
Our CompTIA interview questions encompass a series of inquiries crafted to evaluate the competencies, knowledge, and skills of individuals in the field of information technology, especially those seeking CompTIA certifications. These questions span various domains such as networking, security, hardware, software, and best IT practices. Candidates undergo assessment based on problem-solving skills, comprehension of industry-standard procedures, and their adeptness in applying CompTIA principles. The objective of these interview questions is to assess candidates’ preparedness for roles in IT support, administration, and cybersecurity by evaluating their understanding of fundamental CompTIA concepts.
1. Explore diverse Hard Disk Drive Connector Types.
Ans:
Connector types for Hard Disk Drives (HDD) encompass SATA (Serial ATA) and its iterations like SATA III for heightened data transfer speeds. Older connectors include IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) and SCSI (Small Computer System Interface). These interfaces serve as crucial links between the hard drive and the Motherboard, with SATA being prevalent in modern systems due to its faster data transfer capabilities.
2. Examine different CPU Technologies.
Ans:
CPU technologies exhibit diversity, incorporating architectures such as x86 and ARM. Distinct CPU generations, like Intel’s Core I series or AMD’s Ryzen series, showcase speed, efficiency, and multi-core capabilities advancements. Specialized technologies like Hyper-Threading (HT) or Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) enhance multitasking. Understanding CPU technologies aids in selecting processors tailored to specific computing requirements.
3. Discuss the functions of an Operating System.
Ans:
- Process management
- Memory management
- File system management
- Device management
- Providing a user interface
4. Provide insights into the Components and Terminology of Operating Systems.
Ans:
OS components comprise the kernel (core managing system resources), file system (organizing and accessing data), and device drivers (facilitating hardware communication). Terminology includes
- processes (running programs),
- threads (smallest executable unit within a process), and
- virtual memory (extended RAM using disk space).
Understanding these components and terms contributes to comprehending the internal workings of the OS.
5. Define System Files.
Ans:
System files are vital files integral to the Operating System’s functionality. Examples include dynamic link libraries (DLLs) in Windows or system files in Linux. These files contain essential routines and instructions used by the OS and applications. Altering or deleting system files can impact system stability and performance.
6. Define System Files.
Ans:
System files are vital files integral to the Operating System’s functionality. Examples include dynamic link libraries (DLLs) in Windows or system files in Linux. These files contain essential routines and instructions used by the OS and applications. Altering or deleting system files can impact system stability and performance.
7. Describe the various methods of Installing an Operating System.
Ans:
Operating Systems can be installed through multiple methods, including:
- CD/DVD Installation: Utilizing installation discs.
- USB Installation: Creating a bootable USB drive.
- Network Installation: Installing over a network.
- Virtual Machine Installation: Within virtualization platforms.
The chosen method depends on factors like system specifications and user preferences.
8. Enumerate the essential hardware components required for a functional PC.
Ans:
Essential hardware components include:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Executes instructions.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Temporarily stores active processes.
- Storage (HDD/SSD): Provides permanent data storage.
- Motherboard: Connects components.
- Graphics Card: Renders visual output.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Supplies power.
- Peripheral Devices: Include keyboard, mouse, etc.
Each component plays a crucial role in overall system functionality.
9. Explain the concept of a graphics card or graphic driver.
Ans:
A graphics card, or GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), is a hardware component that renders images and videos. Graphic drivers are software interfaces that enable communication between the GPU and the Operating System, facilitating efficient graphics processing. These components are vital for achieving smooth, high-quality visual experiences in applications and games.
10. Define ROM and distinguish it from RAM.
Ans:
- Read-Only Memory (ROM): Non-volatile memory storing firmware and essential system instructions. It retains data even when the power is off.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Volatile memory for active processes and temporary data storage. It loses data when the power is turned off. Distinguishing factors include volatility and the type of data stored.
11. In the context of RAM, what is Cache RAM?
Ans:
Cache RAM is a small, high-speed memory located on the CPU or between the CPU and main RAM. It stores frequently accessed instructions and data to expedite CPU operations, reducing access time. Cache RAM enhances system performance by providing quicker access to critical data, optimizing the execution of instructions, and improving overall system responsiveness.
