
The scrum master role was created as part of the Scrum framework. The role does not generally have any actual authority (also known as servant-leadership). The name was initially intended to indicate someone who is an expert at Scrum and can therefore coach others. The Scrum Master is also responsible for improving interactions between the Scrum team and the organization in order to maximize the productivity of the Scrum team. Finally, the Scrum Master is responsible to arranges and facilitates the team’s meetings – daily Scrum, planning sessions, sprint retrospective, and etc.
1) What is the duration of a scrum sprint?
Ans:
Generally, the duration of a scrum sprint (scrum cycle) depends upon the size of project and team working on it. The team size may vary from 3-9 members. In general, a scrum script complete in 3-4 weeks. Thus, on an average, the duration of a scrum sprint (scrum cycle) is 4 weeks. This type of sprint-based Agile scrum interview questions is very common in an agile or scrum master interview.
2) What is Velocity?
Ans:
Velocity question is generally posed to understand if you have done some real work and familiar with the term. Its definition “Velocity is the rate at which team progresses print by sprint” should be enough. You can also add saying the important feature of velocity that it can’t be compared to two different scrum teams.
3) What do you know about impediments in Scrum? Give some examples of impediments.
Ans:
Impediments are the obstacles or issues faced by scrum team which slow down their speed of work. If something is trying to block the scrum team from their getting work “Done” then it is an impediment. Impediments can come in any form. Some of the impediments are given as –
- Resource missing or sick team member
- Technical, operational, organizational problems
- Lack of management supportive system
- Business problems
- External issues such as weather, war etc
- Lack of skill or knowledge
While answering impediments related agile scrum interview questions remember that you may be asked the way to remove any of the mentioned impediment.
4) What is the difference and similarity between Agile and Scrum?
Ans:
- Difference between Agile and Scrum – Agile is a broad spectrum, it is a methodology used for project management while Scrum is just a form of the Agile that describes the process and its steps more concisely. Agile is a practice whereas scrum is a procedure to pursue this practice.
- The similarity between Agile and Scrum – The Agile involves completing projects in steps or incrementally. The Agile methodology is considered to be iterative in nature. Being a form of Agile, Scrum is same as that of the Agile. It is also incremental and iterative.
5) What is the increment? Explain.
Ans:
This is one of the commonly asked agile scrum interview questions and a quick answer can be given this way. An increment is the total of all the product backlogs items completed during a sprint. Each increment includes all the previous sprint increment values as it is cumulative. It must be in the available mode in the subsequent release as it is a step to reach your goal.
6) What is the “build-breaker”?
Ans:
The build-breaker is a situation that arises when there is a bug in the software. Due to this sudden unexpected bug, compilation process stops or execution fails or a warning is generated. The responsibility of the tester is then to get the software back to the normal working stage removing the bug.
7) What do you understand by Daily Stand-Up?
Ans:
You may surely get an interview question about daily stand-up. So, what should be the answer to this question? The daily stand-up is an everyday meeting (most preferably held in the morning) in which the whole team meets for almost 15 minutes to find answer to the following three questions –
- What was done yesterday?
- What is your plan for today?
- Is there any impediment or block that restricts you from completing your task?
The daily stand-up is an effective way to motivate the team and make them set a goal for the day.
8) What do you know about Scrum ban?
Ans:
Scrum-ban is a Scrum and Kanban-based model for the software development. This model is specifically used for the projects that need continuous maintenance, have various programming errors or have some sudden changes. This model promotes the completion of a project in minimum time for a programming error or user story.
9) State some of the Agile quality strategies?
Ans:
Some of the Agile quality strategies are –
- Iteration
- Re-factoring
- Dynamic code analysis
- Short feedback cycles
- Reviews and inspection
- Standards and guidelines
- Milestone reviews
10) Do you know about Agile Manifesto & its Principles? Explain in brief.
Ans:
This is the theory which most of agile/scrum roles aspirant should be on tips. Four manifesto values and 12 principles should be explained as much as possible as part of this question. Even if it’s not explained in 100% accurate manner it should be fine but intentions of values and principles should come out e.g.
- Working Software should be demonstrated at regular intervals
- Individuals & interaction – self-organization, self-motivating should be encouraged
- Customer collaboration
- Welcoming change at any point in time in the project
11) Is there any drawback of the Agile model? If yes, explain.
Ans:
Yes, there are some drawbacks of the Agile model, some of them are as follows
- It is not easy to make a prediction about the effort required to complete a task. It becomes more problematic in case of large projects as it becomes difficult to get an idea of the total effort required.
- At sometimes, it’s not possible to properly focus on the design and documentation of the project
- In case the requirements of the client are not understood properly, the final project will not meet the customer requirements. Thus, it will lead to the customer dissatisfaction.
- Only the leader who has considerable experience in Agile methodologies is capable to take important decisions. The team members with little or no experience are not involved in decision-making, thus they don’t get chance to advance their knowledge.
12) What is the use of burn-up and burn-down charts?
Ans:
The burn-up chart illustrates the amount of completed work in a project whereas the burn-down chart depicts the amount of work remained to complete a project. Thus, the burn-up and burn-down charts are used to trace the progress of a project.
13) Define Zero Sprint and Spike in Agile.
