
Desktop support involves providing technical assistance and troubleshooting for computer systems, software, and hardware. It ensures that end-users can effectively utilize their desktops, laptops, and peripherals to perform their tasks efficiently. Desktop support technicians diagnose and resolve issues such as software errors, hardware malfunctions, and network connectivity problems. They play a crucial role in maintaining the smooth operation of IT systems within organizations, enabling users to work productively without disruptions.
1. What is an Active Directory?
Ans:
Active Directory, a Microsoft service within Windows environments, It functions as a directory service for user authentication and authorization, Alongside, it manages resources like computers, printers, and applications, Structured hierarchically, it organizes information for easy access, Active Directory centrally administers network resources and security policies, In essence, it’s pivotal for network administration and user management.
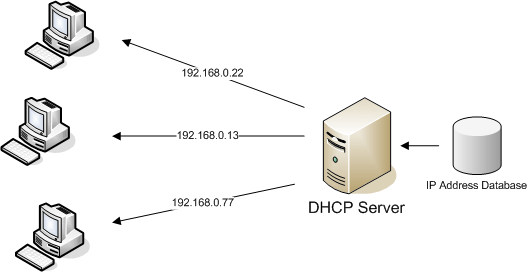
2. What is DHCP, and what is it used for?
Ans:
DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, automates IP address assignment, It assigns IP addresses and network configurations to devices automatically, Thereby obviating manual configurations for network devices, Ensuring efficient IP address allocation within a network, DHCP servers manage a pool of IP addresses, leasing them temporarily, DHCP significantly streamlines network administration and resource management.
3. Which are the OSI model layers arranged from the highest to the lowest?
Ans:
- Application
- Presentation
- Session
- Transport
- Network
- Data Link
- Physical
4. What is DNS?
Ans:
- Serving as the Internet’s address book, it maps human-readable names to numeric IPs,
- Resolving queries from clients seeking domain names for resource location,
- Operating in a distributed hierarchy, DNS servers are organized into zones,
- DNS is pivotal for internet navigation and resource accessibility,.
5. Is a Default Gateway necessary?
Ans:
Indeed, a Default Gateway is essential for external communication of devices; It serves as the entry and exit point for data packets entering or leaving the network, Routing packets to destinations beyond the local subnet: Without a Default Gateway, devices are confined to communicating within the local network. It’s an indispensable component for connectivity to external networks like the Internet, so a Default Gateway is imperative in most networking setups.
6. What differentiates desktop or client OS from server OS?
Ans:
| Feature | Desktop/Client OS | Server OS | |
| Purpose |
Designed for individual users for personal computing tasks |
Designed to manage resources, services, and data for multiple users or clients | |
| User Interface | Graphical User Interface (GUI) optimized for ease of use | Typically no GUI or minimal GUI, often controlled remotely via command line or web interface | |
| Hardware Resources |
Optimized for supporting a single user and a range of hardware configurations |
Optimized for managing server hardware with high performance, scalability, and reliability | |
| Application Support | Focus on supporting a wide range of end-user applications | Focus on running server applications and services, such as web servers, database servers, email servers, etc. |
7. What are an ‘A’ and an ‘MX records?
Ans:
An ‘A’ record in DNS indicates the mapping of a domain name to an IPv4 address, facilitating access to specific web servers or resources. Conversely, an ‘MX’ record designates the mail exchange server responsible for receiving email for a particular domain, enabling efficient email delivery and routing. Both ‘A’ and ‘MX’ records play critical roles in DNS configuration, ensuring proper resolution of domain names and efficient handling of web and email services within networks.
8. What is the IPCONFIG command?
Ans:
- IPCONFIG, a command-line tool in Windows, displays network configuration details,
- It reveals information such as IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway,
- IPCONFIG also provides data on DNS servers and network adapters,
- Frequently utilized for troubleshooting network connectivity issues,
- IPCONFIG can renew or release IP addresses assigned by DHCP servers,
9. Who is a desktop support engineer?
Ans:
- A desktop support engineer is an IT professional offering technical assistance to end-users,
- They resolve hardware and software issues concerning desktop computers,
- Tasks encompass troubleshooting, software installation, and system configuration,
- Integral to maintaining productivity, they ensure smooth desktop system operation,
10. What is SID (Security Identifier)?
Ans:
SID, or Security Identifier, is a unique alphanumeric identifier in Windows OS, Assigned to each object, including users, groups, or computer accounts, It forms the basis for access control and security policy enforcement, SIDs are crucial for authentication and authorization processes, They ensure security and integrity within Windows environments, SID serves as a fundamental element in maintaining Windows system security.
