
ACTE provides a robust collection of SAP Business Objects interview questions and answers for candidates seeking positions in this field. Partnering with reliable employers, ACTE ensures access to diverse job opportunities with competitive salaries and dynamic work environments. The platform’s user-friendly interface allows easy navigation and updates on evolving employer requirements and market trends. The interview questions are designed to acquaint candidates with the nature of queries they may face, covering both fundamental concepts and nuanced scenarios. Whether for freshers or experienced professionals, ACTE’s curated questions and detailed answers facilitate comprehensive preparation, enhancing the likelihood of success in SAP Business Objects interviews.
1. What are SAP Business Objects?
Ans:
SAP Business Objects is a suite of business intelligence (BI) tools developed by SAP. It allows organizations to access, analyze, and share business insights across the enterprise. The suite includes various reporting, querying, analysis, and performance management applications, providing a comprehensive solution for business intelligence needs.
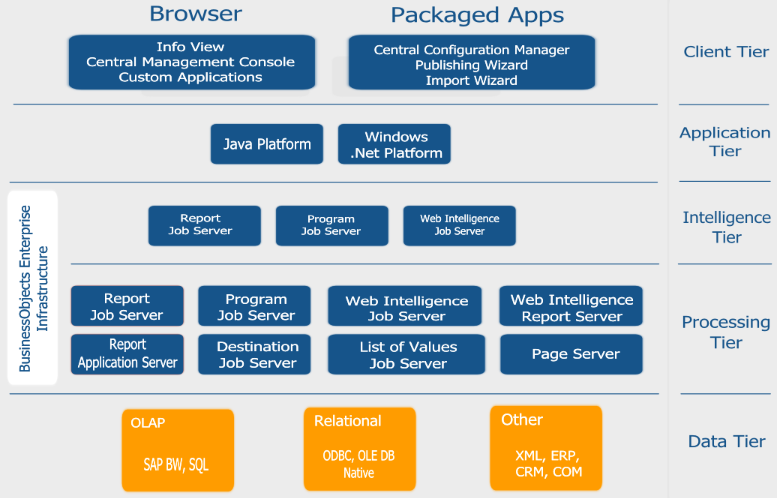
2. Explain the Key Components of SAP Business Objects.
Ans:
The key components of SAP Business Objects include:
- Web Intelligence (WebI): A web-based ad-hoc reporting tool.
- Universe Design Tool: Used to create and maintain universes, which are a semantic layer between databases and reports.
- Central Management Console (CMC): The central hub for managing and configuring Business Objects servers, security, and other settings.
- Central Management Server (CMS): Manages the Business Objects environment, including user authentication and server communication.
- Crystal Reports: A powerful report design tool for creating pixel-perfect, formatted reports.
3. Differentiate Between Universe and Report in Business Objects.
Ans:
Universe:
- Acts as a semantic layer between the database and the report.
- Defines the business terms and relationships, making it easier for non-technical users to create reports.
- Contains metadata that simplifies the querying process for end-users.
Report:
- Represents the final output generated based on data retrieved from a universe or data source.
- Includes charts, tables, and other visualizations.
- Can be created using tools like Web Intelligence or Crystal Reports.
4. What is the Purpose of the Business Objects Repository?
Ans:
The Business Objects repository is a centralized storage system that contains metadata and configuration information for the entire Business Objects environment. It stores details about universes, reports, security settings, user profiles, and server configurations. The repository facilitates collaboration, consistency, and centralized management of BI content and structures across the Business Objects platform.
5. Define a Dimension and a Measure in the Context of Business Objects.
Ans:
Dimension:
- Represents categorical data, typically used for grouping or categorizing information.
- Examples include product categories, regions, or periods.
Measure:
- Represents quantitative, numeric data that can be measured or aggregated.
- Examples include sales revenue, quantity sold, or profit margin.
6. Explain the Difference Between a Prompt and a Filter in Business Objects.
Ans:
Prompt:
- Prompts are used to interactively gather information from the user at the time of report execution.
- Users can input values or make selections for prompts to customize the report output.
