
Design Thinking is an innovation methodology centered around the human experience, emphasizing empathy, creativity, and iterative problem-solving. It entails grasping user needs, questioning assumptions, and fostering innovative solutions through collaborative brainstorming and prototyping. By prioritizing empathy and user input, Design Thinking empowers teams to create products, services, and processes that authentically cater to people’s needs and aspirations.
1. What is Design Thinking?
Ans:
Design Thinking is an innovation methodology centred on human needs. It emphasizes empathy, ideation, and iteration to creatively tackle complex problems. It involves deeply understanding users’ needs, generating diverse ideas, creating prototypes, and iteratively testing them to achieve desirable outcomes. This approach fosters collaborative problem-solving and encourages continuous refinement to drive impactful solutions.
2. Which tools are employed in the process of design thinking?
Ans:
Tools commonly employed in Design Thinking include empathy maps, journey maps, brainstorming sessions, prototyping tools, and various user testing methods. These tools facilitate understanding, creativity, and validation of solutions throughout the design process. Additionally, they help in iterating designs based on user feedback and evolving requirements.
3. Why Design Thinking?
Ans:
Design Thinking fosters a profound understanding of user needs, promotes collaborative and creative problem-solving, and ultimately leads to innovative solutions that resonate with users. It provides a structured yet flexible approach to innovation, enabling organizations to tackle complex challenges effectively. Additionally, it encourages empathy and iterative testing, ensuring that solutions are refined and aligned with real-world user feedback.
4. How do Design Thinking and user experience design relate to each other?
Ans:
- Design Thinking provides the framework for understanding user needs and ideating solutions, while user experience design focuses on creating seamless interactions between users and products.
- Both approaches prioritize empathy, iteration, and user feedback to deliver meaningful, user-centric experiences.
- Additionally, they integrate cross-disciplinary insights to address diverse aspects of user interactions and needs comprehensively.
5. What are the Design Thinking stages?
Ans:
- Design Thinking typically encompasses five stages: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test.
- These stages involve understanding user needs, defining the problem, generating ideas, building prototypes, and testing solutions iteratively.
- Additionally, the process often includes refining and implementing solutions based on feedback and insights gathered throughout the stages.
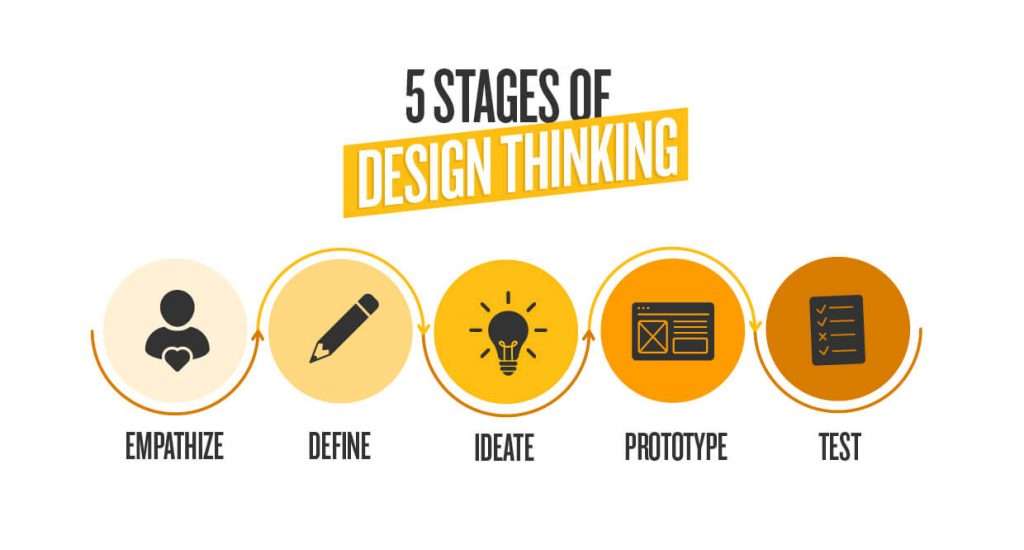
6. What benefits can applying Design Thinking bring to the workplace?
Ans:
- Implementing Design thinking in the workplace can cultivate a culture of innovation, enhance collaboration among team members, and result in solutions more attuned to user needs.
- It encourages experimentation, mitigates the fear of failure, and enhances organizational problem-solving skills.
- Additionally, it drives continuous learning and adaptation, helping teams to stay agile and responsive to evolving market demands.
