
Windows Server is a powerful operating system designed by Microsoft specifically for server usage. It provides a comprehensive set of features and services to support various business needs, from small-scale organizations to large enterprises. Windows Server offers robust functionalities such as Active Directory for user and resource management, DNS and DHCP services for network infrastructure, file and print sharing, web server capabilities, and virtualization support through Hyper-V.
1. What’s Active Directory?
Ans:
Active Directory is a directory service developed by Microsoft that stores information about objects on a network and makes this information available to users and directors. It centralizes network operation and allows for secure authentication and authorization of users and computers. Active Directory is extensively used in Windows-grounded surroundings for managing coffers similar to user accounts, groups, computers, printers, and participating lines.
2. What are the difference between a Workgroup and a sphere?
Ans:
A workgroup is a peer-to-peer network in which individual computers partake in coffers without a centralized authentication medium. Each computer in a workgroup maintains its database of user accounts and security settings. In contrast, a sphere is a centralized network terrain in which a sphere regulator manages users’ authentication and access to network coffers.
3. What’s DHCP and how does it work?
Ans:
- DHCP( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network protocol used to stoutly assign IP addresses and network configuration settings to bias on a network.
- When a device connects to a network, it sends a DHCP Discover communication to find available DHCP servers.
- The DHCP server responds with an Offer, proposing an IP address and settings. The device accepts the offer with a Request, and the server finalizes the process with an Acknowledgment.
4. What’s DNS, and why is it important?
Ans:
DNS( sphere Name System) is a hierarchical picking system that translates sphere names into IP addresses, allowing users to pierce coffers on the Internet using easy-to-forthback names rather than numerical IP addresses. DNS is essential for Internet navigation, dispatch delivery, and other network services. It provides a distributed database that maps sphere names to IP addresses and facilitates the effective resolution of queries to detect coffers on the network.
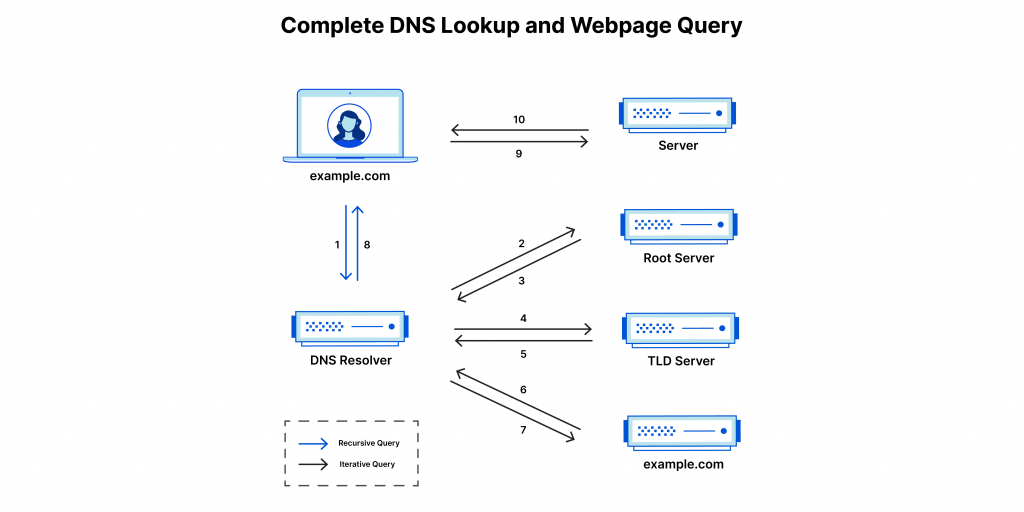
5. What is RAID and its different situations?
Ans:
- RAID( spare Array of Independent Disks) is a data storehouse technology that combines multiple physical disks into a single logical unit for better performance, fault forbearance, or both.
- Everyday RAID situations include RAID 0( striping for performance), RAID 1( mirroring for redundancy), RAID 5( striping with equality for both performance and fault forbearance), RAID 6( striping with double equality for enhanced fault forbearance), and RAID 10( a combination of mirroring and striping).
6. What are Group Policy Objects( GPOs) and how are they used?
Ans:
Group Policy Objects( GPOs) are holders for group policy settings that allow directors to manage configurations for users and computers in an Active Directory terrain. GPOs can apply security settings, emplace software, chart network drives, and perform other executive tasks across the network. They’re linked to Active Directory holders similar to spots, disciplines, or organizational units( OUs) and are reused in a hierarchical order, with settings from advanced-position GPOs potentially being hoofed by settings in lower-position GPOs.