11. Is it possible to reach a client from a place other than the server?
Ans:
Yes, through methods like peer-to-peer connections and remote access protocols. Remote desktop applications enable accessing a client from a distance. Clients can communicate directly with appropriate permissions and configurations. The connectivity method depends on network infrastructure and security measures. Effective communication enhances collaboration and resource sharing.
12. How fast is a BUS?
Ans:
- Bus speed varies based on type and purpose within a computer system.
- Data transfer rates range from megabytes to gigabytes per second.
- High-speed buses like PCI Express (PCIe) are standard in modern systems.
- Critical for overall system performance.
- Technological advancements continuously improve bus speeds.
- Efficient data transmission ensures system responsiveness.
13. What do rights, policies, and permissions mean?
Ans:
- Rights grant privileges to users or groups for specific actions.
- Policies are rules and configurations for managing system behaviour.
- Permissions control access to resources like files and folders.
- They regulate actions such as reading, writing, and executing.
- Together, they form the security framework of an OS or network.
- The proper configuration ensures data integrity and system stability.
14. What is the “Windows Cannot Connect For Updates” issue, and are you familiar with it?
Ans:
This is a common issue when Windows Update fails to connect to Microsoft’s servers. It is caused by network problems, misconfigurations, or corrupted files. Troubleshooting involves checking connectivity and proxy settings. Resetting Windows Update components or performing a clean boot can help. Keeping software and drivers updated prevents recurrence. Addressing this promptly ensures system security and stability.
15. What exactly is a “Blue Screen of Death”?
Ans:
A “Blue Screen of Death” (BSOD) is an error screen displayed by Windows indicating critical system issues that can lead to crashes or instability. It presents diagnostic information, including error codes, to help identify the underlying problem. Common causes include hardware failures, driver issues, and software conflicts. Diagnosing the error details can aid in troubleshooting, and proper system maintenance can help minimize occurrences.
16. What distinguishes an.EXE file from an MSI file?
Ans:
- EXE is a standalone executable program.
- MSI is a package for software installation on Windows.
- .EXE runs instructions directly, while MSI handles installation tasks.
- MSI supports controlled deployment and management.
- Features like silent installations enhance deployment.
- .EXE focuses on execution, while MSI emphasizes installation.
17. What do you mean by “Safe Mode”?
Ans:
- The diagnostic mode in Windows loads essential files and drivers.
- Used to troubleshoot system issues.
- Only basic functionalities are available.
- Accessed during system startup or through advanced options.
- It helps repair errors or remove malware.
- Regular operation resumes upon exit.
18. What is forward and reverse lookup in DNS?
Ans:
DNS forward lookup translates domain names to IP addresses. When users input domain names, DNS performs forward lookups to find corresponding IPs. Conversely, reverse lookup resolves IP addresses to domain names. DNS performs both forward and reverse lookups, which are beneficial for verifying IP authenticity and troubleshooting. These functions ensure the resolution of both domain names and IP addresses.
19. What exactly do you mean by group policy?
Ans:
Feature in Windows for managing system settings across a network. Centralized control over user accounts, computer settings, and security. Settings are stored in Group Policy Objects and are linked to the Active Directory. Defines policies for user rights and software deployment. Ensures consistent configurations. Simplifies administration and enhances security.
20. Describe VPN Server.
Ans:
It’s a dedicated server designed to securely connect remote users to a private network. Establishing encrypted tunnels ensures safe data transmission. The server verifies user identities and encrypts all transmitted data. It allows remote users to access network resources from afar. With support for multiple protocols, it offers both flexibility and enhanced security. It provides a secure connection for users accessing the network remotely.
21. What is Active Directory?
Ans:
- Microsoft provides a directory service that manages network resources in Windows domains.
- Stores information about users, groups, computers, and resources.
- Enables centralized authentication and administration.
- Hosted on domain controllers, ensuring consistency.
- Administrators use tools like Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Integral for user authentication, access control, and resource management.