Ans:
To answer this question, describe Zero Sprint and Agile in detail, as follows
- Zero sprint – Zero Sprint can be defined as the preparation step of the first sprint in Agile. There are some activities that are required to be done before actually starting the project. These activities are considered as the Zero sprint; the examples of such activities are – setting the environment for development, preparation of backlogs etc.
- Spike – Spike is the type of story that can be taken between the sprints. Spikes are commonly used for the activities related to the design or technical issues such as research, design, prototyping, and exploration. There are two types of spikes – functional spikes and technical spikes.
14) What is the role of the Scrum Master?
Ans:
- Here’s how you can answer Scrum Master interview questions like this :
- The scrum master is the leader as well as coach of the Scrum team. The scrum master is responsible to serve and protect his team from any kind of distractions that could affect their performance. The main role of the scrum master is to motivate his team to achieve the sprint goal.
- He is focused to build a self-organized and motivated team where each member is familiar with the implementation of Agile and Scrum principles and applications.
- The scrum master keeps a proper check on the scrum team if they are executing committed tasks properly. He is also responsible to increase the efficiency and productivity of the team so that they can achieve the sprint goal effectively.
15) What do you know about a story point in Scrum?
Ans:
A story point in Scrum is the unit for the estimation of total efforts that are required to perform or complete a particular task. So, here is how you can answer such agile scrum interview questions on a single line.
16) What is the role of Sashimi in Scrum methodology?
Ans:
Sashimi plays an important role in Scrum methodology. Sashimi is a technique used by Scrum to check the completion of all the functions created by the developers. Using this technique, all the requirements such as analysis, designing, coding, testing and documentation that are used in the constitution of a product are checked and only after that the product is displayed.
17) What are the different roles in Scrum?
Ans:
The three scrum roles i.e. Scrum Master, Product Owner and Team should be explained with the details of few primary responsibilities of each role. You can add more details as mentioned below for a particular depending on the role you are getting interviewed for.
- Product owner – A product owner is actually the stakeholder of the project. He represents the project requirements before the team. He is responsible to have a vision of what to build and convey his detailed vision to the team. He is the starting point of an agile scrum software development project.
- Scrum team – Scrum team is formed by the collective contribution of individuals who perform for the accomplishment of a particular project. The team is bound to work for the timely delivery of the requested product.
18) What are the responsibilities of a Scrum Master?
Ans:
Key responsibilities of a Scrum Master involves:
- Tracking and monitoring
- Understanding requirements properly
- Work to reach the project goal
- Process checking master and quality master
- Protect the team from detachments
- Improving the performance of the team
- Lead the meetings and resolve issues
- Resolution of conflicts and impediments
- Communication and reporting
19) What are different ceremonies and their importance in Scrum?
Ans:
- Scrum planning, Scrum – Daily stand up, Scrum review & scrum retrospective ceremonies should be clearly expressed with the purpose of the ceremony. It’s important to remember the time-boxing of the ceremonies for a standard 4 weeks of Sprint or as per the Sprint you have used in your projects.
20) What do you understand by the term Agile testing?
Ans:
Agile testing is a software testing practice that is fully based on the agile principles of software development. It is an iterative methodology where the requirements are the outcome of collaboration between the product owner and team. The agile principles and applications are applied to meet the customer requirements by successful completion of the project.
21) State some major principles of Agile testing.
Ans:
Some major principles of Agile testing are
- Customer satisfaction
- Face to face communication
- Sustainable development
- Quick respond to changes
- Continuous feedback
- Successive improvement
- Self-organized
- Focus on essence
- Error-free clean node
- Collective work
22) What are the skills of a good Agile Tester?
Ans:
An agile tester is one who implements agile software development principles for software testing. Followings are the skills of a good agile tester
- Required to be familiar with the concepts and principles of Agile
- Should have an excellent communication to communicate with the team and the clients
- Ability to set priority for the tasks according to the requirements
- Should be able to understand the requirements properly
- Understanding of the risks involved with a project due to changing requirements
23) What do you understand by the term “Scrum of Scrums”?
Ans:
This is one of the commonly asked scrum master interview questions. Consider a case to understand the meaning of the term scrum of the scrums. Let us assume an active project on which seven teams are currently working. The number of members of each team is also seven. Each team is responsible to lead its own scrum meeting. But, in order to coordinate and communicate with different teams, it is required to organize a separate scrum meeting. The scrum meeting organized to hold a coordination between scrum teams is known as the scrum of scrums. There is one team leader from every team, known as ambassador, who is responsible to represent his team in the scrum of scrums.
24) Scrum is an Agile framework, right? Name a few other Agile frameworks.
Ans:
Yes, Scrum is an Agile framework. Few other Agile frameworks are
- Feature Driven Development
- Test Driven Development
- Kanban
25) Explain some common metrics for Agile.
Ans:
You may definitely come across agile scrum interview questions regarding agile metrics. The question may be related to a particular agile matric or explaining all the metrics. So, the detailed description of some common metrics for Agile is as follows:
- Velocity – Velocity is the average number of points from last 3-4 sprints. It is measured by the summation of the all approved estimates of the stories. It gives an idea of the capacity, progress etc.