7. What’s the difference between a Physical Garçon and a Virtual Garçon?
Ans:
| Aspect | Windows Server Standard Edition | Windows Server Datacenter Edition |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing | Permits running on up to 2 virtual machines or Hyper-V containers when all physical cores in the server are licensed. | Offers unlimited virtualization rights, allowing for running an unlimited number of virtual instances on the licensed server. |
| Virtualization Rights | Limited to 2 virtual instances when all physical cores are licensed. | Provides unlimited virtualization rights, enabling multiple virtual instances without additional licensing costs. |
| Suitability | Suitable for small to medium-sized businesses with moderate virtualization needs. | Aimed at large enterprises with high virtualization requirements and demanding workloads. |
| Cost | Typically cheaper compared to Datacenter Edition due to limited virtualization rights. | Typically more expensive due to unlimited virtualization rights and targeted at larger enterprises with higher workloads. |
8. What is the process of promoting a garçon to a Domain Controller.
Ans:
Promoting a garçon to a Domain Controller involves installing the Active Directory Domain Services( announcement DS) part and running the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard( DCPromo). During the creation process, directors must specify whether the garçon will be the first sphere regulator in a new timber, a fresh sphere regulator in a being sphere, or a read-only sphere Controller( RODC).
9. What’s the purpose of FSMO places in Active Directory?
Ans:
- FSMO( Flexible Single Master Operations) places are technical tasks assigned to sphere regulators in an Active Directory timber.
- These roles handle essential functions like schema variations and sphere-wide operations. The five FSMO roles are Schema Master, Domain Naming Master, PDC Emulator, and Infrastructure Master.
- Proper assignment and operation of FSMO places are essential for the stability and functionality of the Active Directory structure.
10. How do you troubleshoot network connectivity issues on a Windows Garçon?
Ans:
Troubleshooting network connectivity issues on a Windows Garçon involves several ways, including checking physical connections, vindicating IP configurations, testing DNS resolution, and assaying network business with tools like Ping, Tracert, IPCONFIG, and NSLOOKUP. Also, directors can review event logs, firewall settings, and network appendage parcels to identify implicit issues affecting network communication.
11. Explain the purpose of the DHCP Relay Agent.
Ans:
- A DHCP Relay Agent is a network device or software service that on DHCP dispatches between DHCP guests and DHCP servers across different subnets or network parts.
- When a DHCP customer broadcasts a DHCP discover communication to gain an IP address parcel, the Relay Agent intercepts the broadcast and relays it to a DHCP garçon located on a different subnet.
- The DHCP garçon also responds with a DHCP Offer and the Relay Agent the response back to the customer, enabling DHCP communication across routed networks.
12. What are the benefits of enforcing Remote Desktop Services( RDS)?
Ans:
- Remote Desktop Services( RDS) allows users to pierce operations and desktops hosted on remote servers over a network connection.
- Enforcing RDS offers centralized management and improved security via a unified data store. It boosts productivity with remote access and saves costs by minimizing hardware and software maintenance.
- RDS also supports scalability, allowing associations to fluently gauge coffers to accommodate changing user demands and business conditions.
13. What’s the purpose of the Sysvol brochure in Active Directory?
Ans:
The Sysvol( System Volume) brochure in Active Directory is a participating directory that stores public lines related to the sphere policy, Group Policy settings, login scripts, and other system lines critical for the operation of Active Directory services. It ensures harmonious Group Policy operation across all sphere regulators within a sphere and facilitates logon and logoff processes for users by furnishing access to essential scripts and configuration lines.
14. How do you secure Windows Garçon terrain against unauthorized access?
Ans:
Securing a Windows Garcon terrain involves:
- Enforcing various security measures similar to configuring vital word programs.
- Enabling firewalls.
- Applying security updates and patches regularly.
- Enforcing part-grounded access control( RBAC).
- Cracking sensitive data.
- Enabling auditing and monitoring.
- Configuring security programs with Group Policy.
- Planting antivirus and antimalware result
15. What are the difference between NTFS and FAT32 train systems.
Ans:
- NTFS( New Technology Train System) and FAT32( train Allocation Table 32) are train systems used in Windows operating systems to organize and manage lines on fragment drives.
- NTFS offers features similar to train and brochure warrants, encryption, contraction, fragment proportions, and support for larger train sizes and volumes compared to FAT32.
- FAT32, on the other hand, has limited support for train and brochure warrants, lower train size and volume limits, and lacks advanced features like encryption and contraction.
16. What’s Hyper- V and how does it differ from other virtualization platforms?
Ans:
Hyper-V is a Microsoft hypervisor-based virtualization technology for creating and managing virtual machines on Windows Server. It enables multiple operating systems to run on a single physical server, offering efficient resource use and integration with the Windows ecosystem, distinguishing it from platforms like VMware and Citrix. Additionally, it supports various hardware and software configurations, enhancing its versatility for different environments.
17. Explain the purpose of Windows Garçon Update Services( WSUS).
Ans:
Windows Garçon Update Services( WSUS) is a garçon part of Windows Garçon that allows directors to manage the distribution of updates and patches for Microsoft products within an association. WSUS provides a centralized operation press for downloading, approving, and planting updates to Windows operating systems, Microsoft Office, and other Microsoft operations.
18. What are the ways involved in configuring Remote Desktop Services( RDS) in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
- Configuring Remote Desktop Services (RDS) includes installing the Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH), setting up Remote Desktop Licensing, and implementing Remote Desktop Gateway and Web Access.
- Administrators also need to configure users’ access warrants, SSL instruments, and network settings to enable secure remote access to operations and desktops.