22. What is a subnet mask, and how is it used in networking?
Ans:
A subnet mask divides an IP network into subnetworks, specifying which portion of an IP address represents the network and which part represents the host. It enables devices to determine if an IP address is local or requires external routing. By defining network boundaries, subnet masks facilitate efficient data routing and management, ensuring organized and scalable network structures. Additionally, they support network security and performance by isolating different network segments.
23. What is the concept of port forwarding, and how is it explained?
Ans:
Port forwarding involves redirecting incoming network traffic from one port to another, typically on a router or firewall. It enables external access to services hosted on private networks, such as web servers or gaming consoles, by mapping specific ports to corresponding internal IP addresses and ports. This allows users outside the local network to connect to specific services running on devices within the network.
24. What is NAT, and how does it function?
Ans:
NAT (Network Address Translation) is a protocol for translating private IP addresses within a local network into public IP addresses visible on the Internet. It allows multiple devices within a private network to share a single public IP address, conserving IPv4 addresses and enhancing network security by masking internal network structures from external threats. NAT operates by modifying the source and destination IP addresses in data packets as they traverse between private and public networks.
25. Purpose of a firewall in security?
Ans:
- A firewall acts as a security barrier, controlling network traffic to prevent unauthorized access and protect against cyber threats.
- It regulates access based on predefined rules, blocking malicious traffic and safeguarding sensitive data.
- Firewalls monitor network activity, detect potential threats, and mitigate security risks.
26. What are the different RAID levels, and what is their significance?
Ans:
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) encompasses various data storage techniques designed to improve data reliability, availability, and performance. Standard RAID levels include RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10, each offering unique benefits such as data redundancy, striping, or a combination of both. RAID configurations enhance fault tolerance, mitigate data loss risks, and optimize storage efficiency in enterprise environments, ensuring continuous access to critical data and minimizing downtime.
27. What is the concept of VLANs and how are they used?
Ans:
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a logical segmentation of a physical network into multiple virtual networks. It enables isolated communication between devices within the same VLAN while restricting communication with devices in other VLANs. By logically grouping devices based on common characteristics or administrative requirements, VLAN enhances network security, efficiency, and scalability.
28. What are the differences between MAC addresses and IP addresses?
Ans:
- MAC (Media Access Control) addresses are unique identifiers assigned to network interface cards, identifying devices within a local network at the data link layer of the OSI model.
- On the other hand, IP (Internet Protocol) addresses are numeric labels assigned to devices for network communication, operating at the network layer of the OSI model.
- While MAC addresses are hardware-based and remain fixed for each device, IP addresses are logical addresses assigned dynamically or statically and can change based on network configuration or connectivity.
29. How do TCP and UDP differ from each other?
Ans:
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are transport layer protocols for data transmission over networks.
- TCP ensures reliable, ordered data delivery with error checking and congestion control mechanisms suitable for applications requiring guaranteed delivery, such as web browsing and file transfer.
- UDP, in contrast, offers fast, connectionless communication without error correction or flow control, ideal for real-time applications like streaming media or online gaming, where speed is prioritized over reliability.
30. What is the overview of the OSI model layers?
Ans:
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model defines a conceptual framework for understanding network communication processes, dividing them into seven distinct layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. Each layer performs specific functions, such as data encapsulation, routing, and protocol conversion, to facilitate end-to-end communication between devices across interconnected networks.
31. What are the key differences between a router and a switch?
Ans:
- Routers operate at OSI Layer 3, directing traffic between networks,
- Switches function at Layer 2, facilitating communication within a network.
- Routers make decisions based on IP addresses, while switches use MAC addresses,
- Routers offer complex routing functions like NAT and firewalls,
32. What is bandwidth, and why is it important?
Ans:
- Bandwidth denotes the maximum data transfer rate of a network or internet connection.
- It dictates the amount of data transmitted within a given time frame.
- Higher bandwidth ensures faster data transmission and better performance.
- Bandwidth directly impacts network responsiveness and user experience.
33. How does a DNS server handle the resolution process?
Ans:
When users enter domain names, their devices send DNS queries to DNS servers. DNS servers check their records for corresponding IP addresses. DNS servers return the IP addresses to the users’ devices if found. If not found, queries are forwarded to other DNS servers recursively. Once IP addresses are obtained, they’re cached for quicker future queries. Finally, devices utilize these IP addresses to connect to desired websites or services.