- Cumulative Flow Diagram – With the help of a cumulative flow diagram, an inspection is done over the uniform workflow. In this diagram/graph, the x-axis represents time whereas the y-axis represents the number of efforts.
- Work Category Allocation – Work category allocation is an important factor that gives a quick information of the time investment i.e. where the time is being invested and which task should be given priority as a factor of time.
- Time Coverage – It is the time that is given to a code during testing. It is calculated in percentage as a factor of the number of lines of code called by the test suite and the total number of relative lines of code.
- Business Value Delivered – It is a term which denotes the working efficiency of the team. The business objectives are assigned numerical values 1,2,3.. and so on, as per the level of priority, complexity, and ROI.
- Defect Removal Awareness – It is the factor that helps the team to deliver a quality product. The identification of an active number of defects, their awareness, and removal plays an important role in delivering a high-quality product.
- Defect Resolution Time – It is a procedure through which the team members detect the defects (bugs) and set a priority for the defect resolution. The procedure of fixing errors/bugs or defect resolution comprises of multiple processes such as clearing the picture of defect, schedule defect fixation, completing defect fixation, generation, and handling of resolution report.
- Sprint Burn Down Matric – The sprint burndown chart is a graph to represent the number of non-implemented or implemented sprints during as Scrum cycle. This matric helps to track the work completed with the sprint.
26) Is it ever suggested to use waterfall over Scrum? If yes, explain when.
Ans:
Yes, sometimes it is suggested to use a waterfall model over Scrum. It is done when the customer requirements are simple, well-defined, fully understood, predictable, and are not subjected to change until the completion of the project. It may the case that you would haven’t ever used waterfall over Scrum but you need to prepare for such Agile Scrum interview questions.
27) Why does Scrum encourage the use of automated testing for projects?
Ans:
Scrum encourages the use of automated (automated performance or automated regression) testing to make the fastest possible delivery of the project. While answering this question, you may explain some tools that you have used for automated testing.
28) Name some methodologies and development where you have used the Agile model.
Ans:
While answering this type of agile scrum interview questions, keep in mind to mention those methodologies that are familiar with. Some of the methodologies and development where the Agile model can be used are
- Crystal methodologies
- Lean software development
- Dynamic development
- Feature-driven development
29) Share your experience as a Scrum Master/Product Owner/Agile team member and what were your primary responsibilities?
Ans:
Here you have to explain your project details where you worked in Scrum team and defining your role with the responsibilities you held. The trick in this question is whether while explaining you are showing self-organizing and self-motivational team. Also, the interviewer will try to judge how in depth you have worked in the agile/scrum environment based on your explanation.
30) What are the three main artifacts of the Scrum process?
Ans:
The artifacts of Scrum are:
- Product Backlog.
- Sprint Backlog.
- Product Increment.
31) Describe the role of a Product Owner.
Ans:
The Product Owner focuses on the success of the product, ensuring the business value of it. Their main responsibility is to identify and refine the Product Backlog items.
32) Why is Agile methodology necessary?
Ans:
- It helps in achieving customer satisfaction with the rapid delivery of useful software.
- It eases potential changing requirements, even late in a company’s development.
- Repeatedly delivers working software, the main measurement of progress.
- It provides close, daily cooperation between the company and the developers.
- Having self-organizing teams brings, as a result, self-motivated team members.
- In situations of co-location, it assists communication through face-to-face conversations.
- It offers continuous attention to XP.
- It adds simplicity.
33) What are the five phases of risk management?
Ans:
- Risk identification.
- Risk categorization.
- Risk response.
- Risk review.
- Risk closure.
34) What are the main tools used in a Scrum project?
Ans:
- JIRA.
- Rally.
- Version One.
35) What is timeboxing in Scrum?
Ans:
Timeboxing means allotting a fixed unit of time for an activity. The unit of time is called a time box. The maximum length of a time box should be 15 minutes.
36) Is canceling a Sprint possible? Who can cancel a Sprint?
Ans:
A Sprint can be canceled before the Sprint timebox limit ends. Only the Product Owner can cancel the sprint.
37) How is estimation in a Scrum project done? What are the techniques used for estimation?
Ans:
Estimation in a Scrum project is done using relative Agile estimation techniques:
- The T-shirt Estimation Technique.
- The Planning Poker Estimation Technique.
- The Estimation by Analogy Technique.
- The Disaggregation Estimation Technique.
38) What are the roles involved in the Scrum framework?
Ans:
A Scrum framework has three roles:
- Scrum Master.
- Product Owner.
- Development team
39) What is the difference between change management in a Waterfall and an Agile Scrum?
Ans:
- In Waterfall, change management is based on the change management plan, the change tracker and the release plan based on which the consultants deliver their work.
- In Agile, there is no change management plan. The work delivery is only based on the definition of the product backlog.
40) What do you understand by the term scope creep? How do you prevent it from happening?
Ans:
if the requirements are not properly defined at the start and new features are added to the product already being built, a scope creep occurs.
To prevent it:
- The requirements must be clearly specified.
- The project progress must be monitored.
- Effective grooming of sprint backlog must be done.
41) What are the most common risks in a Scrum project?
Ans:
- A scope creep.
- Timeline issues.
- Budget issues.
42) What does DoD mean? How can this be achieved?
