
SAP HANA is a SAP in-memory database management system. It excels in real-time data processing and analytics because to its in-memory data storage, columnar database structure, and powerful analytics and machine learning capabilities. SAP HANA also allows for data integration from many sources, powerful data modelling tools, and high availability via capabilities such as automated failover.
1. What does SAP HANA?
Ans:
SAP HANA, which stands for a High-performance Analytical Application, is one of the greatest solutions now on the market for database administration. It can directly be linked to the ERP systems. It is possible for users to consider the frontend modeling for replication center in this approach.
2. Explain Normalization and De-Normalization.
Ans:
Normalization is nothing but a process that is adopted for purpose of removing the redundant data from database. This is generally done by splitting table into various sections. This actually makes sure of the integrity. On the other side, de-normalization is the act of taking duplicate data into account so that all complicated queries may be improved in terms of overall performance.
3. What does SLT? How do configure it?
Ans:
It stands for the SAP Landscape Transformation. It triggers replication of data from the source to target system where either of the two ends has to SAP HANA. The configuration is performed in Configuration & Monitoring dashboard using the t-code LTR.
4. What does different Replication techniques?
Ans:
- Trigger-based replication using the SLT.
- ETL-based replication using the BODS.
- Extractor data acquisition using the DXC.
5. What does different scenarios in Replication?
Ans:
Load: Starts the initial load of the replication of data from a source system. It is one-time process.
Replicate: Actual phase of the replication. Database triggers and different logging tables for an every table are created in SLT.
Stop: Stops any replication currently in the process. Database triggers are aborted.
Suspend: A Table replication is paused. Database triggers will not be deleted and changes will be filled in the logging tables.
Resume: Restarts replication for the suspended table.
6. Name two types of relational data which can store in SAP HANA.
Ans:
The following two categories of data are available for users to store in the system:
- Column Store.
- Row Store.
7. What sort of advantages do businesses have with effective database management?
Ans:
- By data managing, users are free to derive results that can be considered for long run.
- A lot of complexities related to data can be avoided easily.
- The data can be managed in the sections and can be accessed easily.
- Well-managed data is useful in the designing reports, preparing documents, and assisting different departments in other tasks.
8. What does various tasks in SAP HANA which are performed by Modeling Studio?
Ans:
The first thing it performs is to select the type of tables that will be stored in HANA. The selection of Metadata is also responsibility of the modeling studio. It manages all data services for inputting data from a warehouse or other sites. It only controls connections between ERP instances. The entire data services can be used for the modeling only through modeling studio. Any sort of the another modeling in the SAP HANA itself is handled by studio.
9. Mention some important components of SAP HANA.
Ans:
- SAP HANA Appliance
- Database
- Application Control
- Studio
10. What does different user parameters in Semantic layer?
Ans:
- Measure and Attribute
- Hierarchies
- Parameters/Variables
- New Calculated Column
11. What does transformation rules?
Ans:
In basic terms, they are the rules in responsible for managing a source table. This collection of guidelines and rules forms an important part of the basis for all tasks performed at the table. A few of these rules are also applicable while handling the some replication processes.
12. What does benefits of users can have from SLT Replication in SAP HANA?
Ans:
It is basically approach that has been categorized as a triggered one i.e. users need not to worry about overall impact of performance on the source system. if the size of the data is large, the users may easily check that it is filtering and being transformed. Also, users may ensure real-time data replication. It is possible for users to simply make sure of more source systems to only one system based on the HANA. The reverse action is also more possible.