Filter:
- Filters are conditions applied to the report data to restrict or limit the information displayed.
- Filters are predefined and set during report design.
7. What is a Universe in Business Objects?
Ans:
A Universe in Business Objects is a semantic layer that abstracts the complexity of database structures, providing a business-friendly representation of data. It defines relationships, hierarchies, and business terms, allowing users to create reports without understanding the underlying database structure. Universes act as an intermediary between reports and databases.
8. How Do You Create a Universe in Business Objects?
Ans:
To create a universe in Business Objects:
- Launch the Universe Design Tool.
- Establish a connection to the data source.
- Define classes, objects, and joins to create a semantic layer.
- Resolve loops and ensure the integrity of the universe.
- Add predefined filters and conditions.
- Export the universe to the repository for use in report development.
9. Explain the Concept of Joins in Universe Design.
Ans:
In Universe design, joins define how tables in a database are related. Joins specify the relationships between different data tables, allowing the creation of a unified view for reporting. Common types of joins include inner joins, outer joins (left, correct, complete), and theta joins, each serving different purposes in retrieving and presenting data.
10. What Are the Different Types of Joins Available in Business Objects?
Ans:
The different types of joins available in Business Objects include:
- Inner Join: Retrieves only the matched records from both tables.
- Outer Join (Left, Right, Full): Retrieves all records from one table and matching records from the other.
- Theta Join: Allows the specification of a condition other than equality for joining tables.
11. How Can You Optimise the Performance of a Universe?
Ans:
To optimize the performance of a universe in Business Objects:
- Limit the Number of Objects: Include only the necessary objects in the universe to reduce retrieved data.
- Use Aggregate Awareness: Utilise aggregate awareness to enhance query performance by leveraging pre-aggregated data.
- Indexing: Ensure the database tables are adequately indexed for faster data retrieval.
- Avoid Cartesian Products: Prevent Cartesian products by defining proper joins and avoiding unnecessary Cartesian joins.
- Partition Large Tables: If applicable, partition large tables to improve query performance.
12. What is Web Intelligence (WebI)?
Ans:
Web Intelligence (WebI) is a web-based reporting tool within SAP Business Objects. It allows users to create ad-hoc reports, interactive dashboards, and data visualizations. WebI enables users to connect to various data sources, design reports using a drag-and-drop interface, and share insights with others in the organization.
13. Explain the Difference Between a Block and a Section in WebI.
Ans:
| Aspect | Block | Section | |
| Definition | A Block is a container that holds data and represents a specific set of information in a report. | A Section is a subdivision within a report that allows for the organization of data and layout customization. | |
| Purpose | Blocks are used to display and organize data from the underlying data source. | Sections are used to structure the layout of the report, allowing for the grouping of data and control over formatting. | |
| Data Filtering | Blocks can have their own data filters to limit the displayed information. | Sections do not have data filters directly; data filtering is typically applied at the Block level. | |
| Formatting | Block-level formatting is applied to the data within the Block container. | Section-level formatting is applied to the layout and appearance of the entire section, affecting all content within. | |
| Examples | A Block displaying sales data for a specific product category. | A Section for a page header containing a title, logo, and a Block for detailed sales data below. |
14. How Do You Create a Variable in Web Intelligence?
Ans:
To create a variable in Web Intelligence:
- Open the WebI report in edit mode.
- Navigate to the “Data” tab.
- Click on “Variables.”
- Click “New” to create a new variable.
- Define the variable’s name, type, and formula.
15. What is the Purpose of the “Refresh on Open” Option in WebI?
Ans:
The “Refresh on Open” option in Web Intelligence allows a report to automatically update its data from the underlying data source each time it is opened. This ensures that users view the most up-to-date information without manually triggering a refresh.
16. Can You Schedule WebI Reports? If Yes, How?
Ans:
Yes, Web Intelligence reports can be scheduled for automatic execution and delivery. To prepare a WebI report:
- Open the WebI report in the BI Launchpad.
- Navigate to the “Document” menu.
- Select “Schedule.”
