
Windows administration involves managing and maintaining Windows-based systems and networks to ensure their optimal performance, security, and reliability. This role includes tasks such as installing and configuring operating systems, managing user accounts and permissions, applying updates and patches, and monitoring system performance. Administrators also handle network configurations, implement security measures, and troubleshoot any issues that arise.
1. What methods secure a Windows server against cyber threats?
Ans:
Securing a Windows garçon involves a multi-layered approach. Initially, I’d ensure all necessary security updates and patches are regularly applied to the garçon zilches and software. Next, I’d configure strong firewall rules to control inbound and outbound business. Enforcing robust antivirus and anti-malware results, along with regular reviews, is pivotal. Also, employing the least honor access controls ensures users have only the warrants they need.
2. Explain the approach to troubleshooting performance issues on Windows garçon.
Ans:
Troubleshooting performance issues begins with relating to the source of the problem. I’d start by covering system coffers like CPU, memory, fragment, and network operation using erected-in tools like Task Manager or Performance Monitor. Assaying event logs can give perceptivity to any crimes or warnings. However, I might use technical performance monitoring tools for further in-depth analysis If the issue persists.
3. What ensures the high availability and reliability of Windows servers?
Ans:
- Redundancy and visionary conservation achieve high vacuity and trustability. Enforcing failover clustering ensures that services remain accessible even if one garçon fails.
- Regular backups with offsite storehouses guarantee data integrity and recovery options in case of disasters.
- Monitoring tools help identify implicit issues before they escalate. Cargo balancing distributes incoming business across multiple servers to help load.
- Also, establishing a comprehensive disaster recovery plan and conducting regular drills ensures readiness for any unlooked-for eve
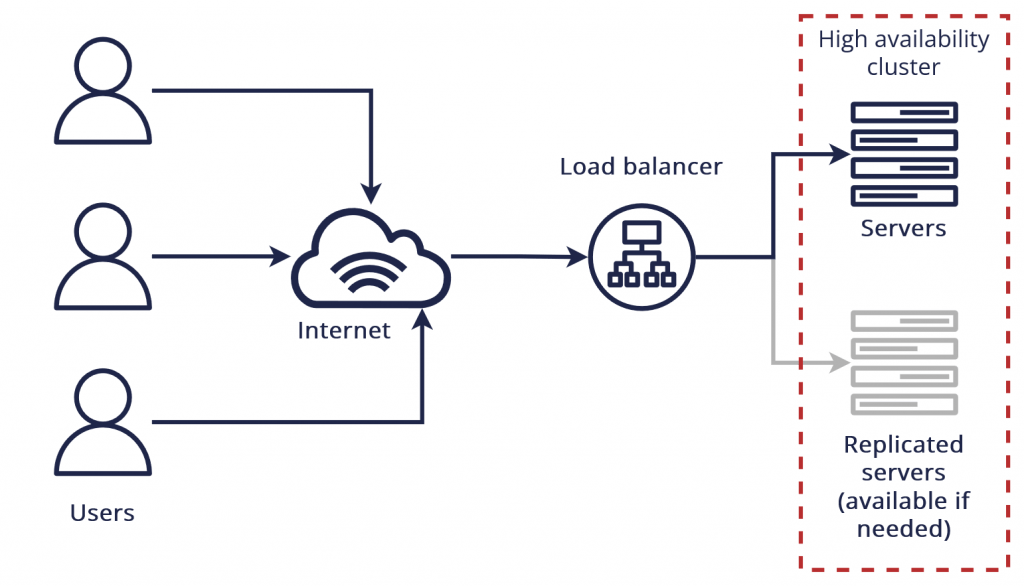
4. What is the different between system administration and network administration?
Ans:
| Aspect | System Administration | Network Administration |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing and maintaining servers and workstations | Managing and maintaining network infrastructure |
| Key Responsibilities | Installing OS, managing user accounts, applying updates | Configuring routers, switches, and firewalls |
| Tools Used | Active Directory, PowerShell, System Center | Network monitoring tools (e.g., Wireshark), VPN |
| Primary Objective | Ensure optimal performance and reliability of systems | Ensure network connectivity, security, and performance |
5. What steps are taken during a critical Windows server failure in business hours?
Ans:
In the event of a critical failure during business hours, nippy action is essential to minimize time-out and alleviate impact. First, I’d incontinently notify applicable stakeholders about the issue, including operation and affected users. Contemporaneously, I’d begin troubleshooting the problem to identify its root cause. Depending on the inflexibility of the issue, I might try to restore services from backups or apply temporary workarounds to regain functionality.
6. What measures ensure compliance with industry regulations on Windows servers?
Ans:
Compliance with assiduity regulations and security norms is consummate to cover sensitive data and maintain trust. Let’s start by relating applicable rules and standards, similar to GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, and understanding their conditions. Enforcing security controls and configurations that align with these norms is pivotal. Regular checkups and assessments help ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for enhancement. Establishing security programs, procedures, and controls facilitates transparency and responsibility.
7. What approach automates routine tasks on Windows servers?
Ans:
- Automating routine executive tasks streamlines operations and reduces mortal error.