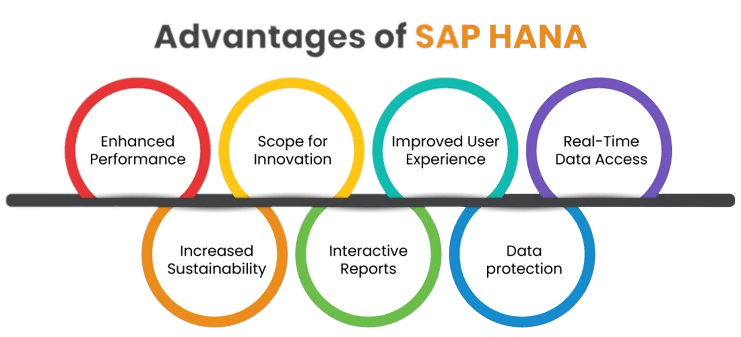
13. What are the advantages of SAP HANA?
Ans:
Lightning-Fast Performance: In-memory processing for rapid data access.
Real-Time Analytics: Immediate insights for quick decision-making.
Advanced Analytics: Includes machine learning for predictive insights.
Simplified IT: Reduces complexity and costs.
Data Integration: Aggregates data from various sources.
14. What does Master Controller Job in the HANA?
Ans:
It is the controller that can be deployed for different reasons and purposes. It simply makes sure that logging tables are created and activates the same in the system. The master controller can also be used to create synonyms. Also, With the use of this method, new entries may be made in the management tables. This method allows loading the entire table.
15. Explain Transaction manager in SAP HANA.
Ans:
All database transactions can be coordinated simply with transaction manager and the users are free to keep close eye on the closed as well as on running transactions. Users receive notifications when transactions are saved or rolled back. The storage engines will function without delay as a result.
16. What does benefits of using Calculation view with Star join?
Ans:
It simplify a design process as allows to select the multiple measures from multiple fact tables and can implement the 3NF using Star Join.
17. How SQL statement is processed?
Ans:
The statement is implemented with the reference to concerned transaction. Every transaction must start with a fresh session for the user. Even though it often takes more effort, doing this usually benefits dividends.
18. What does data redundancy is?
Ans:
Data redundancy means the duplicate data in system. It adds unnecessary cost by grabbing additional cost and can be reason for slow operations of the database.
19. Mention type of relationships in the database.
Ans:
They are:
- One to one
- One to many
- Many to many
One table is directly linked to other tables that are similar in terms of columns under the one to one method.. In middle approach (One to many) one table is directly associated with the another table and that has key relation outside database. In last approach, every single record in tables can relate the multiple number or records which are present in the another table.
20. What does use of Data Foundation, Star Join and Semantics?
Ans:
Data Foundation: to add a column base tables.
Star Join: to add the other type of views.
Semantic: to define the user parameters and to define a measures and dimensions.
21. Why DML compiler is significant according to database management system?
Ans:
The DML compiler is one that is responsible for translations of a DML statements into language that is simple to understand by Query Evaluation engine. It simply makes the sure of no occurrence of errors in database management.
22. What does benefits of SQL?
Ans:
If queries in SQL are simple, the users are free to retrieve very large sum of data more easily from the system. Another good thing about SQL is it is more easy to learn and implement. There is vast support available for a SQL and all queries can be addressed reliably. Using the SQL, the database can be managed very easily and in fact without considering large amount of coding.
23. How does SAP HANA installed and configured??
Ans:
- First, make sure system satisfies the SAP HANA’s hardware and software requirements.
- From SAP support portal, download a SAP HANA software.
- Following installation, SAP HANA must be configured according to the needs.
- After configuring a SAP HANA, must test it to make sure it is operating properly.
24. What does advantages of views can bring to the database?
Ans:
- They simply make sure of accuracy.
- All outcomes can be generated without wastage of the resources
- Access to important data is always restricted and it does not allow any sort of modifications in data.
25. What does Persistence Layer in SAP HANA?
Ans:
The SAP HANA, which plays an essential role, will really make use of it later on. Actually, HANA has a built-in computation engine, and users must use data without taking a backup. The same can create issue during powerful failure and thus it is important to keep backup of a same. This layer comes as savior and it makes sure no loss of data during such situation.
26. What does operating system requirement for SAP HANA?
Ans:
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server Operating system is the requirement for SAP HANA.