Ans:
Definition of Done is formed by a list of tasks that define the work’s quality. It is used to decide whether an activity from the Sprint backlog is completed.
43) How is scrum different from waterfall?
Ans:
The major differences are:
- The feedback from the customer is received at an early stage in Scrum than waterfall, whereas the feedback from the customer is received towards the end of the development cycle.
- Accommodate the new or changed requirement in scrum is easier than the waterfall.
- Scrum focuses on collaborative development than waterfall where the entire development cycle is divided into phases.
- At any point of time, we can roll back the changes in scrum than in waterfall.
- Testing is considered a phase in the waterfall, unlike scrum.
44) How is scrum different from the Iterative model?
Ans:
Scrum is a type of iterative model but it is iterative + incremental.
45) What are the ceremonies you perform in the scrum?
Ans:
There are 3 major ceremonies performed in Scrum:
- Planning Meeting: Here, the entire scrum teams along with the scrum master and product owner meet to discuss each item from the product backlog that they can work on the sprint. When the story is estimated and is well understood by the team, the story then moves into the Sprint Backlog.
- Review Meeting: Here, the scrum team demonstrates their work done to the stakeholders.
Retrospective meeting:
Here, the scrum teams along with the scrum master and product owner meet to retrospect the last sprint they worked on. They majorly discuss on the 3 things:
- What went well?
- What could be done better?
- Action Items
Apart from these three ceremonies, we have one more called “Backlog grooming” meeting.
In this meeting, the scrum team along with the scrum master and product owner. The product owner put forward the business requirements as per the priority and the team discussed over it, identifies the complexity, dependencies, and efforts. The team may also do the story pointing at this stage.
46) What do you think should be the ideal size of a Scrum team?
Ans:
The ideal size is 7 to 9 with +/- 2
47) What do you discuss in the daily stand up meeting?
Ans:
We discuss the following three things:
- What did I do today?
- What I plan to do tomorrow?
- Any impediments/roadblock
48) What is the “Time Boxing” of a scrum process called?
Ans:
It’s called “Sprint”
49) What should be an ideal duration of a sprint?
Ans:
It is recommended to have 2 – 4 weeks of the sprint cycle.
50) How requirements are defined in a scrum?
Ans:
Requirements are termed as “User Stories” in Scrum.
51) What are the different artifacts in scrum?
Ans:
There are two artifacts maintained in Scrum:
- Product Backlog: Containing the prioritized list of business requirements
- Sprint Backlog: Contains the user stories to be done by the scrum team for a sprint.
52) How do you define a user story?
Ans:
The user stories are defined in the format of
- As a <User / type of user>
- I want to <action/feature to implement>
- So that < objective>
53) So in scrum, which entity is responsible for the deliverables? Scrum Master or Product Owner?
Ans:
Neither the scrum master, not the product owner. It’s the responsibility of the team who owns the deliverable.
54) How do you create the Burn-Down chart?
Ans:
- Burn-down chart is a graph that shows the estimated v/s actual effort of the scrum tasks.
- It is a tracking mechanism by which for a particular sprint; day to day tasks are tracked to check whether the stories are progressing towards the completion of the committed story points or not. Here, we should remember that the efforts are measured in terms of user stories and not hours.
55) Do you see any disadvantage of using scrum?
Ans:
I don’t see any disadvantage of using scrum. The problems mainly arise when the scrum team do not either understand the values and principles of the scrum or are not flexible enough to change.
56) During Review, suppose the product owner or stakeholder does not agree to the feature you implemented what would you do?
Ans:
First thing we will not mark the story as done.
We will first confirm the actual requirement from the stakeholder and update the user story and put it into the backlog. Based on the priority, we would be pulling the story in the next sprint.
57) In case, the scrum master is not available, would you still conduct the daily stand up meeting?
Ans:
Yes, we can very well go ahead and do our daily stand up meeting.
58) Where does automation fit into scrum?
Ans:
- Automation plays a vital role in Scrum. In order to have continuous feedback and ensure the quality deliverables we should try to implement TDD, BDD, and ATDD approaches during our development. Automation in scrum is not only related to testing but it is for all aspects of software development.
- As I said before introducing TDD, BDD and ATDD will speed up our development process along with maintaining the quality standards; automating the build and deployment process will also speed up the feature availability in different environments – QA to production.
- As far as testing is concerned, regression testing should be the one that will have the most attention. With the progress of every sprint, the regression suite keeps on increasing and it becomes practically very challenging to execute the regression suite manually for every sprint. Because we have the sprint duration of 2 – 4 weeks, automating it would be imperial.
59) Apart from planning, review, and retrospective, do you know any other ceremony in scrum?
Ans:
We have the Product Backlog Refinement meeting (backlog grooming meeting) where the team, scrum master and product owner meets to understand the business requirements, splits it into user stories, and estimating it.
60) Can you give an example of where scrum cannot be implemented? In that case, what do you suggest?
Ans:
Scrum can be implemented in all kinds of projects. It is not only applicable to software but is also implemented successfully in mechanical and engineering projects.
61) Tell me one big advantage of using scrum?
Ans:
The major advantage is – Early feedback and producing the Minimal Viable Product to the stakeholders.
62) What are Epics?