7. What is the distinction between problem-based and solution-based Thinking?
Ans:
| Aspect | Problem-Based Thinking | Solution-Based Thinking | |
| Approach |
Analytical approach to dissecting the problem’s root causes |
Creative approach to ideating and developing potential solutions | |
| Questioning | Focuses on asking questions to understand the problem deeply | Shifts towards asking questions to generate innovative solutions | |
| Iterative Process |
Often iterative, requiring continuous refinement of problem understanding |
Iterative, involving ongoing iteration and improvement of solutions | |
| Outcome | Aims to accurately define the problem before proposing solutions | Aims to develop effective solutions to address the defined problem |
8. What distinguishes Design thinking from other forms of thought?
Ans:
Design Thinking distinguishes itself by emphasizing empathy, iteration, and user-centric problem-solving. It prioritizes understanding user needs, generating innovative solutions, and testing prototypes iteratively, setting it apart from linear or purely analytical approaches. This approach fosters a more holistic view, integrating user feedback at every stage to refine and enhance the final solution.
9. What are the design thinking principles?
Ans:
- Design Thinking principles encompass empathy, iteration, collaboration, optimism, and a bias toward action.
- These principles guide the approach to problem-solving, urging designers to deeply understand users, iterate on ideas, collaborate effectively, maintain a positive outlook, and take tangible steps toward solutions.
- Additionally, they emphasize a focus on holistic solutions, addressing both functional and emotional aspects of the user experience.
10. Enumerate the reasons why design thinking is ineffective.
Ans:
- Design Thinking may falter if not implemented with genuine empathy and a focus on user needs.
- Other reasons for ineffectiveness include lack of interdisciplinary collaboration, insufficient iteration and Testing, rigid adherence to process at the expense of creativity, and organizational resistance to change.
- Additionally, failing to align the design process with strategic business objectives can undermine its effectiveness.
11. Who is capable of doing it (design thinking)?
Ans:
Individuals who embrace empathy, innovation, and iteration can participate in design thinking, which extends beyond designers to encompass diverse teams, leaders, and individuals from various industries, fostering collaborative problem-solving abilities and approaches. This inclusive approach not only drives creativity but also leads to more effective and user-centered solutions.
12. How can Design Thinking be implemented in a company?
Ans:
Initiate a cultural shift valuing creativity and iterative processes, then embed Design Thinking across the organization, spanning from product development to customer service. Encourage cross-functional collaboration and empower employees to experiment and iterate freely. Foster an environment where feedback is actively sought and used to continuously improve processes and solutions.
13. What kinds of problems can design Thinking solve?
Ans:
- Design thinking is adept at tackling.
- Complex, human-centred problems ranging from
- Product design to process enhancement. It
- Excels in navigating ambiguous issues, nurturing
- Innovation, and uncovering latent user needs,
- Resulting in more viable and impactful solutions.
14. What is the best way to get started with design thinking?
Ans:
- Initiate by profoundly understanding users’ needs.
- Through empathetic immersion, then proceed to
- Ideation, prototyping, and Testing. Cultivate
- A mindset of curiosity and experimentation,
- Encouraging a culture conducive to creative
- Problem-solving endeavours and iterative approaches.
15. What distinguishes design thinking from project-based learning?
Ans:
Design thinking prioritizes empathy, iteration, And user-centric problem-solving, contrasting with project-based learning that focuses on completing. Specific tasks or projects within defined parameters. While design thinking is iterative and emphasizes understanding and solving real-world problems, project-based learning often has predetermined objectives or goals.
16. List out the four essential pillars of design thinking.
Ans:
- Empathy, which involves understanding users’ needs deeply,
- Define where the problem is articulated,
- Ideate, fostering creativity through brainstorming sessions,
- And prototype, transforming ideas into tangible solutions,
- Followed by Testing and iterating based on feedback,
- Establishing a continuous improvement loop.
17. What are the benefits of design thinking?
Ans:
Design thinking fosters innovative problem-solving, enhances empathy and understanding of users, promotes collaboration among diverse teams, and results in more human-centered and practical solutions. It encourages experimentation and iteration, ultimately driving business success and growth, while also adapting to evolving market needs and user expectations.
18. Give some examples of design-led businesses.
Ans:
Apple is known for its sleek, intuitive product designs; Airbnb revolutionized hospitality with a user-centric platform; Tesla combines technology with elegant electric vehicle design; IDEO is a global consultancy solving complex challenges through design; Nike excels in innovative shoe designs and branding strategies; and Google prioritizes user experience in its products and services.
19. What is the ideate phase in the design thinking process?
Ans:
- Ideate is where creativity flourishes,
- Teams generate a plethora of ideas without
- Judgment, aiming for diversity and quantity.
- Techniques such as brainstorming, mind mapping,
- Sketching is utilized to explore
- Innovative solutions to the defined problem,
- Setting the stage for prototyping and Testing.
20. Describe the empathy stage in design thinking.
Ans:
Empathy is fundamental in design thinking. It involves a deep understanding of users’ needs, Desires, and behaviours through observation, interviews, And immersion. It necessitates setting aside assumptions, actively listening, and empathizing with users’ perspectives, ensuring solutions are genuinely human-centred and address actual pain points.