- Proper configuration of RDS ensures adequate remote access and enhances users’ productivity while maintaining security and compliance conditions.
19. Explain the purpose of Group Policy in Windows Garçon surroundings.
Ans:
Group Policy is an essential point in Windows Garçon surroundings used to manage and apply system settings, security programs, and configurations for users and computers within an Active Directory sphere. Directors can use Group Policy to define and apply programs such as word conditions, software installation settings, desktop restrictions, and security options, ensuring thickness and compliance across the network.
20. What’s the purpose of DHCP Failover in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
- DHCP Failover is a point in Windows Garçon DHCP service that provides high vacuity and fault forbearance for DHCP services by replicating DHCP parcel information and configuration settings between two DHCP servers.
- In the event of a garçon failure or conservation, the standby garçon can take over DHCP service operations, ensuring continued IP address assignment and network connectivity for guests.
- DHCP Failover helps minimize time-out, ameliorate network trustability, and streamline DHCP operation in surroundings where DHCP vacuity is critical for business operations.
21. What are the difference between Garçon Core and Full Garçon installations in Windows Garçon.
Ans:
Garçon Core is a minimum installation option in Windows Garçon that includes only essential factors needed for running core garçon places and features. It lacks a graphical user interface( GUI) and is managed primarily through command-line tools or remote operation tools. In discrepancy, Full Garçon installations include a GUI and fresh factors similar to Windows Explorer, Internet Explorer, and operation tools, furnishing a more user-friendly interface for managing garçon configurations and performing executive tasks.
22. What’s the purpose of Active Directory spots in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
- Active Directory spots are logical groupings of network subnets that represent physical locales in an association’s network structure.
- They’re used to optimize authentication and replication business, ensure adequate access to sphere coffers, and ameliorate fault forbearance and disaster recovery capabilities.
- By defining roles, administrators can manage replication topology, prioritize authentication requests, and optimize resource access based on network proximity.
23. Explain the conception of Windows Garçon Failover Clustering.
Ans:
Windows Garçon Failover Clustering is a high-vacuum point that allows multiple waiters( bumps) to work together to give nonstop service vacuity for operations and services. Failover Clustering automatically detects and responds to garçon or operation failures by transferring workloads from failed bumps to healthy bumps, minimizing time-out, and ensuring continued service vacuity.
24. What’s the purpose of Network cargo Balancing( NLB) in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
- NLB uses a distributed algorithm to balance the cargo among cluster bumps, ensuring optimal resource application and performance.
- It enhances fault forbearance by automatically detecting and turning Businesses down from failed bumps to healthy bumps, minimizing time-out, and ensuring nonstop service vacuity.
- NLB is generally used for web servers, FTP servers, and other TCP/IP-ground services that bear scalability and trustability.
25. Explain the difference between TCP and UDP protocols.
Ans:
- TCP( Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP( users Datagram Protocol) are two generally used transport subcaste protocols in computer networks.
- TCP provides dependable, connection-acquainted communication between biases by establishing a connection, ensuring data delivery, and running inflow control and error correction.
- UDP, on the other hand, is a connectionless, unreliable protocol that delivers data packets without establishing a connection or guaranteeing delivery.
26. What is the purpose of Windows Firewall in Windows Garçon.
Ans:
Windows Firewall is an erected-insecurity point in Windows Garçon that helps cover the garçon from unauthorized access and vicious network business. It acts as a hedge between the garçon and the network, filtering incoming and gregarious Business grounded on predefined rules and security programs. Windows Firewall can block or allow grounded companies on various criteria, such as IP addresses, anchorages, protocols, and operations, furnishing grainy control over network communication.
27. What’s the purpose of Dynamic Access Control( DAC) in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
- Dynamic Access Control( DAC) is a point in Windows Garçon that allows directors to define and apply centralized access control programs grounded on user attributes, resource parcels, and business conditions.
- DAC enables fine-granulated access control by using claims-grounded authorization to estimate access requests and stoutly apply warrants to lines, flyers, and other coffers.
- DAC enhances security, compliance, and data governance by administering harmonious access control programs across the association.
28. What’s the purpose of Active Directory Certificate Services( announcement CS) in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) is a server role in Windows Server that allows organizations to implement and manage a public key infrastructure (PKI) for issuing and managing digital certificates. It facilitates secure communication, authentication, and encryption within a network. Administrators can issue certificates, validate requests, revoke certificates, and manage templates and registration processes.
29. Explain the purpose of Network Policy Garçon( NPS) in Windows Garçon.
Ans:
- Network Policy Garçon( NPS) is a garçon part in Windows Garçon that provides centralized authentication, authorization, and account( AAA) services for network access control.
- NPS allows directors to define and apply network access programs grounded on users’ identity, device health, and other attributes, ensuring secure and biddable access to network coffers.
- NPS is generally used in VPN, wireless, and wired network surroundings to control access and secure network communication.
30. What’s the purpose of Hyper-V- V Replica in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
- Hyperactive- V Replica is a disaster recovery point in Windows Garçon Hyper-V- V that provides asynchronous replication of virtual machines( VMs) between primary and replica Hyper-V- V hosts.
