
ITIL, which stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a widely embraced framework in IT service management. Offering a comprehensive set of best practices and guidelines, ITIL enables organizations to deliver IT services that are closely aligned with their requirements. It facilitates the enhancement of service quality, cost reduction, and improved customer satisfaction through structured processes for managing incidents, problems, changes, and service levels.
1. What is ITSM?
Ans:
ITSM stands for IT Service Management. It encompasses IT services’ planning, delivery, operation, and continual improvement.ITSM focuses on meeting customer needs and aligning IT services with business goals.ITSM frameworks like ITIL provide guidelines for effective service management practices.ITSM aims to ensure the efficient and effective delivery of IT services.
2. Explain the Service Value System.
Ans:
The Service Value System (SVS) is a core component of ITIL® 4. It offers a holistic approach to creating value through services.SVS comprises interconnected components, including Guiding Principles, Governance, Service Value Chain, Practices, and Continual Improvement. It aids organizations in understanding how different elements collaborate to create value for customers.SVS guides the effective and efficient delivery of valuable services.
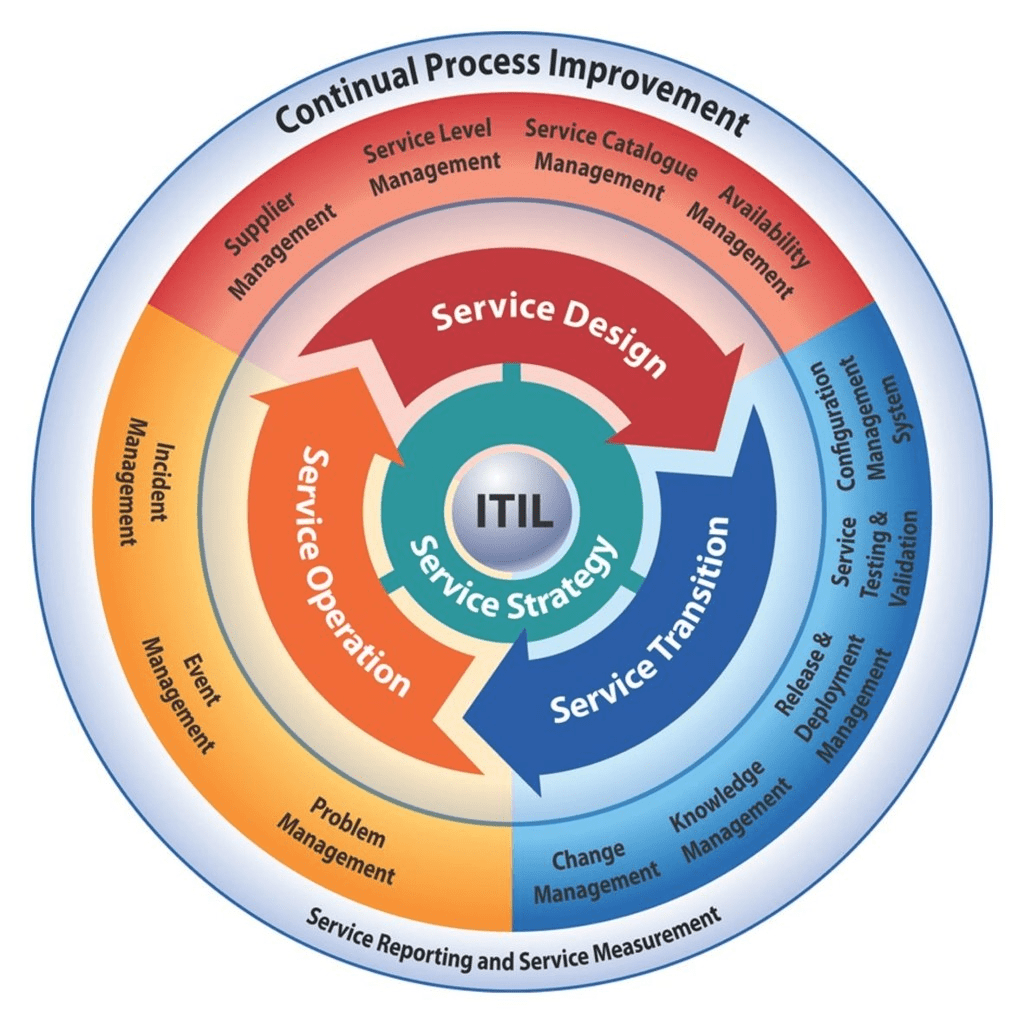
3. Explain the phases of the ITIL® Lifecycle.
Ans:
- The five phases of the ITIL® Lifecycle are service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continuous service improvement (CSI).
- Each phase represents a distinct stage in the lifecycle of a service, from conception to retirement.