- I’d use scripting languages like PowerShell to produce scripts for tasks like user provisioning, software deployment, and system monitoring. Scheduled tasks and job scheduling tools enable the robotization of repetitious tasks at specified intervals.
- Enforcing configuration operation tools like Puppet or Ansible allows for the unity and operation of garçon configurations at scale.
- Regularly reviewing and streamlining robotization scripts ensures they remain effective and aligned with evolving business conditions.
8. What strategy ensures comprehensive and reliable Windows server backups?
Ans:
Ensuring comprehensive and dependable backups is essential for data protection and disaster recovery. I’d start by relating critical data and systems that need to be backed up regularly. Enforcing a backup schedule with applicable retention programs ensures a balance between data protection and storehouse effectiveness. Testing backup and recovery procedures regularly verifies their effectiveness and proactively identifies any implicit issues.
9. What actions are taken when a Windows server becomes unresponsive?
Ans:
Dealing with an unresponsive or crashed Windows garçon requires a systematic approach to restore functionality instantly. First, I’d try to establish remote access to the garçon to diagnose the issue. However, I’d physically pierce the garçon to perform troubleshooting similar to checking tackle status and reviewing event logs If remote access isn’t possible. Depending on the inflexibility of the issue, I might essay to renew specific services, perform a soft reboot, or initiate a graceful arrestment and restart.
10. How is it kept current with the latest developments in Windows server administration?
Ans:
- Staying streamlined with the rearmost developments and stylish practices is pivotal for effective Windows garçon administration.
- I’d regularly follow Microsoft’s sanctioned attestation, blogs, and adverts for updates on new features, security patches, and stylish practices.
- Sharing in online forums, user groups, and professional networks allows for knowledge sharing and collaboration with peers in the field.
- Attending webinars, conferences, and training sessions provides openings for hands-on literacy and skill improvement.
11. Describe the approach to enforcing disaster recovery results for Windows servers.
Ans:
Enforcing robust disaster recovery results involves a comprehensive approach to ensure business durability in the face of unlooked-for events. I’d start by conducting a threat assessment to identify implicit pitfalls and their impact on critical systems and data. Grounded in the evaluation, I’d design a disaster recovery plan outlining procedures for data backup, replication, and restoration.
12. What troubleshooting steps address network connectivity issues on Windows servers?
Ans:
- Troubleshooting network connectivity issues on Windows servers requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the underpinning causes.
- I’d start by checking the garçon’s network configuration, including IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS settings.
- Using tools like clunk traceroute and helps diagnose connectivity issues at various network layers.
- Reviewing firewall settings and network security programs ensures the business isn’t being blocked unintentionally.
13. What strategy manages software updates and patches on Windows servers?
Ans:
Managing software updates and patches is critical for maintaining security and stability. I’d apply a structured approach starting with testing updates in anon-production terrain to ensure comity and stability. Exercising Windows Garçon Update Services( WSUS) or a patch operation result automates the deployment of updates across servers while allowing for centralized control and reporting. Regularly listed conservation windows minimize dislocation to services during the update installation.
14. What steps are taken to resolve disk space issues on a Windows server?
Ans:
Fragment space issues can impact garçon performance and stability, so take prompt action to resolve them. I’d begin by relating the source of the fragment space consumption using tools like Disk Cleanup, TreeSize, or PowerShell scripts. Removing gratuitous lines, temporary data, and old log lines can free up fragment space temporarily. Enforcing fragment proportions and monitoring tools helps prevent fragment space issues by administering storehouse limits and furnishing early warnings.
15. What approach ensures system security against internal threats on Windows servers?
Ans:
- Guarding Windows servers against internal pitfalls involves a combination of preventative measures and access controls.
- I’d start by enforcing user authentication mechanisms like vital watchwords and multi-factor authentication, as well as regard walkout programs to help prevent unauthorized access.
- PartPart-grounded access control( RBAC) ensures users only have the warrants necessary for their job places, minimizing the threat of bigwig pitfalls.
16. What methods address server performance decline over time?
Ans:
- Addressing garçon performance declination requires visionary monitoring and optimization strategies.
- I’d start by relating performance backups using performance monitoring tools like PerfMon or Resource Monitor to dissect CPU, memory, fragment, and network applications.
- Tuning garçon configurations, optimizing operations, and streamlining motorists or firmware can address specific performance issues.
- Scaling coffers vertically by upgrading tackle factors or horizontally by adding further servers helps accommodate adding workloads.
17. What strategy secures remote access to Windows servers?
Ans:
Securing remote access to Windows servers is essential to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. I’d start by enforcing robust authentication mechanisms similar to Remote Desktop Gateway( RD Gateway) or VPN with multi-factor authentication to corroborate users’ individualities. Enabling Network Level Authentication( NLA) adds a redundant subcaste of security by taking users to authenticate before establishing a remote desktop session.
18. What is the approach for disaster recovery planning in virtualized Windows servers?
Ans:
Disaster recovery planning in a virtualized terrain requires specific considerations to ensure rapid-fire recovery and minimum time-out. I’d start by using virtualization features similar to shots, replication, and live migration to produce flexible and flexible garçon architectures. Enforcing backup and recovery results that integrate seamlessly with virtualization platforms ensures data integrity and recoverability.