21. How does Design Thinking drive innovation in organizations?
Ans:
Design Thinking fosters a culture of creativity by prioritizing empathy. It encourages the exploration of unconventional solutions to complex problems. Through iterative processes, it rapidly refines ideas and prototypes. It empowers teams to embrace failure as a means of learning and improvement. Design Thinking integrates diverse perspectives, leading to holistic innovations. Ultimately, it drives organizational growth by consistently delivering user-centric solutions.
22. Real-world successes of Design Thinking?
Ans:
- Airbnb’s redesign of its website and user experience led to exponential growth.
- IBM’s transformation of its approach to enterprise software design enhances usability.
- The redesign of the emergency room experience at the Mayo Clinic improved patient care.
- Procter & Gamble’s creation of the Swiffer revolutionized the home cleaning industry.
- The development of the iPhone by Apple set new standards for mobile technology.
- The OXO Good Grips kitchen tools were redesigned, making them accessible to all users.
23. Design Thinking’s impact on customer-centric solutions?
Ans:
- Design Thinking ensures a deep understanding of customer needs through empathy.
- It enables the creation of solutions tailored to specific user experiences.
- By iterating based on user feedback, it continuously improves customer satisfaction.
- Design Thinking fosters long-term relationships by addressing evolving needs.
- It facilitates the delivery of intuitive and user-friendly products and services.
24. What is the role of iteration in Design Thinking?
Ans:
Iteration allows for continuous refinement of ideas and prototypes. It enables teams to gather feedback and incorporate user insights. Through iteration, Design Thinking mitigates risks by testing and validating assumptions. It encourages experimentation and the exploration of alternative solutions. Iteration fosters a culture of learning and adaptability within organizations. Ultimately, it leads to the development of more effective and innovative solutions.
25. How is collaboration promoted through Design Thinking?
Ans:
Design Thinking encourages interdisciplinary teams to work together. It provides a structured framework for open communication and idea sharing. Collaborative workshops and brainstorming sessions are integral to the process. By valuing diverse perspectives, it fosters a culture of inclusion and creativity. Design Thinking promotes collective ownership of solutions and outcomes. Ultimately, it strengthens team dynamics and enhances problem-solving capabilities.
26. Common challenges in implementing Design Thinking?
Ans:
- Resistance to change and entrenched organizational culture.
- Limited resources and time constraints for experimentation and iteration.
- Difficulty in maintaining momentum and enthusiasm throughout the process.
- Siloed Thinking and need for cross-functional collaboration.
- Misalignment between Design Thinking goals and broader business objectives.
- Overemphasis on ideation without sufficient focus on implementation and execution.
27. Addressing diverse user needs in Design Thinking?
Ans:
- Design Thinking emphasizes empathy to understand diverse user perspectives.
- It involves stakeholders from various backgrounds throughout the process.
- Techniques like user personas and journey mapping help identify unique needs.
- Iterative prototyping allows for feedback and iteration based on diverse inputs.
- Design Thinking fosters a culture of inclusivity and accessibility.
- Ultimately, it ensures that solutions are tailored to meet the needs of all users.
28. Importance of prototyping in Design Thinking?
Ans:
- Prototyping allows for early Testing and validation of ideas.
- It enables stakeholders to visualize concepts and provide feedback.
- Prototypes facilitate communication and alignment among team members.
- Through the iteration of prototypes, Design Thinking refines solutions iteratively.
- Prototyping reduces risks by uncovering potential flaws and usability issues.
- Ultimately, it leads to the development of more robust and user-centric solutions.
29. Measuring success in Design Thinking initiatives?
Ans:
The impact on user experience and satisfaction measure success in Design Thinking. Key metrics may include usability, customer retention, and Net Promoter Score. Qualitative feedback through user interviews and observations informs success. Iterative progress and the ability to pivot based on feedback are indicators. Successful implementation of solutions that address identified needs.
30. How is human-centered problem-solving encouraged with Design Thinking?
Ans:
It emphasizes empathy to develop solutions that resonate with human experiences. Iterative processes allow for refinement based on user feedback and insights. Design Thinking promotes creativity and divergent Thinking in problem-solving. It fosters a culture where users are actively involved in shaping solutions. Ultimately, it leads to the development of more meaningful and impactful innovations.
31. Storytelling’s role in Design Thinking?
Ans:
- Storytelling in Design Thinking helps convey insights and solutions.
- It creates empathy and understanding among stakeholders.
- It frames problems and solutions in a compelling narrative.
- It facilitates collaboration and alignment within teams.
- It engages stakeholders emotionally, driving action and buy-in.
- It aids in communicating complex ideas simply and memorably.
32. Adapting Design Thinking to different industries?
Ans:
- Understand industry-specific challenges and user needs.
- Tailor methodologies and tools to fit industry contexts.
- Collaborate with domain experts for insights and guidance.
- Iterate and refine approaches based on industry feedback.