- Service Strategy involves understanding customer needs and defining IT service offerings.
- Service Design focuses on designing new or modified services and IT infrastructure.
- Service Transition deals with transitioning services into production environments.
4. What are the 4 Ps of ITIL®?
Ans:
- The 4 Ps of ITIL® include People, Processes, Products (Technology), and Partners (Suppliers).
- People refer to the human resources involved in delivering IT services.
- Processes encompass structured activities and workflows for managing services.
- Products (Technology) include tools and technology supporting service delivery.
- Partners (Suppliers) are external entities contributing to IT service delivery.
- Together, these elements form the foundation for effective IT service management.
5. What is ITIL®?
Ans:
ITIL® refers to the Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It’s a framework that outlines best practices for IT service management (ITSM).ITIL® offers guidance on aligning IT services with business objectives. It comprises practices to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of IT service delivery. Widely adopted globally, ITIL® fosters improved service quality and customer satisfaction.
6. Which processes does the ITIL V3 framework consist of?
Ans:
The ITIL V3 framework encompasses processes such as Incident Management, Problem Management, Change Management, Service Level Management, and others. These processes are designed to ensure efficient and effective IT service delivery. They address various aspects of service management, from handling incidents and problems to managing changes and service levels. ITIL V3 processes aid organizations in streamlining IT service delivery and support functions.
7. Explain the benefits of ITIL.
Ans:
- ITIL offers numerous benefits, including improved service quality, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased productivity.
- It provides a standardized framework and common language for IT service management practices.
- ITIL helps streamline processes, reduce costs, and mitigate risks associated with IT service delivery.
- ITIL facilitates improved coordination between IT and other business units by promoting better communication and collaboration.
8. What are the benefits of implementing an ITIL service desk?
Ans:
- Implementing an ITIL service desk can lead to quicker incident resolution and heightened customer satisfaction.
- It standardizes service management processes, promoting greater efficiency.
- An ITIL service desk is a central point of contact for IT-related issues, enhancing communication and coordination.
- It enables comprehensive tracking and Management of service requests, incidents, and changes.
- Organizations leverage ITIL principles to improve service delivery and support, resulting in better business outcomes.
9. Explain the difference between a project and a process.
Ans:
| Aspect | Project | Process | |
| Nature and Purpose |
Temporary endeavor with specific objectives |
Ongoing and repetitive activities | |
| Duration and Lifecycle | Defined beginning and end; passes through phases | Continuous operation with no predefined end | |
| Uniqueness vs Repetition |
Unique; one-time endeavor |
Repeatable and standardized | |
| Management Approach | Managed using project management methodologies | Managed using process management methodologies | |
| Flexibility and Adaptability |
Subject to changes but impacts timelines, budgets |
Designed to be stable with less flexibility |
10. How does an Incident Management System work?
Ans:
An Incident Management System categorizes, prioritizes, and resolves incidents reported by users or detected through monitoring tools. Incidents are logged, assigned priority, and investigated according to predefined procedures and service level agreements. Communication with affected users and stakeholders is maintained throughout, providing updates on incident status and resolution progress.
11. What are the stages of incident management in ITIL?
Ans:
- Recognition: Identifying when an incident occurs.
- Documentation: Recording incident details for tracking purposes.
- Categorization: Assigning incidents to specific categories for better organization.
- Prioritization: Determining the importance of incidents to allocate resources effectively.
- Investigation and Diagnosis: Analyzing incidents to identify their root causes.
- Resolution and Restoration: Implementing solutions to restore normal operations.
12. What is an SLA?
Ans:
An SLA, or Service Level Agreement, is a contract between a service provider and a customer that outlines the agreed-upon level of service expected by both parties.SLAs define the scope, quality, and respective responsibilities of the service provider and the customer. They incorporate metrics for measuring service performance to ensure accountability and transparency. Breaches of SLAs may result in penalties or compensation.
13. Explain different types of SLA.
Ans:
- Customer-based SLA: Tailored to meet the specific needs of individual customers.
- Service-based SLA: Applies uniformly to all customers using a particular service.
- Multi-level SLA: Involves different SLAs catering to various levels of service.
- Operational-level SLA: Focuses on day-to-day operational processes.
- Underpinning Contract (UC) SLA: Agreement with third-party vendors or suppliers supporting service delivery.
- Corporate-level SLA: Encompasses agreements spanning the entire organization.
14. What is the purpose of Problem Management in ITIL?
Ans:
Problem Management aims to prevent the recurrence of incidents by addressing their root causes. It involves analyzing trends and patterns to facilitate proactive resolution. Improving overall service quality minimizes disruptions and enhances IT infrastructure stability and reliability. Problem Management fosters continuous improvement of IT services.
