
These SAP QM Interview Questions are specifically created to help you become familiar with the kind of questions you could be asked on the subject of SAP QM during your interview. In my experience, competent interviewers seldom prepare specific questions for you to answer during the interview; instead, they often begin with a basic explanation of the topic and then go on depending on how you respond to additional conversation and clarifications.We’ll go over the most common SAP QM interview questions and their thorough responses. We will go through scenario-based interview questions for SAP QM, interview questions and answers for experienced candidates, and interview questions for freshmen.
1. Explain the key components of SAP QM.
Ans:
Quality Planning (QP):
- Master Inspection Characteristics (MIC)
- Inspection Methods
- Sampling Schemes
Quality Notifications (QN)
- Recording Quality Issues
- Notification Types
Quality Certificates:
- Certificate Profiles
- Certificate Processing
Quality Information System (QIS)
- Reporting and Analysis
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Integration with other SAP Modules
Quality Management in Logistics:
- Inspection at Goods Receipt
- Inspection at Goods Issue.
2. What is Quality Planning in SAP QM?
Ans:
Quality Planning involves defining inspection plans and inspection methods for products. It includes specifications for sampling procedures, inspection characteristics, and the frequency of inspections. Quality Planning is a key component that focuses on defining the necessary steps and criteria for ensuring the quality of products and processes. Quality Planning involves the creation and management of data related to quality specifications, inspection methods, and sampling procedures.
3. What is the purpose of the Quality Notification in SAP QM?
Ans:
Quality Notifications are used to report and manage quality issues such as defects, non-conformities, or other problems. They serve as a means to initiate corrective actions and track the resolution of quality-related concerns. ● Issue Identification and Recording
- Initiating Corrective and Preventive Actions
- Responsibility Assignment
- Workflow Management
- Communication Tool
4. How do you configure Inspection Types in SAP QM?
Ans:
Types in SAP Quality Management (QM) involve defining the different categories of inspections that can be performed on materials during various stages of the procurement or production processes. Inspection types determine the purpose, scope, and procedures for quality inspections.
5. What are the different types of Inspection Lots in SAP QM?
Ans:
There are several types of inspection lots in SAP QM, including Goods Receipt Inspection (01), In-Process Inspection (04), and Customer Complaint (08), among others. Each type corresponds to a specific stage in the production or quality process.
6. How can you link SAP QM with other SAP modules?
Ans:
SAP QM can be integrated with other SAP modules like Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), and Sales and Distribution (SD) to ensure seamless information flow. Integration points include inspection lots triggered by goods receipt or production orders.
7. Explain the purpose of the Quality Info Record in SAP QM.
Ans:
The Quality Info Record in SAP QM is used to store quality-related information for a material or vendor. It includes data such as inspection methods, sampling procedures, and other quality-specific details. The Quality Info Record is closely associated with procurement processes, ensuring that the quality requirements are met consistently.
8. How can you trigger an inspection in SAP QM?
Ans:
Inspections in SAP QM can be triggered by various events, such as goods receipt, production order completion, or manually through a quality notification. These inspections help ensure that the product or material meets predefined quality standards. The specific method of triggering an inspection can depend on the type of inspection, whether it’s an incoming inspection, an in-process inspection, or a final inspection.
9. Explain the difference between Quality Inspection and Quality Control in SAP QM.
Ans:
- Quality Inspection: This is a broader term that encompasses the entire process of evaluating and verifying the quality of products or processes. Quality Inspection in SAP QM involves planning, execution, and documentation of inspections to ensure that materials, products, or processes meet specified quality standards.
- Quality Control: Quality Control is a subset of Quality Inspection. It specifically refers to the activities and processes undertaken to monitor and control the quality of products during or after production. It involves methods and techniques to detect, correct, and prevent defects.
10. What is a Quality Notification in SAP QM?
Ans:
A Quality Notification in SAP QM is a document used to record and manage quality-related issues. It captures information about problems, defects, or non-conformances and initiates follow-up actions such as inspections, rejections, or corrective actions. It serves as a tool to initiate and track the resolution of quality problems in various business processes.
11. How can you perform batch management in SAP QM?
Ans:
Batch management in SAP QM involves tracking and managing materials based on batches. This is crucial for industries where the characteristics of each batch may vary. Inspection lots are created for each batch, and quality inspections are carried out accordingly.