- It allows associations to produce and maintain clones of VMs at a secondary point or in the pall for data protection and disaster recovery purposes.
- Directors can use Hyper-V- V Replica to apply cost-effective and dependable disaster recovery results for virtualized workloads, enhancing business durability and adaptability.
31. Explain the purpose of Windows Garçon Provisory in Windows Garçon.
Ans:
Windows Garçon Provisory is an erected- -backup and recovery point in Windows Garçon that allows directors to back up critical data, system state, and entire garçon volumes to the original or network storehouse. It provides listed backups, incremental backups, and bare-essence recovery capabilities to cover servers from data loss and tackle failures and other disasters.
32. What’s the purpose of Windows Deployment Services( WDS) in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
- Windows Deployment Services( WDS) is a garçon part in Windows Garçon that enables network-grounded deployment of Windows operating systems to customer computers.
- It allows directors to produce and manage Windows images, motorist packages, and configuration settings for automated deployment across the network.
- By using WDS, directors can streamline the deployment process, reduce deployment time, and ensure the thickness and standardization of Windows installations across the association.
33. Explain the term PowerShell.
Ans:
PowerShell is a powerful command-line shell and scripting language developed by Microsoft, primarily designed for system administration tasks and automation. It provides a comprehensive set of commands, known as cmdlets (pronounced “command-lets”), which allow users to perform various administrative tasks, manage system components, and interact with different software and services within the Windows operating system environment.
34. What’s the difference between a stage-alone garçon and a member garçon in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
- In discrepancy, a member garçon is a garçon that belongs to a Windows sphere and relies on Active Directory for user authentication and access control.
- It provides services and coffers to sphere users while using sphere-grounded security programs and centralized operations.
- Member servers play a part in the sphere structure by hosting operations, train shares, and other services accessible to sphere users.
35. What’s tattooing in terms of Registry?
Ans:
- Tattooing in registry refers to the practice of making endless changes to the Windows registry that persist indeed after the Group Policy settings that initiated the changes are removed or no longer applied.
- This can be done when Group Policy settings modify registry keys that aren’t regressed to their original state upon policy junking, leaving behind” tattooed” registry settings.
- Tattooed registry settings can lead to inconsistent system configurations, policy conflicts, and difficulties in troubleshooting.
36. What’s the difference between a train share and a train system in Windows Garçon?
Ans:
A file share is a network-accessible directory that enables users to store, access, and share files collaboratively. In contrast, a file system organizes and manages files and directories on storage devices, defining how data is stored, retrieved, and accessed, including naming conventions and permissions. While a file share facilitates access over a network, the file system governs the actual storage and management of those files.
37. What’s Microsoft Azure, and how does it integrate with Windows Garçon?
Ans:
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services for infrastructure, platforms, and software. Windows Server integrates with Azure for on-premises deployments, virtual machine migration, backup and disaster recovery, and application hosting, providing services like Azure Active Directory and Azure App Service to enhance scalability and resource efficiency. This seamless integration enables organizations to extend their domain infrastructure to the cloud while improving flexibility and performance.
38. Name the types of FSMO places.
Ans:
- FSMO( Flexible Single Master Operations) places are technical tasks assigned to sphere regulators in an Active Directory timber. The types of FSMO places are
- Schema Master Manages updates and variations to the Active Directory schema.
- Sphere Naming Master Controls the addition or junking of disciplines in the timber.
- Relieve Master Allocates relative identifiers( RIDs) to sphere regulators for creating security headliners.
- Structure Master Maintains references to objects in other disciplines for cross-domain object references.
39. Name the commands for checking TCP/ IP configurations.
Ans:
- Several commands are generally used to check TCP/ IP configurations in Windows Garçon.
- Ipconfig Displays the TCP/ IP configuration for all network appendages.
- Clunk tests connectivity to a remote host by transferring ICMP echo requests.
- Nslookup Performs DNS queries to resolve sphere names to IP addresses and vice versa.
- Tracert traces the route taken by packets to a destination host.
40. What are the part of original DNS servers?
Ans:
Original DNS servers, also known as DNS purposefulness, play a pivotal part in network structure by resolving sphere names to IP addresses. They cache DNS records obtained from authoritative DNS servers, reducing the need for repeated queries to external DNS servers and perfecting network performance. Also, original DNS servers can be configured with forwarders to route DNS queries to external DNS servers efficiently.
41. Define the term INODE.
Ans:
- An INODE, short for Index Node, is a data structure used in Unix-like operating systems to represent a train or directory on a train system.
- INODEs give a means for the operating system to detect and manage lines efficiently, easing train system operations similar to reading, jotting, and executing lines.
- Each train or directory in a train system is associated with a unique INODE number, which allows the operating system to access and manipulate train metadata and contents.
42. What is the difference between operation and scheme partition?
Ans:
An Operation Partition is a logical segment within Active Directory that stores application-specific data, enabling replication across domain controllers, with each controller potentially hosting different partitions based on installed applications. In contrast, the Schema Partition holds the Active Directory schema, which defines the structure and attributes of directory objects. Changes to the schema impact the entire directory and are replicated to all domain controllers to ensure consistency across the forest.