12. Define the function of a modem.
Ans:
A modem, short for Modulator-Demodulator, is a device that converts digital signals from computers into analog signals for transmission over analog communication lines, such as telephone lines. Its crucial role is facilitating data exchange between digital devices over various communication mediums, allowing devices to communicate over networks, including the Internet, through dial-up or DSL connections.
13. Describe the purpose of FireWire.
Ans:
FireWire, also known as IEEE 1394, is a high-speed serial bus interface designed to connect digital devices like cameras, external hard drives, and audio to computers. Recognized for its efficiency in handling real-time data streams, FireWire enables swift data transfer, making it particularly advantageous in multimedia applications.
14. Define a Storage Device.
Ans:
A storage device refers to hardware designed for storing and retrieving digital data. This includes non-volatile storage mediums that retain data even when powered off. Examples encompass Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SSDs), USB drives, and optical discs. These devices are crucial in preserving data for short-term and long-term use.
15. Explain the role of a System Board (Motherboard).
Ans:
The System Board, commonly known as the Motherboard, is the central circuit board within a computer system. It is the primary platform for integrating and connecting various hardware components, including the CPU, memory, storage devices, and expansion cards. By facilitating communication between these components, the Motherboard ensures the cohesive operation of the entire system.
16. Elaborate on Computer Memory.
Ans:
Computer memory encompasses temporary storage for actively processing and storing data. It includes types like Random Access Memory (RAM) and cache memory. RAM, being volatile, holds data for running applications, while cache memory provides high-speed access to frequently used instructions and data, contributing to overall system performance enhancement.
17. Identify various types of RAM.
Ans:
Diverse RAM types comprise:
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM): Requires constant refreshing.
- SRAM (Static RAM): Faster and more expensive, without continuous refreshing.
- DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous DRAM): Common in modern systems, offering high data transfer rates.
- DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 SDRAM: Successive generations with improved performance.
18. How many cycles per second does one gigahertz (GHz) represent?
Ans:
One gigahertz (GHz) signifies one billion cycles per second. It measures the clock speed of a processor, indicating the number of instructions it can execute in a second. A higher gigahertz value often correlates with increased processing speed.
19. Define the term microprocessor.
Ans:
A microprocessor serves as a computer’s central processing unit (CPU), acting as the core processing unit. It executes instructions, performs arithmetic and logic operations, and oversees the overall functionality of the computer. Microprocessors are pivotal components in modern computing devices.
20. What does GUI (Graphical User Interface) mean?
Ans:
GUI, or Graphical User Interface, denotes a visual interaction method with computers and software. Utilizing graphical elements such as icons, buttons, and windows, GUI allows users to perform tasks through clicking and dragging rather than relying on text-based commands. GUIs enhance user-friendliness and accessibility in operating systems and applications.
21. Specify the meaning of “SSL/TLS” and elucidate its role in ensuring secure communication.
Ans:
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are cryptographic protocols designed to secure communication over computer networks, typically the Internet. Providing encryption and authentication, SSL/TLS safeguards data during transmission. Widely used in securing online transactions and sensitive information exchange, these protocols ensure confidentiality and integrity between a user’s browser and a web server.
22. Clarify the operational role of a proxy server.
Ans:
A proxy server is an intermediary between client devices and the Internet. It processes client requests, forwards them to the destination (like a website), retrieves the response, and sends the data back to clients. Proxy servers enhance security, content filtering, and network performance. They can also anonymize user identity by concealing their IP addresses.
23. Walk through the steps involved in the process of public key encryption.
Ans:
Public key encryption involves:
- Key Pair Generation: Creating a public-private key pair.
- Key Distribution: Sharing the public key openly while securing the private key.
- Encryption: Encrypting data using the recipient’s public key.
- Decryption: The recipient uses their private key to decrypt the received data.
This process ensures secure communication without the need for a shared secret key.