12. What is SAP QM, and how does it contribute to the business process?
Ans:
SAP QM is a module within the SAP ERP system that focuses on managing quality throughout the business processes. It ensures that the products meet the required quality standards. SAP QM integrates quality management functions into different business processes like procurement, production, and sales. It helps in maintaining and improving product quality, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
13. What is the purpose of the Inspection Lot in SAP QM?
Ans:
An Inspection Lot in SAP QM is a collection of materials that have similar characteristics or belong to a common batch. It is created when quality-relevant activities are triggered, such as goods receipt, production completion, or during the procurement process. The Inspection Lot serves as a container for inspection data and results, enabling organizations to track and manage the quality of materials throughout their lifecycle.
14. How does SAP QM integrate with other SAP modules?
Ans:
SAP QM integrates with various SAP modules to ensure a seamless flow of information across different business processes. It is closely linked to Materials Management (MM) for procurement, Production Planning (PP) for production processes, Sales and Distribution (SD) for sales processes, and Plant Maintenance (PM) for managing equipment and maintenance-related quality aspects.
15. How does SAP QM support batch management?
Ans:
SAP QM plays a crucial role in batch management by linking quality data to specific batches of materials. Inspection Lots are often associated with batches, allowing organizations to track the quality history of each batch. This integration ensures that only materials meeting quality standards are used or delivered, contributing to overall product quality and compliance.
16. What is the purpose of the Quality Info Record in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Quality Info Record in SAP QM is used to store information about the quality requirements and specifications for material from a specific vendor. It includes details such as inspection parameters, sampling procedures, and acceptance criteria. Quality Info Records help streamline the inspection process by providing a standardized set of quality expectations for materials procured from specific vendors.
17. How can you configure the usage decision in SAP QM?
Ans:
Configuration of the usage decision in SAP QM involves setting up the criteria and rules that determine whether a material is accepted, rejected, or requires further inspection. This includes defining inspection types, inspection codes, and inspection catalogues. Additionally, the configuration specifies the actions to be taken based on inspection results, such as updating stock statuses, triggering notifications, and generating quality certificates.
18. What is the significance of the Quality Score in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Quality Score in SAP QM represents a numerical value assigned to the overall quality of a product or process. It is calculated based on various quality parameters and inspection results. The Quality Score provides a quick and standardized way to assess and communicate the quality status. Organizations can use it for trend analysis, benchmarking, and making informed decisions related to quality improvement initiatives.
19. What is SAP QM, and how does it integrate with other SAP modules?
Ans:
SAP QM is a module within the SAP ERP system that focuses on managing quality processes and controls. It integrates with other SAP modules such as Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), and Sales and Distribution (SD) to ensure end-to-end quality management across the supply chain. QM facilitates quality planning, inspection, and notification processes.
20. Explain the concept of Quality Notifications in SAP QM.
Ans:
Quality Notifications in SAP QM are used to record and manage issues related to quality, such as defects, complaints, or non-conformities. They serve as a tool for initiating corrective and preventive actions. Notifications can be created manually or automatically triggered during inspection lot processing. They play a crucial role in the continuous improvement of quality processes.
21. What is the purpose of the Quality Control Chart in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Quality Control Chart in SAP QM provides a graphical representation of quality data over time. It helps in analyzing trends, variations, and patterns in quality parameters. By visually presenting data, the control chart assists quality professionals in making informed decisions and taking corrective actions to maintain or improve product quality.
22. How can you configure Sampling Procedures in SAP QM?
Ans:
Sampling Procedures in SAP QM are configured in the IMG (Implementation Guide). The path for configuration is Logistics – Quality Management – Quality Inspection – Inspection Lot Creation – Inspection Lot Creation – Inspection for Goods Movement – Define Sampling Procedure. Here, you can define sampling procedures based on various criteria, such as inspection type, material, and plant.
23. Explain the usage of the Results Recording process in SAP QM.
Ans:
Results Recording in SAP QM involves capturing and documenting the inspection results obtained during quality inspections. It includes recording values, characteristics, and defects observed during the inspection process. The recorded results are then used for further analysis, documentation, and decision-making regarding the acceptance or rejection of inspected materials.
