server-side script that other scripts or Business Rules can call.
- It promotes code reuse and modularity, enhancing maintainability and performance.
- The script includes functions and logic for complex operations, and it can be accessed via the GlideAjax class for client-server communication.
- They help organize code and simplify debugging. Script Includes are defined in the “System Definition” module.
37. What is the approach for handling SLA (Service Level Agreement) in ServiceNow?
Ans:
SLAs in ServiceNow are managed through the “Service Level Management” application. Define SLA definitions with specific conditions and targets for service delivery. Attach SLAs to tasks and monitor their progress using the SLA timeline. Set up breach conditions and escalation rules to handle violations. Use workflows to automate actions based on SLA status. Regularly review SLA performance with reports and dashboards to ensure compliance.
38. What is a UI Action in ServiceNow?
Ans:
A UI Action in ServiceNow is a customizable button, link, or menu item that performs specific tasks. UI Actions can be added to forms, lists, or related lists to enhance user interaction. They can execute server-side or client-side scripts to perform operations like record updates, navigation, or invoking other scripts. UI Actions improve the user experience by providing quick access to frequently used functions. The “UI Actions” module is where they are configured.
39. What method is utilized in ServiceNow to look up a text or record?
Ans:
- In ServiceNow, the “GlideRecord” API is used to perform database operations, including looking up records.
- It provides methods to query, insert, update, and delete records from the ServiceNow database.
- Using GlideRecord, developers can write scripts to search for records based on specified criteria.
- This API is essential for server-side scripting and automating processes. It makes efficient data modification and retrieval possible. GlideRecord is widely used in business rules, scheduled jobs, and workflows.
40. How is a Virtual Agent set up in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To set up a Virtual Agent in ServiceNow, navigate to the “Virtual Agent” application and use the Virtual Agent Designer.
- Using the drag-and-drop interface, create topics and define conversation flows. Using scripts and APIs, integrate the Virtual Agent with backend systems.
- Test the agent’s responses and refine dialogues as needed. Deploy the Virtual Agent across channels like web, mobile, and messaging platforms. Monitor its performance to improve user interactions and satisfaction.
41. What are the different types of Client Scripts in ServiceNow?
Ans:
ServiceNow offers three types of Client Scripts: onLoad, onChange, and onSubmit. OnLoad scripts run when a form is loaded, which is useful for initializing variables or making UI adjustments. OnChange scripts trigger when a field value changes, allowing dynamic updates or validations. OnSubmit scripts execute when a form is submitted, which is ideal for final validations or actions before saving data.
42. What methods are used to manage access control in ServiceNow?
Ans:
Access control in ServiceNow is managed through roles and access controls. Roles define permissions for users based on their responsibilities. Access controls specify which roles can access specific tables, fields, and UI actions. Access can also be controlled through ACLs (Access Control Lists) and business rules for finer control over data visibility and modification.
43. What is the ServiceNow Agile Development module?
Ans:
- The ServiceNow Agile Development module facilitates agile project management within ServiceNow.
- It supports Scrum and Kanban methodologies for software development.
- Teams can manage backlogs, sprints, and user stories directly within the platform.
- It integrates with other ServiceNow modules for seamless collaboration and reporting.
- This module enhances transparency, efficiency, and adaptability in project execution.
44. What is the process for creating a custom table in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To create a custom table in ServiceNow, navigate to Application Navigator > System Definition > Tables.
- Click New and define the table’s label and name, and extend from an existing table or create a new one.
- Customize fields, forms, and related lists as needed for data entry and display.
- Use business rules and client scripts to automate actions and validations.
- Ensure appropriate security and access controls are set for the new table.
45. Explain the concept of Data Sources in ServiceNow.
Ans:
Data Sources in ServiceNow allow integration with external systems and databases. They define how ServiceNow connects and interacts with external data. Common types include REST, SOAP, JDBC, and LDAP sources. Administrators configure data sources through Integration Hub or Import Sets. Data Sources enable ServiceNow to leverage external data for processes, reporting, and automation.
46. How is the Flow Designer utilized in ServiceNow?
Ans:
The ServiceNow Flow Designer enables the visual orchestration of processes and automation. Users can create flows by dragging and connecting predefined actions and integrations. Flows automate tasks across applications and modules without writing traditional code. It supports conditional logic, loops, and error handling for complex workflows. The Flow Designer simplifies and accelerates automation efforts in ServiceNow.
47. What is the Event Management module in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- The Event Management module in ServiceNow monitors and manages IT infrastructure events.
- It consolidates event data from various sources into a single platform.
- Event rules classify and prioritize events based on predefined criteria.