15. What are the stages in the overall Problem Management Process?
Ans:
- Problem Identification: Recognizing and recording problems.
- Problem Control: Investigating, categorizing, and prioritizing problems.
- Error Control: Identifying known errors and implementing temporary solutions.
- Problem Resolution: Finding permanent solutions and implementing changes.
- Problem Closure: Verify solution effectiveness and close problem records.
- Proactive Problem Management: Identifying potential issues before they affect services.
16. What is a Known Error?
Ans:
A Known Error refers to a documented problem with a known root cause and a workaround. It is managed within the IT organization and helps expedite incident resolution, minimizing service downtime. Known Errors are typically documented in the Known Error Database (KEDB). Resolving Known Errors often involves implementing permanent fixes.
17. How does a known error close?
Ans:
A Known Error is closed once a permanent solution is implemented and its effectiveness is tested. With the solution in place, the workaround becomes unnecessary. Closure of a Known Error is documented in the KEDB, and closure reports may be shared with relevant stakeholders. Regular reviews ensure the ongoing effectiveness of the solution.
18. What is the purpose of Configuration Management in ITIL?
Ans:
- Configuration Management maintains accurate records of IT assets and their configurations.
- It elucidates the relationships between components, facilitating effective change and incident management.
- Configuration Management supports various ITIL processes, including problem and release management.
- It aids in controlling and managing IT infrastructure, enabling informed decision-making regarding investments and resource allocation.
19. What is a plan–do–check–act (PDSA) cycle, and define its phases?
Ans:
- The plan–do–check–act (PDSA) cycle is a four-step iterative management method.
- Plan: Identify objectives and processes to achieve them.
- Do: Implement the plan on a small scale.
- Check: Evaluate results against objectives.
- Act: Make necessary adjustments and implement changes.
- PDSA fosters continuous improvement and problem-solving, which is commonly used in quality management and process improvement initiatives.
20. What are the objectives of Incident Management?
Ans:
- Incident Management aims to restore normal service operations promptly, minimizing business disruption.
- It focuses on efficiently resolving incidents with minimal impact on users.
- Incident Management involves categorizing, prioritizing, and escalating incidents based on urgency and severity.
- It seeks to identify root causes to prevent incident recurrence.
- Incident Management ensures accurate incident documentation for future reference and analysis.
21. Explain the responsibilities of an ITIL Service Desk.
Ans:
Act as the primary point of contact for all IT-related inquiries and issues.Document and categorize incidents and service requests efficiently. Provide initial diagnosis and resolution or escalate issues to the appropriate support teams. Maintain communication with users, updating them on incident statuses and resolution progress. Ensure prompt incident resolution within agreed-upon service levels.
22. What’s the difference between proactive and reactive problem management?
Ans:
- Proactive Problem Management aims to preemptively identify and resolve potential issues before they escalate into incidents.
- Reactive Problem Management focuses on addressing problems post-incident to prevent their recurrence.
- Proactive Management involves analyzing trends and taking preventive measures.
- Reactive Management entails root cause analysis and implementing permanent solutions.
23. What is the objective of ITIL Change Management?
Ans:
Ensure the adoption of standardized methods and procedures for handling changes efficiently and promptly. Minimize the adverse impact of changes on IT services by appropriately assessing and managing risks. Facilitate effective communication and coordination among stakeholders involved in the change process. Record, evaluate, authorize, prioritize, plan, test, implement, document, and review changes meticulously in a controlled manner.
24. What is Post Implementation Review (PIR)?
Ans:
PIR evaluates the effectiveness and success of a change after its implementation. It assesses whether the change achieved its objectives and delivered the expected benefits.PIR identifies lessons learned and areas for improvement within the change management process. The review aids in refining future change implementation strategies. Stakeholders affected by or involved in the change participate in the PIR process.
25. What is the main objective of Capacity Management, and what are its subprocesses?
Ans:
Objective: Ensure IT resources adequately meet present and future business needs cost-effectively.
Subprocesses:
- Business Capacity Management: Align IT capacity with current and future business requirements.
- Service Capacity Management: Manage capacity to uphold agreed-upon service levels.
- Component Capacity Management: Oversee capacity for individual IT components.
- Capacity Planning: Predict future capacity demands based on business growth and needs.
- Performance Management: Monitor and optimize the performance of IT services and components.
26. What is an Operational-level agreement (OLA)?
Ans:
OLA delineates the agreed operational level of service among internal support groups. It specifies each support group’s responsibilities in delivering IT services.OLAs reinforce SLAs by ensuring internal support groups fulfill their service obligations. Details such as response times, escalation procedures, and service availability may be included in OLAs.While not legally binding contracts, OLAs serve as internal agreements.