27. How to secure Sap Hana user connection?
Ans:
A Sap Hana database user is first and foremost secured by the password. However, a password is more often required at command line in order to connect and execute batch or SQL script. Anyone can see what the username and password are. A special key can be made in reference to the specific user in order to prevent that circumstance. The username and password are invisible by the use of that key.
28. What does the best way to manage, operate, and monitor Sap Hana systems?
Ans:
Sap Hana is a young database with the interesting features of SAP HANA. First of all Sap Hana is in-memory database. It is accessible for the administration by various channels. Directly from Server, It is not most convenient method but can use hdbsql to manage databases. With web-based interface Hana cockpit, can browse and manage the sap Hana environments. The Client Hana Studio is a comprehensive tool for managing Sap Hana, but it must be physically installed, it is dependent on client hardware.
29. What does different compression techniques?
Ans:
There are the three different compression techniques:
- Run-length encoding
- Cluster encoding
- Dictionary encoding
30. What does advantage of SLT replication?
Ans:
- The trigger-based methodology used by SAP SLT has no obvious performance effects on the source system.
- It offers the filtering capability and transformation.
- It enables a real-time data replication, replicating only related data into the HANA from non-SAP and SAP source systems.
- It Replication from a several source systems to one HANA system is allowed, also from one source system to the multiple HANA systems is allowed.
31. How does ensure the security of data in SAP HANA?
Ans:
SAP HANA offers the number of techniques to ensure a data security, including
- Use of secure communication protocols.
- The implementation of role-based access control.
- Activation of a data encryption.
32. What does Various components of SAP HANA?
Ans:
- SAP HANA DB
- SAP HANA Studio
- SAP HANA Appliance
- SAP HANA Application Cloud
33. Why is SAP HANA a unique model?
Ans:
SAP HANA is considered as unique ERP tool in many possible ways. The reasons are:
- SAP HANA is first-ever technology used for handling both the OLTP and OLAP application processing methods.
- SAP HANA supports query processing environment for both the structured and unstructured data sets. This can be used in a relational database tables and structured data sets.
- This tool contains the multi-core process engine used to process data sets parallelly. The parallel process can be done using the different columns of same database tables.
- Using column database set, this tool optimizes various data structures and more easy to store large amounts of the compressed data sets.
34. Name the platforms which support SAP HANA.
Ans:
SAP HANA supports the following the various platforms;
- A Microsoft Windows VISTA versions 7, 8 servers 2008 (32-bit memory)
- A Microsoft windows operating system versions 7,8,10 servers’ 2008/R2 (memory 64-bits)
- A SUSE LINUX operating server (SLES) version 11 (memory 64-bits)
- A Red Hat Enterprise Server (RHEL) version 6 (64-bit memory)
- A MAC operating system OS X Mavericks version 10.9.
35. List the compressions techniques of SAP HANA technology.
Ans:
There are 3 compression techniques available in the SAP HANA technology such as;
- Run-length encoding
- Cluster encoding
- Dictionary encoding.
36. What does different building blocks used in SAP HANA environment?
Ans:
- In-memory computing engine.
- A Database (Replication agent and replication server)
- A SAP business objects BI 4 (designer tools, a data server designers, and data servers, etc.)
- SAP HANA studio (Eclipse-based tool)
- Clients.
37. How does perform system updates and upgrades in SAP HANA?
Ans:
To perform a system updates and upgrades in SAP HANA, need to follow a defined upgrade path and ensure that all the requirements are met. This involves the creating backups, applying support packages, and testing system before and after upgrade.
38. List the architectural components used in SAP HANA.
Ans:
The SAP HANA architecture consists of the various components that make a system architecture.
- Index system server
- Name server system
- Pre-processor server system
- SAP HANA model studio repository
- XS engine system.