- Emphasize flexibility and experimentation in implementation.
- Continuously evaluate and adjust strategies for optimal results.
33. Design Thinking in non-design fields?
Ans:
Apply human-centred methodologies to problem-solving—Foster creativity and innovation across diverse disciplines. Prioritize user needs and experiences in decision-making. Promote collaboration and empathy among stakeholders. Adapt design processes to suit specific industry requirements. Drive solutions that effectively address complex challenges.
34. Identifying unmet user needs with Design Thinking?
Ans:
Conduct in-depth user research to uncover latent needs. Empathize with users to understand their perspectives deeply. Employ techniques like interviews, observations, and surveys. Analyze data to identify patterns and pain points—iterate and prototype solutions based on user feedback. Continuously validate and refine solutions to meet evolving needs.
35. “Fail fast, fail cheap” in Design Thinking?
Ans:
- Encourage experimentation and rapid prototyping.
- Embrace failure as an opportunity for learning and growth.
- Test ideas quickly and inexpensively to gather insights.
- Iterate based on feedback to improve solutions iteratively.
- Minimize investment in unsuccessful concepts early in the process.
- Foster a culture that values iteration and resilience.
36. Action bias in Design Thinking?
Ans:
- Prioritize action and experimentation over prolonged analysis.
- Encourage quick iteration and prototyping to drive progress.
- Emphasize learning through doing and feedback.
- Cultivate a bias towards tangible outcomes and solutions.
- Foster a culture that values agility and adaptability.
- Balance action with reflection to optimize decision-making.
37. What is the misconceptions about Design Thinking?
Ans:
Viewing it solely as a linear, step-by-step process, believing it’s exclusive to Design or creative industries, assuming it’s a one-size-fits-all solution to all problems, underestimating the importance of rigorous research and analysis, overlooking the need for cross-disciplinary collaboration, and neglecting the emotional and empathetic aspects of the process.
38. How is Design Thinking integrated with agile and lean methodologies?
Ans:
Integrate iterative design cycles with agile development methodologies. Incorporate rapid user feedback loops into development cycles. Highlight the importance of flexibility and adaptability within both approaches. Encourage collaboration among Design, development, and product teams. Leverage lean principles to optimize workflows and reduce inefficiencies. Commit to ongoing iteration and enhancement of products guided by user insights.
39. Empathy’s role in creativity in Design Thinking?
Ans:
- Empathy fosters a deeper understanding of user needs.
- It inspires innovative solutions that resonate with users.
- Empathetic Design encourages inclusivity and accessibility.
- It drives human-centered approaches to problem-solving.
- Empathy promotes collaboration and co-creation with stakeholders.
- It fuels a passion for making meaningful impacts on people’s lives.
40. Creating a Design Thinking culture in organizations?
Ans:
- Promote leadership support and commitment to design thinking.
- Encourage a mindset of curiosity, experimentation, and iteration.
- Foster cross-functional collaboration and empathy.
- Celebrate and recognize successes and lessons learned.
- Embed design thinking principles into organizational processes and values.
41. Key characteristics of successful design thinkers?
Ans:
Flexibility involves adapting based on feedback, empathy means deeply understanding users’ perspectives, creativity is about generating inventive solutions, collaboration entails working seamlessly in diverse teams, and iteration embraces a cycle of testing, refining, and retesting, all of which together drive continuous improvement and innovation.
42. Role of observation in design thinking?
Ans:
Observing helps designers grasp user behaviours and needs accurately. It uncovers insights crucial for effectively informing design decisions. Through observation, designers identify pain points and potential areas for improvement. It fosters empathy by allowing designers to see the world from users’ viewpoints. Observation fuels ideation by revealing unmet needs and preferences. Designers can refine their approaches by observing how users interact with their designs.
43. Contribution of design thinking to product innovation?
Ans:
Design thinking prioritizes human-centred approaches to problem-solving. It fosters a deep understanding of user needs, leading to more relevant products. Iterative prototyping enables the refinement of innovative ideas into viable products. Creative ideation generates fresh solutions to challenges, driving innovation. Design thinking promotes a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation. Ultimately, it results in products that better meet users’ evolving needs.
44. Strategies for overcoming resistance to change with design thinking?
Ans:
- Engage stakeholders early in the design process to foster ownership.
- Showcase the benefits and positive outcomes associated with change.
- Utilize storytelling to illustrate the necessity and potential of change.
- Involve individuals in the design process to increase their investment in the outcome.
- Begin with small, manageable changes to build momentum and confidence.
- Provide ample support and resources to facilitate the transition effectively.
45. Using design thinking to enhance customer engagement?
Ans:
- Understanding customer needs deeply through empathy-driven research.
- Crafting solutions that directly address identified pain points and desires.
- Encouraging co-creation by involving customers in the design process.
- Iterating rapidly based on customer feedback to enhance engagement.
- Placing the customer at the center ensures more meaningful and lasting engagement.