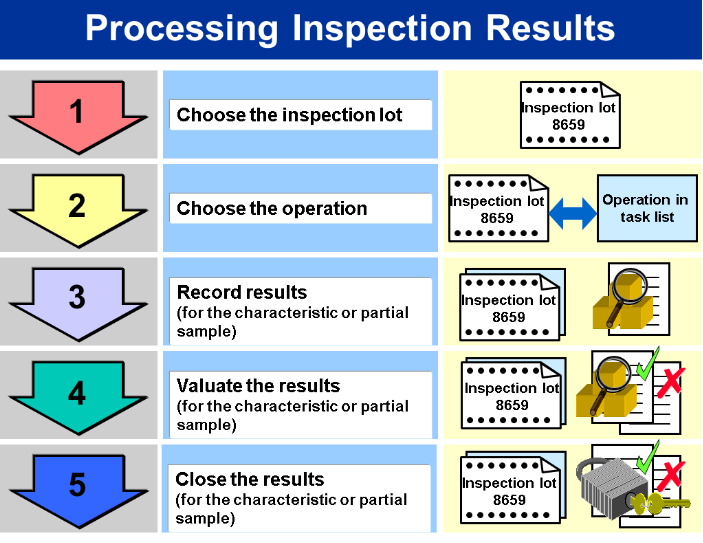
24. How does SAP QM contribute to an organization’s overall compliance?
Ans:
SAP QM contributes to organizational compliance by providing a structured framework for quality management processes. It ensures that products meet specified quality standards and regulatory requirements. Through features such as audit management, document management, and adherence to industry-specific quality norms, SAP QM helps organizations achieve and maintain compliance with quality and regulatory standards.
25. What is an Inspection Lot in SAP QM?
Ans:
An inspection lot in SAP QM is a collection of items or materials that are subject to quality inspection. It represents a batch or a specific quantity of a product that needs to undergo quality control processes. Inspection lots are created based on certain triggers, such as goods receipt, production order, or manual creation.
26. What is the purpose of an Inspection Plan in SAP QM?
Ans:
An Inspection Plan in SAP QM outlines the steps and criteria for inspecting a material or product. It includes information such as inspection characteristics, sampling procedures, and acceptance criteria. Inspection Plans help in standardizing the quality control process and ensure consistency in inspections.
27. What is the usage decision in SAP QM?
Ans:
The usage decision in SAP QM is a key step in the inspection process, where the system determines whether the inspected material meets the defined quality standards. It results in one of the following decisions: unrestricted use, restricted use, or rejection. This decision has implications for the further processing and usage of the material.
28. Explain the significance of the Quality Information System (QIS) in SAP QM.
Ans:
The Quality Information System (QIS) in SAP QM provides tools for reporting, analyzing, and evaluating quality data. It allows users to generate various types of reports, such as inspection lot reports, quality trend analyses, and compliance reports. QIS helps organizations make informed decisions based on their quality performance data.
29. How can you link an Inspection Plan to a Material Master in SAP QM?
Ans:
The material master and the inspection plan are assigned to the material and relevant plant using the “Inspection Setup” view. This linkage ensures that the specified inspection plan is applied when the material undergoes quality inspections.
30. How do you configure Inspection Types in SAP QM?
Ans:
The link between the Material Master and the Inspection Plan is established through the inspection setup in the material master. You can assign an inspection type and inspection plan to a material in the QM view of the material master.
31. Explain the difference between Quality Inspection and Quality Control in SAP QM.
Ans:
| Aspect | Quality Inspection | Quality Control | |
| Definition | The process of examining and testing products at various stages of the production process to ensure that they meet specified quality standards. | The activities performed to ensure that the products or processes meet the defined quality requirements. | |
| Scope | Generally includes inspections at various stages of production, such as goods receipt, in-process inspections, and final product inspections. | Can encompass a broader range of activities, including inspections, monitoring, measurement, and testing of both products and processes. | |
| Timing | Often occurs at specific points in the production process, such as during goods receipt, production, or before the release of the final product. | Can be ongoing and continuous throughout the production process, from raw material inspection to finished product verification. | |
| Focus | Primarily focuses on the inspection of physical products and ensuring that they meet predefined quality criteria. | Encompasses a broader focus on quality management, including process control, documentation, and overall quality assurance. |
32. How do you link SAP QM with other SAP modules?
Ans:
- SAP QM can be integrated with other SAP modules like Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), and Sales and Distribution (SD).
- For example, in MM, the integration involves inspection during the receipt of goods. In PP, it includes inspection during production, and in SD, it involves managing quality informationrelated to customer orders. Integration ensures that quality processes are seamless and information is shared across the organization.
33. Can you explain the concept of Dynamic Modification in Inspection Plans?
Ans:
Dynamic Modification in Inspection Plans allows for real-time adjustments to the inspection process based on changing conditions. For example, suppose a characteristic’s tolerance needs to be adjusted during production due to variations in raw materials. In that case, Dynamic Modification allows for on-the-fly changes to the inspection plan without having to create a new one.