- Set the scheduling parameters, including frequency and destination (email, file repository, etc.).
- Save the schedule.
17. Explain the Purpose of Input Controls in WebI.
Ans:
Input Controls in Web Intelligence allow users to filter and analyze data in a report interactively. Users can define input control conditions, such as ranges or lists, to restrict the data displayed in the information dynamically. This provides a way for end-users to customize their analysis without modifying the report structure.
18. How Do You Implement Security in Business Objects?
Ans:
Security in Business Objects can be implemented through the following steps:
- User Authentication: Use authentication methods like Windows AD, LDAP, or SAP authentication.
- User Groups: Assign users to predefined or custom user groups based on their roles.
- Access Levels: Define access levels for different user groups, specifying permissions for viewing or modifying BI content.
- Folder Security: Control access to specific folders in the repository.
- Object-Level Security: Restrict access to particular reports, universes, or other BI objects.
- Row-Level Security: Implement security at the data level, restricting user access to specific rows of data.
19. What is the Purpose of the Central Management Console (CMC)?
Ans:
The Central Management Console (CMC) in SAP Business Objects is a web-based tool used for central administration and configuration of the entire Business Objects environment. Critical functions of the CMC include managing servers, scheduling, security settings, user and group management, and monitoring system activity. It is a central hub for administrators to maintain and control the Business Objects landscape.
20. Explain the Difference Between Object-Level and Row-Level Security.
Ans:
Object-Level Security:
- Involves securing access to specific BI objects such as reports, universes, or folders.
- Users or groups are granted or denied permission to view or modify these objects.
Row-Level Security:
- Involves securing access to specific rows of data within reports.
- Users or groups are restricted in their ability to view or retrieve particular data rows based on predefined security conditions.
21. How Do You Manage User Privileges in Business Objects?
Ans:
The Central Management Console (CMC) manages user privileges in Business Objects. To manage user privileges:
- Open the CMC.
- Navigate to the “Users and Groups” area.
- Assign users to appropriate groups.
- Define access levels and permissions for each group.
- Ensure that security settings align with organizational roles and responsibilities.
22. What is the Purpose of the Central Management Server (CMS)?
Ans:
The Central Management Server (CMS) in Business Objects is a core component responsible for managing the environment. Its essential functions include user authentication, communication between servers, and coordination of activities within the system. The CMS is a central hub for managing metadata, security, and communication between different components of the Business Objects platform.
23. Explain the Concept of Auditing in Business Objects.
Ans:
Auditing in Business Objects involves tracking and recording user activities and system events to ensure compliance, monitor usage, and enhance security. Critical aspects of auditing include:
User Activity Logging: Recording user logins, access to reports, and modifications made to BI objects.
System Event Logging: Capturing system-level events, errors, and changes in the Business Objects environment.
Security Auditing: Monitoring changes to security settings, role assignments, and user privileges.
Audit Reports: Generating reports based on audit data to analyze and review system activity.
24. How Do You Back Up and Restore a Business Objects System?
Ans:
Backup:
- Use the Central Management Console (CMC) to export content, including reports, universes, and security settings.
- Regularly back up the Business Objects repository database.
- Ensure that server configurations and CMS data are included in the backup.
Restore:
- Install a fresh instance of Business Objects.
- Restore the repository database and other relevant backup files.
- Import the exported content using the CMC.
25. What Are the Key Parameters to Consider for System Performance Tuning?
Ans:
Critical parameters for system performance tuning in Business Objects include:
- Memory Allocation: Adjust memory settings for servers based on system resources.
- Caching: Configure caching settings to optimize the retrieval of frequently accessed data.
- Parallel Processing: Utilise parallel processing options to enhance query execution.
- Indexing: Properly index database tables to improve query performance.
- Query Stripping: Optimise queries by removing unnecessary elements.
- Connection Pooling: Configure connection pooling for efficient database connections.
- Server Load Balancing: Distribute server loads to balance resource utilization.