39. Name the components of Index server.
Ans:
- Relational data engine
- Connection and session manager
- Planning engine system
- Calc engine system
- Persistence layer
40. Explain sizing in SAP HANA?
Ans:
Sizing in SAP HANA explains the hardware requirements for specific SAP HANA installation process. Hardware components are considered as a important for sizing parts of the System CPU memory or RAM and hard disk requirements. The tough task here is that estimate a size of the SAP HANA server that will be best suited for user’s requirements.
Sizing in SAP HANA can be performed in the three ways;
- Using a quick sizer tool.
- Using a DB script.
- Using a ABAP report.
41. Define the rows storage in SAP HANA?
Ans:
Row storage: Row storage is the data storage method that horizontally stores datastores the data in a horizontal way. Users can store data sets as similar to a disk databases. Row storage in the SAP HANA can be stored in main memory whereas traditional storage can be used to store a data in disk databases.
42. What does different perspectives in SAP HANA studio?
Ans:
The following are some commonly used perspectives as follows;
- The SAP HANA administration console.
- The SAP HANA modeler control.
- Application server development.
- Life cycle management in the SAP server.
- SAP HANA development.
- ABAP module development.
- Business warehouse (BW) modeling.
43. Define SAP HANA system Monitor.
Ans:
The SAP HANA monitor in studio can be used to perform a tasks like administering and monitor a system’s performance and availability of SAP HANA architectural components. Also, users can access SAP HANA system’s details, configurations, and services offered by various SAP HANA components. SAP HANA system monitor can also be used to monitor the several database aspects are like alerts, trace disk, log disks, data disk, memory, data volume, and disk space, etc.
44. What does three types of information views?
Ans:
- Attribute View
- Analytic View
- Calculation view.
45. What does the types of SAP HANA engines?
Ans:
- Join engine.
- OLAP engine.
- Calculation engine.
46. Mention the types of packages used in SAP HANA?
Ans:
The packages in the SAP HANA are nothing but folders which holds the modeling related database objects. call it a package because it contains all the information related to the modeling studio in complete package wise and later and can use it for transition purposes (Import/Export) purposes. This information may be a type information view, Sub-package details, analytical privilege, and procedures.
In SAP HANA, there are two different types of packages:
- Structural package
- Non-structural package
47. What does Schemas in SAP HANA?
Ans:
The schemas are the type of database element of system which resides in the catalog node of SAP HANA model. The relational SAP HANA database can be divided into the sub-databases within SAP HANA nodes. Schemas are like container that contains an information like element details, objects, or relational database details.
48. Distinguish Differences between OLAP and relation connection to SAP HANA?
Ans:
Relation connection: Relation connection can be used when there is need to access a conventional database tables. Relational connections are can be created by IDT or UDT semantic layers.
OLAP: The OLAP connection is used to access the multidimensional data cubes and it also establishes direct connection to SAP HANA business layer of the database model to relational connection. These connections help users to connect to database tables or information views in SAP HANA.
49. Define referential join in SAP HANA?
Ans:
The referential join in SAP HANA is the default join type in data modeling. This join is almost similar to inner join. The only difference is that referential integrity can be formed when using the referential join otherwise it cannot be formed. Referential join can be formed between the fact table and master data table.
50. What does SAP HANA business objects reporting tools?
Ans:
- SAP Lumina.
- Web Intelligence.
- Design studio.
- SAP crystal reports.
- Universe designers.
- Dashboard designer.
51. Distinguish Difference between catalog and content node?
Ans:
The catalog node acts as database directory for SAP HANA model and also holds structured information about the physical objects.
The content node contains information about design-time repository data objects and also holds packages are attributes, views, calculation, and analytical views.
52. Mention the different ways to create a table in SAP HANA?
Ans:
There are two possible ways to create table in SAP HANA;
- Command-line method
- GUI based methods
53. What does types of connecting drivers used by SAP HANA reporting tools?
Ans:
The SAP HANA uses four types of connecting drivers are
- ODBO (OLE DB used for OLAP)
- ODBC driver
- JDBC driver
- BICS driver
54. Explain Parallel Processing in Sap Hana.
Ans:
Using a columnar information garage technique, the workload in the SAP HANA is divided vertically. The columnar technique permits can linear searching and aggregation of information instead of -dimensional facts structure. If more than one column is to be processed, every assignment is assigned to various processor. Operations on one column are then collimated with aid of column divisions processed by unique processors.