24. What steps are involved in establishing a wireless network?
Ans:
Steps for setting up a wireless network include:
- Acquiring Necessary Equipment: Router, modem, and wireless devices.
- Router Configuration: Configuring the router with a unique SSID and security settings.
- Connecting Devices: Linking devices to the wireless network using provided credentials.
- Security Measures: Enabling encryption (e.g., WPA2) and setting a strong password.
- Network Testing: Verify connectivity and adjust settings if needed.
25. Provide an overview of DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory).
Ans:
DRAM is a volatile memory used for temporary data storage in computers. It requires constant refreshing to maintain data integrity. Widely used as the main memory, DRAM offers high storage capacity at a relatively lower cost compared to other RAM types.
26. Can the utilization of DRAM enhance the speed of your PC?
Ans:
Yes, utilizing DRAM significantly boosts PC speed. As the primary memory accessed by the CPU for active programs and data, increasing DRAM improves overall system performance. This allows more data to be stored in fast-access memory, reducing reliance on slower retrieval from storage devices.
27. What is the purpose of creating partitions on a hard drive?
Ans:
Creating partitions on a hard drive involves dividing storage space for:
- Isolating Operating System: Keeping the OS in a dedicated partition.
- Organizing Data: Segregating user data for better management.
- Dual Boot Systems: Facilitating multiple operating systems on a single drive.
- Backup and Recovery: Simplifying backup and recovery for specific partitions.
28. How many bytes constitute 1 kilobyte?
Ans:
1 kilobyte equals 1024 bytes, a standard unit for measuring digital information storage.
29. Define IP addresses.
Ans:
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a numerical label assigned to devices on a network. It identifies the host or network interface and provides its location in the network.
30. Explain the function of a gateway.
Ans:
A gateway connects different networks, serving as an entry point. It facilitates data flow between networks with varying communication protocols, enabling seamless communication and connection to the Internet.
31. What is the OSI model and its significance?
Ans:
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model functions as a conceptual framework that standardizes the operations of telecommunication or computing systems, organizing them into seven distinct layers. Each layer is assigned a specific role, and these layers facilitate communication across diverse systems. The OSI model comprises the following seven layers, arranged from bottom to top:
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
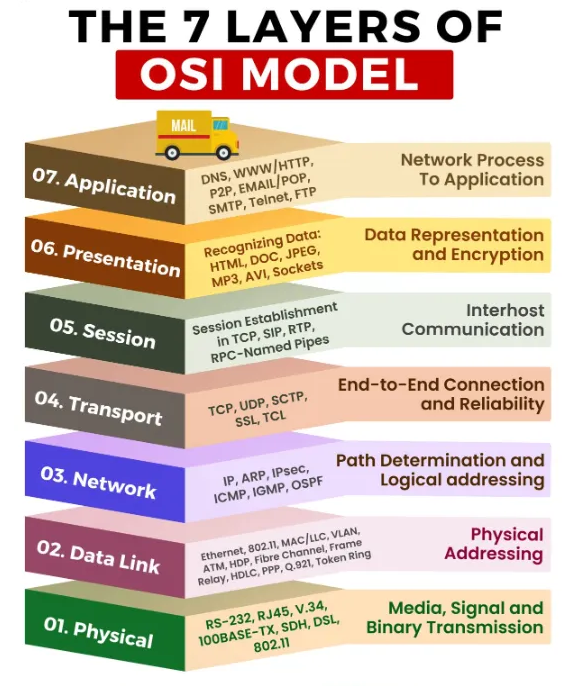
Significance of the OSI Model:
- Interoperability
- Design and Troubleshooting
- Education and Communication
- Protocols and Standards
- Modularity and Scalability
- Guidance for Network Development
32. How would you characterize a network?
Ans:
A network can be defined as a system of interconnected computers, devices, or systems designed to facilitate communication and resource sharing. Networks, categorized by geographical scope into Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), etc., enable collaborative data exchange among interconnected entities.