26. How Can Business Objects Integrate with SAP BW?
Ans:
Business Objects can integrate with SAP BW (Business Warehouse) through the following methods:
OLAP Connections: Use OLAP connections to connect Web Intelligence to SAP BW InfoProviders.
BICS (Business Intelligence Consumer Services): Leverage BICS connectivity for enhanced performance and functionality.
SAP BW Queries: Directly connect to SAP BW Queries to retrieve data for reporting.
Data Federator: Integrate SAP BW data with non-SAP data sources using Data Federator.
27. Explain the Integration Between Business Objects and SAP HANA.
Ans:
Integration between Business Objects and SAP HANA involves direct connectivity and optimized performance for reporting on HANA data. Key points include:
- Native Connectivity: Business Objects offers native connectors directly connecting to SAP HANA.
- In-Memory Processing: Leverage HANA’s in-memory processing for fast data retrieval and analysis.
- SAP HANA Live Universe: Create universes on top of SAP HANA Live for real-time reporting.
- Predictive Analytics: Use the integration for advanced analytics and predictive modeling with SAP HANA.
28. What is the Purpose of a Live Office in Business Objects?
Ans:
Live Office in Business Objects is a tool that allows users to embed live data from Business Objects reports and analytics directly into Microsoft Office applications such as Excel, Word, and PowerPoint. It enables users to maintain a dynamic link between the Office document and the underlying BI content, ensuring the data is always up-to-date.
29. How Do You Integrate Business Objects with External Databases?
Ans:
Business Objects can be integrated with external databases using the following methods:
- ODBC/JDBC Connections: Establish ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) or JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) connections to external databases.
- Import Wizard: Use the Import Wizard to import data from external databases into Business Objects.
- Universe Design: Create a universe that includes external database tables, enabling reporting on external data.
- Data Federation: Utilise Data Federator to integrate data from multiple external sources into Business Objects reports.
30. What Are Alerters in WebI Reports?
Ans:
Alerters in Web Intelligence reports are used to highlight or draw attention to specific data based on predefined conditions. Alerts allow users to set up conditional formatting rules that dynamically change the appearance of data, such as changing the font color or applying icons based on specified criteria.
31. Explain the Use of Calculations and Breaks in Business Objects Reports.
Ans:
Calculations:
Calculations in Business Objects reports involve creating custom calculations or formulas to perform operations on data. Examples include creating a calculated field for profit margin or percentage change.
Breaks:
Breaks in reports are used to organize and group data based on specific criteria. They create breaks in the report layout, allowing users to see subtotals and totals for each group.
32. How Do You Create a Drill-Down Report in Business Objects?
Ans:
To create a drill-down report in Business Objects:
- Design the initial information with the summary data.
- Add drillable elements to the report, such as hyperlinks or buttons.
- Define the drill-down path by linking the drillable elements to detailed reports or sub-reports.
- Specify parameters or filters to pass context from the summary report to the detailed descriptions.
- Users can click on the drillable elements to navigate the detailed information.
33. What is the Purpose of a Sub-report in Business Objects?
Ans:
A sub-report in Business Objects is a report embedded within another word. The purpose of a sub-report is to:
Provide Additional Detail: Present more detailed data-related information in the main report.
Reuse Content: Allow the reuse of existing reports within a more extensive report.
Enhance Interactivity: Enable users to drill down into specific details without leaving the main message.
34. What is the Business Objects SDK, and How is it Used?
Ans:
The Business Objects SDK (Software Development Kit) is a set of tools and libraries that allows developers to create custom applications, extend functionality, and automate tasks within the Business Objects environment. It provides APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for interacting with various components, such as universes, reports, and user management. The SDK allows developers to integrate Business Objects functionality into other applications or build custom solutions.
35. Can You Provide Examples of Scenarios Where You Would Use the SDK?
Ans:
Examples of scenarios where the Business Objects SDK may be used include:
Automating Report Generation: Creating scripts or applications to automate the generation of reports at scheduled intervals.
Customizing User Interfaces: Building custom interfaces that interact with Business Objects content.
Integration with External Systems: Developing connectors or bridges to integrate Business Objects with other enterprise systems.