34. What are some key challenges in implementing SAP QM, and how can they be addressed?
Ans:
Common challenges in implementing SAP QM include resistance to change, data migration issues, and the need for extensive training. To address these challenges, organizations should invest in change management, conduct thorough data cleansing and migration activities, and provide comprehensive training programs for end-users.
35. What is SAP QM, and how does it contribute to an organization’s quality management processes?
Ans:
SAP QM is a module within the SAP ERP system that helps organizations manage and optimize their quality management processes. It encompasses various functions such as quality planning, inspection, notification, and control of quality processes across the supply chain. SAP QM ensures that products meet predefined quality standards and supports continuous improvement by providing tools for quality control and analysis.
36. What is an inspection plan in SAP QM, and how is it created?
Ans:
- An inspection plan in SAP QM is a set of instructions detailing the steps and criteria for inspecting a product or process.
- It includes information such as inspection characteristics, sampling procedures, and inspection methods.
- Inspection plans can be created using the transaction code QP01 or by copying existing plans and modifying them as needed.
- They are then assigned to material master records or other objects to link the inspection requirements to specific materials or processes.
37. Can you explain the difference between a quality inspection and a quality notification in SAP QM?
Ans:
A quality inspection in SAP QM involves the actual examination and evaluation of a product or process based on predefined criteria outlined in the inspection plan. It is a proactive approach to ensuring product quality. On the other hand, a quality notification is a reactive process in which issues related to quality are recorded and managed. This could include customer complaints, defects, or any deviations from the quality standards.
38. How does SAP QM integrate with other modules in SAP ERP?
Ans:
SAP QM integrates with various SAP ERP modules to ensure a seamless flow of information across the organization. It closely interacts with Materials Management (MM) for procurement and inventory processes, Production Planning (PP) for quality control during manufacturing, and Sales and Distribution (SD) for handling quality-related issues with customers. Additionally, SAP QM interfaces with Plant Maintenance (PM) for equipment inspection and with Controlling (CO) for cost-related aspects of quality management.
39. Explain the concept of Batch Management in SAP QM.
Ans:
Batch Management in SAP QM involves the management and tracking of materials based on batches. A batch is a group of materials produced or processed together with similar characteristics. This functionality ensures traceability and facilitates the identification of specific batches during quality inspections. It is particularly important in industries where the characteristics of a product may vary between batches.
40. How can you create an Inspection Lot in SAP QM?
Ans:
Inspection Lots can be created automatically during goods receipt and production or manually using the transaction code QA01. During the receipt of goods, the system checks the material and creates an Inspection Lot if the material is subject to inspection. In production, Inspection Lots can be created during the confirmation process.
41. What is the purpose of the Inspection Plan in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Inspection Plan in SAP QM is a master data object that defines the inspection scope and the inspection characteristics for a material. It includes details such as the inspection methods, sampling procedures, and the list of characteristics to be inspected. Inspection Plans are used as templates for creating Inspection Lots and help ensure consistent and standardized quality control processes.
42. How can you record results in SAP QM?
Ans:
Results recording in SAP QM involves entering and documenting the inspection results for each characteristic of a material. This can be done using transaction codes QE51N or QE01, where the user selects the Inspection Lot, enters the measured values, and records the results. The system then compares the results with the specified tolerances and determines the overall inspection status.
43. Explain the significance of the Quality Score in SAP QM.
Ans:
The Quality Score in SAP QM is a key performance indicator that reflects the overall quality status of a material or product. It is calculated based on the inspection results of various characteristics and is used to determine whether the material meets the defined quality standards. A higher Quality Score indicates better quality, while a lower score may trigger further investigation and corrective actions.
44. Explain the purpose of the Quality Info Record in SAP QM.
Ans:
The Quality Info Record in SAP QM is used to store quality-related information for a material or a vendor. It includes details such as the acceptable quality level, inspection methods, and sampling procedures. This information is crucial for the system to determine the inspection type and other parameters automatically when processing quality-related transactions.
45. Explain the concept of a Usage Decision in SAP QM.
Ans:
A Usage Decision in SAP QM is the final step in the inspection process, where the system evaluates the inspection results and determines whether the material is suitable for use or needs to be restricted or rejected. The decision is based on predefined criteria and quality standards.