33. Elaborate on the distinctions between a hub and a switch.
Ans:
| Feature | Hub | Switch | |
| Functionality |
Distributes incoming data to all ports, broadcasting. |
Selectively forwards data to the port where the destination device is connected. | |
| Traffic Handling | Shares available bandwidth among connected devices; operates in half-duplex. | Provides dedicated bandwidth per port, enabling simultaneous full-duplex data transmission. | |
| Collision Domain |
Single collision domain; if one device transmits, others must wait. |
Multiple collision domains; simultaneous data transmission on different ports minimizes collisions. | |
| Address Learning | Lacks address learning capability; lacks intelligence about connected devices. | Learns MAC addresses of connected devices, creating a MAC address table for efficient data forwarding. | |
| Broadcasts and Efficiency |
Broadcasts can lead to network congestion and reduced efficiency. |
Limits broadcasts by directing traffic only to the intended port, enhancing network efficiency. | |
| Security |
Less secure; all connected devices can see each other’s traffic. |
More secure; isolates traffic, reducing the chance of unauthorized access. | |
| Cost | Generally less expensive. | Tends to be more expensive than hubs. | |
| Commonly Used in | Small networks or for basic connectivity. | Larger networks where efficient data transfer and reduced collisions are essential. |
34. What is the complete form of VPN?
Ans:
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It establishes a secure, encrypted connection over a public network, like the Internet. VPNs ensure privacy and secure data transmission, enabling users to access resources as if directly connected to a private network.
35. Define DNS (Domain Name System).
Ans:
DNS, or Domain Name System, is a hierarchical system translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses. This system allows users to access resources using easy-to-remember domain names while computers use IP addresses for communication, playing a crucial role in internet navigation.
36. Elaborate on the functioning of NAT (Network Address Translation).
Ans:
NAT, or Network Address Translation, allows multiple devices on a local network to share a single public IP address for internet communication. It translates private IP addresses used within the local network into a single public IP address, enhancing security and conserving IP address space.
37. Define “load balancing” in the context of networking.
Ans:
Load balancing involves distributing network traffic across multiple servers to ensure efficient resource utilization and prevent overload on any single server. This optimization enhances the performance, availability, and reliability of networked applications.
38. In what ways does a network problem differ from a DNS problem?
Ans:
A network problem encompasses issues affecting overall connectivity and device communication, including hardware failures or configuration errors. In contrast, a DNS problem specifically refers to difficulties resolving domain names to IP addresses, hindering access to resources using domain names.
39. How do you establish a VLAN, and what does VLAN stand for?
Ans:
VLAN, or Virtual Local Area Network, is established by configuring switches to create virtual segments within a physical network. Devices in the same VLAN can communicate as if on the same physical network, even in different physical locations.
40. Explain the purpose of Active Directory.
Ans:
Active Directory (AD), developed by Microsoft, is a directory service primarily used in Windows environments. It centralizes network management by providing a database of network resources and facilitating authentication, authorization, and organizational structuring of network resources.
41. Define DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Ans:
DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a network protocol automating the assignment of IP addresses and configuration parameters to devices within a network. It dynamically manages and allocates IP addresses, streamlining network administration and configuration for devices such as computers, printers, and smartphones.
42. What is the process for configuring a default router or default gateway?
Ans:
Configuring a default router or gateway involves accessing the device’s network settings and specifying the router’s IP address designated as the default gateway. This setting allows the device to direct network traffic to the default gateway for destinations beyond its local subnet.
43. Identify the various classes of networks.
Ans:
Networks are categorized based on size and scope:
- Local Area Network (LAN): Confined to a small area, like an office or home.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): Spans more significant geographic regions, connecting LANs across cities or countries.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Covers a town or large campus.
- Personal Area Network (PAN): Involves devices within an individual’s personal space.
44. Describe circular logging and its function.
Ans:
Circular logging is a system method where log entries overwrite once the log reaches capacity. This ensures a constant log file size, with new entries replacing the oldest ones, creating a continuous loop or circle of log information.
45. Which protocol is employed in a directory service?
Ans:
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is commonly used in a directory service. LDAP is a standard protocol for accessing and managing directory services, providing a means to organize and query directory information.