- Automated actions or notifications can be triggered based on event types and severity.
- This module enhances IT service visibility, incident response, and proactive problem management.
48. What steps are involved in implementing a ServiceNow IntegrationHub?
Ans:
- Implementing a ServiceNow IntegrationHub involves creating integrations using pre-built connectors.
- Connectors facilitate communication with external systems through APIs and protocols.
- IntegrationHub actions are orchestrated using Flows in ServiceNow Flow Designer.
- Administrators configure mappings and transformations for data synchronization.
- It enables ServiceNow to automate processes involving diverse applications and data sources.
49. What is the purpose of ServiceNow’s Performance Analytics?
Ans:
ServiceNow’s Performance Analytics provides visual insights and metrics on service performance. It aggregates and analyzes data from ServiceNow applications and external sources. Key performance indicators (KPIs) help monitor and improve service delivery. Interactive dashboards and reports offer real-time visibility into organizational metrics. Performance Analytics supports data-driven decision-making and continuous service improvement.
50. What is the procedure for creating a ServiceNow Dashboard?
Ans:
- Navigate to Performance Analytics > Dashboards.
- Click New Dashboard and define its name, description, and layout.
- Add widgets such as line charts, gauges, or lists to visualize data.
- Configure data sources and filters to display relevant information.
- Customize colors, labels, and interactivity options for user-friendly navigation.
- Publish the dashboard to make it available to appropriate users or groups.
51. Explain the difference between UI Policy and Data Policy.
Ans:
- UI Policy controls the behavior of fields on forms based on conditions.
- It hides, sets as mandatory, or makes fields read-only dynamically.
- Data Policy enforces data consistency and standards in ServiceNow.
- It validates and formats data entered into fields.
- UI Policies affect form interactions, while Data Policies focus on data integrity.
- Both are essential for enhancing user experience and maintaining data quality.
52. What is the function of ServiceNow’s Service Portal?
Ans:
- Service Portal provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with ServiceNow services.
- It allows users to access catalogs, forms, and knowledge articles.
- Service Portal supports customization to match organizational branding and needs.
- Users can request services, view status updates, and engage with IT support seamlessly.
- It enhances user satisfaction by offering a centralized self-service platform.
- Service Portal improves efficiency through streamlined service delivery processes.
53. How are data imports performed in ServiceNow?
Ans:
Data imports in ServiceNow are performed using Import Sets. Import Sets facilitate loading data from various sources like Excel or CSV files. Field mapping ensures data is correctly aligned with target tables. Transform Maps converts imported data into ServiceNow records. Scheduled imports automate regular data updates. Data imports are crucial for maintaining up-to-date records in ServiceNow.
54. What are the types of ServiceNow tables?
Ans:
ServiceNow tables include Configuration, Task, and Custom tables. Configuration tables store system and application settings. Task tables manage records related to processes and workflows. Custom tables are created to store specific business data. Each table type has predefined functionalities and relationships. Tables in ServiceNow form the basis for organizing and managing data effectively.
55. What is the process for creating a REST API in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- REST APIs in ServiceNow are created using the API Explorer.
- Define the API endpoint and HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
- Secure the API by setting authentication and access controls.
- Document API functionalities and parameters for user reference.
- To make sure the API is functional, test it with programs like Postman.
- REST APIs enable integration with external systems and data exchange.
56. What is the HR Service Delivery module in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- The HR Service Delivery module automates HR processes within ServiceNow.
- It includes functionalities for employee onboarding, offboarding, and case management.
- HR agents use the module to handle employee inquiries and requests.
- Integration with HR systems ensures data consistency and accuracy.
- HR Service Delivery enhances employee experience through self-service options.
- It streamlines HR operations and improves service delivery efficiency.
57. How is a ServiceNow MID Server configured?
Ans:
Configure a ServiceNow MID Server using the MID Server Configuration form. Specify connectivity details and credentials for communication with ServiceNow instances. Install the MID Server software on designated servers or virtual machines. Validate connectivity and test MID Server functionality after configuration. MID Servers facilitate secure communication between ServiceNow and on-premise systems. Proper configuration ensures reliable data synchronization and service integration.
58. What is the significance of ServiceNow’s Project Portfolio Management (PPM)?
Ans:
ServiceNow’s PPM enables organizations to manage and prioritize project portfolios. It provides visibility into project status, resources, and financials. PPM facilitates decision-making based on real-time data and analytics. Project managers use PPM to align projects with business objectives. It streamlines project schedules and the distribution of resources. PPM enhances project governance and ensures strategic alignment.