46. How can you integrate SAP QM with other SAP modules?
Ans:
SAP QM can be integrated with other SAP modules like Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), and Sales and Distribution (SD). Integration involves sharing relevant information and documents between modules. For example, inspection results from QM can influence stock postings in MM, or quality-related information can be passed to SD for customer notifications.
47. What is the purpose of the Quality Management Information System (QMIS) in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Quality Management Information System (QMIS) in SAP QM provides comprehensive reporting and analysis tools for quality-related data. It allows users to generate various reports, charts, and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor and analyze the efficiency of quality processes. QMIS helps organizations make informed decisions and continuously improve their quality management practices.
48. What is the purpose of Quality Planning in SAP QM?
Ans:
Quality Planning in SAP QM involves defining inspection plans, inspection methods, and other criteria to ensure that quality checks are carried out at various stages of the production process. It helps in setting up the framework for quality assurance.
49. How do you create an Inspection Lot in SAP QM?
Ans:
An inspection lot is created in SAP QM when a production order is created. During the receipt of goods, an inspection lot is generated automatically. Inspection Lots are created to initiate the quality control process, allowing organizations to perform inspections, record inspection results, and make usage decisions based on the quality status.
50. Explain the concept of Batch Management in SAP QM.
Ans:
Batch Management in SAP QM involves managing materials based on batches. It allows organizations to systematically control and monitor the quality of goods by associating them with specific batch numbers. It allows for traceability and helps in tracking the entire history of a batch, including quality information, from production to consumption.
51. What is the purpose of the Dynamic Modification Rule in SAP QM?
Ans:
- Dynamic Modification Rules in SAP QM allow you to dynamically adjust the inspection scope or sampling procedure based on specific criteria, such as vendor, material, or inspection type.
- Dynamic Modification Rule is a configuration element that allows organizations to dynamically adjust the inspection scope or characteristics based on certain conditions during the inspection process.
- The purpose of the Dynamic Modification Rule is to provide flexibility in quality management by allowing for changes to the inspection plan or criteria based on real-time factors.
52. What is a Quality Inspection Plan?
Ans:
A Quality Inspection Plan is a structured set of instructions and criteria that define how the quality inspection process for a particular material or product should be carried out. It is a key component of the Quality Management (QM) module in SAP and other enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. The purpose of a Quality Inspection Plan is to establish the parameters for inspecting and evaluating the quality characteristics of materials during various stages of the production or procurement process.
53. What is the purpose of the Results Recording in SAP QM?
Ans:
Results Recording in SAP QM involves recording the actual measurement values obtained during the inspection process. This data is then compared against the specified tolerances and quality specifications to determine whether the product meets the required quality standards.
54. Explain the concept of Quality Management in Procurement.
Ans:
Quality Management in Procurement ensures that materials procured from vendors meet the specified quality standards. This involves the use of Quality Info Records, vendor evaluations, and inspection plans to define and control the quality requirements for incoming materials. It involves various activities and processes aimed at controlling and assuring the quality of goods and services acquired from suppliers.
55. What is the purpose of Quality Planning in SAP QM?
Ans:
Quality Planning in SAP QM involves defining the quality specifications and inspection plans for the products. It ensures that quality standards are met by specifying inspection points, sampling procedures, and other relevant details. The purpose of Quality Planning is to define, plan, and set up the necessary activities and criteria for inspecting products or materials.
56. What is the purpose of the Usage Decision in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Usage Decision in SAP QM is a crucial step in the inspection process. It involves determining whether the inspected material meets the specified quality criteria and can be used or delivered. The decision is recorded and has a significant impact on subsequent processes. The purpose of the Usage Decision is to determine whether an inspected product or material meets the specified quality requirements and whether it can be released for use, restricted, or rejected.
57. What is the purpose of Quality Notifications in SAP QM?
Ans:
Quality Notifications in SAP QM are used to document and manage quality-related issues, such as defects, complaints, or non-conformances. They help initiate corrective and preventive actions and track the resolution of quality problems. The purpose of Quality Notifications is to provide a systematic way to report, track, and manage non-conformances, defects, and other quality-related incidents within an organization.
58. Explain the difference between Quality Inspection and Quality Control in SAP QM.
Ans:
Quality Inspection in SAP QM refers to the overall process of examining and evaluating the quality of products based on predefined criteria. Quality Control, on the other hand, is a part of Quality Inspection and specifically focuses on monitoring and controlling the quality of processes and products to ensure they meet the required standards.