Ans:
Epics are equivocal user stories or we can say these are the user stories that are not defined and are kept for future sprints.
63) In case you receive a story in the last day of the sprint to test and you find there are defects, what will you do? Will you mark the story as done?
Ans:
A story is done only when it is development complete + QA complete + acceptance criteria is met + it is eligible to be shipped into production. In this case, if there are defects, the story is partially done and not completely done, so I will spill it over to the next sprint.
64) What is a Stroy Board in scrum?
Ans:
An important principle in Scrum is the idea of transparency. That’s why making things visible for the entire team to see is really important. A big factor of this is the Story Board. It is a visual representation of a software project’s progress which generally has four columns, namely, ‘To do’, In Progress’, ‘Test’, and ‘Done’.
65) What are the three main artifacts of Scrum Process?
Ans:
Artifacts are just physical records that provide project details when developing a product. Scrum Artifacts include:
- Product Backlog – A document that outlines the list of tasks and every requirement that the final product needs
- Sprint Backlog – List of all items from the product backlog that need to be worked on during a sprint
- Product Increment – Sum of product work completed during a Sprint, combined with all work completed during previous sprints
66) Mention what is the objective behind holding a Sprint retrospective meeting?
Ans:
During sprint retrospective, the team discusses what went right, what went wrong, and how to improve. They decide on how to fix the problems and create a plan for improvements to be enacted during the next sprint.
67) What is the release candidate in Scrum?
Ans:
A Release Candidate in Scrum is a build or version of the software that is ready and can be released to production. Further, testing such as User Acceptance Testing (UAT) may be performed on this version of the product.
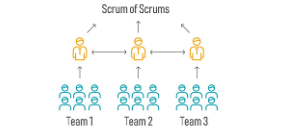
68) Explain what is a scrum of scrums.
Ans:
This is one of the commonly asked scrum master interview questions. For example, let’s say there is an active project with seven teams working on it. The number of members of each team is also seven and are responsible to lead their own scrum meeting. But, in order to coordinate and communicate with different teams, they need to organize a separate scrum meeting. This meeting is called the scrum of scrums. The responsible person from each team attends the meeting and discuss their work and progress.
69) List some of the popular project management tools that you have heard of.
Ans:
Some popular tools used in the project management are Rally Software, Version One, XPlanner, EasyBacklog Agilefant, and many others.
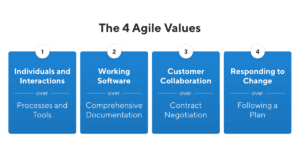
70) Do you know about Agile Manifesto? Explain in brief.
Ans:
The Agile Manifesto is a statement that is comprised of 4 key values and 12 principles that form the core of agile. Agile comes in a number of forms. Every subset of agile applies the four values and 12 principles in different ways, but all of them rely on them to guide the development and delivery of high-quality, working software.
71) What is the Empirical Process Control? How is scrum based on that?
Ans:
Empirical process control is a core Scrum principle and relies on the three main ideas: transparency, inspection, and adaptation. With empirical process control, you don’t fix the scope of the product nor the processes of how to build it. Instead, you create a small shippable piece of product in short cycles, inspect what and how you create it and adapt the product and the way you build it, with built-in mechanisms for transparency to enable clear inspection.

72) What are some qualities that should be present in a good Agile tester?
Ans:
Some basic skills that every agile tester should have are:Staying Focused.
- Sharing Ideas Effectively.
- Having Automated Scripts.
- Continuous Integration.
- Examining Test Results.
- Understanding How to Code.
- Having an Analytical Mindset.
- Clear Demonstration of Data.
73) Do you hold any agile certification? Why did you choose this certification?
Ans:
This sort of question might seem awkward if you don’t have any certification. In such cases, stay calm and just let the interviewer know if are planning to take any in the future. If yes, then mention why you have that particular certification. For your reference, here are some certifications generally looked by organizations:
- ACP (Agile Certified Practitioner)
- ASM (Agile Scrum Master)
- CSM (Certified Scrum Master)
- PSM (Professional Scrum Master)
- Safe Agilist
74) Are you a certified scrum master?
Ans:
Don’t panic if you don’t have a certification and they ask you this question! Be confident and answer if you have a scrum master certification or not. If you are a certified scrum master, just share the details of your certification like certification type, score obtained, and the year of passing. In case you are not certified to highlight your experience in the particular field and let the interviewer know if you are planning to take one in the future.
75) Are Agile and Scrum the same?