43. What are the various zones in the Windows DNS garçon?
Ans:
- The Primary Zone Contains the authoritative DNS data for a sphere. Changes to records are made directly in the primary zone database train.
- Stub Zone Contains information about name waiters for a specific zone. It’s used to resolve queries between separate DNS namespaces.
- Forward Lookup Zone Charts sphere names to IP addresses, rephrasing hostnames to IP addresses.
44. Separate Windows and Windows Garçon.
Ans:
Windows refers to customer operating systems designed for particular computers and end-user bias. Examples include Windows 10 and Windows 11 Windows is optimized for desktop operation, furnishing features acclimatized for individual users, such as gaming, entertainment, and productivity operations. Windows Garçon Windows Garçon is a garçon operating system designed for hosting and managing network services and operations.
45. What’s the Windows Garçon Storage Spaces point, and how does it work?
Ans:
- Windows Server Storage Spaces is a storage virtualization technology that allows administrators to combine physical disks into storage pools and create virtual disks with different levels of resiliency and performance.
- Storage Spaces provides inflexibility in allocating storehouse coffers, allowing directors to produce tiered storehouse results with support for features similar to mirroring, equality, and storehouse tiering.
- By using Storage Spaces, associations can optimize storehouse applications, enhance data protection, and scale storehouse capacity to meet evolving business requirements.
46. What do you understand about Proxy Garçon?
Ans:
A deputy garçon acts as a conciliator between guests and servers, easing communication and furnishing various functions, such as hiding, filtering, and anonymization. When a customer requests to pierce a resource on the Internet, the request is encouraged to the deputy garçon, which also communicates with the target garçon on behalf of the customer. Proxy servers can enhance security by filtering out vicious content and monitoring and logging network business.
47. What’s the part of the relief master in Active Directory?
Ans:
The reliever( Relative Identifier) master is one of the Flexible Single Master Operations( FSMO) placed in the Active Directory responsible for allocating and managing unique relief pools for each sphere regulator within a sphere. The relief master ensures that each security star, similar to users’ accounts, groups, and computer objects, receives an encyclopedia ally unique identifier( SID) composed of a sphere SID and a distinctive relief.
48. Define triumphs garçon?
Ans:
- Triumphs ( Windows Internet Name Service) is a heritage network service used in Windows-grounded surroundings to resolve NetBIOS names to IP addresses.
- Triumphs servers maintain a dynamic database of NetBIOS name-to-IP address mappings, allowing guests to query the triumphs garçon to resolve NetBIOS names into IP addresses.
- Triumphs were generally used in aged Windows networking surroundings, particularly in surroundings with mixed operating systems or heritage operations that calculate on NetBIOS name resolution.
49. What’s the difference between Windows Garçon Provisory and third-party backup results?
Ans:
- Windows Garçon Provisory is an erected- backup and recovery point in Windows Garçon that provides introductory backup capabilities, similar to full garçon backups, incremental backups, and bare-essence recovery.
- They frequently give broader support for various operating systems, operations, and storehouse platforms.
- While Windows Garçon Provisory is included with Windows Garçon at no additional cost, third-party backup results generally bear licensing freights but offer further comprehensive backup and recovery capabilities.
50. What’s the significant advantage of GPMC?
Ans:
The Group Policy Management Console( GPMC) is a Microsoft Management Console( MMC) snap-in used to manage Group Policy objects( GPOs) in Windows surroundings. One significant advantage of GPMC is its centralized and intuitive interface for managing GPOs across an Active Directory sphere or timber. GPMC provides directors with a comprehensive set of tools for creating, editing, linking, and managing GPOs, as well as for controlling heritage and troubleshooting Group Policy issues.
51. What is the process to coagulate Group policy?
Ans:
- Backing up Group Policy objects( GPOs) ensures that their configurations and settings are saved in case of accidental omission, corruption, or other issues.
- Open the Group Policy Management Console( GPMC).
- Right-click on the GPO you want to back up and elect” Back Up.”
- Specify a position to store the backup lines.
- Optionally, describe the backup.
- Click”Back Up to initiate the backup process.
52. Define Trust Relationship.
Ans:
A trust relationship is a logical relationship established between two disciplines in an Active Directory timber that allows users, groups, and computers in one sphere to pierce coffers in another sphere. Trust connections define the compass and warrants of cross-domain access, allowing authentication and authorization mechanisms to operate across sphere boundaries. Trust connections can be one-way or two-way, transitive or non-transitive, and can have different trust types, similar to parent-child trusts, timber trusts, or external trusts.
53. DefineNTDS.DIT.
Ans:
- The NT Directory Services Database (NTDS.DIT) is the primary database used by Active Directory Domain Services on Windows Server. It stores directory data such as user accounts, groups, computer objects, and their attributes, along with schema and configuration information.
- Log files are used by the Microsoft Exchange Server database engine (ESE) to record changes made to the Exchange database (EDB). They maintain a sequential record of all transactions, including additions, modifications, and deletions, and are crucial for database recovery, ensuring data integrity and adaptability in Exchange environments. This functionality allows administrators to quickly restore the database to a consistent state following system failures or corruption.