34. Whst is the Purpose and function of Proxy server?
Ans:
- A proxy server is an intermediary between users’ devices and the Internet.
- It enhances security by concealing users’ IP addresses and locations.
- Proxy servers can cache frequently accessed web pages, speeding up access.
- Proxy servers provide anonymity and privacy for users.
- They intercept client requests and forward them to destination servers.
35. What is the difference between a hub and a switch?
Ans:
- Hubs function at OSI Layer 1, broadcasting data to all connected devices.
- Switches operate at Layer 2, intelligently forwarding data to intended recipients.
- Hubs create a single collision domain, leading to network congestion.
- Hubs offer lower security and slower data transmission compared to switches.
- Switches deliver superior performance and scalability in modern networks.
36. What is the purpose of NAT in home routers?
Ans:
NAT enables multiple devices in a local network to share a single public IP address. It translates private IP addresses of local devices to a single public IP for internet communication. NAT bolsters security by concealing internal IP addresses from external networks. It conserves public IP addresses, allowing numerous devices to utilize one address simultaneously.
37. What is packet switching, and how does it work?
Ans:
Packet switching breaks data into small packets, each with a segment of the original data and routing information. These packets are sent independently across the network, potentially taking different paths, and are reassembled at the destination using the routing information. This method enhances network efficiency and resilience by optimizing data transmission and avoiding single points of failure.
38. What is the Explanation of DHCP?
Ans:
- DHCP leasing involves temporarily assigning IP addresses to devices on a network.
- DHCP servers dynamically allocate IP addresses from a pool to requesting devices.
- Leases typically have predetermined durations, after which they expire.
- Devices must periodically renew their leases to maintain network connectivity.
39. How does a DHCP server handle the process of assigning IP addresses?
Ans:
- When devices connect to a network, they send DHCP discover messages.
- DHCP servers respond with DHCP offers, providing available IP addresses.
- Devices then send DHCP requests to confirm the offered IP addresses.
- Upon confirmation, DHCP servers send DHCP acknowledgments.
- Devices configure their network settings with the assigned IP addresses.
40. What is the role of a network gateway in routing?
Ans:
A network gateway serves as an entry and exit point between different networks. It routes data between a local network and external networks like the Internet. Gateways perform protocol translation and encapsulation for data transmission. Gateways enforce security policies by filtering and inspecting incoming and outgoing traffic. They may also provide network address translation (NAT) for private network access to the Internet.
41. What is the purpose of a subnet and how is it used?
Ans:
Subnetting divides a network into smaller segments, which helps manage traffic more efficiently, improves organization and security, and simplifies troubleshooting and administration. Each subnet has its own network address, optimizing performance and enhancing overall network scalability. This segmentation also supports better control of network resources and policies.
42. What is IP routing and why is it significant?
Ans:
- IP routing forwards data packets between networks.
- It involves determining the optimal path for packet transmission.
- Routing protocols like OSPF or BGP are used for this.
- Significantly, routing connects disparate networks globally.
- It ensures data reaches its intended destination accurately.
43. How does DNS caching improve speed?
Ans:
- DNS cache stores recently accessed DNS records locally.
- This reduces the need to query external DNS servers.
- Consequently, it speeds up domain name resolution.
- Cached records are retrieved more swiftly.
- It enhances overall browsing and network performance.
44. What is the function of ARP in networking?
Ans:
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) maps IP addresses to MAC addresses. It ensures data is correctly routed within a local network and resolves IP addresses to their corresponding MAC addresses, which is crucial for communication within the same subnet. ARP operates at the Data Link layer of the OSI model. Essentially, ARP enables devices to communicate locally.
45. What is the Purpose of NAT traversal in VPN?
Ans:
NAT traversal allows VPN connections to pass through NAT devices. It overcomes the limitations posed by NAT on VPN traffic. NAT traversal techniques like UDP encapsulation are employed. Purposefully, it ensures seamless VPN connectivity over NAT-enabled networks. This is vital for remote access and site-to-site VPNs. Ultimately, NAT traversal enhances VPN interoperability.
46. What does QoS mean in network management and how is it explained?
Ans:
- Quality of Service (QoS) prioritizes network traffic.
- It ensures critical data receives preferential treatment.