46. Importance of input in design thinking?
Ans:
Feedback offers invaluable insights for refining and enhancing designs. It serves as a validation mechanism for assumptions and ideas. Incorporating feedback ensures designs remain user-centric and effective. Early and frequent feedback minimizes the risk of costly errors and missteps. Iterative feedback loops enable continuous improvement and iteration. Ultimately, feedback ensures that designs meet user needs and expectations proficiently.
47. What is the significance of divergent and convergent Thinking in Design?
Ans:
- Divergent Thinking fosters the exploration of a broad range of ideas and possibilities.
- Convergent Thinking aids in focusing and refining the multitude of generated ideas.
- Divergent Thinking fuels creativity and encourages innovative approaches.
- Convergent Thinking facilitates decision-making and prioritization of ideas.
- Both divergent and convergent Thinking are pivotal for the iterative design process.
- Balancing these thinking modes leads to the development of impactful and inventive solutions.
48. Applying design thinking to social and environmental challenges?
Ans:
- Design thinking promotes empathy toward affected communities and ecosystems.
- It facilitates creative problem-solving to tackle complex social and ecological issues.
- Stakeholder engagement ensures that solutions are inclusive and sustainable.
- Prototyping allows for testing and refining solutions in real-world contexts.
- Collaboration across disciplines enables the creation of holistic and practical solutions.
- Ultimately, design thinking empowers communities to actively participate in solving their challenges.
49. Incorporating Design thinking into education?
Ans:
Curriculum Integration involves infusing Design thinking into various subjects. Project-based learning involves assigning real-world projects to apply design thinking. Design Challenges involve tasking students with problem-solving challenges. Collaborative Learning Fosters teamwork and diverse perspectives. Empathy Development involves encouraging understanding of others’ needs. Prototyping and Testing involve iterating solutions based on feedback.
50. The intersection of design thinking and digital transformation?
Ans:
- Design thinking informs user-centric approaches to digital product development.
- It ensures that technology solutions effectively address user needs and preferences.
- Rapid prototyping facilitates agile development processes essential for digital transformation.
- Iterative improvement based on user feedback drives innovation in digital experiences.
- Design thinking emphasizes the importance of user satisfaction and engagement in digital solutions.
51. What is the concept of “design sprints” in design thinking?
Ans:
Design sprints are intensive workshops for rapid ideation, prototyping, and Testing. Lasting five days, they encourage cross-functional collaboration for efficient problem-solving. By focusing on tangible outcomes, they accelerate innovation and reduce time to market. Design sprints promote creativity and user-centred solutions within a condensed timeframe. They offer a structured approach to applying design thinking principles to real-world challenges.
52. Ethical considerations in design thinking?
Ans:
Ethical principles like transparency, inclusivity, and social responsibility are vital. Designers must consider the impacts on diverse stakeholders and communities. Issues like data privacy, environmental sustainability, and cultural sensitivity need attention. Mitigating biases and avoiding harmful stereotypes is crucial. Thorough ethical evaluations ensure design thinking contributes to positive societal outcomes.
53. Design thinking’s impact on brand differentiation?
Ans:
- Design thinking creates unique and meaningful experiences for customers, aiding brand differentiation.
- By empathizing with user needs, companies develop standout products and services.
- Design-led innovation builds brand loyalty through memorable interactions.
- Iterative refinement aligns offerings with evolving market demands.
- Ultimately, design thinking fosters distinctive brand identities and competitive advantage.
54. Successful design thinking projects in healthcare?
Ans:
- Redesigning hospital layouts and signage reduces patient stress and confusion.
- Health apps enable remote monitoring, improving patient care.
- Innovative medical devices enhance treatment adherence and engagement.
- Improved communication channels between providers and patients ensure better understanding.
- These examples showcase design thinking’s ability to address complex healthcare challenges effectively.
55. How does design thinking maintain organizational relevance?
Ans:
Empathy maps deepen insights into user thoughts, feelings, and motivations. They visually represent user personas, highlighting pain points and behaviors. By empathizing with users, designers identify opportunities to enhance satisfaction. Empathy maps foster collaboration and a shared understanding among team members, ultimately leading to more user-centered and effective solutions.
56. What is the role of empathy maps in understanding user needs?
Ans:
Empathy maps deepen insights into user thoughts, feelings, and motivations. They visually represent user personas, highlighting pain points and behaviors. By empathizing with users, designers identify opportunities to enhance satisfaction. Empathy maps foster collaboration and a shared understanding among team members.
57. Fostering innovation culture through design thinking?
Ans:
- Design thinking fosters an innovation culture by promoting openness, experimentation, and collaboration.
- Diverse perspectives and cross-functional collaboration stimulate creativity.
- Leadership support and employee empowerment are crucial.
- Design thinking workshops and training programs provide platforms for innovative exploration.