46. Explain what “subnetting” means in networking.
Ans:
Subnetting involves dividing an IP network into smaller subnets. This optimizes IP address use, enhances security, and improves network performance. Each subnet functions as an independent network within the more extensive network.
47. Illustrate the importance of a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) in enhancing network security.
Ans:
A DMZ is a network segment acting as a buffer between an organization’s internal network and the external, untrusted network, like the Internet. Placing public-access servers or services in the DMZ enhances security by isolating them from the internal network, adding an extra layer of protection against external threats.\
48. Define “social engineering” within the realm of security.
Ans:
Social engineering is a cyber attack that manipulates individuals to disclose confidential information or perform actions compromising security. Attackers use psychological manipulation, often exploiting trust or authority to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
49. What constitutes a VPN tunnel, and how does its operation unfold?
Ans:
A VPN tunnel is a secure, encrypted connection established over an untrusted network like the Internet. It creates a private communication channel between two endpoints, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. VPN tunnels operate by encapsulating data in encrypted packets, safeguarding it from unauthorized access during transmission.
50. Break down the concept of RAID within storage systems.
Ans:
RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a storage technology using multiple hard drives to enhance data reliability, performance, or both. Various RAID levels offer configurations like mirroring for redundancy (RAID 1) or striping for improved performance (RAID 0).
51. Define “ping” as it applies to networking.
Ans:
“Ping” is a network utility sending a small data packet, an ICMP echo request, to a target device. The target device, if reachable, responds with an ICMP echo reply. Pinging is commonly used for testing and troubleshooting network connectivity, measuring the round-trip time between the source and the target device.
52. What role does a DNS server play in the communication within a network?
Ans:
A DNS (Domain Name System) server serves as a vital element in network communication by converting human-readable domain names into corresponding IP addresses. This translation enables devices to locate and connect effectively.
53. Distinguish between symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods.
Ans:
| Feature | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
| Key Types |
Utilizes a single shared secret key for both encryption and decryption. |
Involves a pair of public and private keys for distinct encryption and decryption functions. |
| Key Distribution | Requires secure distribution of the shared key to all communicating parties. | Public keys can be freely distributed, while private keys remain confidential. |
| Computational Complexity |
Generally faster and computationally less demanding. |
Slower and computationally more intensive when compared to symmetric encryption. |
| Security | Both parties must securely manage and store the shared key. | Enhanced security, as private keys are kept confidential, and only public keys are shared. |
| Scalability |
Scaling can be challenging due to complexities in key management. |
More scalable, with each participant managing their unique key pair. |
| Use Cases |
Commonly used for bulk data encryption, such as file and disk encryption. |
Applied for secure communication, digital signatures, and key exchange protocols. |
| Examples | Examples include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard). | Examples encompass RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography). |
54. Detail the function of a networking packet.
Ans:
A networking packet, a data unit transmitted over a network, carries essential information like source and destination addresses, data, and control details. Packets play a fundamental role in efficient data transmission, enabling information to be efficiently disassembled, transmitted, and reassembled at its destination.
55. Highlight the significance of a MAC address in networking.
Ans:
A MAC (Media Access Control) address, a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces, ensures proper communication within a local network. By uniquely identifying each device, MAC addresses play a pivotal role in controlling data flow and preventing unauthorized access within the local network.
56. Elaborate on the responsibilities of a firewall in ensuring network security.
Ans:
A firewall, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on pre-established security rules, acts as a barrier between a secure internal network and external networks. It prevents unauthorized access, mitigates risks, and ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data.
57. Define “spoofing” within the context of cybersecurity.
Ans:
Spoofing involves creating deceptive or false information to deceive systems, users, or networks. Cybersecurity forms include IP spoofing (manipulating source IP addresses) and email spoofing (altering sender addresses). The goal is to gain unauthorized access or deceive recipients into trusting malicious content.
58. How does a proxy server contribute to enhancing privacy on the Internet?
Ans:
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between a user’s device and the Internet, concealing the user’s IP address and location. This enhances privacy by preventing direct communication between the user and web servers, offering additional security features like content filtering and access control.