- QoS mechanisms manage bandwidth allocation and congestion.
- This leads to optimized network performance.
- QoS enhances the user experience for applications.
47. How is the MAC address table related to switches?
Ans:
- MAC address tables are vital for switch operation.
- They store mappings of MAC addresses to switch ports.
- This enables switches to forward frames accurately.
- MAC tables are dynamically updated as devices connect.
- They facilitate efficient local network communication.
- MAC address tables form the basis of switch functionality.
48. What is the WINS server’s role in Windows networking?
Ans:
Windows Internet Name Service (WINS) resolves NetBIOS names to IP addresses, enabling seamless communication between Windows systems. WINS servers maintain a database of NetBIOS name-to-IP mappings, simplifying network resource access in Windows environments. WINS facilitates backward compatibility, especially in legacy setups. Overall, WINS servers streamline Windows networking.
49. What is the purpose of a network gateway in virtualized environments?
Ans:
- In virtualized environments, the network gateway connects virtual machines to external networks.
- It serves as the entry and exit point for VM traffic.
- The gateway facilitates communication between virtual and physical networks.
- It often performs network address translation (NAT) for outbound traffic.
- Additionally, it enforces security policies and firewall rules.
50. What are the differences between unicast, multicast, and broadcast?
Ans:
- Unicast transmits data from one sender to one receiver.
- Multicast delivers data from one sender to multiple specific receivers.
- Broadcast sends data from one sender to all devices within a network.
- Unicast is efficient for one-to-one communication.
- Multicast conserves bandwidth by targeting particular recipients.
- Broadcast is suitable for addressing all devices in a network segment.
51. How does a VPN tunnel ensure secure communication?
Ans:
A VPN tunnel secures data transmission through encryption, guaranteeing confidentiality and data integrity. User authentication protocols ensure secure access. The data travels through a protected channel, guarding against eavesdropping and tampering threats. It is widely employed for secure remote access and site-to-site connections, providing a crucial layer of security for sensitive communications.
52. What role does a network proxy play in filtering web traffic?
Ans:
A network proxy filters and controls web traffic requests as an intermediary between clients and servers. It can block unauthorized or malicious content. Enhances security and privacy measures within a network. Allows for caching and optimizing access speed. Commonly utilized in corporate networks for enforcing policy controls. Acts as a gatekeeper to ensure secure and regulated web communication.
53. What is the significance of the ARP cache?
Ans:
- The ARP cache stores mappings between IP and MAC addresses.
- It accelerates network communication by reducing lookup frequency.
- Devices need to locate each other on a local network.
- Facilitates efficient packet routing within the network.
- Vulnerable to ARP spoofing attacks if not properly secured.
54. What is the purpose of subnetting in IP addressing?
Ans:
- Subnetting divides a network into smaller, more manageable segments.
- It aids in the efficient allocation of IP addresses.
- Enhances network performance and security.
- Reduces broadcast traffic within segmented networks.
- Enables scalability and simplifies network management.
- It is crucial for effective IP address management in large networks.
55. What are the differences between static and dynamic routing protocols?
Ans:
- Administrators manually configure static routes.
- Dynamic routing protocols adjust routes automatically based on network changes.
- While static routing is more straightforward, it could be more adaptable to changes.
- Dynamic protocols like OSPF and BGP exchange routing information between routers.
- Dynamic routing scales better in large and dynamic networks.
- Examples of dynamic protocols include OSPF, BGP, and RIP.
56. What is the role of a DMZ in network security?
Ans:
The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) isolates untrusted external networks from internal ones. It hosts internet-facing services like web servers for added security. It provides an extra layer of security by segregating critical infrastructure and permitting controlled access to specific resources. Deploying a DMZ enhances overall network security. It is commonly integrated into firewall configurations for heightened security measures.
57. What is the role of a DHCP relay agent in large-scale networks?
Ans:
DHCP relay agents forward DHCP messages between clients and servers. They facilitate dynamic IP address allocation in subnets without DHCP servers, centralize DHCP server deployment in large networks, reduce broadcast traffic, and ease DHCP server load. They also ensure efficient IP address management, which is integral for maintaining seamless network connectivity in expansive networks.
58. How are DNS zones organized in terms of records?
Ans:
- It contains DNS records for a specific domain or subdomain.
- Organizes records like A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, and TXT.