Ans:
Agile is a set of methods and practices based on the values and principles expressed in the Agile Manifesto. While Scrum is a framework for handling roles, events, artifacts, and rules/guidelines to implement the Agile Mindset. The table below lists the key differences between Scrum & Agile.
| Features | Agile | Scrum |
|---|---|---|
| Nature & Scope | Agile is a mentality and a set of principles | Scrum is a framework that implements agile principles |
| Planning | Planning occurs at three levels: release planning, iteration planning, and daily planning | Next sprint is planned after the team has completed the current sprint activities |
| Flexibility to Changes | Agile is very flexible and hence adapts to changes very quickly | Rigid framework & there is no much room for frequent changes |
| Design & Execution | Agile execution is quite simple and it usually something that isn’t done before | Works on trying new and creative ideas, which yields concise and smart outcomes |
| Monitoring Process | Requires detailed tracking & it takes place after every milestone of the overall design | Monitoring takes place after compilation of certain features rather than after each design |
| Leadership Role | A leader is accountable for the work done (or not done) by the team | There is no ‘team leader’, instead its fosters a multi-functional and self-organized team |
| Mode of Communication | The effective mode of communication is face-to-face within a team on a regular basis | Communication is done on a daily/weekly basis with respect to the schedule |
| Estimation Time & Delivery | The priority is always to satisfy the customer by providing continuous delivery of valuable software | Delivers build to clients to get their feedback, after each sprint |
| Customer Feedback | Encourages regular feedback during various processes from business users | Regular feedback is taken from end-users but in a more orderly fashion, like after every sprint |
76) What is the difference between Epic, User stories & Tasks?
Ans:
- Epic – It is a group of related user stories
- User Stories – They define the real business prerequisite & are is shaped up by the business holder
- Tasks – To accomplish the business requirements, development team create tasks
77) What is the difference between Sprint and Iteration in Scrum?
Ans:
- Iteration is a terminology used to define a single development cycle in general agile methods. It is a highly common term used in the iterative and incremental development process
- Sprint is used to define one development cycle or iterative step in a specialized agile methodology referred to as Scrum. Sprint is scrum specific, and not all forms of iterations are Sprints
78) What is the difference between the Sprint Planning Meeting & Sprint Retrospective Meeting?
Ans:
- A sprint planning meeting is a meeting in which all the scrum roles have a discussion about the team’s priority features and product backlog items
- A sprint retrospective meeting is a meeting in which all the scrum roles have a discussion about the good part of the sprint, the bad part of the sprint, and the sprint improvements
79) How is scrum different from other Iterative models?
Ans:
Scrum is not just an iterative model but it is also an iterative model with incremental progress. Other popular subsets of agile include KanBan, XP, Lean, FDD, etc.
80) A member of the Scrum team does not want to participate in the sprint planning meetings and considers meeting as a waste of time. How do you deal with that kind of attitude?
Ans:
- As a scrum master, you need to know the status of your team. So, if one of your team members thinks meetings are waste its high time to know why he/she is adopting such a behavior. Since scrum teams are usually of small size, so, each member of the team is really important. As Scrum Master, you should try to talk to the team member individually by asking open-ended questions to find out the reason for not attending the meeting. Try to convince him/her why meetings are an important part of the scrum framework.
- If the issue is still not resolved, you can set up a meeting with his reporting manager to talk about the concern and lookout for ways to help the team member.
81) Your team is picking reasonable action items but is later not delivering on them. How do you handle this?
Ans:
As a scrum master, you need to do a follow up to solve the issue. Find out the root cause, see if the problem is due to external factor or internal factor. If it’s because of an external factor, you need to address and eliminate the cause. The team can then catch up during a later sprint. If there is no external impediment, the problem is likely due to motivation, attitude, or personal issues within the team. In that case, you need to encourage team members responsible to do the right thing and overcome the problem.
82) How would you coordinate between multiple scrum teams?
Ans:
The way you can handle multiple teams depends on the size and coupling between those teams, and there are various frameworks to help you with it, like:
- SAFe – Scaled Agile Framework
- LeSS – Large Scale Scrum
- SoS – Scrum of Scrum.
83) One of the Agile Manifesto values says “People over processes”. Isn’t the Scrum master role which enforces “the process” a contradiction?
Ans:
It is really important to understand what exactly does the enforcement mean and what its boundaries are. Enforcement doesn’t mean forcing the team to follow the process, but it implies putting into practice the core principles of the Scrum to help the team be successful. Scrum Master, the facilitator of the team helps the team achieve its goal. Also, he will try to show the benefits of adopting the processes and help the team acquire an understanding of the scrum processes which is like showing the right path but it is totally up to the team if they want to walk through it or not.
84) In case you receive a story on the last day of the sprint to test and you find there are defects, what will you do? Will you mark the story to ‘done’?
Ans:
A story is said to be ‘done’ only when it is completely developed, has passed QA testing, acceptance criteria ais met and is eligible to be shipped into production. So, if the story you received passes all these conditions then you can add it to the ‘done’ list. In case, if there are defects, the story is partially done and not completely done, you will have to spill it over to next sprint.
85) Your team is constantly failing to meet commitments, and its performance velocity is volatile. What might the possible reasons be?
Ans:
This question basically addresses various issues. There are many possible factors that might combine to make a team’s velocity volatile, like:
- New team members are being hired
- Team members are leaving
- Levels of seniority in the team is causing issues
- Working in uncharted territory
- Working with legacy code, probably undocumented
- Unexpected technical debt
- Wy to many holidays and sick leave
86) What is time boxing in Scrum?
Ans:
Time boxing means allotting a fixed unit of time for an activity. So the time is over activity is over – irrespective of the result. This brings in discipline, predictability and creates a situation for inspect and adapt. Every event in Scrum is time boxed which Must not be extended like Sprint, Daily Scrum etc.
87) When do we exercise canceling a Sprint? Who can cancel a Sprint?