55. List advantages of using Sap Hana Database.
Ans:
- With the HANA technology, may create a gen-next programs giving powerful and green results within digital economic system.
- By use of unmarried statistics-in reminiscence, SAP HANA helps clean the transaction process and fault-tolerant analytics
- Easy and easy operations the use of open-supply, unified platform within a cloud
- A High-degree Data Integration to get right of entry to large quantities of facts
56. Explain Slt.
Ans:
SLT expands to the SAP Landscape Transformation relating to cause –primarily based replication. SLT replication permits a records switch from supply to goal, in which supply can be SAP or non-SAP whilst goal gadget has to be SAP HANA with the HANA database. Users can accomplish the data replication from multiple assets. The 3 replication strategies supported by the way of HANA are:
- SLT
- Business Objects Data Services (BODS) from SAP
- SAP HANA Direct Extractor Connection (DXC)
57. How to Perform Backup And Recovery Operations?
Ans:
During normal operation, statistics is by default saved to the disk at savepoints in the SAPHANA. As quickly a there is any update and transaction, logs turn out to be lively and get saved from a disk memory. In case of electricity failure, the database restarts like the any other DB returning to closing savepoint log kingdom. SAP HANA requires a backup to defend towards the disk failure and reset DB to preceding nation. The backups concurrently because customers preserve appearing responsibilities.
58. What does Business Objects Universes in SAP HANA?
Ans:
There are two ways in which the reporting the tools can connect to SAP HANA. One way is direct OLAP connection and another is indirect relational connection.
In relational connection type, reporting tools fetch data from universe layer instead of connecting directly to the SAP HANA. Thus, SAP Business Objects Universe acts like middle layer between the reporting tools and SAP HANA.
Reporting the tools such as WebI, Crystal Reports for an Enterprise and Dashboard designer use Universe as intermediate layer to connect to the SAP HANA. Although, option of connecting directly to the SAP HANA is available in current versions of a Web Intelligence.
59. What does set operators? How many of them are supported in the SAP HANA?
Ans:
Can use the set operators to combine the multiple queries and return a single result set in output.
Operator: UNION
Description: This operator is used to combine outputs of two or more SQL select a statements or query expressions.
Operator: UNION ALL
Description: This operator is used to combine all outputs of two or more SQL select statements or query expressions. It also includes the all duplicate rows.
Operator: INTERSECT
Description: This operator is used to combine outputs of two or more SQL select a statements or query expressions and return all common rows.
60. What data types are supported in SAP HANA SQL scripting?
Ans:
- Binary data type
- Boolean data type
- Numeric data typeCharacteristic string data type
- Datetime data type
- Large Object (LOB) data type
- Multi-valued data type
- Spatial data type
61. Distinguish difference between VARCHAR and NVARCHAR in SAP HANA SQL?
Ans:
VARCHAR
The VARCHAR data type assigns the character string of variable length.
NVARCHAR
The NVARCHAR explains the character set string of variable length of Unicode characters.
62. How can perform data profiling in SAP HANA?
Ans:
SQL data profiling is the process of refining a data and analyzing it to get better understanding of it. The main purpose behind a data profiling is to check data coming from the different sources, identify the problems in it and fix the problems to maintain data quality.
In SAP HANA Studio, can conduct profiling for data in the tables or data in views.
- Open a SAP HANA Studio and login to HANA system.
- Expand schema in the Catalog tab and select table or view.
- Right-click on name of the view or table and select a option Open Data Preview.
63. What does JSON object expressions in SAP HANA?
Ans:
The JSON Object expressions used in the SAP HANA generate JSON object. A typical JSON object has a two elements; Key and Value.