59. What are the different types of Inspection Methods in SAP QM?
Ans:
SAP QM supports various Inspection Methods, including Inspection with Inspection Points, Inspection with Time Intervals, and Inspection Using 100% Sampling. The choice of method depends on the characteristics of the product and the desired level of quality control.
● Single-Level Inspection
● Two-Level Inspection
● Stock Transfer Inspection
● Source Inspection
● Returnable Packaging Inspection
● In-Process Inspection
60. How can you link SAP QM with other modules in SAP ERP?
Ans:
SAP QM is integrated with other SAP ERP modules such as Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), and Sales and Distribution (SD). For example, in the procurement process, quality inspections are triggered during goods receipt in MM. This integration ensures a seamless flow of information and processes across different functional areas.
61. Explain the role of SAP QM in a manufacturing environment.
Ans:
SAP QM plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of raw materials, intermediate products, and finished goods. It helps in defining and executing inspection plans, recording and managing quality issues, and maintaining traceability throughout the production process. This ensures that the final products meet the specified quality standards.
62. What is the purpose of Results Recording in SAP QM?
Ans:
Results Recording in SAP QM involves documenting the actual inspection results obtained during the quality inspection process. This data is then used to compare against the specified criteria in the inspection plan to determine if the product meets quality standards.
63. Explain the integration of SAP QM with other SAP modules.
Ans:
SAP QM is closely integrated with other SAP modules, such as Materials Management (MM), Production Planning (PP), and Sales and Distribution (SD). For example, inspection lots can be created during goods receipt in MM, production orders in PP, or deliveries in SD, ensuring that quality is monitored throughout the supply chain.
64. How do you handle recurring inspections in SAP QM?
Ans:
Recurring inspections in SAP QM involve regularly inspecting materials at predefined intervals. This is achieved through the scheduling of inspection intervals in the inspection plan. The system automatically generates inspection lots based on the defined schedule, ensuring that the materials are consistently monitored for quality.
65. How does SAP QM support the management of Inspection Characteristics?
Ans:
SAP QM provides comprehensive support for managing Inspection Characteristics throughout various stages of the quality management lifecycle. Here’s how SAP QM supports the management of Inspection Characteristics:
● Creation and Maintenance
● Integration with Material Master
● Sampling Procedures and Plans
● Dynamic Modification Rules
● RecordingResults Recording
66. Explain the relationship between SAP QM and SAP HANA.
Ans:
SAP HANA is an in-memory database platform that enhances the performance of SAP applications. In the context of SAP QM, HANA can significantly improve the speed of data processing and analytics, leading to faster and more efficient quality management processes.
67. How can you perform a Goods Receipt Inspection in SAP QM?
Ans:
Goods Receipt Inspection in SAP QM involves creating an inspection lot when goods are received. The system checks the material against predefined inspection criteria, and inspection results are recorded. This process ensures that the received goods meet the specified quality standards. If the material meets the specifications, it is accepted; otherwise, follow-up actions are initiated.
68. What are the key reports available in SAP QM for monitoring and analyzing quality data?
Ans:
SAP QM provides various reports, including Inspection Lot Reports, Quality Notification Reports, and Certificate Reports. These reports offer insights into inspection results, quality issues, and compliance with standards.
69. How does SAP QM handle Batch Management?
Ans:
SAP QM integrates with Batch Management in the SAP ERP system. It allows you to link inspection lots to batches, ensuring that quality data is associated with specific batches of materials. This integration facilitates traceability and quality control for each batch. Batch Management in SAP QM integrates with other SAP modules, such as Materials Management (MM) and Production Planning (PP), and plays a crucial role in traceability, quality control, and compliance.
70. Can you explain the difference between Inspection Characteristics and Inspection Specifications?
Ans:
Inspection Characteristics in SAP QM represent measurable or observable properties of a material that need to be inspected. Inspection Specifications, on the other hand, define the acceptable limits or criteria for those characteristics. Together, characteristics and specifications ensure that the product meets the required quality standards.
71. What are the different types of sampling procedures in SAP QM?
Ans:
SAP QM supports various sampling procedures, including single sampling, double sampling, and skip-lot sampling. These procedures determine the number of samples to be inspected and the acceptance criteria based on statistical methods. Sampling procedures play a crucial role in determining how and when samples are to be taken during the inspection process. Sampling procedures help define the criteria for selecting samples from a batch or lot for quality inspection.
72. Explain the concept of Batch Management in SAP QM.
Ans:
Batch Management in SAP QM allows you to manage materials based on batches or lots. It is crucial for traceability and ensures that quality-related information is associated with specific batches, making it easier to track and manage the quality of materials.