Ans:
Cancellation of a sprint is generally a rare case as there are losses associated with it. Cancellation seems viable only in case of the Sprint Goal is no more valid and changes cannot be finished in the given sprint. A Sprint can be canceled before the Sprint time box ends & only the Product Owner can cancel the sprint. In case of cancellation, the DONE PBI’s (PBI = Product Backlog Items) are marked done and remaining goes back to PB. After this we plan for new sprint.
Issues: This can be a little impractical in case if there are multiple teams working together on the same Product and all the teams are dependent on each other. However, the situation sensitivity needs to be exercised in such cases.
88) Can we apply Kanban in place of Scrum?
Ans:
Philosophies behind both frameworks are quite different. Kanban believes in delivering as soon as possible and it does not have time boxes like Sprints. However, Scrum believes in Time box oriented free collaboration among team members to come out with innovative solutions and work items. Scrum does not believe in Silos however Kanban may have silos.
Kanban focuses on WORK and Scrum focuses on Collaborative interaction among team members. Scrum speaks about mandatory roles and responsibilities however Kanban do not speak anything on roles so the implementation aspects are different.
89) What is MVP & MMP?
Ans:
An MVP is set of minimum requirements or features with which it looks like the product if shipped can be used by the users well and they feel the major value is delivered. However MMP is the minimal set of a requirement that is ready to be shipped to market and can be marketed that guarantees the usefulness to the customer. MMP is fully realized version however MVP may the one which is not fully ready for market but estimated to be valuable if completed and released.
Example MMP: www.redbus.com released the first version without capability of billing and disbursal of tickets. The caveat here is you must validate that this minimum feature product solves few major problems for the users and they feel it’s good for us. So with Red bus even without payment capability, the users were able to see the buses details and send info about with bus they want to book and bus operators used to call them and reserve seats. SO the major problem of travel and communication hassle was solved.
MVP: Imagine Red bus is ready with the code and can be released however they do not have the real Bus data that can be used by users for booking then they have an MVP but not MMP.
90) What is TDD (test driven development)?
Ans:
TDD is defined as programming practice which starts before the development phase starts, unlike Traditional testing. It instructs developers to write new code only if an automated test has failed. The primary goal of TDD is to make the code clearer, simple and bug-free.
- TDD is an iterative development process. Each iteration starts with a set of tests written for a new piece of functionality. These tests are supposed to fail during the start of iteration as there will be no application code corresponding to the tests. In the next phase of the iteration, Application code is written with an intention to pass all the tests written earlier in the iteration. Once the application code is ready tests are run.
- Any failures in the test run are marked and more Application code is written/re-factored to make these tests pass. Once application code is added/re-factored the tests are run again. This cycle keeps on happening until all the tests pass. Once all the tests pass, we can be sure that all the features for which tests were written have been developed.
Following steps define how to perform TDD test
- Add a test.
- Run all tests and see if any new test fails.
- Write some code.
- Run tests and Refactor code.
- Repeat.
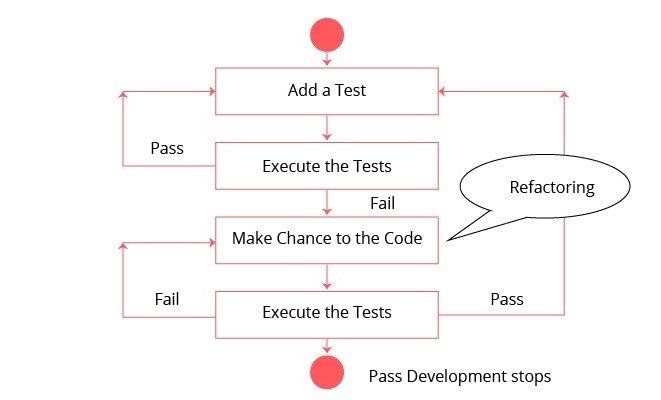
Benefits of TDD
- The unit test proves that the code actually works
- Can drive the design of the program
- Refactoring allows improving the design of the code
- Low-Level regression test suite
- Test first reduce the cost of the bugs
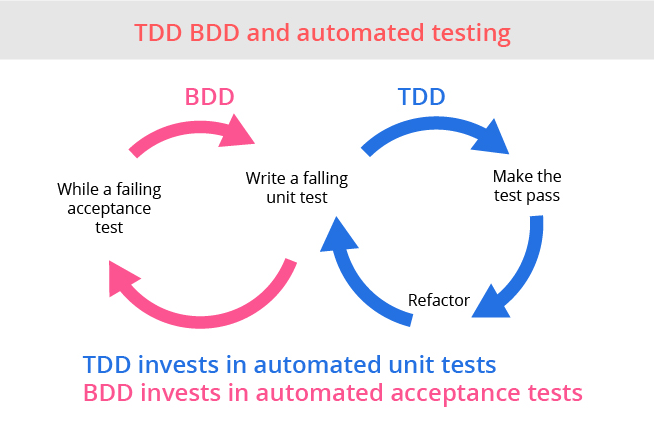
91) What is BDD (Behavior-driven development)?
Ans:
BDD is an extension of TDD. The major difference between TDD and BDD are:
- Tests are written in plain descriptive English type grammar
- Tests are explained as the behavior of an application and are more user-focused
- Using examples to clarify requirements
This difference brings in the need to have a language which can define, in an understandable format.