58. Storytelling’s role in communicating design solutions?
Ans:
- Storytelling conveys the narrative behind design solutions, engaging stakeholders emotionally.
- It communicates user experiences, benefits, and impact effectively.
- By framing solutions within compelling narratives, designers inspire stakeholder support.
- Storytelling humanizes the design process, making it relatable and understandable.
- Ultimately, it enriches communication, driving empathy, understanding, and adoption.
59. Strategies for promoting a user-centred mindset?
Ans:
Engaging directly with users through interviews and observation builds empathy. Interdisciplinary collaboration ensures diverse perspectives are considered. Iterative prototyping and Testing validate assumptions and refine solutions. Creating a culture that values user-centricity reinforces this mindset. Ultimately, placing users at the center drives products that better meet their needs.
60. Is there a balance between feasibility, viability, and desirability in product development with design thinking?
Ans:
Balancing feasibility, viability, and desirability involves aligning technical, business, and user aspects. Iterative prototyping explores and validates the feasibility of solutions. Considering business objectives ensures the viability of proposed solutions. Prioritizing user needs and emotions fulfills their desires. Iterative refinement achieves a harmonious balance, maximizing product success.
61. How can design Thinking be applied to service design?
Ans:
- Design thinking in service design begins with understanding user needs.
- It involves empathy, ideation, prototyping, and Testing stages.
- Service blueprints and customer journey maps help visualize solutions.
- Iterative refinement based on feedback enhances service effectiveness.
- Co-creation with users ensures solutions meet their evolving needs.
- Continuous improvement loops foster innovation in service delivery.
62. What are the risks of not using design thinking in organizational processes?
Ans:
- A lack of user-centricity may lead to better solutions.
- Failure to innovate can result in stagnant products or services.
- More efficient processes may persist with optimization.
- Reduced customer satisfaction could impact brand reputation.
- Missed opportunities for differentiation in competitive markets.
- Need help adapting to changing consumer demands and preferences.
63. How does design thinking support sustainable business practices?
Ans:
Design thinking emphasizes understanding environmental impacts. It encourages the creation of products and services with minimal waste. Iterative prototyping allows for refining sustainable solutions. Collaboration with stakeholders promotes eco-friendly innovations. Designing for longevity and durability reduces resource consumption. Considering social and environmental factors ensures ethical practices.
64. How do users measure the ROI of design thinking initiatives?
Ans:
Measure efficiency gains in product development cycles, assess cost savings from avoiding rework through early prototyping, quantify revenue growth attributed to innovative solutions, monitor employee engagement and retention linked to a creative culture, and analyze market share increases resulting from user-centric products, while also tracking customer satisfaction improvements due to enhanced product features.
65. How does Design thinking impact the development of inclusive products?
Ans:
- An empathetic understanding of diverse user perspectives informs Design.
- Co-creation with marginalized communities ensures inclusivity.
- Iterative prototyping allows for feedback incorporation from various users.
- Accessibility features are integrated from the initial design stages.
- Testing with diverse user groups identifies and addresses biases.
- Inclusive design principles result in products that are usable to all.
66. What is the role of experimentation in design thinking?
Ans:
- Experimentation fosters a culture of innovation and risk-taking.
- Rapid prototyping allows for the quick and cheap Testing of ideas.
- Failures provide valuable insights for iterative improvements.
- Experimentation encourages creativity and out-of-the-box thinking.
- It helps validate assumptions and hypotheses early in the process.
- Successful experiments lead to scalable and impactful solutions.
67. Strategies for fostering creativity in design thinking workshops?
Ans:
- Encourage brainstorming sessions without judgment.
- Use techniques like mind mapping and random stimuli to generate ideas.
- Rotate facilitators to bring fresh perspectives and energy.
- Incorporate diverse perspectives and interdisciplinary teams.
- Allow for breaks and activities that promote relaxation and inspiration.
68. Using design thinking to address systemic issues in organizations?
Ans:
Identify root causes through an empathetic understanding of stakeholders. Encourage cross-functional collaboration to tackle complex problems. Implement iterative problem-solving processes to test and refine solutions. Prioritize transparency and communication to address resistance to change. Develop long-term strategies with sustainability and scalability in mind. Empower employees at all levels to contribute to problem-solving efforts.
69. Examples of Design thinking in government projects?
Ans:
Redesigning public transportation systems for better accessibility.Streamlining bureaucratic processes for citizen services.Designing inclusive public spaces for people of all abilities.Creating digital platforms for transparent and accessible governance.Developing educational programs using user-centric approaches.Implementing community engagement initiatives for policy development.
70. How does design thinking complement market research?
Ans:
- Design thinking provides qualitative insights into user behaviours and needs.
- It goes beyond traditional market research by focusing on empathy and innovation.
- Iterative prototyping allows for quick validation of market assumptions.
- Design thinking helps identify unmet or latent customer needs.