27. List the various knowledge management systems.
Ans:
- Document Management Systems (DMS)
- Knowledge Bases
- Wikis
- Forums or Discussion Boards
- Expert Systems
- Lessons Learned Databases
28. What is the role of Continual Service Improvement (CSI) in ITIL?
Ans:
- CSI endeavors to enhance the quality of IT services over time.
- It identifies improvement opportunities through metrics, measurements, and analysis.
- CSI fosters a culture of ongoing improvement within the organization.
- Ensuring alignment with evolving business needs and objectives is central to CSI.
- Evaluation of processes, services, and technology for potential enhancements is part of CSI.
- CSI drives efficiency, effectiveness, and innovation throughout the IT service lifecycle.
29. Explain the concept of Service Strategy in ITIL.
Ans:
Service Strategy defines how IT services contribute to realizing business objectives. Understanding customer needs and market opportunities is integral to Service Strategy, Which Also guides decision-making regarding service offerings and differentiation. Alignment of IT resources with business priorities and value creation is pivotal in Service Strategy.
30. What are the critical components of Service Design according to ITIL?
Ans:
- Service Catalog Management
- Service Level Management
- Capacity Management
- Availability Management
- IT Service Continuity Management
- Information Security Management
- Supplier Management
- Design Coordination
31. How does Service Transition facilitate the smooth deployment of changes in ITIL?
Ans:
Service Transition ensures changes are thoroughly planned before implementation. It manages risks associated with changes, minimizing disruptions to services. Coordinating activities across departments facilitates seamless deployment. Service Transition verifies that changes meet requirements and are appropriately documented. It ensures effective communication with stakeholders throughout the change process.
32. Describe the purpose of Service Operation in ITIL.
Ans:
Service Operation ensures that IT services are delivered effectively and efficiently. It handles day-to-day activities to maintain service levels and meet business needs. Service Operation monitors and resolves incidents and service requests promptly. It manages access to services and supports operational activities such as backups and batch processing.
33. What is the role of the Service Desk in Incident Management?
Ans:
- The Service Desk serves as the single point of contact for users reporting incidents.
- It logs and categorizes incidents, ensuring accurate tracking documentation.
- Service Desk prioritizes incidents based on impact and urgency.
- It facilitates communication between users and support teams throughout the incident lifecycle.
34. How does ITIL address the Management of Service Requests?
Ans:
ITIL defines processes for handling Service Requests efficiently and consistently. It ensures that Service Requests are logged, categorized, and prioritized appropriately. Predefined workflows and service levels guide Service Request fulfillment.ITIL emphasizes timely and transparent communication with requestors. Continuous monitoring and improvement are integrated into Service Request management processes.
35. Explain the Change Advisory Board’s (CAB) role in Change Management.
Ans:
- The Change Advisory Board (CAB) evaluates and approves proposed changes.
- It assesses potential impacts and risks associated with changes.
- CAB ensures that changes align with business objectives and IT strategies.
- It provides expert advice and guidance to change initiators.
36. What purpose is ITIL’s Emergency Change Advisory Board (ECAB)?
Ans:
- The Emergency Change Advisory Board (ECAB) handles urgent changes that cannot undergo standard approval processes.
- It assesses the risks and impacts of emergency changes to determine appropriate actions.
- ECAB ensures that emergency changes are necessary and justified to mitigate immediate threats.
- It expedites decision-making while maintaining oversight and control over emergency changes.
37. Describe the objectives of Release and Deployment Management in ITIL.
Ans:
Release and Deployment Management aims to deliver new or changed services into the live environment efficiently and with minimal disruptions. It ensures that releases are planned, tested, and documented thoroughly. Release and Deployment Management coordinates with various stakeholders to schedule and implement releases. It verifies that releases meet quality criteria and are compatible with existing services and infrastructure.
38. How does ITIL address the Management of IT assets and configurations?
Ans:
- ITIL establishes processes for managing IT assets and configurations throughout their lifecycle.
- It maintains accurate records of assets and configurations, aiding decision-making and resource allocation.
- ITIL ensures that configuration changes are controlled and documented to prevent unauthorized modifications.
- Regular audits and reviews are conducted to verify configuration accuracy and compliance.
39. Explain the concept of a Configuration Item (CI) in ITIL.
Ans:
Any component that must be controlled to provide an IT service is called a configuration item (CI). CIs can range from hardware and software to documentation and people.ITIL maintains a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) to store information about CIs and their relationships.CIs are uniquely identified and tracked throughout their lifecycle to ensure accurate configuration management.
40. What is the purpose of the Deming Cycle in ITIL?
Ans:
- The Deming Cycle, or the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, is a systematic approach to continuous improvement.
- It involves planning, implementing, evaluating, and adjusting processes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
- The Deming Cycle fosters a culture of learning and adaptation within organizations.