59. Define a “man-in-the-middle attack.”
Ans:
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack occurs when an unauthorized third party intercepts and potentially alters communication between two parties. This attacker can eavesdrop on sensitive information, manipulate data, or impersonate one of the communicating entities, resulting in security breaches.
60. Outline the steps involved in the SSL handshake process.
Ans:
The SSL (Secure Socket Layer) handshake initiates a secure connection between a client and a server. Steps include:
- ClientHello: Initiating the connection.
- ServerHello: Responding to the client.
- Key Exchange: Agreeing on encryption methods.
- Authentication: Verifying server and client identities.
- Finished: Confirming the establishment of a secure connection.
61. Define “brute-force attack” concerning password security.
Ans:
A brute-force attack involves systematically attempting all possible password combinations until the correct one is discovered. This method relies on computational power, emphasizing the need for strong, complex passwords and implementing account lockout policies to deter such attacks.
62. Differentiate between a hash function and encryption.
Ans:
| Feature | Hash Function | Encryption |
| Purpose |
Produces a fixed-size hash value or digest from input data. |
Converts plaintext into ciphertext to ensure secure communication or storage. |
| Reversibility | Irreversible; the hash value cannot be transformed back to the original data. | Reversible; ciphertext can be decrypted using the appropriate key to recover the original plaintext. |
| Key Usage |
Typically does not involve the use of keys. |
Requires keys, either symmetric or asymmetric, for encryption and decryption processes. |
| Common Algorithms | Examples include MD5, SHA-256, SHA-3. | Examples include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman). |
| Use Cases |
Used for data integrity verification and password hashing. |
Applied in secure communication, ensuring data confidentiality and authentication. |
| Output Length |
Fixed-length output, irrespective of input size. |
Variable-length output depending on the encryption algorithm and input data size. |
| Collision Probability | Possible (due to fixed output length), but modern hash functions aim for collision resistance. | Extremely rare, especially in secure encryption algorithms. |
| Examples of Output | Hash value example: e.g., “5d41402abc4b2a76b9719d911017c592” (MD5). | Ciphertext example: e.g., “U2FsdGVkX1/fEZn0u3uV6gsZr9+LPg==” (AES encryption). |
63. Explain the purpose of a honeynet in the realm of cybersecurity.
Ans:
A honeynet is a cybersecurity tool designed to attract and detect potential attackers by mimicking a vulnerable network. Its objective is to observe and analyze malicious activities, strategies, and tactics without jeopardizing an actual production environment. Honeynets offer valuable insights into emerging cyber threats, bolstering overall cybersecurity defenses.
64. Define “malware signature” within antivirus protection.
Ans:
A malware signature is a distinctive, recognizable pattern or characteristic associated with malicious software. Antivirus programs leverage these signatures to identify and detect specific threats. By scanning files for these unique patterns, antivirus solutions play a vital role in preemptive cybersecurity measures, identifying and eliminating known malware.
65. Discuss the concept of a hash collision in the field of cryptography.
Ans:
In cryptography, a hash collision occurs when two distinct inputs produce the same hash value. Ideally, hash functions should generate unique hash values for different inputs. Collisions pose a security risk as attackers could create malicious input resulting in the same hash as legitimate data, compromising the integrity of cryptographic systems.
66. How does a VPN concentrator contribute to secure communication?
Ans:
A VPN concentrator enhances secure communication by managing and facilitating multiple VPN connections. It processes and aggregates VPN traffic, ensuring encryption and authentication. This centralized device plays a crucial role in maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted across the VPN network.
67. Define “BYOD” (Bring Your Device) within a corporate setting.
Ans:
BYOD, or Bring Your Device, describes the practice where employees use their devices, such as laptops or smartphones, for work-related tasks within a corporate environment. While fostering flexibility and productivity, BYOD introduces security challenges, necessitating robust organizational policies and security measures to safeguard sensitive data.