- Market research provides quantitative data to complement qualitative insights.
- Integrating both approaches ensures a holistic understanding of the market and users.
71. What is the importance of a “design thinking mindset” in organizational culture?
Ans:
- It stimulates innovation and creativity within teams.
- It fosters a user-centric approach to problem-solving.
- It cultivates adaptability and resilience amidst change.
- It enhances empathy towards the needs of end-users.
- It results in more effective solutions to intricate problems.
72. Pitfalls to avoid when implementing design thinking?
Ans:
I need to pay more attention to the pivotal role of empathy in the process and avoid hastening through phases without thorough research. I also need to refrain from feedback from end-users and stakeholders. I need to be more focused on creativity with practical execution. More accurate information on the importance of diverse perspectives needs to be provided. Finally, I need to iterate and refine solutions based on Testing.
73. Contribution of design thinking to continuous improvement?
Ans:
It identifies improvement areas through user feedback, promotes iteration and refinement of solutions, fosters a culture of experimentation and learning, facilitates spotting emerging trends and needs, supports the optimization of processes and products over time, and enables responsiveness to evolving customer demands, ultimately driving sustained growth and competitive advantage.
74. Strategies for scaling Design thinking in large organizations?
Ans:
- Establishing specialized Design thinking teams or departments.
- Providing comprehensive training and resources across all departments.
- Implementing a consistent framework and methodology.
- Garnering leadership support and buy-in for design thinking initiatives.
- Establishing networks for sharing best practices and lessons learned.
- Embedding design thinking principles into organizational values and processes.
75. How does Design thinking foster a customer-centric culture?
Ans:
- It prioritizes understanding and empathizing with customers.
- It involves customers in the design and testing phases.
- It focuses on solving real problems and fulfilling user needs.
- It encourages a shift towards user-centric Thinking from product-centric.
- It values feedback and iteration based on user experiences.
- It fosters a deep comprehension of the customer journey and pain points.
76. What is the role of empathy in prototyping and Design Thinking?
Ans:
It aids designers in grasping users’ emotional responses, guides the development of prototypes that resonate with users, enables anticipation of user needs and preferences, facilitates crafting more intuitive and user-friendly solutions, encourages iteration based on empathy-driven insights, and fortifies the connection between users and the final product.
77. What is the influence of design thinking on digital products/services?
Ans:
It emphasizes user experience and interface design, promotes iterative development based on user feedback, drives the creation of intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, facilitates the integration of user needs into product development, supports rapid prototyping and Testing of digital solutions, and fosters innovation and differentiation in the digital marketplace.
78. What is the role of co-creation in the design thinking process?
Ans:
- It engages stakeholders and end-users in the design process.
- It facilitates a deeper understanding of user needs and perspectives.
- It generates innovative ideas and solutions through collaboration.
- It builds trust and buy-in among stakeholders.
- It encourages ownership and commitment to the final solution.
79. How does design thinking encourage interdisciplinary cooperation?
Ans:
- It values diverse perspectives and expertise from various fields.
- It breaks down silos between departments and disciplines.
- It encourages cross-functional teams to collaborate on projects.
- It facilitates knowledge sharing and learning across disciplines.
- It fosters creative problem-solving through diverse viewpoints.
- It results in more holistic and innovative solutions.
80. Overcoming resistance to ambiguity in design thinking?
Ans:
- Highlighting the value of experimentation and learning from failure.
- Providing clear examples of how ambiguity leads to innovation.
- Cultivating a culture that embraces uncertainty as a path to discovery.
- Offering support and resources for navigating ambiguity.
- Celebrating successes and lessons learned from handling ambiguity.
81. What makes a successful design thinker?
Ans:
Success in design thinking is characterized by embodying empathy, blending creativity with adept problem-solving skills. Navigating ambiguity with ease, they iterate persistently, fostering collaborative environments conducive to creativity. Essential traits include adaptability and a steadfast focus on users, yielding innovative solutions deeply resonant with their needs.
82. How is observation used in design thinking?
Ans:
Observation catalyzes empathy, facilitating profound user understanding. It uncovers nuanced insights within daily interactions, guiding the design process toward solutions that hold genuine meaning. Through meticulous observation, patterns emerge, steering iterative Design and validating initial assumptions. Observing without preconceptions sparks creativity, enabling novel viewpoints and ensuring solutions authentically address user needs.
83. How does design thinking drive product innovation?
Ans:
- Design thinking propels product innovation by championing a user-centric ethos,traversing through empathy, creativity, and prototyping stages.
- By intimately grasping user needs and challenges, it births innovative solutions tailored to address them adeptly.
- Swift prototyping and iterative Testing refine concepts, culminating in products that authentically resonate with users, fostering competitive advantage and market triumph.
84. What are the strategies to overcome resistance to change with design thinking?
Ans:
- To surmount resistance to change, involve stakeholders from the outset, cultivating a sense of ownership and buy-in.