- Facilitates delegation and efficient management of DNS data.
- Enhances DNS resolution efficiency and scalability.
- A critical component of internet naming and addressing infrastructure.
59. What is the purpose and function of a network switch?
Ans:
- A network switch connects devices within a local area network (LAN).
- Operating at the data link layer, it forwards data based on MAC addresses.
- Provides dedicated bandwidth to connected devices.
- Improves network performance compared to hubs.
- Enables secure and efficient data transfer within LANs.
- A fundamental component for local network connectivity.
60. What are the differences between half-duplex and full-duplex communication?
Ans:
- In half-duplex, communication occurs in both directions but not simultaneously.
- Half-duplex devices can’t send and receive data simultaneously.
- Full-duplex communication requires separate channels for sending and receiving.
- Full-duplex typically offers higher throughput than half-duplex.
61. What is the significance of VLAN tagging in network segmentation?
Ans:
VLAN tagging is crucial in segregating network traffic and enhancing security and transmission efficiency. It logically divides networks into distinct segments, Facilitating better management and control. Furthermore, it aids in prioritizing traffic flow While simplifying maintenance tasks within the network.
62. What is network segmentation and what are its benefits?
Ans:
Network segmentation involves dividing networks into smaller, manageable sections, It offers various benefits, such as heightened security and improved performance. It isolates critical systems and sensitive data, Reducing the potential impact of security breaches or system failures. Additionally, it enhances network efficiency And provides better control and oversight of network resources.
63. Explain the role of a network administrator.
Ans:
- Network administrators are tasked with the management of computer networks,
- Ensuring seamless operation and functionality.
- Their duties encompass configuring, monitoring, and maintaining network equipment,
- Along with troubleshooting issues and implementing security measures.
- Furthermore, they oversee network performance,
- And ensure adherence to organizational policies and standards.
64. What is a network protocol, and what are its types?
Ans:
A network protocol establishes rules and standards for communication between devices, Governing the exchange of data within a network. Varieties include TCP/IP, UDP, HTTP, and FTP, Each serving specific purposes and functionalities. These protocols dictate the formatting and transmission of data, Enabling efficient exchange between network entities.
65. What is the purpose of subnet masks?
Ans:
- Subnet masks define the boundaries of IP networks,
- Distinguishing between network and host portions of an IP address.
- They determine which part of an IP address pertains to the network,
- And which portion identifies individual hosts within that network.
- Subnet masks facilitate efficient data routing,
- By directing traffic within the appropriate network segments.
66. How does a network switch function?
Ans:
- A network switch connects devices within a local network,
- Utilizing hardware addresses to route data accurately.
- Operating at the data link layer of the OSI model,
- It scrutinizes incoming data packets and forwards them accordingly.
- By minimizing collisions and providing dedicated bandwidth,
- Switches enhance network performance and efficiency.
67. What is a MAC address, and why is it important?
Ans:
A MAC address is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces, E. It enablesmmunication within a specific network segment. I distinguish devices from one another and facilitate case the routing of data packets.MAC addresses play a pivotal role in network communication and security, Preventing unauthorized access and ensuring accurate data delivery.
68. What are the Difference between public and private IP addresses.
Ans:
- ISPs assign public IP addresses, globally unique identifiers allowing devices to connect over the Internet.
- Conversely, private IP addresses are only meant for internal usage on a network.
- Unavailable over the Internet directly.
- Private IP addresses can only be used within a network; public IP addresses enable communication.
69. What is a DNS resolver, and what is its function?
Ans:
A DNS resolver converts domain names into corresponding IP addresses, facilitating communication between clients and servers on the Internet. It queries DNS servers to obtain IP address information, streamlining internet usability and efficiency. By resolving domain names, DNS resolvers simplify access to resources, making browsing and connectivity more seamless.
70. How does DHCP lease renewal work?
Ans:
- DHCP lease renewal occurs when a client device seeks to extend its IP lease,
- I am contacting the DHCP server for an extension.
- The DHCP server may grant the renewal request,
- We are extending the duration of the client’s IP address lease.
- Failure to renew the lease results in the IP address returning to the available pool,
- You are allowing other devices within the network to utilize it.