A “key” is the string literal which must be in double quotes “” always. And a
64. Why does triggers used in SAP HANA?
Ans:
Use SQL triggers in SAP HANA for the several purposes such as:
- Auditing operations
- Synchronous the replication of data tables
- To store the information on accessing the table
- Security authorization processes
- To prevent the invalid transactions
- An Event logging processes
- To enforce a referential integrity
- To automatically generate a derived column values
65. Explain the three types of SQL statements used in SAP HANA.
Ans:
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Use data manipulation language (DML) within a schema objects to manipulate and manage data in them.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL statements and keywords explain the structure of data in databases and schemas.
Data Control Language (DCL)
The DCL statements control user access and privileges to database.
66. Distinguish different between Synchronous, Synchronous in-memory, and Synchronous full-sync replication modes?
Ans:
Synchronous mode: In synchronous mode of system replication, the primary node waits and halts its transactions till time the secondary node sends an acknowledgment indicating it has received a data log and persisted log volumes on its disk.
Synchronous in-memory mode: Synchronous in-memory mode is a default replication mode. The primary node waits for confirmation message sent by a secondary node upon receiving log successfully. Until then, primary node/system commits no transactions.
Synchronous full sync mode: The full sync mode ensures the complete data protection i.e. zero data loss because it blocks transactions on the primary node until replication is successfully completed on a secondary node.
67. Explain run-length encoding compression used in SAP HANA.
Ans:
Run-length compression: In run-length encoding compression method, it stores the only one of repeating value IDs along with its start position. Suppose a data value with the value ID 5 appears 3 times consecutively starting from position 0.
Then compression will store only one instance off value ID 5 and start position as 0. Thus, call it run length encoding because it stores start positions as run-length values.
- Method type: RLE
- Applied to: Main storage
- Applied on: A Several frequent column values
68. What does SAP HANA sidecar?
Ans:
SAP HANA sidecar is a SAP HANA platform serving as secondary database and computing platform to the full-service, already existing system with its own traditional database.
SAP HANA sidecar approach uses the SAP HANA system for storage and computational capabilities to carry out the operations related to data and database objects of the other systems.
69. How does data imported/exported using Developer Mode in SAP HANA?
Ans:
The Developer Mode method is an essentially used to import/export individual database objects from the target system to a location in a local client system. It is different from delivery unit method as in it, have to export multiple packages enclosed in single unit and cannot export individual files.
70. What does SAP Support Mode?
Ans:
Use the SAP Support Mode to export database objects and data for a SAP support purposes. Users use this export method in case errors to seek help in the troubleshooting and debugging from a SAP Support team.
In SAP Support Mode option, simply have to select data object facing issues and add it into Selected section. Then choose export location, i.e. to server or local client. Add required details and click on Finish. It will export a database object to support team’s system successfully.
71. What does X.509 and its relation to SAP HANA?
Ans:
It is indirect method of security, authenticating users to let them access the SAP HANA. It gives the User-specific x.509 certificates to the users requesting access into SAP HANA database from a SAP HANA XS system.
72. Enlist the scenarios in which object privileges are used in SAP HANA.?
Ans:
Object privileges used in various scenarios are given below:
- We can use the object privileges to authorize a run time database objects.
- Object privileges are used as a source privileges to authorize access of remote data sources connected to the SAP HANA through SAP HANA smart data access.
- can use the object privileges to authorize activated repository objects like calculation views.
- can use the object privileges to authorize a schema containing activated repository object.
73. Which privileges need to work on schema, table or views in SAP HANA?
Ans:
An authenticated HANA system user requires a object privileges listed below to have permission to work on schemas, tables or views.
- ALL PRIVILEGES
- CREATE ANY
- CREATE VIRTUAL FUNCTION PACKAGE
- ALTER
- CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE
- DEBUG
- DELETE
- DROP
- EXECUTE
- INDEX
74. What does the most probable reasons for SAP HANA system lockdown?
Ans:
The most probable reasons for system to go into lockdown mode are explained below:
- Expiration of temporary license which stays valid only for the 90 days from SAP HANA database installation.