54. What’sEDB.Log?
Ans:
Log files are used by the Microsoft Exchange Server database engine (ESE) to record changes made to the Exchange database (EDB). They maintain a sequential record of all transactions, including additions, modifications, and deletions, and are crucial for database recovery, ensuring data integrity and adaptability in Exchange environments. This functionality allows administrators to quickly restore the database to a consistent state following system failures or corruption.
55. DefineEDB.Che.
Ans:
- It is a train extension associated with the checkpoint lines used by the Microsoft Exchange Garçon database machine( ESE) to track the progress of database deals.
- Checkpoint lines, also known as checkpoint(. che) lines, contain information about the state of the Exchange database at specific points in time.
- They record the last married sale in the database and help minimize the time needed for database recovery in the event of a system failure.EDB.Che lines work in confluence with EDB.
56. What’s Resin inRes1.log andRes2.log.
Ans:
In the environment of sale log lines( similar asRes1.log andRes2.log) in Microsoft Exchange Garçon surroundings,” Res” generally stands for” Reserved.” These log lines are part of the sales log sequence generated by the Exchange database machine( ESE) to record changes made to the Exchange database. The” Res” designation may indicate that these log lines are reserved for storing transactional data pending commit to the database or for maintaining a reserve of available log lines for unborn use.
57. Explain the part of Flexible Single Master Operations.
Ans:
- Flexible Single Master Operations( FSMO) places are technical tasks assigned to specific sphere regulators in an Active Directory timber.
- Sphere Naming Master Controls the addition or junking of disciplines in the timber.
- Relieve Master Allocates relative identifiers( RIDs) to sphere regulators for creating security headliners.
- PDC Emulator Provides backward comity for aged guests and manages word changes and time synchronization.
58. What’s KCC?
Ans:
KCC( Knowledge thickness Checker) is a erected- in process in Active Directory that runs on all sphere regulators and is responsible for generating and maintaining the replication topology within a sphere or timber. The KCC stoutly calculates the most effective replication paths between sphere regulators grounded on point topology, connectivity, and replication links. It ensures that changes made to the directory are replicated directly and efficiently to all sphere regulators, maintaining directory thickness and integrity.
59. Define SID.
Ans:
- A Security Identifier( SID) is a unique alphanumeric identifier assigned to each security star( similar to user accounts, groups, and computers) in a Windows terrain.
- SIDs are used by Windows security mechanisms to control access to coffers and apply security programs.
- Each SIDE consists of a sphere identifier( SID) and a unique identifier( relieve) that uniquely identifies the security star within the sphere.
60. What means to Caching-only servers in terms of DNS?
Ans:
Hiding-only servers, also known as DNS purposefulness, are DNS servers configured to perform DNS resolution queries on behalf of guests and cache the results for unborn use. These waiters don’t host authoritative DNS zones but rather calculate recursive queries to other DNS servers to resolve sphere names into IP addresses. Once a DNS resolution query is successfully resolved, the hiding-only garçon stores the result in its cache for a specified time( TTL) determined by the authoritative DNS garçon.
61. Where is the announcement database stored?
Ans:
- The Active Directory( announcement) database, namedNTDS.DIT( NT Directory Services Database Information Tree) is stored on sphere regulators in a Windows Garçon terrain.
- By dereliction, NTDS.DIT is located in the SystemRoot NTDS directory on each sphere regulator.
- This train contains the directory data, including user accounts, groups, computer objects, and their associated attributes, as well as the schema and configuration information for the Active Directory timber.
62. Define APIPA?
Ans:
APIPA( Automatic Private IP Addressing) is a point in Windows operating systems that automatically assigns IP addresses to computers and biases on a network when a DHCP( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) garçon is unapproachable. When a device configured to use DHCP fails to gain an IP address from a DHCP garçon, it automatically configures itself with an IP address in the range of 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254, along with a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
63. What is a garçon director is?
Ans:
Garçon director is an operation tool in Windows Garçon operating systems that provides a unified interface for installing, configuring, and managing garçon places and features and tackling original and remote servers. It consolidates various executive tools and serviceability, similar to Active Directory Domain Services( announcement DS), DNS( sphere Name System), DHCP( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), and train services, into a single press.
64. Define the Visio illustration.
Ans:
- A Visio illustration is a visual representation or graphical illustration created using Microsoft Visio, a diagramming and vector plate operation.
- Visio plates depict complex systems, processes, workflows, networks, and organizational structures in a visually charming and easy-to-understand format.
- They correspond to various shapes, symbols, connectors, and textbook markers arranged on an oil to convey information effectively.
65. What’s Kerberos?
Ans:
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol that ensures secure authentication for users and services in distributed environments. It uses symmetric key cryptography and a trusted Key Distribution Center (KDC) to issue time-limited tickets, enabling clients to request service tickets using a ticket-granting ticket (TGT) obtained from the KDC. This protocol enhances security by minimizing the need for repeated password transmission over the network.
66. What’s the part of RAS servers in the Microsoft world?
Ans:
- RAS( Remote Access Service) servers play a pivotal part in furnishing remote access connectivity to users and bias in the Microsoft world.