71. What is the purpose of a network bridge?
Ans:
A network bridge facilitates communication between different network segments by forwarding data packets. It operates at the data link layer of the OSI model, enhancing connectivity and extending network coverage. Analyzing MAC addresses efficiently directs traffic, reduces congestion, and optimizes network performance. Additionally, it helps integrate and manage disparate network segments, improving overall network organization and efficiency.
72. Explain the concept of network latency.
Ans:
Network latency refers to the delay in data transmission between a source and destination over a network. It encompasses factors such as propagation delay, processing delay, and queuing delay. Lower latency indicates quicker data transfer, which is crucial for real-time applications like gaming and video conferencing. Reducing latency improves the responsiveness and overall user experience in network communications.
73. What is a network interface card (NIC)?
Ans:
- A network interface card (NIC) is a hardware component that enables a device to connect to a network.
- It serves as the interface between the device and the network, facilitating communication by converting data into a format suitable for transmission over the network.
74. What is the role of a network router?
Ans:
A network router directs data packets between different networks based on their IP addresses, operating at the network layer of the OSI model. It determines the optimal path for data transmission, ensuring efficient traffic management and connectivity. Routers also provide security features by controlling and filtering traffic between networks, which helps protect against unauthorized access and network threats.
75. What impact does ARP poisoning have on network security?
Ans:
ARP poisoning involves manipulating the ARP table to redirect network traffic, which can lead to significant security breaches. This attack allows malicious actors to intercept, alter, or eavesdrop on data transmitted between devices, compromising both confidentiality and data integrity. Implementing ARP spoofing detection and prevention measures is essential to safeguard against these threats and maintain network security.
76. What is the role of a network gateway?
Ans:
A network gateway serves as the entry and exit point for data traveling between different networks or network segments, facilitating communication across various protocols or architectures. It ensures seamless connectivity and interoperability between disparate network systems. Additionally, it often performs tasks like protocol translation, traffic filtering, and network address translation (NAT) to enhance overall network functionality and security.
77. What is the concept of network topology?
Ans:
- Network topology refers to the arrangement of nodes and connections in a network.
- It defines how devices are interconnected, such as in a bus, star, ring, or mesh topology.
- Understanding network topology is vital for effectively designing, managing, and troubleshooting networks.
78. What is a ping command used for?
Ans:
The ping command tests the connectivity between two network devices by sending ICMP echo request packets. It measures the round-trip time for data to travel from the source to the destination and back. Ping is a fundamental tool for diagnosing network issues, assessing network performance, and checking the availability of networked systems.
79. Describe the function of a network hub.
Ans:
A network hub is an essential networking device that connects multiple devices in a network and allows them to communicate. It operates at the physical layer of the OSI model, broadcasting data to all connected devices indiscriminately. However, it needs more intelligence for efficient traffic management, making it less commonly used in modern networks.
80. What is a default route in networking?
Ans:
- A default route, a gateway of last resort, is a routing table entry used by a device to forward packets when no specific route matches the destination IP address.
- It directs traffic to a predefined destination, typically the gateway or router responsible for forwarding packets to external networks.
- Default routes enable devices to communicate beyond their local network.
81. What is the concept of network redundancy?
Ans:
Network redundancy involves duplicating vital network elements to ensure reliability and fault tolerance. In case of component failure, redundant counterparts seamlessly take over, preventing downtime and maintaining continuous network functionality. This proactive approach enhances infrastructure resilience, minimizing disruptions and meeting the demands of modern digital environments.
82. What is the role of a DNS forwarder?
Ans:
DNS forwarders streamline DNS queries by directing them from clients to external DNS servers, optimizing resolution efficiency and security. Through caching responses and filtering requests, they enhance overall DNS performance and protect against potential threats. Additionally, forwarders reduce the load on internal DNS servers by offloading query processing.
83. Explain the difference between TCP and UDP ports.
Ans:
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) ports are crucial communication endpoints in networking. TCP ports ensure reliable, ordered data delivery, maintaining integrity through sequence control and acknowledgment mechanisms. In contrast, UDP ports prioritize speed but sacrifice reliability, as they transmit data without ensuring delivery or sequence preservation, making them ideal for real-time applications where speed is paramount over reliability.
84. What is a subnet calculator used for?
Ans:
- A subnet calculator aids in partitioning a network into smaller, manageable subnets by determining suitable subnet masks and address ranges.
- This assists in efficient IP address allocation and network organization.