59. What are the methods for performing Asset Management in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- Asset Management in ServiceNow involves tracking and managing IT assets.
- Create asset records and associate them with users or departments.
- Utilize CMDB to maintain relationships and dependencies between assets.
- Implement lifecycle management to track asset procurement, deployment, and retirement.
- Use workflows for asset requests, approvals, and inventory updates.
- Asset Management improves asset utilization and supports compliance efforts.
60. What defines a Catalog Item in ServiceNow, and how is one created?
Ans:
- A Catalog Item in ServiceNow represents a requestable service or product available in the Service Catalog.
- Define Catalog Items with details such as description, category, and pricing.
- Specify fulfillment details, including assignment groups and workflows.
- Use variables to customize options available to users when requesting the item.
- Test Catalog Items to ensure functionality and user experience.
61. How are form validations handled in ServiceNow?
Ans:
Form validations in ServiceNow are crucial for maintaining data integrity and effectively enforcing business rules. They are primarily handled through client-side scripts such as Business Rules and Client Scripts. These scripts execute before records are saved, ensuring that field inputs meet specified criteria and align with organizational policies. By validating inputs on the client side, errors and incorrect data submissions are caught early, improving the general user experience and decreasing the possibility of data inconsistencies.
62. What is the purpose of the Change Management module in ServiceNow?
Ans:
The Change Management module in ServiceNow plays a crucial role in overseeing the entire lifecycle of changes to IT infrastructure and services. It encompasses comprehensive planning, meticulous scheduling, and rigorous control to ensure that every change is carefully evaluated, prioritized, and implemented. This process is designed to minimize service disruption and downtime while adhering strictly to organizational policies, regulatory standards, and best practices.
63. What is the process for creating a custom field in a ServiceNow table?
Ans:
- To add a custom field in ServiceNow, administrators navigate to the table’s configuration, select “Columns,” and then “Add a new column.”
- They define the field’s properties, such as data type and label.
- Once saved, the new field is ready for use in managing records within that table.
64. What is a Script Action in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- A Script Action in ServiceNow is a reusable script that executes specific actions triggered by events or conditions.
- These scripts automate tasks, update records, or integrate with external systems, enhancing platform functionality and streamlining workflow processes effectively.
65. Explain the use of the Discovery module in ServiceNow.
Ans:
The Discovery module in ServiceNow automates the discovery and mapping of IT infrastructure and services across an organization’s network. It uses various methods like IP probing, SNMP, WMI, and SSH to identify devices, applications, and their interdependencies. This automation provides crucial visibility into the IT landscape, ensuring accurate configuration management and supporting IT operations and services.
66. How are incidents managed in ServiceNow?
Ans:
Incident Management in ServiceNow starts when users report incidents through various channels. These incidents are logged, categorized based on their nature and impact, and prioritized to determine the order of resolution. They are then assigned to the appropriate support teams or individuals responsible for resolving them. Throughout the process, the module facilitates efficient communication among stakeholders, tracks the status of each incident in real-time, and ensures that incidents are handled promptly to minimize disruptions to business operations.
67. What are the steps for configuring workflows in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- Workflows in ServiceNow are configured using the Workflow Editor.
- Administrators define sequential steps, conditions, and approvals required to automate business processes visually.
- This approach helps streamline operations, enforce compliance, and improve efficiency across service management tasks.
68. What are the types of Transform Maps in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- Transform Maps in ServiceNow serve two primary purposes: Import and Export.
- Import Transform Maps map external data sources to ServiceNow tables, facilitating data integration.
- Export Transform Maps define how ServiceNow data is exported to external systems, ensuring consistency and interoperability.
69. Explain the concept of ServiceNow Service Mapping.
Ans:
ServiceNow Service Mapping automates the discovery, mapping, and visualization of relationships between IT components and services across an organization’s infrastructure. Creating a comprehensive view of these dependencies facilitates accurate impact analysis during incidents and changes. This capability not only speeds up incident resolution by pinpointing affected services quickly but also enhances proactive management of IT services and resources.
70. How is the ServiceNow UI customized?
Ans:
Customizing the ServiceNow UI involves leveraging tools like UI Policies, UI Actions, and Client Scripts to tailor the platform to specific organizational requirements. UI Policies allow administrators to dynamically control form field visibility, mandatory fields, and read-only states based on predefined conditions. UI Actions enable the addition of custom buttons and actions to forms and lists, enhancing user interaction and workflow efficiency.
71. What is a UI Macro in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- A UI Macro in ServiceNow is a reusable script that renders UI components on forms, lists, and UI pages.
- It helps standardize UI elements across the platform and promote reusability. UI Macros can include scripts, HTML, and references to other macros or UI elements.