19. What strategy enforces role-based access control (RBAC) on Windows servers?
Ans:
- Enforcing RBAC on Windows servers involves defining places and associated warrants grounded on job functions to apply the principle of least honor.
- I’d start by conducting a thorough analysis of users’ locations and the situations where they need access.
- Using tools like Active Directory Groups and Organizational Units( OUs), I’d organize users into logical groups grounded on their liabilities.
- Assigning warrants to groups rather than individual users streamlines administration and ensures thickness.
20. What measures ensure compliance with GDPR or HIPAA on Windows servers?
Ans:
- Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations requires a combination of specialized controls, programs, and procedures.
- I’d start by classifying data grounded on perceptivity and enforcing access controls to circumscribe unauthorized access.
- Cracking data at rest and in conveyance using technologies like BitLocker and TLS/ SSL ensures data confidentiality and integrity.
- Regular auditing and logging of access events help track data operation and demonstrate compliance with nonsupervisory conditions.
21. What strategy is used for monitoring and maintaining Windows server performance?
Ans:
Monitoring and maintaining Windows garçon performance involves nonstop monitoring, analysis, and optimization to ensure optimal operation. I’d start by setting up performance monitoring tools like Performance Examiner or third-party results to track crucial performance pointers similar to CPU operation, memory application, fragment I/ O, and network business. Assaying performance data helps identify trends, anomalies, and implicit backups that may affect garçon performance.
22. What steps are taken in a security incident involving a compromised Windows server?
Ans:
- Handling a security incident involving a compromised Windows garçon requires a nippy and regular response to contain the trouble and alleviate further damage.
- I’d start by segregating the compromised garçon from the network to help prevent the spread of malware or unauthorized access.
- Collecting and conserving substantiation similar to logs and system shots facilitates forensic analysis and discourse.
- They are enforcing incident response procedures outlined in the association’s security policy to attendants the response sweats, including notifying applicable stakeholders and authorities if necessary.
23. What approach secures remote administration for Windows servers?
Ans:
Enforcing secure remote administration for Windows servers involves planting secure protocols, access controls, and covering mechanisms to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. I’d start by configuring Remote Desktop Protocol( RDP) or PowerShell Remoting with encryption and network position authentication to ensure secure communication between directors and servers.
24. What methods ensure high availability and fault tolerance for critical services on Windows servers?
Ans:
- Ensuring high vacuity and fault forbearance for critical services involves designing flexible infrastructures and enforcing redundancy measures.
- I’d start by planting services across multiple servers in a clustered configuration using technologies like Windows Failover Clustering. Exercising cargo balancing results distributes incoming business across clustered bumps to help load and ensure scalability.
- Enforcing spare power inventories, network connections, and storehouse arrays minimizes single points of failure and enhances system trustability.
25. What strategies secure Windows server environments against ransomware attacks?
Ans:
Securing Windows server environments against ransomware attacks requires a multi-layered approach encompassing prevention, detection, and response strategies. I’d start by enforcing best security practices such as user education, software updates, and vulnerability management to mitigate common attack vectors. Additionally, implementing regular backups and ensuring data integrity can provide a crucial safety net in case of an attack.
26. What is the approach for managing Windows server configurations for consistency and compliance?
Ans:
Managing Windows server configurations involves establishing standardized settings, automating tasks, and conducting compliance checks. This begins with defining configurations using tools like the Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit or Group Policy Objects (GPOs) to apply security settings across servers. Enforcing configuration management solutions such as Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) or PowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC) automates deployment and ensures consistency across server environments.
27. What strategy addresses capacity planning for Windows server environments?
Ans:
Capacity planning for Windows garçon surroundings involves:
- Assaying current resource operation.
- Soothsaying future demands.
- Consequently, coffers are provided to ensure optimal performance and scalability.
I’d start by collecting performance criteria and assaying literal trends to identify operation patterns and implicit backups. Exercising capacity planning tools and modeling ways helps prognosticate unborn resource conditions grounded on projected growth and workload changes.
28. What actions are taken when a Windows server experiences a security breach or data leak?
Ans:
Handling a security breach or data leak on a Windows garçon requires a rapid-fire and comprehensive response to contain the incident, alleviate further damage, and restore system integrity. I’d start by segregating the affected garçon from the network to help prevent unauthorized access and data exfiltration and enforcing incident response procedures outlined in the association’s security policy attendants the response sweats, including notifying applicable stakeholders, law enforcement agencies and nonsupervisory authorities if necessary.
29. What methods enforce access controls and permission management on Windows servers?
Ans:
- Enforcing access controls and warrants on Windows train waiters involves defining user groups, setting warrants on participating flyers and lines, and regularly reviewing access rights.
- Let’s start by organizing users into logical groups grounded on their job places and liabilities. Exercising NTFS warrants and share warrants allows grainy control over who can pierce, modify, or cancel lines and flyers.
- Regularly auditing warrants and access logs helps identify any unauthorized access attempts or disagreements.
30. What strategy optimizes Windows server performance for database operations?
Ans:
Optimizing Windows garçon performance for database operations involves fine-tuning system configurations, and tackling coffers and database settings to maximize output and responsiveness. I’d start by assaying database performance criteria and relating performance backups similar to CPU, memory, fragment I/ O, and network quiescence. Optimizing garçon tackle by adding further memory, upgrading storehouse bias to SSDs, and adding CPU cores enhances database performance and scalability.