85. What is the purpose of a network load balancer?
Ans:
Network load balancers evenly distribute incoming traffic among multiple servers, ensuring optimal resource utilization and preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. By spreading the workload, they enhance reliability and minimize the risk of downtime due to server overload, ultimately improving the overall performance and availability of the network infrastructure.
86. How does a network packet sniffer work?
Ans:
- A packet sniffer intercepts and records network traffic traversing a specific interface, capturing data packets for analysis.
- It reveals packet contents, source/destination addresses, and protocols employed, aiding network troubleshooting and security monitoring.
87. What is the purpose of a network bridge?
Ans:
A network bridge serves as a vital link, seamlessly connecting disparate network segments and enabling the transfer of data between them at the OSI model’s data link layer, also known as Layer 2. By extending the network infrastructure, bridges facilitate seamless communication and collaboration across various segments, fostering efficient data exchange and enhancing connectivity throughout the network architecture.
88. What is bandwidth throttling, and how does it work?
Ans:
Bandwidth throttling, often employed by ISPs or network administrators, intentionally restricts internet connection speeds for various purposes. This practice is utilized to effectively manage data consumption, alleviate network congestion, or prioritize certain types of traffic over others based on specific requirements or policies. By regulating the flow of data, bandwidth throttling helps maintain stable network performance and ensures equitable access to available resources.
89. What is the significance of a network diagram?
Ans:
- A network diagram visually depicts a network’s topology, connections, and components.
- It aids in planning, troubleshooting, and documenting network infrastructure, facilitating efficient management and maintenance.
90. What is the role of a network proxy server, and how does it benefit network management?
Ans:
A network proxy server acts as an intermediary between clients and external servers, intercepting and fulfilling client requests on their behalf. It enhances security, privacy, and performance by caching data, filtering content, and masking client IP addresses. Additionally, it helps in monitoring network usage, enforcing access policies, and can provide detailed analytics on traffic patterns.
91. How does network encryption enhance security?
Ans:
Network encryption boosts security by scrambling data transmitted over networks, rendering it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Through encryption algorithms, sensitive information remains protected, thwarting interception and tampering attempts, thus ensuring confidentiality and integrity. This safeguarding measure fortifies network communication against eavesdropping and data breaches.
92. What is the purpose of network caching?
Ans:
- Network caching stores frequently accessed data,
- We are reducing the need to fetch it from distant servers.
- It accelerates data retrieval, enhancing network performance,
- We are conserving bandwidth and lowering user latency.
- By storing copies of data locally, it optimizes resource usage,
- We are improving overall efficiency and user experience.
93. Describe the function of a network repeater.
Ans:
A network repeater regenerates incoming signals, amplifying and retransmitting them to extend the network’s reach. It boosts signal strength, combating attenuation over long distances and enabling data transmission over larger areas or through obstacles. Operating at the physical layer enhances communication reliability, ensuring data integrity and minimizing packet loss effectively.
94. What is the purpose of a network traceroute?
Ans:
- Network traceroute maps the route packets take
- From a source to a destination across the network.
- It identifies each hop and measures transit time,
- We are aiding in network troubleshooting and performance analysis.
- By revealing network topology and potential bottlenecks,
- It helps optimize routing and diagnose connectivity issues efficiently.
95. What is the concept of a network broadcast domain?
Ans:
A network broadcast domain comprises all devices that receive broadcast messages within a network segment. Broadcasts are packets sent to all devices in the domain, facilitating communication between nodes without specifying recipients. Segmentation of broadcast domains limits broadcast traffic, improving network efficiency by reducing unnecessary data transmission.
96. How does a network switch differ from a network router?
Ans:
- A network switch manages local network communication using MAC addresses, while a router connects different networks using IP addresses.
- Switches facilitate communication within LANs, while routers enable data transmission between LANs and the Internet.
- Switches forward data within the same network, creating one broadcast domain, while routers create multiple broadcast domains for different networks.
97. What is the scope and super scope?
Ans:
- In DHCP, a scope delineates a range of assignable IP addresses,
- It encompasses configuration details like subnet mask and default gateway,
- A Super Scope amalgamates multiple scopes for DHCP server management,
- Permitting management of multiple IP address ranges effectively,
- Super Scope facilitates flexible IP address assignment management,