- They are managed through the UI Macros module in ServiceNow. UI Macros simplify UI customization and enhance user experience by providing consistent UI elements.
72. What is the process for using the ServiceNow Mobile App?
Ans:
- The ServiceNow Mobile App allows users to access ServiceNow functionalities on mobile devices.
- Users can view, update, and create records, incidents, and tasks directly from their mobile devices.
- It supports push notifications for alerts and updates. The app provides offline capabilities, allowing users to work without an internet connection and sync data later.
- Users can access the ServiceNow Mobile App from app shops, enter their login information, and additionally start using it.
73. What is the significance of the Knowledge Base in ServiceNow?
Ans:
The ServiceNow Knowledge Base centralizes information and solutions for common issues and inquiries. It helps users find answers to questions without contacting support, reducing resolution time. Knowledge articles in ServiceNow can include troubleshooting steps, FAQs, and best practices. It supports self-service by empowering users to resolve issues independently. Knowledge articles can be categorized, tagged, and linked to related records for easy navigation.
74. How is a ServiceNow Scoped Application created?
Ans:
To create a Scoped Application in ServiceNow, navigate to Application Studio in the ServiceNow instance. Click on “Create Application” and provide details like name, version, and description. Scoped Applications isolate customizations to prevent conflicts with other applications or platform upgrades. Developers can create tables, scripts, UI components, and business rules within the Scoped Application. Scoped Applications are packaged for deployment and can include dependencies managed through the Studio.
75. What is a GlideAjax in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- GlideAjax in ServiceNow is a server-side API used for asynchronous communication between client scripts and server-side scripts.
- It enables client scripts to call server-side scripts without reloading the entire page.
- GlideAjax requests are sent asynchronously, allowing the user to continue interacting with the interface.
- It helps in performing server-side operations like database queries or updates based on client-side actions.
76. What methods are used to handle notifications in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- The ServiceNow Notifications module manages notifications. Administrators can configure notifications for various events, such as task assignments, approvals, or system alerts.
- Users receive notifications via email, SMS, or through the ServiceNow interface.
- Notification settings can be customized based on user roles, preferences, and urgency.
- Users can manage their notification preferences through the User Preferences section.
77. What are the different types of ACLs in ServiceNow?
Ans:
ACLs (Access Control Lists) in ServiceNow define permissions and access rights for records and fields. There are four types of ACLs: Field, Table, Extended, and Application. Field ACLs control access to specific fields within a table. Table ACLs control access to entire tables, including create, read, update, and delete operations. Extended ACLs grant additional permissions beyond the standard CRUD operations. Application ACLs restrict access to application resources and functionalities based on user roles.
78. How are data exports performed in ServiceNow?
Ans:
In ServiceNow, data exports can be performed using the “Export to PDF,” “Export to Excel,” or “Export to CSV” options available in lists and reports. Users can customize the export format and content based on their requirements. Scheduled exports can be set up using Scheduled Data Exports to run at specified intervals. Data exports can include filtered records, specific fields, or aggregated data based on user-defined criteria. Exported files can be downloaded or shared with stakeholders for further analysis or reporting.
79. What is the purpose of the ServiceNow Problem Management module?
Ans:
- The ServiceNow Problem Management module identifies the root causes of recurring incidents to prevent future occurrences.
- It facilitates the investigation, diagnosis, and resolution of underlying problems affecting IT services.
- Problem records in ServiceNow are linked to related incidents and changes for holistic management.
- Problem Management aims to minimize business disruptions and improve service reliability.
- It uses problem categorization, prioritization, and escalation to ensure timely resolution.
80. What is the process for creating a Scheduled Job in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To create a Scheduled Job in ServiceNow, navigate to Scheduled Jobs under System Definition in the ServiceNow instance.
- In order to add a new Scheduled Job record, click “New.”
- Specify details such as script, frequency, start time, and recurrence pattern for the job.
- Scheduled Jobs execute server-side scripts at specified intervals to automate tasks like data cleanup or maintenance.
- Jobs can be monitored and managed through the Scheduled Jobs module for status and execution history.
81. Explain the use of the ServiceNow CMDB.
Ans:
ServiceNow CMDB (Configuration Management Database) is used to manage configuration items (CIs) and their relationships within an organization’s IT infrastructure. It provides a single source of truth for IT assets, helping to track configurations, dependencies, and changes. This aids in maintaining accurate information for incident, problem, and change management processes, ensuring better service delivery and reducing risks associated with changes.