- When have not renewed a permanent license key and temporary key has also expired after 28 days.
- The hardware key changes while using the temporary license key.
- When have an enforced license key type and exceed the permitted memory usage on it
- When delete all the existing license keys on the system.
75. Distinguish difference between unenforced and enforced licence keys?
| Aspect | Unenforced Keys | Enforced Keys | |
| Monitoring & Control |
Limited monitoring |
Active monitoring | |
| Restrictions | Minimal or none | Specific restrictions | |
| Compliance | Not actively enforced | Actively enforced | |
| Violation Consequences |
Few consequences |
Potential penalties |
76. What does auditing policies in SAP HANA auditing?
Ans:
The audit policies explain and decide which activities or events in the SAP HANA need auditing. The administrators need to enable newly created audit policy as it will not get triggered on assigned action unless the enabled manually and explicitly.
The administrator is free to enable or disable audit policy as per requirement. To enable or disable audit policy, administrator must have AUDIT ADMIN privilege.
77. What does maximum possible number of tables and columns within each table in SAP HANA?
Ans:
- The maximum number of tables which can create under schema is 131072 in SAP HANA system
- The maximum number of the columns which can create in table is 1000 under HANA system schema.
78. What does compelling SAP HANA use cases?
Ans:
Real-time analytics as supported by the SAP HANA and has numerous potential use cases including:
- A Profitability reporting and forecasting
- Retail merchandising and supply chain optimizationA Security and fraud detection
- Energy use monitoring and optimization and
- Telecommunications network monitoring and optimization.
79. What does analytical privileges in SAP HANA?
Ans:
In SAP HANA, analytical privileges are data access restrictions that explain and assign to be selected users of SAP HANA.
They work as a data security tools for SAP HANA users and clients. Analytical privileges are provided a row-level data security to SAP HANA users contrary to object-level security which object privileges assign. This restricts users to see only selected section of data from an entire data set.
80. What does System Requirements for SAP HANA?
Ans:
- CPU: An Intel Xeon E5 – 26xx v2/v3, 8 cores minimum, up to 1.5TB, 2 socket, and scale up only.
- RAM: minimum of be 128 GB Ram to max memory supported by system.
- Drives & Storage: Minimum 2 times of memory.
- An Operation system: SUSE Linux Latest.
81. What does Catalog in SAP HANA?
Ans:
In SAP HANA, catalog represents a SAP HANA’s data dictionary which includes all the data structures, data, and tables which can be used. All views and physical tables can be found under a catalog nod.
82. What does mean by Calculation View in SAP HANA?
Ans:
In SAP HANA, calculation views are used by the developers to consume attribute and the other calculation views. They are also used to perform more complex calculations.
There are two methods are available to create calculation view in the SAP HANA:
- SQL Editor
- Graphical Editor
83. What does index in SAP HANA?
Ans:
An index, which stores the sorted copy of the data in those columns, is created using the one or more columns from database tables. When query containing the indexed columns is executed, SAP HANA can quicklylocate relevant data and create the results by using index.Indexes can be created for both the single columns and groups of a several columns. With indexes, SAP HANA queries may be executed more quickly, especially for large databases with the lots of rows. Indexes have a certain drawbacks, though, including the increasing database size and slowing down insert, update, and delete operations.
84. What does Decision Table and explain its types?
Ans:
In SAP HANA, decision table is tabular representation of decision-making process. It doesn’t portray static solutions or answers, and standardized logical process and allows the developers to insert values in both actions and conditions related to the decision.
85. What does SAP HANA cockpit?
Ans:
SAP HANA cockpit is SAP Fiori Launchpad site that allows with a single point-of-access to range of Web-based applications for online administration of SAP HANA. And access the SAP HANA cockpit through the Web browser.