73. What is the purpose of the Quality Score in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Quality Score in SAP QM is a numerical value assigned to a material or vendor based on their historical quality performance. It helps in assessing the overall quality reliability and can be used to make informed decisions regarding procurement or production. In SAP QM, organizations often define and measure key performance indicators and metrics to evaluate the quality of materials, products, and processes.
74. How does SAP QM support the handling of non-conforming materials?
Ans:
SAP QM allows you to create Quality Notifications for non-conforming materials. Non-conforming materials are those that do not meet specified quality standards or criteria, and effective management of such materials is critical for ensuring product quality, compliance, and customer satisfaction. These notifications trigger the initiation of corrective and preventive actions, helping to address and resolve quality issues systematically.
75. What is the use of the Quality Level in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Quality Level in SAP QM is a classification that indicates the permissible defect rate for a material or product. “Quality Level” is used to classify materials or products based on their quality attributes and compliance with specified quality standards. Quality Levels provide a way to differentiate between different levels of quality within a product range. The use of Quality Levels is particularly relevant for organizations that produce or handle materials with varying quality characteristics.
76. Explain the concept of Sampling Procedures in SAP QM.
Ans:
Sampling Procedures in SAP QM define how the inspection lot is to be sampled during the inspection. It includes specifications for sample size, acceptance criteria, and the sampling method. Sampling Procedures play a crucial role in determining the accuracy of the inspection results.
77. What role does the Results Recording play in SAP QM inspections?
Ans:
Results Recording in SAP QM involves recording the actual inspection results for each inspection characteristic. It captures measured values, qualitative assessments, or other relevant data. Results Recording is a critical step in determining the quality status of the inspected material. The Results Recording functionality plays a central role in capturing and storing the data obtained during inspections, which is then used for making informed decisions about the quality of the inspected material or product.
78. How does SAP QM support the management of Non-Conformance?
Ans:
SAP QM manages non-conformances through Quality Notifications. When a defect or deviation is identified, a Quality Notification is created, triggering a workflow for investigation, corrective actions, and preventive measures. This ensures effective handling of non-conformities. Non-conformance refers to situations where a product, process, or system deviates from specified requirements or standards, and it requires corrective actions to address the discrepancies.
79. Explain the concept of Quality Level in SAP QM.
Ans:
Quality Level in SAP QM represents the acceptable quality level for a product or material. It is defined in the material master and influences inspection activities. Quality Levels help categorize materials based on their quality requirements and standards.”Quality Level” refers to a classification or categorization assigned to materials or products based on their quality characteristics and compliance with specified quality standards. Quality Levels provide a way to differentiate between different levels of quality within a product range.
80. What are the key elements of an Inspection Plan in SAP QM?
Ans:
An Inspection Plan in SAP QM consists of inspection characteristics, sampling procedures, inspection methods, and the specification of acceptance criteria. It is a comprehensive document that guides the quality inspection process. The key elements of an Inspection Plan in SAP QM include:
● Material or Material Type
● Inspection Type
● Inspection Scope
● Sampling Procedure
● Sampling Scheme
● Inspection Characteristics
81. How can you create an Inspection Lot manually in SAP QM?
Ans:
In SAP QM, you can create an Inspection Lot manually using the transaction code QA01. Here, you enter the material or batch number, inspection type, and other relevant information to initiate the inspection process.
82. What is the purpose of the Quality Information Record in SAP QM?
Ans:
Quality Information Record” in standard SAP Quality Management (QM) documentation. The Quality Information Record in SAP QM stores information about the quality control requirements for a material. It includes data such as inspection plans, specifications, and other quality-related details to streamline the quality management process.
83. Explain the significance of the Results Recording feature in SAP QM.
Ans:
Results Recording in SAP QM involves entering and documenting the actual inspection results. It allows users to compare the recorded results with the specified tolerances and determine whether the material or product meets the quality standards. It involves the recording and documentation of actual measurement values, observations, and assessments obtained during the inspection of materials or products.
84. Explain the concept of Quality Levels in SAP QM.
Ans:
Quality Levels in SAP QM allow you to define different levels of inspection severity for characteristics within an inspection plan. This helps in categorizing characteristics based on their criticality and applying appropriate inspection criteria.”Quality Levels” are used to classify materials or products based on their quality attributes and compliance with specified quality standards. Quality Levels provide a way to differentiate between different levels of quality within a product range.