- It promotes iterative improvements based on data-driven analysis and feedback.
41. Describe the role of Service Level Manager in ITIL.
Ans:
- Service Level Managers establish and uphold SLAs with customers.
- They ensure services meet agreed-upon standards.
- We are monitoring service performance and rectifying deviations.
- We are collaborating with other ITIL processes to enhance service quality.
- We are conducting regular reviews and negotiations with stakeholders.
- Acting as the primary point of contact for SLA-related concerns.
42. How does ITIL manage relationships with external service providers?
Ans:
ITIL maintains transparent communication with external providers, establishes contracts and agreements to outline service expectations, regularly evaluates provider performance against predefined metrics, and resolves any issues or discrepancies. It also collaborates with providers to continuously improve services and ensures alignment of external services with organizational objectives.
43. What is the purpose of Financial Management for IT Services (ITIL)?
Ans:
Financial Management ensures cost-effective service delivery. Appropriately budgeting and allocating resources and monitoring and controlling IT expenditures provide stakeholders with financial transparency and support decision-making by assessing IT investments’ economic impact and optimizing financial resources’ use for maximum organizational value.
44. Describe the role of the Service Catalog in ITIL.
Ans:
- The Service Catalog serves as a centralized repository for available services.
- Detailed information about service offerings is provided.
- We are assisting users in understanding available services.
- We are facilitating service request and fulfillment processes.
- It is aligning IT services with business requirements and priorities.
45. How does ITIL ensure continual improvement of IT services?
Ans:
- ITIL fosters a culture of ongoing enhancement.
- It is regularly evaluating service performance against set objectives.
- It is identifying areas for improvement through feedback and analysis.
- We are implementing changes and monitoring their effects.
- I am learning from both successes and failures to refine processes.
- Ensuring IT services evolve to meet evolving business needs.
46. Explain the concept of a Major Incident in ITIL.
Ans:
A major incident denotes a significant service disruption. It impacts many users or critical business processes, requiring swift response and resolution. Special procedures and resources are activated during such incidents, intensifying communication and coordination. The primary objective is to restore regular service operations.
47. What is the purpose of the ITIL Knowledge Management process?
Ans:
- ITIL Knowledge Management captures, stores, and disseminates knowledge.
- Ensuring valuable information is accessible for decision-making.
- We are facilitating learning from past experiences and best practices.
- I am assisting in problem-solving and incident resolution.
- We are enhancing efficiency by minimizing the need to rediscover knowledge.
48. Describe the difference between a Change Model and a Standard Change in ITIL.
Ans:
- Change Model: Predetermined procedures for managing specific change types.
- Standard Change: Routine changes with low risk and established procedures.
- Change Models offer guidance for complex changes.
- Standard Changes adhere to predefined approval and implementation steps.
- Change Models are adaptable to various scenarios.
- Standard Changes streamline repetitive changes for efficiency and consistency.
49. How does ITI ensure compliance with regulatory requirements?
Ans:
ITIL incorporates regulatory compliance into its processes, conducting regular audits and assessments, aligning policies and procedures with regulatory standards, integrating compliance requirements into service design and delivery, and implementing training and awareness initiatives to ensure staff adherence to regulations. It also actively identifies and mitigates non-compliance risks.
50. What is the role of a Change Manager in ITIL Change Management?
Ans:
- Change Managers oversee the Change Management process.
- We are assessing change requests for potential impact and risk.
- Ensuring changes align with business objectives and policies.
- I am coordinating change implementation and communication.
- We are monitoring the progress of the change and addressing any issues.
- We are facilitating continuous improvement of the change process.
51. How does ITI manage Service Assets and Configuration Items (SACM)?
Ans:
SACM involves maintaining records of service assets and configuration items. It ensures a curated documentation of configurations and their relationships. SACM helps understand the impact of changes on IT services. It facilitates effective change management and incident resolution. SACM supports other ITIL processes like problem and release management.
52. Explain the purpose of Access Management in ITIL.
Ans:
- Access Management ensures authorized users have appropriate access to services.
- It protects against unauthorized access and security breaches.
- Access Management maintains confidentiality, integrity, and availability of services.
- It defines and monitors access rights, roles, and privileges.
- Access Management helps ensure compliance with security policies and regulations.
53. What is the role of the Problem Manager in ITIL Problem Management?
Ans:
- The problem manager heads the process of problem management.
- They identify and address the root causes of incidents.
- Problem Managers coordinate investigations and prioritize problems.
- They facilitate communication between stakeholders and IT teams.
- Problem Managers ensure the effectiveness of problem-resolution activities.
- Overall, they drive continuous improvement and minimize service disruptions.