31. What measures ensure secure authentication for remote users on Windows servers?
Ans:
Ensuring secure authentication and authorization for remote users penetrating Windows servers involves enforcing strong authentication styles and access controls. I’d start by configuring Remote Desktop Services( RDS) with Network Level Authentication( NLA) and administering multi-factor authentication for remote access. Exercising virtual private network( VPN) results with instrument-grounded authentication adds a redundant subcaste of security to remote connections.
32. What is the disaster recovery planning approach for Windows servers in a cold cloud environment?
Ans:
Ensuring secure authentication and authorization for remote users penetrating Windows servers involves enforcing strong authentication styles and access controls. I’d start by configuring Remote Desktop Services( RDS) with Network Level Authentication( NLA) and administering multi-factor authentication for remote access. Exercising virtual private network( VPN) results with instrument-grounded authentication adds a redundant subcaste of security to remote connections.
33. What strategies secure Windows servers against malware and ransomware attacks?
Ans:
- Securing Windows servers against malware and ransomware attacks involves enforcing a multi-layered defense strategy encompassing preventative, operative, and remedial measures.
- I’d start by planting endpoint protection results with real-time trouble discovery and geste monitoring to identify and block vicious conditioning.
- Enforcing dispatch filtering and web security gateways helps prevent malware infections through phishing emails and vicious websites.
- Regularly streamlining antivirus delineations and security patches ensures protection against arising pitfalls.
34. What is the approach for managing software licensing and compliance on Windows servers?
Ans:
Managing software licensing and compliance on Windows servers involves inventorying software means, tracking license operation, and ensuring compliance with seller agreements and nonsupervisory conditions. I’d start by conducting a software asset force to identify installed operations and their associated licenses. Exercising software asset operation( SAM) tools helps track license entitlements, operation, and renewal dates.
35. What methods ensure Windows server configurations remain consistent across multiple environments?
Ans:
- Ensuring harmonious Windows garçon configurations across multiple surroundings involves enforcing configuration operation tools and processes to automate deployment and apply norms.
- I’d start by defining standardized configuration instances for waiters using tools like Group Policy Objects( GPOs) or configuration operation fabrics similar to Poppet or Cook.
- Automating configuration deployment and drift discovery ensures thickness and minimizes homemade crimes.
36. What strategies monitor and optimize Active Directory performance on Windows servers?
Ans:
Monitoring and optimizing Active Directory performance on Windows servers involves visionary operation of directory services, replication, and authentication processes to ensure optimal performance and scalability. I’d start by covering crucial performance pointers similar to LDAP response times, sphere regulator CPU and memory operation, and replication quiescence using erected-in tools like Performance Examiner or third-party monitoring results.
37. What measures enforce data encryption and data loss prevention (DLP) on Windows servers?
Ans:
- Enforcing data encryption and DLP measures on Windows waiters involves guarding sensitive data at rest, in conveyance, and during processing to help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- I’d start by relating sensitive data and classifying them based on their confidentiality and integrity conditions.
- Exercising encryption technologies similar to BitLocker for fragment encryption and Cracking train System( EFS) for train-position encryption ensures data confidentiality and protection against unauthorized access.
38. What is the approach for server provisioning and deployment in a Windows environment?
Ans:
- Handling garçon provisioning and deployment in a Windows terrain involves automating deployment tasks, maintaining standardized configurations, and ensuring scalability and trustability.
- I’d start by defining garçon provisioning templates or golden images with pre-configured settings, operations, and security configurations using tools like Microsoft Deployment Toolkit( MDT) or System Center Configuration Manager( SCCM).
- Automating garçon deployment workflows with deployment scripts or configuration operation tools like PowerShell DSC( Asked State Configuration) ensures thickness and reduces homemade crimes.
39. Define garçon and sphere.
Ans:
A garçon is a computer or device on a network that manages network coffers. It can give services similar to a data storehouse, access to lines, recycling power, or network connectivity to other computers or guests. A sphere, in the environment of computer networking, refers to a group of computers that partake in a standard set of rules, programs, and databases. Disciplines are generally used in surroundings like Microsoft Windows networks, where users can log in to any computer within the sphere using a single set of credentials.
40. What is an active directory?
Ans:
Microsoft’s Active Directory is a directory service developed for Windows Server networks. It stores information about objects on a network and makes it available to users and administrators. It allows for centralized management of network resources, such as user accounts, groups, computers, printers, and other network resources. Additionally, it provides authentication and authorization services to ensure secure access to these resources.
41. What is meant by Active Directory Certificate Services (ADC)?
Ans:
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): AD CS enables establishing and managing a PKI, facilitating the issuance and administration of digital certificates.
- Certificate Issuance: It allows organizations to issue digital certificates for various purposes, including securing communications, authenticating users, and ensuring data integrity.
- Identity Verification: AD CS enhances network security by validating users’ and devices’ identities through the use of certificates.
- Centralized Management: It provides a unified platform for overseeing the lifecycle of certificates, including their issuance, renewal, and revocation, ensuring efficient security management.