- RAS servers enable remote users to establish secure connections to commercial networks over dial-up, VPN( Virtual Private Network), or direct internet connections.
- They grease remote access to network coffers, similar to lines, operations, and internal systems, allowing users to work ever from anywhere with an internet connection.
67. What are VPN coverts?
Ans:
VPN( Virtual Private Network) coverts are translated connections established over a public network, similar to the Internet, to produce a secure communication channel between two or further endpoints. These endpoints can be individual computers, routers, or entire networks. VPN converts synopsized data packets within translated protocols, similar to IPsec( Internet Protocol Security) or SSL/ TLS( Secure Sockets Subcaste/ Transport Layer Security), to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of transmitted data.
68. What’s the structure as a service( IaaS)?
Ans:
VPN( Virtual Private Network) coverts are translated connections established over a public network, similar to the Internet, to produce a secure communication channel between two or further endpoints. These endpoints can be individual computers, routers, or entire networks. VPN converts synopsized data packets within translated protocols, similar to IPsec( Internet Protocol Security) or SSL/ TLS( Secure Sockets Subcaste/ Transport Layer Security), to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of transmitted data.
69. What’s the model for IaaS in pall computing?
Ans:
The model for structure as a Service( IaaS) in pall computing follows a consumption-grounded pressuring model, where guests pay only for the computing coffers they use on-demand. This model offers inflexibility and scalability, allowing associations to gauge their structure up or down according to workload conditions without incurring outspoken capital charges. IaaS providers generally offer a range of virtualized coffers, including cipher cases, storehouse volumes, and networking services, accessible via tone-service doors or APIs.
70. What’s Platform as a Service( PaaS)?
Ans:
- Platform as a Service( PaaS) is a pall computing service model that provides a platform and terrain for developing, planting, and managing operations over the Internet.
- With PaaS, inventors can make, test, and emplace operations without fussing about underpinning structure factors, similar to servers, operating systems, and middleware.
- PaaS providers offer a comprehensive set of development tools, fabrics, and runtime surroundings that streamline the operation development lifecycle and epitome down structure complications.
71. What’s Microsoft’s Office for the Web?
Ans:
Microsoft’s Office for the Web, also known as Office Online, is a pall- ground suite of productivity operations offered by Microsoft as part of its Office 365 subscription service. Office for the Web includes web-grounded performances of popular Microsoft Office operations, similar to Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and OneNote, accessible via a web cybersurfer.
72. What’s One Drive for Business
Ans:
- OneDrive for Business is a pall- ground train storehouse and sharing service handled by Microsoft as part of its Office 365 suite of productivity tools.
- It offers a secure, centralized storehouse for business documents, lines, and flyers, accessible from any device with internet connectivity.
- OneDrive for Business allows users to store, sync, and share lines securely, unite on documents in real time, access interpretation history, and train recovery features.
73. What’s Azure?
Ans:
Azure is Microsoft’s pall calculating platform and services, offering a wide range of structure, platform, and software services for structure, planting, and managing operations and services through Microsoft- managed data centers encyclopedia ally. Azure provides scalable computing coffers, including virtual machines, databases, storehouses, networking, and analytics, as well as inventor tools, AI( Artificial Intelligence), IoT( Internet of Effects), and machine literacy services.
74. What’s Azure announcement Connect?
Ans:
- Azure AD Connect is a Microsoft tool that links on-premises Active Directory with Azure Active Directory. It offers a unified identity and access management platform for both cloud and local resources.
- Azure Announcement Connect facilitates user authentication, single sign-on ( SSO), and identity confederation between on-demand and pall-ground operations and services.
- It synchronizes user accounts, groups, and directory objects between on-premises Active Directory and Azure AD, ensuring consistent identity management and access control across environments.
75. What are the benefits of using Azure Announcement Connect?
Ans:
- Unified Identity Management enables flawless integration and synchronization of on-demand Active Directory with Azure announcement, furnishing a single identity and access operation result.
- A single subscribe- ( SSO) Facilitates secure and accessible access to all-grounded operations and services with a single set of credentials.
- It simplifies Administration and Streamlines identity operation tasks with automated provisioning, synchronization, and covering capabilities.
76. How does Azure charge for its services?
Ans:
Azure employs a pay- as- you- go pricing model, where guests are billed grounded on their factual operation of Azure services and coffers. Azure charges guests for cipher coffers, storehouses, networking, databases, and other services consumed on an hourly or yearly basis. Pricing varies depending on factors such as resource operation, service position agreements( SLAs), data transfer, storehouse capacity, and geographic region.
77. How can you pierce PowerShell on a Windows machine?
Ans:
- Start Menu Click on the launch button, type” PowerShell” in the hunt bar, and elect” Windows PowerShell” or” Windows PowerShell( x86)” from the hunt results.
- Run Dialog Press Win R to open the Run dialog, type” Powershell,” and press Enter.
- PowerShell ISE PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment( ISE) provides an interactive scripting terrain with features like syntax pressing, remedying, and tab completion.