82. What is the function of the ServiceNow Orchestration module?
Ans:
ServiceNow Orchestration automates tasks and processes across different systems and applications. It integrates with third-party tools and systems to streamline workflows, automate complex processes, and enforce best practices. Orchestration helps organizations achieve operational efficiency by reducing manual effort, improving accuracy, and enabling faster response times to business needs and IT incidents.
83. How is a Data Policy created in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To create a Data Policy in ServiceNow, navigate to System Definition > Data Policies.
- Define the conditions under which the policy applies, such as table, field, and conditions.
- Specify the actions to enforce, like mandatory fields, read-only access, or encryption.
- Save the policy to activate it, ensuring data governance and compliance with organizational rules and regulations.
84. What are the different types of tables in ServiceNow?
Ans:
ServiceNow tables can be categorized into three main types: Core Tables, which store fundamental platform data like users and groups; Extended Tables, which extend core tables with custom fields or business logic; and Custom Tables, created by administrators to store specific data unique to an organization’s needs. Each table type supports different functionalities and customization options within the ServiceNow platform.
85. What is the procedure for using ServiceNow’s Visual Task Board?
Ans:
ServiceNow’s Visual Task Board visualizes tasks and their statuses, facilitating task management and tracking. Users can drag and drop tasks across customizable columns (like To Do, In Progress, Done) to update their status. It provides a clear, real-time overview of task progress, improves team collaboration, and enhances workflow efficiency by simplifying task assignment, prioritization, and monitoring.
86. What is the significance of the Incident Lifecycle in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- The Incident Lifecycle in ServiceNow defines stages from incident creation to resolution.
- It includes stages like New, Assigned, Work in Progress, Resolved, and Closed.
- Each stage has defined workflows and responsibilities, ensuring incidents are handled promptly and efficiently.
- This structured approach improves incident management by providing clear accountability, reducing resolution times, and enhancing service quality.
87. How is user authentication implemented in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- Implement user authentication in ServiceNow by configuring Authentication Sources under System Security.
- Choose authentication methods like LDAP, SAML, OAuth, or local ServiceNow authentication.
- Configure settings such as server URLs, credentials, and attribute mappings.
- Test and validate the configuration to ensure users can securely access ServiceNow with proper authentication methods aligned with organizational security policies.
88. What steps are involved in performing instance cloning in ServiceNow?
Ans:
Instance cloning in ServiceNow involves creating a duplicate of an existing instance for testing or development purposes. Use the System Clone application to initiate the process, selecting source and target instances. Customize settings such as data to include (full or partial), schema options, and configuration choices. Monitor and validate the cloning process to ensure data integrity and functionality consistency across instances.
89. Explain the concept of ServiceNow Service Catalog Items.
Ans:
ServiceNow Service Catalog Items are predefined services or products available to users via the Service Catalog. They represent IT or business services users can request, such as software installations, equipment provisioning, or service requests. Each catalog item includes details like description, fulfillment processes, costs, and approval workflows. Service Catalog Items streamline service delivery, enhance user experience, and improve service request management efficiency.
90. What is the process for creating a REST Message in ServiceNow?
Ans:
- To create a REST Message in ServiceNow, go to System Web Services > Outbound > REST Message.
- Define endpoint URL, HTTP method, authentication type, and request/response formats.
- Optionally configure headers, parameters, and authentication credentials.
- Test and validate the message to ensure proper connectivity and data exchange with external REST APIs.
- Use REST Messages to integrate ServiceNow with external systems, enabling data synchronization and automation.
91. What is the purpose of the Facilities Management module in ServiceNow?
Ans:
The Facilities Management module in ServiceNow streamlines the management of physical spaces, assets, and resources within an organization. It allows facilities teams to efficiently handle tasks such as space planning, asset tracking, maintenance scheduling, and service requests. Centralizing these processes enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and improves workplace productivity.
92. How is ServiceNow’s Agent Workspace configured?
Ans:
Configuring ServiceNow’s Agent Workspace involves setting up personalized dashboards, widgets, and layouts tailored to support service agents’ workflows and priorities. Agents can customize their workspace to include relevant tools, task lists, and knowledge articles that streamline incident management, problem resolution, and service requests. Integration with AI-driven automation enhances efficiency by suggesting solutions and automating routine tasks, improving overall service delivery and customer satisfaction.
93. What is the use of the Financial Management module in ServiceNow?
Ans:
The Financial Management module in ServiceNow enables organizations to manage their financial operations and expenditures effectively. It supports budget planning, cost tracking, invoice management, and financial reporting processes. By consolidating financial data from various sources into a single platform, it enhances transparency, accuracy, and compliance with financial regulations.