42. Define active directory partition. What are its types, and how can it be configured?
Ans:
An Active Directory partition is a logical division within the Active Directory database that stores specific types of data. There are three main types of Active Directory partitions: sphere partition, Configuration partition, and Schema partition. These partitions can be configured to replicate data to other sphere regulators within the sphere or timber, depending on the data’s compass.
43. What steps are taken to backup Active Directory?
Ans:
To take an Active Directory backup, you can use built-in tools like Windows Server Backup or third-party backup solutions. Windows Server Backup allows you to perform full, incremental, or custom backups of Active Directory data, including system state data. Additionally, scheduling regular backups is crucial to ensure data integrity and availability. Implementing offsite or cloud backup storage can further enhance disaster recovery options and protect against data loss.
44. Where is the active directory partition stored?
Ans:
- To take an Active Directory backup, you can use erected-in tools like Windows Garçon Provisory or third-party backup results.
- Windows Garçon Provisory allows you to perform full, incremental, or custom backups of Active Directory data, including system state data.
- Additionally, it is essential to ensure that backups are scheduled regularly and tested for integrity to guarantee that recovery processes will be effective when needed.
45. What is known about group policies?
Ans:
Group programs( GPOs) in Windows environments are sets of rules and configurations that network directors use to control and manage the working terrain of user and computer accounts. GPOs can apply security settings, install software, chart network drives, and perform a wide range of other executive tasks across an entire network. They’re centrally managed from a sphere regulator and can be applied to specific users, groups, or computers within an Active Directory sphere.
46. What is understood about DNS scavenging?
Ans:
- DNS Scavenging is a process in the Domain Name System( DNS) that automatically removes banal or obsolete resource records from a DNS zone.
- Banal records can accumulate over time and lead to inefficiencies or inconsistencies in DNS queries.
- DNS Scavenging helps maintain DNS integrity and performance by periodically drawing up outdated records.
- This can ameliorate the delicacy of name resolution and reduce network business.
47. What methods force DNS dynamic updates?
Ans:
To force a DNS dynamic update, administrators can use command-line tools like ‘ipconfig /registerdns’ on the client machine or ‘dnscmd /clear cache’ on the DNS server. Additionally, configuring DNS zones to allow secure dynamic updates ensures that only authenticated clients can update their DNS records securely. Properly managing permissions and access controls for DNS records is essential to maintaining network security. Regular monitoring of DNS logs can also help identify unauthorized update attempts and potential security threats.
48. What are the active directory database files
Ans:
The Active Directory database files include the NTDS. Dit file is the primary database file that stores all directory data for Active Directory Domain Services. Additionally, transaction log files (.log) record changes to the database and checkpoint files (.chk) indicate the last transaction committed. These log files play a crucial role in ensuring data integrity and recovery. Furthermore, the database structure supports efficient searching and retrieval of objects within the Active Directory environment.
49. What is known about Group Policy Objects (GPOs)?
Ans:
GPOs( Group Policy Objects) are holders for group policy settings that allow directors to manage configurations for users and computers in an Active Directory environment. GPOs can be linked to spots, disciplines, or organizational units( OUs) and are reused in a hierarchical order, with settings from advanced-position GPOs potentially being hoofed by settings in lower-position GPOs.
50. Explain the primary, secondary, and end zones.
Ans:
- Primary, secondary, and end zones are different types of DNS zones used for name resolution in DNS waiters.
- A primary zone is the authoritative source for DNS information and can be streamlined directly.
- Secondary zones are read-only clones of primary zones that are streamlined through zone transfers from the primary zone.
- Kindle zones contain only the resource records necessary to identify the authoritative DNS waiters for a particular zone and are used to resolve names between different DNS namespaces.
51. What is the difference between a thread and a computer process?
Ans:
A thread is the lowest unit of prosecution within a process, representing a single successional inflow of control. Vestments within the same process share the same memory space and coffers, allowing them to communicate and attend efficiently. In contrast, a computer process is a vessel for a set of coffers, including memory, CPU time, and other system attributes, used to execute a program.
52. What are some particular attributes of a director?
Ans:
Some particular attributes of a director include strong communication chops for effectively conveying specialized information to different cultures, problem-working capacities to troubleshoot complex issues efficiently, attention to detail to ensure accurate configurations and attestation, rigidity to fleetly changing technology geographies, leadership rates to coordinate brigades and systems effectively, and a commitment to nonstop literacy to stay streamlined with the rearmost advancements in the field
53. What is known about Windows server trims?
Ans:
- Triumphs( Windows Internet Name Service)? Waiters are used for NetBIOS name resolution in Windows-grounded networks.
- They dynamically map NetBIOS names to IP addresses, easing communication between computers and bias within the network.
- Triumph servers help overcome the limitations of broadcasts in large networks by furnishing a centralized database for name resolution, perfecting network effectiveness and trustability.
54. What is the difference between global, universal, and original groups?
Ans:
Windows Active Directory uses different groups to organize and administer user and computer accounts. These groups are global, universal, and domain-local. Global groups organize user accounts within the same domain and generally assign permissions to resources within that domain. Universal groups can contain users from any domain within the forest and are typically used for assigning permissions across multiple domains.