54. Describe the relationship between Incident and Problem Management in ITIL.
Ans:
- The goal of incident management is to resume operations following disruptions.
- Problem Management aims to prevent incidents from recurring.
- Incident Management handles individual incidents, while Problem Management addresses underlying issues.
- They collaborate to ensure incidents are resolved, and root causes are addressed.
- Incident Management feeds information to Problem Management for analysis.
55. How does ITI address the Management of Service Portfolios?
Ans:
ITIL manages Service Portfolios to align services with business needs. It involves categorizing services based on value, risk, and strategic importance. Service Port Olios undergoes continual evaluation and optimization.ITIL ensures transparency and accountability in Service Portfolio management. It enables me to form decisions regarding service investments and retirements.
56. Explain the purpose of Service Validation and Testing in ITIL.
Ans:
Service Validation and Testing verify that services meet business requirements, ensure they’re fit for purpose, and meet quality standards. They also identify and mitigate risks associated with service changes, validate service designs, and ensure they align with business needs: service Validation and Testing support Service Transition activities.
57. What is the role of a Service Owner in ITIL?
Ans:
- The Service Owner is accountable for the delivery of a specific IT service.
- They represent the interests of stakeholders and ensure service requirements are met.
- Service Owners oversee service strategy, design, transition, and operation.
- They manage the lifecycle of the service and its associated assets.
- Service Owners collaborate with other ITIL roles to ensure service excellence.
58. Purpose of ITIL Service Transition Planning and Support?
Ans:
- Service Transition Planning and Support facilitate smooth transitions of services into operation.
- It ensures the coordination of resources and activities during service transitions.
- Service Transition Planning and Support minimize risks and disruptions to services.
- It maintains clear communication and stakeholder engagement throughout transitions.
- The process helps in evaluating the readiness of services for deployment.
59. How does ITIL address the Management of service Continuity?
Ans:
ITIL ensures service availability through Service Continuity Management. It identifies and mitigates risks to service continuity. Service Continuity Management develops and maintains continuity plans and strategies. It conducts regular testing and exercises to update continuity plans. Service Continuity Management ensures swift recovery from disruptions.
60. What is the role of the ITIL Change Evaluation process?
Ans:
- The Change Evaluation process assesses proposed changes for potential risks and impacts.
- It ensures changes align with business objectives and service requirements.
- Change Evaluation considers factors such as cost, resources, and feasibility.
- It helps prioritize and authorize modifications based on their impact and urgency.
- The process monitors and reviews implemented changes to ensure desired outcomes.
62. How does ITIL address the Management of Knowledge Management systems?
Ans:
- Establishes processes for creating, storing, and sharing knowledge.
- Encourages cooperation and the exchange of knowledge.
- Defines roles and responsibilities for managing knowledge assets.
- Ensures knowledge is accessible to relevant stakeholders.
- Facilitates continuous improvement by learning from past experiences.
- Enhances decision-making and problem-solving capabilities.
63. Describe the purpose of the ITIL Supplier Management process.
Ans:
Oversees interactions with outside vendors and suppliers.Ensures suppliers meet agreed-upon service levels and quality standards.Coordinates procurement activities and contracts with suppliers.Identifies and mitigates risks associated with supplier relationships.Facilitates cost-effective sourcing and supplier performance evaluation.Supports overall service delivery and quality assurance.
64. What is the role of the ITIL Service Level Ma agement process?
Ans:
- Defines, negotiates, and manages Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
- Ensures services meet agreed-upon performance targets.
- Monitors and reports on service levels to stakeholders.
- Addresses deviations from SLAs and implements corrective actions.
- Collaborates with other ITIL processes to improve service quality.
- Supports customer satisfaction and business alignment objectives.
65. How does ITIL ensure practical Service Report ng and Management?
Ans:
Establishes processes for collecting, analyzing, and presenting service-related data.Generates reports to communicate service performance and trends.Provides insights for decision-making and continuous improvement.Ensures transparency and accountability in service delivery.Facilitates timely identification and resolution of service issues.Supports compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
66. Explain the purpose of the ITIL Service Measurement and Reporting process.
Ans:
Defines metrics and KPIs to measure service performance.Collects and analyzes data to assess service effectiveness.Generates reports for stakeholders to facilitate informed decision-making.Monitors trends and patterns to anticipate service needs.Supports the achievement of business objectives through effective service management.
67. What is the role of a Service Level Agreement (SLA) in ITIL?
Ans:
- Defines agreed-upon levels of service between a service provider and customer.
- Sets expectations for service quality, scope, and responsibilities.
- Establishes measurable targets and performance indicators.
- Guides service delivery and ensures accountability.
- Facilitates communication and alignment between parties.
- Forms the basis for monitoring, reporting, and continuous improvement.