User Management: Automating user provisioning, role assignments, and security settings.
36. How Do You Optimise the Performance of a WebI Report?
Ans:
To optimize the performance of a Web Intelligence report:
- Limit Data Retrieval: Only retrieve necessary data by applying appropriate filters and conditions.
- Use Query Stripping: Remove unnecessary objects and elements from the query.
- Aggregate Awareness: Leverage aggregate awareness to use pre-aggregated data where applicable.
- Indexing: Ensure that the database tables involved are properly indexed.
- Avoid Complex Formulas: Minimise the use of complex formulas that can slow down data processing.
- Data Cache: Utilise the data cache for frequently accessed data.
37. Explain the Role of Indexes in Business Objects Performance.
Ans:
Indexes in Business Objects performance enhance data retrieval speed by providing a quick lookup mechanism for data in database tables. Well-designed indexes on relevant columns can significantly improve query performance, especially when filtering, sorting, or searching for specific data. Indexes reduce the time it takes to access and retrieve data, contributing to overall system performance.
38. How Do You Troubleshoot Performance Issues in Business Objects?
Ans:
To troubleshoot performance issues in Business Objects:
- Review Query Execution Plans: Analyse the query execution plans to identify bottlenecks.
- Database Profiling: Use database profiling tools to monitor and optimize database performance.
- Server Logs: Check server logs for error messages or warnings related to performance.
- Index Analysis: Examine indexes on database tables to ensure they are optimized.
- Query Optimization: Review and optimise complex queries or joins.
- Cache Management: Monitor and manage data caching to ensure effective use.
39. What Are Common Issues You May Encounter During Report Development, and How Do You Address Them?
Ans:
Data Connection Issues: Verify database connections and credentials.
Misaligned Data Types: Ensure data types in the report match those in the database.
Formula Errors: Check for syntax errors and inconsistencies in formulas.
Slow Data Retrieval: Optimise queries, use indexes, and consider caching options.
Formatting Issues: Adjust formatting settings to achieve the desired layout.
Security Restrictions: Resolve security-related issues by adjusting user privileges.
40. How Can You Connect Business Objects to Different Data Sources?
Ans:
To connect Business Objects to different data sources:
- OLE DB and ODBC Connections: Use OLE DB (Object Linking and Embedding Database) or ODBC connections for relational databases.
- JDBC Connections: Connect to databases using JDBC (Java Database Connectivity).
- XML and Web Services: Access data from XML files or web services.
- SAP BW and SAP HANA Connectivity: Utilise native connectors for SAP BW and SAP HANA.
- Universe Design: Create universes that define the data structure and relationships.
41. Explain the Purpose of Data Federator in Business Objects.
Ans:
Data Federator in Business Objects is a tool used for virtualization and federating data from multiple, heterogeneous sources. It allows users to create a single semantic layer across various databases, applications, and data warehouses. Data Federator provides a unified view of data, enabling users to query and report on disparate sources without needing physical data integration.
42. How Do You Perform Version Upgrades in Business Objects?
Ans:
To perform version upgrades in Business Objects:
Backup: Ensure a comprehensive backup of the existing environment, including content and configuration.
Read Documentation: Review the upgrade documentation provided by SAP for the specific version.
Pre-Upgrade Tasks: Complete pre-upgrade tasks, such as resolving compatibility issues and checking system requirements.
Upgrade Software: Install the new version of Business Objects software on the servers.
Post-Upgrade Tasks: Complete post-upgrade tasks, such as updating configurations, applying patches, and testing reports.
43. What Are the Considerations When Migrating Reports from One Version to Another?
Ans:
Considerations when migrating reports between versions include:
Compatibility: Ensure the report design and features are compatible with the target version.
Data Source Changes: Verify that the data sources and connections are supported in the new version.
Formatting and Layout: Check for any changes in formatting or layout that may affect the report’s appearance.
Formula Compatibility: Validate formulas and calculations for compatibility with the new version.
User Training: Train users on any new features or changes introduced in the upgraded version.