55. What is the process for restoring Active Directory partitions?
Ans:
- Yes, Active Directory partitions can be restored using backup and restore procedures.
- By performing a system-state backup of a sphere regulator, which includes Active Directory data, directors can restore Active Directory partitions in the event of data loss or corruption.
- Still, it’s pivotal to follow stylish practices and test the restoration process to ensure data integrity and minimize time-out in product surroundings.
56. What is the difference between an antivirus and a firewall?
Ans:
Antivirus software is designed to describe and remove vicious software, similar to contagions, worms, and Trojans, from a computer system. It scans lines and processes for known patterns of vicious law and may also include features like real-time protection and heuristic analysis to identify new pitfalls. It acts as a hedge between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, filtering business to help unauthorized access and cover against cyber trouble
57. What is known about timber?
Ans:
In Windows Active Directory, a timber is a collection of one or more disciplines grouped and connected by trust connections. It represents the top-position hierarchical structure within Active Directory and is composed of multiple sphere trees that partake in a standard schema, configuration, and global roster. Timbers provide a means of organizing and managing a large-scale network structure, allowing for centralized administration and resource sharing across multiple disciplines.
58. What is the top end of the MCSA Windows Garçon 2012?
Ans:
- The top end of the MCSA( Microsoft Certified Results Associate) Windows Garçon 2012 instrument is to validate the chops and knowledge needed to administer and manage Windows Garçon 2012 surroundings effectively.
- This instrument covers various aspects of Windows Garçon 2012, including installation, configuration, administration, storehouse, networking, and security.
- It equips IT professionals with the necessary grit to emplace, manage, and maintain Windows Garçon 2012 structure in enterprise surroundings, ensuring optimal performance, trustability, and security.
59. What is the difference between a computer system and a thread?
Ans:
A computer system refers to a set of instructions or procedures designed to perform a specific task or achieve a particular ideal within a computer program or operation. It encapsulates a series of conduct that can be executed singly to negotiate a asked outgrowth. On the other hand, a thread is the lowest unit of prosecution within a process, representing a single successional inflow of control.
60. How is it determined which server supports which role?
Ans:
- To determine which garçon supports which part in a Windows Garçon terrain, directors can use tools similar to Garçon Director or PowerShell.
- Garçon Director provides a graphical interface for managing garçon places and features across multiple servers, allowing directors to view the installed places and features on each garçon within the network.
- Also, PowerShell cmdlets like Get—WindowsFeature can be used to query the areas and features installed on a specific garçon or multiple waiters, furnishing detailed information about the supported places and their status.
61. Explain IntelliMirror.
Ans:
IntelliMirror is a point introduced in Windows Garçon operating systems that facilitates centralized operation and deployment of users’ desktop settings, operations, and data. It allows directors to produce and apply harmonious computing surroundings for users by furnishing features similar to roving users’ biographies, brochure redirection, offline lines and flyers, and software installation and conservation.
62. What makes MCSA SQL Garçon more effective?
Ans:
The MCSA SQL Server certification validates the skills and knowledge required to design, implement, and maintain databases using Microsoft SQL Server. It covers database administration, development, querying, and business intelligence. The certification emphasizes industry-standard database management practices, advanced data handling techniques, and optimization strategies, enabling IT professionals to enhance the performance, scalability, and reliability of SQL Server databases in various enterprise environments.
63. Define Domain Controller.
Ans:
- A Domain Controller( DC) is a garçon of a Windows Active Directory sphere that is responsible for authenticating users, recycling login requests, and administering security programs within the sphere.
- It stores a replica of the Active Directory database and maintains a secure channel with other sphere regulators to replicate changes made to the directory data.
- Sphere regulators play a pivotal part in maintaining the integrity and vacuity of directory services, ensuring flawless authentication and access to network coffers for users and computers within the sphere.
64. Explain authorizing DHCP waiters in Active Directory.
Ans:
Authorizing DHCP waiters in Active Directory involves granting authorization to a DHCP garçon to operate in an Active Directory sphere. This process ensures that only authorized DHCP waiters can lease IP addresses and give network configuration settings to guests within the sphere. To allow a DHCP garçon, a director must have Enterprise Admin or Domain Admin boons. The DHCP garçon sends a DHCP Discover packet to the network, and if it receives an authorization response from an Active Directory sphere regulator, it becomes a sanctioned DHCP garçon.
65. How can one configure Active Directory Partitions?
Ans:
- Configuring Active Directory partitions involves managing the logical divisions within the Active Directory database where directory data is stored.
- Directors can configure Active Directory partitions using tools like Active Directory spots and Services or ADSI Edit.
- They can produce, modify, or cancel partitions grounded on the specific conditions of their terrain.
- Configuration options include defining replication reaches, conforming replication frequency, and specifying replication mates to control how directory data is distributed and accompanied across sphere regulators.
66. Explain OU.
Ans:
An Organizational Unit (OU) is a container in Active Directory used to organize and manage objects like user accounts, computer accounts, and groups. OUs provide a hierarchical structure for delegating administrative tasks and applying Group Policy settings to specific groups. Administrators can create OUs to reflect the organizational structure, divisions, or locations, enabling centralized management and granular control over directory objects and resources.