68. Explain the fundamental concept of cloud computing.
Ans:
Cloud computing involves delivering services over the Internet, including storage, processing power, and applications. Users access and utilize these resources on-demand, paying only for consumed services. Cloud computing offers scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, transforming how businesses manage and deploy IT infrastructure.
69. What characterizes a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack?
Ans:
A DDoS attack is characterized by overwhelming a target system or network with high traffic volume from multiple sources. The objective is to disrupt normal operations, causing a denial of service for legitimate users. DDoS attacks employ distributed methods, often utilizing botnets, posing a substantial threat to online services and businesses.
70. Define “biometric authentication.”
Ans:
Biometric authentication utilizes distinctive physical or behavioral characteristics, like fingerprints, iris scans, or facial features, to verify an individual’s identity. This method offers a secure and convenient way to authenticate users as biometric features are challenging to replicate, enhancing the overall security of access control systems.
71. Describe the role of WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) in wireless security.
Ans:
WPA2, or Wi-Fi Protected Access 2, is a security protocol to safeguard wireless networks from unauthorized access and data compromise. It employs robust encryption algorithms to secure Wi-Fi communication, ensuring a formidable defense against cyber threats. WPA2 serves as a standard for wireless security, preserving the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over Wi-Fi networks.
72. What is the purpose of a subnet mask in the realm of IP addressing?
Ans:
In IP addressing, a subnet mask is a numeric value defining the division of an IP address into network and host segments. It aids in organizing and managing IP addresses within a network, facilitating efficient routing and logical segmentation. Subnet masks are pivotal in IP subnetting, contributing to adequately functioning and optimizing IP networks.
73. Elaborate on the distinctions between a virus and a worm.
Ans:
- Virus: A virus is a form of malware that attaches itself to legitimate files, spreading when those files are executed. Its propagation often relies on human interaction, such as sharing infected files.
- Worm: In contrast, worms are independent malware that can self-replicate and spread across networks without needing a host program. They exploit network vulnerabilities and can rapidly propagate without user involvement.
74. Define “zero-day exploit” within the field of cybersecurity.
Ans:
A zero-day exploit refers to a cyber attack exploiting a software vulnerability on the day it becomes publicly known or discovered. The term “zero-day” implies that developers have no time to address and patch the vulnerability before malicious actors exploit it.
75. Define “ARP poisoning” in the context of network security.
Ans:
ARP poisoning, or ARP spoofing, is a technique where an attacker sends false ARP messages to associate their MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate device on a local network. This manipulation can lead to traffic interception and unauthorized access, enabling attackers to eavesdrop on or manipulate network communications.
76. Distinguish between a data breach and a security incident.
Ans:
- Data Breach: A data breach involves unauthorized access, disclosure, or acquisition of sensitive data, exposing confidential information to unauthorized entities.
- Security Incident: A security incident is a broader term covering any adverse event or violation of security policies, encompassing not only data breaches but also events like system compromises, malware infections, or unauthorized access attempts.
77. What function does a security token serve in the context of two-factor authentication?
Ans:
A security token, whether physical or virtual, generates one-time codes or passwords. Two-factor authentication (2FA) serves as the second factor, alongside the user’s password. Users enter their password (first factor) and the code from the security token (second factor), enhancing security by requiring dual verification forms.
78. Define the term “security baseline” regarding system hardening.
Ans:
A security baseline establishes a set of minimum security controls and configurations for securing and hardening a system. It is a reference for system administrators, ensuring consistent and secure configurations across devices and networks. Security baselines help mitigate vulnerabilities and improve overall cybersecurity posture.
79. Explain the purpose of a password policy in the domain of cybersecurity.
Ans:
A password policy outlines rules and requirements for creating, managing, and using passwords within an organization. It establishes guidelines for solid and complex passwords, regular password changes, and secure storage practices. A well-defined password policy is essential for safeguarding user accounts and preventing unauthorized access.
80. What is the significance of using salt in password hashing?
Ans:
The significance of using salt in password hashing lies in its ability to thwart precomputed attacks, such as rainbow table attacks. By adding a unique salt to each password before hashing, even identical passwords yield different hash results, enhancing security. Salt ensures that attackers cannot use precomputed tables to crack passwords, improving overall password security quickly.