Features of BDD
- Shifting from thinking in “tests” to thinking in “behavior”
- Collaboration between Business stakeholders, Business Analysts, QA Team and developers
- Ubiquitous language, it is easy to describe
- Driven by Business Value
- Extends Test Driven Development (TDD) by utilizing natural language that non-technical stakeholders can understand
- BDD frameworks such as Cucumber or JBehave are an enabler, acting as a “bridge” between Business & Technical Language
Example:
Scenario: Duplicate email Where someone tries to create an account for an email address that already exists.
Given I have chosen to sign up But I enter an email address that has already registered Then I should be told that the email is already registered And I should be offered the option to recover my password
Now after a look at the above example code, anybody can understand the workings of the test and what it is intended to do. It gives an unexpected powerful impact by enabling people to visualize the system before it has been built. Any of the business users would read and understand the test and able to give you the feedback that whether it reflects their understanding of what the system should do, and it can even lead to thinking of other scenarios that need to be considered too.
Advantages of BDD:
- Writing BDD tests in an omnipresent language, a language structured around the domain model and widely used by all team members comprising of developers, testers, BAs, and customers.
- Connecting technical with nontechnical members of a software team.
- Allowing direct interaction with the developer’s code, but BDD tests are written in a language which can also be made out by business stakeholders.
- Last but not least, acceptance tests can be executed automatically, while it is performed manually by business stakeholders.
92) What happens during Sprint 0?
Ans:
There is no such thing as Sprint 0. It is not a valid Sprint from Scrum timeboxed events. “Sprint 0” has become a phrase misused to describe the planning that occurs prior to the first sprint like refining product backlog, architecture envisioning, prioritizing and release planning etc. This term is confused with the term “Release 0”. It is ideal to talk about Release 0 as opposed to Sprint 0.
93) Why Backlog grooming is important?
Ans:
This is important because:
- It increases the efficiency of the team by reducing uncertainty and unknowns from user stories.
- It helps weed out redundant and not required anymore type of scenarios
- It helps adjust the estimates and priorities at the given point of time
- Sprint planning becomes a matter of few minutes if backlog is groomed properly.
94) Name two techniques for prioritizing user stories?
Ans:
- MoSCoW
- 100 Point Method.
95) How can tracer bullet be used?
Ans:
Tracer bullet can be used as a spike with the current architecture or the current set of best practices. The purpose of a tracer bullet is to examine how an end-to-end process will work and examine feasibility.
- Tracer ammunition, which is a part of bullet built with a small pyrotechnic charge in their base
- It is a fictional detective, alter ego of Calvin in the comic strip Calvin and Hobbes
- It is used in Scrum (software development) to describe a proof-of-concept deliverable
- Pathfinder (library science) – a term for those pathfinders produced by the Library of Congress.
96) How can QA add value to an agile team?
Ans:
- QA can provide value addition by thinking differently about the various scenarios to test a story. They can provide quick feedback to the developers whether new functionality is working fine or not.
- QA is not a separate silo but is part of a cross-functional project team. It is included in the project from the beginning, and the whole team works together on user stories using the same tracking tools. The Director of the QA team works closely with the executive management team to identify technology and staffing needs in relation to project pipelines.
- Quality Assurance is empowered to support projects and add value in whatever way the situation requires. Examples include design reviews, requirements assessments, browser and device support, process, tools, risk assessments, and helping to determine “Definition of Ready” and “Definition of Done.”
- QA sits with the project team whenever possible, allowing for increased conversation and problem-solving in real time. The QA team attends and contributes to all relevant planning meetings and sprint ceremonies and also work directly with clients on quality and testing processes.
- Members of QA teams always learn as individuals, as project team members, and as representatives of a skilled discipline within the organization. Our process and approach to testing evolve to keep up with advances in technology and the changing needs of clients. What works for one client or project might differ radically from another. Flexibility is the key.
97) What do you know about “Planning Poker” technique?
Ans:
Planning poker, also known as Scrum Poker, is a card-based agile technique that is used for planning and estimation. To start a session of planning poker technique, the agile user story is read by the product owner. The steps performed in the poker planning technique are –
- Each estimator has a deck of poker cards with the values such as 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, and so on, to denote story points, ideal days or something else that the team uses for estimation.
- Each estimator has a discussion with the product owner and then privately selects a card on the basis of their independent estimation.
- If the cards with same value are selected by all estimators, it is considered as an estimate. If not, the estimator discusses the high and low value of their estimates.
- Then again, each estimator privately selects a card and reveals. This process of poker planning is repeated to reach a general agreement.
98) What should a “Definition of Ready” consist of?
Ans:
- A “Definition of Ready” is an agreement between the scrum team and the product owner about what must be included in a user story before the story can be considered ready for estimation. It defines what a good user story looks like. Another approach, however, is to use a framework for how we think about user stories. One such framework is the INVEST mnemonic by Bill Wake, which specifies:
- Independent: The user story should be self-contained, in a way that there is no inherent dependency on another user story.
- Negotiable: User stories, until they become part of an iteration, can always be changed and rewritten. Valuable: A user story must deliver value to the end user.