67. When MSI trains aren’t possible, how can one install an app?
Ans:
- When an MSI train isn’t available for installing an operation, directors can use indispensable deployment styles similar to scripting, homemade installation, or third-party deployment tools.
- Scripting involves writing scripts using languages like PowerShell or VBScript to automate the installation process by executing commands or running installation routines.
- Homemade installation involves installing the operation manually on each computer by following the installation wizard or copying lines to the target system.
68. How to performNon-authoritativeRestore?
Ans:
To perform a non-authoritative restore of Active Directory, administrators use Windows Server Backup or similar tools to restore the system state data of a domain controller. The domain controller is booted into Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM), and the backup is restored. Afterward, the domain controller restarts and replicates with other domain controllers to incorporate any changes since the backup, ensuring data consistency across the domain.
69. Explain the SYSVOL brochure.
Ans:
SYSVOL( System Volume) is a participating directory that stores public lines related to the sphere policy, Group Policy settings, and scripts for logon and logoff processes in a Windows Active Directory terrain. It’s replicated among all sphere regulators and is essential for the proper functioning of Active Directory services. SYSVOL contains Group Policy objects( GPOs), login scripts, and other system lines that are centrally accessible to guests and sphere regulators within the sphere, easing harmonious configuration and policy enforcement across the network.
70. Define GPO.
Ans:
- A Group Policy Object( GPO) is a collection of settings in a Windows Active Directory terrain that defines how computers and users should be configured within a sphere.
- GPOs are used to apply security programs, emplace software, manage users’ settings, and configure system settings across multiple computers and users in the network.
- They give centralized operation and thickness in configuration settings, allowing directors to apply programs grounded on organizational units, spots, or disciplines.
71. Explain about winning waiters.
Ans:
Triumphs ( Windows Internet Name Service) waiters are used for NetBIOS name resolution in Windows-grounded networks. They give a dynamic mapping between NetBIOS names and IP addresses, easing communication between computers and bias within the network. Triumphs waiters help overcome the limitations of broadcasts in large networks by furnishing a centralized database for name resolution, perfecting network effectiveness and trustability.
72. Why are the MCSA credentials more in demand?
Ans:
The MCSA( Microsoft Certified Results Associate) credentials are mainly in demand due to several factors. Initially, Microsoft technologies were extensively used in enterprise surroundings worldwide, making MCSA instruments precious for IT professionals seeking career openings in various fields of endeavor. Also, MCSA instruments validate the practical chops and knowledge needed to design, apply, and manage Microsoft results effectively, enhancing employability and credibility in the job request.
73. Can a third-party directory service be joined to Active Directory?
Ans:
- Yes, it’s possible to join a third-party Directory service to an Active Directory terrain using directory synchronization tools or identity confederation services.
- Directory synchronization tools like Azure Active Directory Connect allow associations to attend users’ accounts, groups, and other directory objects between Active Directory and third-party directory services similar to Azure Announcement, Google Workspace, or LDAP directories.
74. What is INODE?
Ans:
- INODE( Index Node) is a data structure used in Unix-like operating systems, including Linux and macOS, to represent and manage lines and directories on a train system.
- Each train or Directory in a train system is associated with an INODE, which stores metadata about the train or Directory, similar to its warrants, power, size, timestamps, and fragment block pointers.
- INODEs grease effective train system operations by furnishing a means to detect and manage data blocks associated with lines and directories, enabling train storehouse, reclamation, and operation in the train system.
75. Can Group Policy be inherited by the child sphere?
Ans:
Yes, Group Policy settings can be inherited by child disciplines within an Active Directory timber. Heritage of Group Policy settings occurs by dereliction, where child disciplines inherit GPOs linked to parent disciplines unless explicitly blocked or walked at the child sphere position. Directors can produce and manage GPOs at the timber, sphere, or organizational unit( OU) position, allowing for centralized administration and harmonious policy enforcement across the Active Directory scale.
76. Explain RAID in Windows Garçon
Ans:
RAID( spare Array of Independent Disks) in Windows Garçon is a data storehouse technology that combines multiple physical fragment drives into a single logical unit to facilitate performance, redundancy, or both. Windows Garçon supports various RAID situations, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10, each offering different trade-offs between performance, redundancy, and capacity application.
77. Explain Netlogon Folder.
Ans:
- The Netlogon brochure is a participating system brochure on sphere regulators in a Windows Active Directory terrain.
- It contains essential coffers for network logon and authentication processes, including scripts, programs, and other lines needed for sphere regulator communication and authentication services.
- The Netlogon brochure also stores logon scripts configured through Group Policy, which are executed when users log on to computers that are members of the sphere.
78. Define moping objects.
Ans:
- A moping object in Active Directory refers to an object that exists on a sphere regulator but has been deleted from the directory replication system.
- Lingering objects can occur due to replication issues or inconsistencies between sphere regulators, leading to implicit data inconsistencies and functional problems within the Active Directory sphere.
- Relating and resolving moping objects is critical for maintaining the integrity and trustability of Active Directory services, as they can spawn replication conflicts, authentication failures, or other issues affecting the functionality of the sphere.