81. Distinguish between a vulnerability and an exploit.
Ans:
- Vulnerability: A vulnerability is a weakness or flaw in a system, application, or process that could be exploited by attackers, representing a potential entry point for unauthorized access.
- Exploit: An exploit is a piece of software, code, or technique attackers use to exploit a specific vulnerability. Exploits leverage vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access, disrupt services, or execute malicious actions on a system.
82. Clarify the intent behind the tracert command.
Ans:
The tracer command, or traceroute, maps the route data takes from a source to a destination on a network. By displaying the sequence of intermediate devices (routers) and their corresponding time delays, tracert aids in diagnosing network issues and evaluating the path data follows.
83. Define “firewall rule” within network security.
Ans:
A firewall rule is a predefined instruction within a firewall that dictates the handling of network traffic based on specified criteria. These criteria may include source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols. Firewall rules regulate traffic flow to enforce security policies and guard against unauthorized access or malicious activities.
84. What function does a Certificate Revocation List (CRL) serve in PKI?
Ans:
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) catalogs digital certificates revoked or invalidated before expiration. In Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), CRLs play a pivotal role in verifying the validity of certificates and preventing the use of compromised or unauthorized certificates during secure communication.
85. Detail the role of a load balancer in a web server environment.
Ans:
A load balancer distributes incoming web traffic across multiple servers to optimize resource usage, prevent server overload, and enhance system performance. By ensuring even distribution of requests, a load balancer improves web applications’ scalability, availability, and responsiveness, contributing to a more reliable and efficient web server environment.
86. Elaborate on the concept of a rainbow table in the context of password cracking.
Ans:
A rainbow table is a precomputed table containing numerous potential password hashes and their corresponding plaintext passwords. In password cracking, attackers use rainbow tables to swiftly match hashed passwords found in a system against entries in the table. Implementing robust password hashing and salting practices helps mitigate the effectiveness of rainbow table attacks.
87. What is the objective of a penetration test in the field of cybersecurity?
Ans:
The objective of a penetration test, or pen test, is to simulate a real-world cyber attack on a system, network, or application. Ethical hackers, known as penetration testers, identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that affect potential entry points for malicious actors. The goal is to assess security posture, fortify defenses, and enhance cybersecurity resilience.
88. Define “rootkit” in the context of malware.
Ans:
A rootkit is malicious software that provides unauthorized access and control over a computer system or network. Rootkits are designed to operate covertly, compromising core operating system functions. They can enable attackers to execute malicious commands, evade detection, and maintain persistent access to the compromised system.
89. What role does a network sniffer play in cybersecurity?
Ans:
A network or packet sniffer captures and analyzes network traffic for monitoring, diagnosing network issues, and detecting potential malicious activities. While aiding cybersecurity by revealing communication patterns, network sniffers must be securely configured to prevent possible exploitation by unauthorized eavesdropping.
90. Explain the concept of a session hijacking attack.
Ans:
Session hijacking involves the unauthorized interception or manipulation of an active session between a user and a system. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities to take control of the session, potentially gaining access to sensitive information or conducting actions on behalf of the legitimate user. Encryption and secure session management are crucial preventive measures against session hijacking.
91. Describe the function of a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system.
Ans:
A Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system gathers, analyzes, and correlates security-related information and events from diverse sources within an organization’s IT infrastructure. Offering real-time monitoring, threat detection, and incident response capabilities, SIEM systems assist organizations in promptly identifying and responding to security incidents, contributing to proactive cybersecurity.
92. Define “ciphertext” within the domain of encryption.
Ans:
Ciphertext is the encrypted output resulting from applying an encryption algorithm to plaintext. Representing the unreadable and scrambled form of data, ciphertext ensures the confidentiality of information during secure communication. The recipient uses a corresponding decryption key to decrypt and retrieve the original data, making ciphertext a fundamental concept in encryption for safeguarding sensitive information.