68. Describe the role of ITIL Service Continuity Management.
Ans:
- E-series continuity of IT services in the event of disruptions or disasters.
- Identifies risks, assesses impacts, and develops mitigation strategies.
- Establishes plans and procedures for responding to incidents.
- Tests and validates continuity plans to ensure effectiveness.
- Coordinates with other ITIL processes for integrated risk management.
- Minimizes service downtime and maintains business resilience.
69. Explain the purpose of the ITIL Service Transition Process.
Ans:
M manages the transition of new or modified services into operation. It ensures changes are implemented efficiently with minimal disruption. It coordinates activities across different ITIL lifecycle stages. It verifies service requirements and readiness before deployment. It facilitates knowledge transfer and training for support teams. It supports the overall goal of delivering quality services to customers.
70. What is the ITIL approach to Service Desk to s?
Ans:
Implements tools to streamline service desk operations and workflows.Supports incident and request management processes.Provides a centralized platform for logging and tracking service issues.Enables efficient communication and collaboration among support teams.Integrates with other ITIL processes for seamless service delivery.Enhances customer satisfaction through timely resolution and support.
71. How does ITIL Knowledge Management contribute to Transition?
Ans:
- Knowledge Management in ITIL Transition ensures seamless transfer of information.
- It facilitates capturing, storing, and sharing valuable insights and expertise.
- Enhances efficiency by providing access to relevant knowledge during transitions.
- It helps in minimizing risks and errors by leveraging past experiences.
- Supports continuous improvement by learning from previous transitions.
72. Identify the purpose of ITIL Service Design Coordination.
Ans:
- Service design Coordination in ITIL ensures alignment with business needs and IT capabilities.
- It coordinates the design activities across different service components.
- Facilitates integration of new or changed services into the service environment.
- Ensures consistency and coherence in service design processes.
73. How does ITIL ensure effective Change management?
Ans:
ITIL ensures effective Change Management through structured processes and controls. It defines clear procedures for requesting, evaluating, and implementing changes. It utilizes change models and impact assessments to minimize risks. It implements change authorization to ensure better governance and accountability.
74. Define the purpose of the ITIL Service Strategy.
Ans:
- ITIL Service Strategy sets the direction and objectives for IT service management.
- It aligns IT services with business goals and objectives.
- Defines policies and guidelines for designing, transitioning, and operating services.
- Ensures that IT investments contribute to business value and ROI.
- Facilitates strategic decision-making regarding service provision and resource allocation.
75. Outline the role of ITIL Demand Management.
Ans:
- ITIL Demand Management anticipates, influences, and manages customer demand for services.
- It analyzes patterns and trends to forecast future demand accurately.
- It helps in optimizing resource utilization and capacity planning.
- Aligns service provision with business needs to ensure customer satisfaction.
- Facilitates proactive service improvement based on changing demand patterns.
76. What is the purpose of ITIL Service Portfolio Management?
Ans:
ITIL Service Portfolio Management provides a comprehensive view of all services offered by an organization. It categorizes services into three categories: service pipeline, service catalog, and retired services. This helps in making informed decisions regarding service investment and retirement. It also aligns service offerings with business objectives and customer needs.
77. How does ITIL approach SLA management?
Ans:
ITIL approaches SLA management by defining clear agreements between service providers and customers. It specifies service levels, performance metrics, and responsibilities in SLAs. ITIL regularly monitors and reviews SLA compliance to ensure service quality. It facilitates communication and negotiation to address changes or breaches in SLAs. ITIL also encourages collaboration between IT and business stakeholders to align SLAs with business objectives.
78. Discuss the role of ITIL Access Management.
Ans:
- ITIL Access Management ensures authorized users have appropriate access to IT services.
- It defines policies, processes, and procedures for granting, modifying, and revoking access rights.
- Implements controls to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive information.
- Facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements and security standards.
- Provides a secure and efficient access management system for IT services.
79. State the purpose of ITIL Event Management.
Ans:
ITIL Event management identifies and manages events that may impact IT services. It monitors and analyzes events to determine their significance and potential impact. It facilitates proactive response to prevent incidents and minimize service disruptions. It integrates with other ITIL processes to facilitate incident, problem, and change management.
80. Explain the role of ITIL Problem Management in Operation.
Ans:
- ITIL Problem Management in Operation aims to minimize the impact of incidents by addressing their root causes.
- It investigates and analyzes recurring incidents to identify underlying problems.
- Facilitates the implementation of permanent solutions to prevent incidents from recurring.
- Collaborates with other ITIL processes to improve service quality and reliability.