85. How does SAP QM contribute to Continuous Improvement in a manufacturing process?
Ans:
SAP QM supports Continuous Improvement by providing tools for analyzing quality data, initiating corrective and preventive actions through quality notifications, and integrating with other SAP modules to ensure that feedback from quality inspections is used to enhance overall business processes.
86. How can you link an Inspection Lot to an Inspection Plan in SAP QM?
Ans:
Inspection Lots are linked to Inspection Plans through the material master record. The inspection type defined in the material master determines the Inspection Plan to be used when creating an Inspection Lot.
87. Explain the significance of the Quality Score in SAP QM.
Ans:
The Quality Score is a numerical value assigned to an inspection lot based on the inspection results. It provides a quick indicator of the overall quality of the material or product. Quality Score” might be a metric or rating assigned to assess the overall quality of a product, process, or supplier. This score could be calculated based on various factors, such as compliance with specifications, the number of defects, customer complaints, or other relevant quality indicators.
88. How can SAP QM contribute to the overall improvement of a company’s quality management processes?
Ans:
A comprehensive solution that can significantly contribute to the overall improvement of a company’s quality management processes. SAP QM contributes to improved quality management by streamlining inspection processes, providing real-time visibility into quality data, facilitating quick response to quality issues through Quality Notifications, and supporting continuous improvement initiatives through the analysis of inspection results.
89. Discuss the role of SAP QM in regulatory compliance.
Ans:
SAP QM plays a crucial role in ensuring regulatory compliance by providing tools to document and manage quality-related information. Regulatory compliance refers to the adherence to laws, regulations, standards, and guidelines relevant to a specific industry or business sector. It helps companies adhere to industry-specific standards and regulations by enforcing quality checks and maintaining accurate records of quality-related activities.
90. What is the purpose of the SAP QM Results Recording transaction?
Ans:
The Results Recording transaction (e.g., QE51N) is used to record the actual inspection results against the defined inspection characteristics. It allows inspectors to enter measurements, observations, or qualitative assessments, which are then used to determine the quality status of the inspected material. This transaction allows users to enter actual measurement values, observations, and assessments for inspection characteristics associated with a specific inspection lot.
91. Explain the concept of Dynamic Modification Rules in SAP QM.
Ans:
Dynamic Modification Rules in SAP QM allow you to dynamically change the inspection plan during the inspection process based on certain criteria. For example, you can adjust the sampling procedure or change inspection characteristics based on specific conditions like production shifts or material variations.
92. How can you trigger an Automatic Usage Decision in SAP QM?
Ans:
An Automatic Usage Decision in SAP QM can be triggered based on predefined rules and criteria. The system automatically makes this decision without manual intervention. For example, if all inspection results meet acceptance criteria, the system can automatically set the usage decision to “Accepted.”
93. How does SAP QM contribute to Regulatory Compliance?
Ans:
SAP QM helps organizations achieve and maintain regulatory compliance by providing tools for documenting and tracking quality-related activities. It supports the creation of documentation, such as quality certificates and batch records, and facilitates adherence to industry-specific regulations and standards.
94. What is the purpose of the Quality Information System (QIS) in SAP QM?
Ans:
The Quality Information System in SAP QM allows users to analyze and evaluate quality-related data. It provides a range of tools and reports for tracking quality performance, identifying trends, and making informed decisions to improve overall quality management.
95. How does SAP QM handle Sampling Procedures?
Ans:
Sampling Procedures in SAP QM define the rules for selecting samples during inspections. They specify the sample size, inspection frequency, and the criteria for accepting or rejecting a batch based on the sample results. In SAP Quality Management (QM), sampling procedures play a crucial role in determining the criteria and methodology for selecting samples from a batch or lot for inspection. SAP QM provides a comprehensive set of functionalities to handle sampling procedures efficiently.
96. What is the significance of the Inspection Point in SAP QM?
Ans:
Inspection Points are specific stages in the production or procurement process where the quality of materials or products is assessed. They are defined in the inspection plan and serve as checkpoints for conducting inspections.”Inspection Point” refers to a specific stage or location within a production or inspection process where quality checks or inspections are conducted on a material or product.
97. What is the role of Quality Management in the Procurement process in SAP QM?
Ans:
SAP QM ensures that materials procured meet the specified quality standards. The primary objective is to ensure that the materials or products procured by an organization meet the specified quality standards and requirements. This involves conducting inspections upon receipt of goods, managing vendor quality evaluations, and handling quality-related issues through notifications.