To open a SAP HANA Cockpit → Right click on the HANA system in Studio → configuration and monitoring → open SAP HANA cockpit
86. Distinguish difference between Catalog and Content tab?
Ans:
Catalog: This contains the RDBMS objects like schemas, tables, views, procedures, etc. And can open SQL editor and design database objects.
Content:This is used to keep a design time repository. And can create a new packages and design Information views in HANA system. Various views can be created under the content tab to meet business requirement and to perform the analytical report on top of the modelling views.
87. What does tenant database in SAP HANA?
Ans:
A tenant database in the SAP HANA is a feature that enables operation of numerous separate databases on a single HANA system. Every tenant database in the same system is totally isolated from other databases and has its unique collection of the tables, views, and other database objects.
88. What does different methods of data replication in HANA?
Ans:
- SAP LT Replication SLT
- SAP Data Services
- Direct Extract Connection DXC
89. How can use Data provisioning in SAP HANA studio?
Ans:
Go to the SAP HANA Modeler Perspective → Data Provisioning.
90. What does restricted user in SAP HANA system?
Ans:
Restricted users are those users who access the HANA system with some applications and don’t have SQL privileges on HANA system. When these users are created don’t have any access initially.
91. What does different privilege types that can be assigned to user in HANA studio?
Ans:
- System Privilege
- Object Privilege
- Analytic Privilege
- Package Privilege
- Application Privilege
- Privilege on roles
92. How can connect SAP HANA to Microsoft Excel?
Ans:
MDX Provider is used to connect MS Excel to the SAP HANA database system. It provides the driver to connect HANA system to Excel and is further used for a data modelling. And can use Microsoft Office Excel 2010/2013 for connectivity with the HANA for both 32 bit and 64 bit Windows.
93. How can limit the size of a data backup files in HANA system?
Ans:
This can be done in the File Based data backup settings. In Backup tab, go to Configuration → Limit Maximum file Size check box and enter a file size.
94. What does critical services HANA DB Server Consists?
Ans:
- Index Server
- Name Server
- Statistics Server
- Preprocessor ServerXS Engine
95. What do understand from in-memory computing? What its significance in SAP HANA?
Ans:
In the in-memory computing, a large amount of data as information is stored in Random-Access Memory (RAM) instead of external storage disks.
This technology replaces traditional way of storing data in disks and uses the relational database management methods to fetch and process data. In-memory computing technology is much cheaper and quicker than the traditional database system.
96. Name the components of an index server.
Ans:
There are six main components of index server:
- Relational data engine
- Connection and Session manager
- Authorization manager
- Planning engine
- Calc engine
- Persistence layer
97. Explain SAP HANA Information Modeler?
Ans:
Information Modeler lets us design the information views or models on top of SAP HANA database using tables in it. Such models are created to be serve a business logic and operation. They are generated directly on top of HANA database layer.
The information modeler provides interface and tools to select the attributes and measures from database tables so that user can create multiple information views using physical tables of transactional data stored in a databases.
98. What does types of SAP HANA engines?
Ans:
Join Engine: use the join engine every time an attribute view is created or be used, or a join condition is applied in the native SQL command.
OLAP Engine: use the OLAP engine in creation of analytic views. use it only when attributes are used in analytical view and no calculation is done. If operations like the calculations, counters, restricted measures are used other engines like a calculation engine is used along with OLAP engine.
Calculation Engine: use the calculation engine in calculation along with used in other views like the analytical and attribute view whenever apply complex logic and calculation operations.
99. Explain the different types of joins in SAP HANA.
Ans:
- Standard Database Join
- SAP HANA Specific Joins
- Referential join
- Text join
100. What does SAP Business Objects BI 4 reporting tools?
Ans:
The list of reporting and dashboarding tools are available under SAP Business Objects BI 4 package is:
- SAP Lumira
- Web Intelligence
- SAP Crystal Reports
- Design Studio
- Dashboard designer
- Universe Designer (IDT/UDT)
- BusinessObjects Explorer
- Analysis Office
- MS Excel