81. Assess ITIL’s effectiveness in Incident Management.
Ans:
TIL ensures incidents are promptly recognized and resolved. It employs a structured approach to handling incidents. Resource allocation is optimized through proper categorization and prioritization.ITIL minimizes service disruptions through effective incident management. It fosters continuous improvement in incident response strategies. Overall, ITIL enhances IT service reliability and customer satisfaction.
82. Describe the purpose of ITIL Service Reporting.
Ans:
- ITIL Service Reporting offers insights into IT service performance.
- Key metrics and service levels are documented in reports.
- Stakeholders benefit from informed decision-making facilitated by Service Reporting.
- It fosters transparency and accountability within service delivery.
- Service management effectiveness is enhanced through comprehensive reporting in ITIL.
83. How does ITIL manage Service Catalogs?
Ans:
ITIL defines and maintains Service Catalogs to exhibit available IT services. These catalogs provide detailed information on service offerings and associated costs, aiding users in understanding service options.ITIL ensures that Service Catalogs remain updated and accessible. Service visibility is improved, leading to enhanced service delivery efficiency. Ultimately, service catalogs heightened customer satisfaction and service alignment with business needs.
84. Define the role of the ITIL Service Transition Manager.
Ans:
- The ITIL Service Transition Manager oversees the integration of new or modified services.
- Ensuring smooth coordination among stakeholders during transitions is a primary role.
- Service Transition Managers manage risks associated with service changes.
- Quality criteria verification before deployment is ensured.
- Facilitating efficient change management processes is among the duties.
85. Elaborate on the role of ITIL Application Management.
Ans:
- ITIL Application Management oversees the lifecycle of applications within the IT environment.
- Alignment of applications with business objectives is ensured.
- Handling of application development, maintenance, and retirement falls under its purview.
- Optimization of application performance and availability is prioritized.
- Coordination with other ITIL processes ensures seamless service delivery.
86. How does ITIL ensure effective Knowledge Management?
Ans:
ITIL facilitates creating, documenting, and disseminating knowledge across the organization. Processes for capturing and managing tacit and explicit knowledge are established. Relevant stakeholders are ensured access to insights and best practices. ITIL promotes a culture of learning and continuous improvement. Utilizing knowledge assets enhances problem-solving and decision-making capabilities.
87. State the purpose of ITIL Request Fulfillment.
Ans:
- ITIL Request Fulfillment manages user requests for IT services.
- Efficient and prompt processing of requests is ensured.
- The aim is to meet agreed-upon service levels for request resolution.
- A streamlined process for handling standard service requests is provided.
- Enhanced user satisfaction is achieved through timely service delivery.
88. Describe the role of ITIL Technical Management.
Ans:
- ITIL Technical Management oversees technical aspects of IT service delivery.
- They ensure infrastructure and tools support service requirements.
- Technical Management handles technology-related incidents and problems.
- They collaborate with other ITIL roles to maintain service quality.
- Monitoring system performance and capacity falls under their responsibility.
- Technical Management ensures IT infrastructure aligns with business needs.
89. Explain the purpose of the ITIL Service Operation Manager.
Ans:
The Service Operation Manager ensures IT services are delivered efficiently. They manage day-to-day operations, including incident and problem resolution. Service Operation Managers coordinate with various teams to maintain service levels. They oversee service requests, access management, and event monitoring. Continuous improvement of service operation processes is a key focus.
90. How does ITIL address Service Level Requirements?
Ans:
ITIL establishes Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to meet service requirements. It defines service scope, quality, and responsibilities between parties. Regular monitoring and reporting ensure adherence to SLAs.Service Level Management identifies and resolves deviations from agreed-upon standards.ITIL emphasizes continuous improvement to meet evolving service level needs.
91. Discuss the role of the ITIL Service Design Manager.
Ans:
- ITIL Service Design Managers plan and design IT services.
- They translate business requirements into service design specifications.
- Service Design Managers ensure new or changed services meet business needs.
- They coordinate with various stakeholders to finalize service designs.
- Risk assessment and capacity planning are part of their responsibilities.
- Service Design Managers aim to optimize service performance and value.
92. Identify the purpose of ITIL Change Evaluation.
Ans:
- ITIL Change Evaluation assesses proposed changes’ impact on services.
- It ensures changes are evaluated and authorized before implementation.
- Change Evaluation minimizes risks and disruptions caused by changes.
- Rigorous testing and evaluation processes are employed.
- It considers both technical and business aspects of proposed changes.
- Change Evaluation aims to enhance service stability and reliability.
93. How does ITIL align with business objectives?
Ans:
ITIL aligns with business objectives by focusing on delivering value through IT services. It ensures IT services support business goals and requirements. Regular reviews and feedback loops ensure alignment with evolving business needs.ITIL processes prioritize customer satisfaction and service quality. Continuous improvement initiatives refine IT services to better meet business objectives.