- Articulate the merits of change, proactively addressing concerns.
- Foster a culture that embraces experimentation and learns from setbacks.
- Enlist end-users in the design process to ensure relevance and acceptance.
- Utilize storytelling to illustrate the potential impact and possibilities of change and progress incrementally, allowing for gradual adjustments and adaptations.
85. Using design thinking to enhance customer engagement?
Ans:
Design thinking unveils latent customer needs, crafting experiences that deeply resonate with them. Iterative prototyping and Testing ensure alignment with user expectations, fostering loyalty and advocacy through empathetic solutions. Co-creation with customers instills a sense of ownership, resulting in inspiring and delightful products and services.
86. What is the role of feedback in design thinking?
Ans:
Feedback serves as a guiding beacon, steering iterations in design thinking. It validates assumptions, hones prototypes, and informs decision-making. Timely feedback cultivates a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring solutions remain pertinent and efficacious. Qualitative and quantitative feedback offer invaluable insights, aiding teams in course correction and pivoting as necessary.
87. What is the importance of divergent and convergent Thinking in Design?
Ans:
- Divergent Thinking sparks ideas, fostering creativity and exploration throughout the design process.
- Convergent Thinking then sieves and amalgamates these ideas, distilling them into actionable insights and solutions.
- Both modes complement each other, striking a balance between exploration and focus.
88. Applying design thinking to social or environmental challenges?
Ans:
Design thinking tackles social and environmental dilemmas head-on, prioritizing empathy, sustainability, and inclusivity. It engages stakeholders to grasp diverse perspectives, co-creating solutions that effectively tackle root issues. Swift prototyping and testing enable iterative refinement, ensuring scalability and impact in solutions, while fostering innovation that adapts to emerging challenges and opportunities.
89. Are you integrating Design thinking into education?
Ans:
Integrating design thinking nurtures critical Thinking and creativity, equipping students with indispensable problem-solving skills for the future. It fosters experimentation and experiential learning, cultivating resilience and adaptability in students. Real-world design challenges provide contextual learning experiences, fostering peer collaboration and empathy. Educators play a pivotal role as facilitators, guiding students through the design process, empowering them to confront complex challenges with confidence.
90. The intersection of design thinking and digital transformation?
Ans:
- Design thinking and digital transformation intersect to drive innovation and agility in the digital realm.
- Design thinking informs the creation of user-centric digital solutions, ensuring seamless experiences that evolve with user needs.
- Agile methodologies integrate seamlessly with design thinking, facilitating rapid iteration,
- Digital tools enhance collaboration and prototyping, expediting the design process and leading to transformative digital products and services.
91. Explaining “design sprints” in design thinking?
Ans:
- “Design sprints” are intensive workshops where teams collaborate.
- They aim to solve complex problems and generate innovative solutions.
- Typically, they last for five days, each dedicated to a specific stage.
- This process involves understanding, ideating, prototyping, and testing ideas.
- Design sprints emphasize rapid iteration and user-centered design principles.
- Ultimately, they help expedite the innovation process and foster creativity within teams.
92. Ethical considerations in design thinking?
Ans:
Ethical considerations in design thinking involve respecting user privacy and autonomy. Designers must ensure transparency and consent in data collection and usage. Equity and inclusivity should be prioritized to avoid reinforcing biases or discrimination. There’s a responsibility to consider the broader societal impact of design decisions. Ethical dilemmas may arise when balancing business objectives with user well-being.
93. What is the impact of design thinking on brand and competition?
Ans:
- Design thinking can differentiate brands by delivering superior user experiences.
- It fosters innovation, leading to products and services that stand out in the market.
- By understanding customer needs deeply, brands can create more compelling offerings.
- This approach builds customer loyalty and strengthens brand reputation over time.
- In competitive markets, design thinking gives companies an edge by anticipating and meeting evolving needs.
- Overall, it cultivates a culture of innovation that sustains long-term competitiveness.
94. Successful Design thinking in healthcare?
Ans:
- Successful Design thinking in healthcare prioritizes patient-centric solutions.
- It involves multidisciplinary teams collaborating to address complex healthcare challenges.
- Empathy plays a crucial role in understanding patients’ needs and experiences.
- Prototyping and iterative Testing allow for rapid refinement of solutions.
- Integration with healthcare professionals ensures the practicality and feasibility of implementations.
- Ultimately, successful Design thinking improves patient outcomes and enhances the healthcare experience.
95. What is design thinking’s role in staying relevant in markets?
Ans:
Design thinking enables businesses to adapt effectively to changing market dynamics. It fosters a culture of innovation that encourages continuous improvement and adaptation. By understanding and addressing evolving customer needs, businesses can stay ahead of competitors. Design thinking helps identify emerging trends and opportunities for product or service development. It encourages experimentation and risk-taking, which is vital for staying relevant in dynamic markets.