79. Is VOIP important
Ans:
Voice over Internet Protocol( VoIP) is an important technology that enables the transmission of voice dispatches over the Internet or other IP-ground networks. VoIP offers multitudinous benefits, including cost savings, inflexibility, scalability, and advanced features compared to traditional phone systems. It allows associations to streamline communication processes, enhance collaboration, and facilitate productivity by integrating voice, videotape, and data services over a single network structure.
80. Explain the introductory function of the sphere regulator.
Ans:
The introductory function of a sphere regulator in a Windows Active Directory terrain is to authenticate users and computers, apply security programs, and give access to network coffers within the sphere. Sphere regulators store a replica of the Active Directory database, which contains information about users, groups, computers, and other directory objects.
81. What SYSVOL issues have been observed in the environment?
Ans:
Some common Sysvol issues observed in surroundings include replication failures, authorization issues, missing or corrupted lines, and inconsistencies between sphere regulators. These issues can impact the functionality of Group Policy processing, logon script prosecution, and overall Active Directory operations. Resolving Sysvol issues generally involves:
- Troubleshooting replication problems.
- Vindicating warrants on the Sysvol share and its contents.
- Restoring missing or spoiled lines from backups.
- Ensuring proper configuration of sphere regulators and replication topology.
82. What is the purpose of establishing the original DNS waiters?
Ans:
Original DNS waiters are established to give sphere name resolution services within an original network terrain. These waiters maintain a database of sphere names and their corresponding IP addresses, allowing guests to resolve hostnames to IP addresses and vice versa. By planting original DNS waiters, associations can ameliorate network performance, reduce reliance on external DNS waiters, and enhance security by resolving DNS queries locally.
83. List the queries of DNS.
Ans:
- DNS( sphere Name System) serves several types of queries, including recursive queries, iterative queries, and rear DNS queries.
- DNS guests make recursive queries to resolve sphere names into IP addresses, and the DNS garçon is responsible for completely resolving the query by either furnishing the requested information or pertaining the customer to another DNS garçon.
- DNS waiters make iterative queries to other DNS waiters, where the queried garçon provides as important information as possible, either in the query or by pertaining the querying garçon to another DNS garçon.
84. Where is the announcement database kept?
Ans:
The Active Directory( announcement) database is stored on sphere regulators in a Windows Active Directory terrain. Specifically, it’s kept in the TDS.dit train, which is located in the SystemRoot NTDS directory on each sphere regulator’s original hard drive. The announcement database contains information about objects similar to users’ accounts, groups, computers, and organizational units, as well as their attributes and connections.
85. Explain DNS Scavenging.
Ans:
- DNS Scavenging is a process in the Domain Name System( DNS) that automatically removes banal or obsolete resource records from a DNS zone.
- Banal records can accumulate over time and lead to inefficiencies or inconsistencies in DNS queries.
- DNS Scavenging helps maintain the integrity and performance of DNS by periodically drawing up outdated records, which can facilitate the delicacy of name resolution and reduce network business.
- Directors can configure DNS scavenging settings to specify when and how frequently banal records should be scavenged from DNS zones.
86. Define global roster.
Ans:
- SID( Security Identifier) is a unique identifier assigned to each security star( similar to users’ accounts, groups, and computers) in Windows operating systems.
- SIDs are used to control access to coffers and objects in the system, allowing directors to assign warrants and define security programs grounded on users or group individualities.
- SIDs are composed of a sphere identifier( for sphere accounts) or a well-known security identifier authority( for original accounts) and a relative identifier( relieve) that uniquely identifies the security star within its sphere or system.
87. Describe an active directory and schema.
Ans:
Active Directory (AD) is a Microsoft directory service that manages user accounts, computers, and other resources within a network. It facilitates authentication, authorization, and centralized management of network objects. The AD schema outlines the directory’s structure, detailing the types of objects (such as users and groups) and their associated attributes. It acts as a framework for organizing and storing data in AD.
88. Explain the Dora Procedure & its regulation.
Ans:
- The DORA procedure refers to the sequence of ways a DHCP customer can gain an IP address from a DHCP garçon.
- In this procedure, the DHCP customer first sends a Discover communication to discover available DHCP waiters on the network.
- The DHCP garçon responded with an offer communication, offering an IP address parcel to the customer.
- The customer also sent a request communication to the named DHCP garçon requesting the provided IP address. Eventually, the DHCP garçon sends an Acknowledgement, attesting the IP address parcel to the customer.
89. Define GUID.
Ans:
GUID( Encyclopedically Unique Identifier) is a 128-bit value that’s encyclopedically unique and generally represented as a hexadecimal string. GUIDs are used to uniquely identify objects, deals, and other realities in computer systems and software operations. In Windows environments, GUIDs are generally used to identify Active Directory objects, similar to user accounts, groups, computers, and organizational units.
90. What are the benefits of GPMC?
Ans:
- Centralized Management GPMC allows directors to produce, edit, and link GPOs from a single press, streamlining the operation of Group Policy settings across the entire sphere or timber.
- Delegation of Authority GPMC enables directors to delegate specific Group Policy operation tasks to other users or groups, empowering them to manage Group Policy settings within their compass of responsibility.
- Reporting and Analysis GPMC provides reporting and analysis tools to help directors track GPO settings, identify conflicts or inconsistencies, and troubleshoot Group Policy-related issues.