78. What ways does PowerShell provide support for IntelliSense?
Ans:
IntelliSense is a point in PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment( ISE) and Visual Studio Code that provides environment-apprehensive law completion, parameter hints, and syntax checking while codifying commands or scripts. PowerShell supports IntelliSense by assaying the command syntax, parameters, and available cmdlets grounded on the installed modules and active session.
79. What methods can users use to modify a service in PowerShell?
Ans:
- Users can modify a service in PowerShell using cmdlets handed by the Service Management module.
- Standard cmdlets for managing services include Get- Service, Start- Service, Stop- Service, renew- Service, and Set- Service.
- To modify a service, users can use the Set-Service cmdlet to change its parcels, similar to the incipiency type, display name, or description.
80. How do you get back with PowerShell’s stop-service command?
Ans:
- Type” Get- Help Stop- Service” in the PowerShell press, and it’ll display detailed information about the Stop- Service cmdlet, including its syntax, parameters, exemplifications, and related commands.
- Also, you can use the”- Online” parameter with Get- Help to open the online attestation for Stop- Service in your dereliction web cybersurfer, furnishing access to fresh coffers, community conversations, and troubleshooting tips related to stopping services in PowerShell.
81. How do you terminate a Win or M service in PowerShell?
Ans:
In PowerShell, you can terminate a Windows service using the Stop-Service cmdlet. To stop a service, use the command” Stop- Service- Name ServiceName,” replacing” ServiceName” with the name of the service you want to terminate. Alternatively, you can use the Get-Service cmdlet to recoup a list of running services and pipe the affair to the Stop-Service cmdlet to stop multiple services at once.
82. What are some other useful commands in PowerShell?
Ans:
- Get- Reuse Retrieves information about running processes on the system.
- Get- EventLog Retrieves event log entries from original or remote computers.
- Test- Connection Tests network connectivity to a remote host using ICMP clunk.
- Get- ChildItem Retrieves lines and directories in a specified position.
83. What’s the “ get gusto command ” in PowerShell?
Ans:
In PowerShell, the Get-Command cmdlet is used to recoup information about cmdlets, functions, scripts, aliases, and executables available in the current PowerShell session. By dereliction, Get-Command displays a list of all commands loaded into memory. You can filter the affair by specifying parameters similar as- Name, Module, or- Verb to search for specific commands. Get-Command is an essential tool for exploring available commands, discovering their operation, and learning PowerShell syntax and capabilities.
84. How do you use “ get command ” and “ gusto noun ” in PowerShell?Why must multiple disciplines be in active directory design?
Ans:
- For illustration,” Get- Service,” Stop-Process,” and” New- Item” are examples of cmdlets following the” gusto Noun” convention.
- By using” Get- Command” with specific pollutants, similar as- Verb or- Noun, users can search for cmdlets grounded on their separate verbs or nouns, easing command discovery and disquisition in PowerShell.
- Understanding this convention and exercising Get-Command effectively can help users navigate and work PowerShell’s expansive command library efficiently.
85. What’s the global roster in ActiveDirectory?What are the places of enterprise and sphere admins in Active Directory?
Ans:
- The global roster( GC) is a distributed data depository in Active Directory that contains a partial replica of all objects in the timber.
- It stores a subset of attributes for every object in the directory, making it possible to search for objects and attributes across the entire timber without demanding to communicate individual sphere regulators.
- The global roster is essential for easing timber-wide quests,cross-domain authentication, and universal group class queries in multi-domain surroundings.
86. What’s the purpose of the configuration partition in Active Directory?
Ans:
The configuration partition in Active Directory serves as a depository for configuration data that defines the structure and topology of the entire timber. It stores information about spots, disciplines, trusts, schema extensions, and replication settings, allowing directors to manage the global settings and configuration parameters for the entire Active Directory structure.
87. How do you link your garçon to Azure Active Directory in the pall?
Ans:
- To link a garçon to Azure Active Directory( Azure announcement) in the pall, directors can use Azure Announcement Connect, a tool handed by Microsoft for coinciding- demesne Active Directory with Azure announcement.
- By installing and configuring Azure announcement Connect on the garçon, directors can establish a secure and automated synchronization process between the on-demand Active Directory terrain and Azure announcement.
88. What’s the D S Rimpasse? What’s the purpose of disabling IPv6 on the Ethernet appendage?
Ans:
To connect a server to Azure Active Directory, administrators can use Azure AD Connect, a Microsoft tool for synchronizing on-premises Active Directory with Azure AD. By configuring this tool, they establish secure synchronization, allowing users to access cloud services like Microsoft 365 with their existing credentials, facilitating single sign-on and centralized identity management. This streamlines user access and enhances security across hybrid environments.
89. What are the ways to recover misplaced places in Active Directory?
Ans:
- Transfer places If the sphere regulator holding the places is still functional, use the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in or the NTDSUTIL command-line tool to transfer them to another sphere regulator.
- Seize places If the sphere regulator holding the places is permanently unapproachable, use the NTDSUTIL command-line tool to seize the places onto another sphere regulator.
- Authoritative Restore Perform an authoritative restore of Active Directory from a backup to recover misplaced places and their associated data.