44. What Are Some Best Practices for Universe Design?
Ans:
Use Descriptive Names: Name classes and objects in a way that reflects their business meaning.
Avoid Cartesian Products: Prevent Cartesian products by defining proper joins and avoiding unnecessary joins.
Aggregate Awareness: Leverage aggregate awareness for improved query performance.
Define Hierarchies: Create hierarchies to organize data logically and facilitate user understanding.
Optimise Joins: Use the correct types of joins and optimize join paths for efficient query processing.
Document Universes: Provide thorough documentation for universes to aid in understanding and maintenance.
Regular Maintenance: Periodically review and update universes to accommodate changes in business requirements.
45. How Do You Ensure Optimal Performance in a Business Objects Environment?
Ans:
To ensure optimal performance in a Business Objects environment, consider the following practices:
Optimise Queries: Design queries efficiently to retrieve only necessary data.
Indexing: Ensure database tables are appropriately indexed for faster data retrieval.
Caching: Utilise caching mechanisms to store and reuse frequently accessed data.
Aggregations: Leverage aggregate awareness to use pre-aggregated data where applicable.
Server Configuration: Adjust server parameters based on system resources and workload.
Query Stripping: Remove unnecessary objects and elements from queries to reduce load.
Parallel Processing: Configure parallel processing options to enhance query execution.
Regular Monitoring: Monitor system performance regularly and make adjustments as needed.
46. Describe a Challenging Scenario You Encountered in Business Objects and How You Resolved It.
Ans:
In a challenging scenario, I encountered a report performance issue where a complex query was causing slow execution times. To address this, I took the following steps:
Query Optimization: Analysed the query and identified areas for optimization, such as rewriting complex joins and conditions.
Index Review: Examined database indexes to ensure they were optimized for the question.
Caching Strategy: Adjusted caching settings to store frequently accessed data and reduce query execution times.
Server Resource Allocation: Increased server resources to accommodate the workload and improve overall system performance.
Scheduled Maintenance: Implemented a regular maintenance schedule to review and optimize queries, ensuring ongoing performance.
47. How Would You Handle a Situation Where a Report Is Not Delivering the Expected Results?
Ans:
If a report is not delivering the expected results, the following steps can be taken:
- Review Report Design
- Examine Query and Filters
- Data Validation
- Check Universe and Joins
- Error Messages
- Collaborate with Users
- Debugging Tools
- Documentation
48. Explain the Steps You Would Take to Troubleshoot a Universe Connectivity Issue.
Ans:
To troubleshoot a universe connectivity issue, follow these steps:
- Check Connection Parameters
- Test Connection
- Review Database Client
- Firewall and Network Configuration
- Database Server Availability
- Check Universe Integrity
- User Credentials
- Database Connectivity Logs
- Review System and Application Logs
- Collaborate with Database Administrators
49. What Do You Think Are the Emerging Trends in Business Objects and Business Intelligence?
Ans:
Emerging trends in Business Objects and business intelligence include:
- Augmented Analytics
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Cloud-Based BI
- Data Democratisation
- Embedded Analytics
- Mobile BI
- Data Governance and Security
- Real-Time Analytics
50. What Is the Role of Business Intelligence in an Organization?
Ans:
The role of business intelligence in an organization includes:
- Data Analysis
- Decision Support
- Performance Monitoring
- Strategic Planning
- Operational Efficiency
- Predictive Analytics
- Data Visualization
- Data-Driven Culture
51. How Can Business Intelligence Contribute to Decision-Making Processes?
Ans:
Business intelligence contributes to decision-making processes by:
- Providing Insights
- Enabling Data-Driven Decisions
- Improving Visibility
- Facilitating Forecasting
- Identifying Opportunities and Risks
- Enhancing Collaboration
- Monitoring Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Supporting Strategic Planning
52. Explain the Importance of Data Quality in Business Intelligence.
Ans:
Data quality is crucial in business intelligence for the following reasons:
- Accurate Decision-Making
- Trustworthiness
- Consistency
- Effective Analytics
- Compliance
- Customer Satisfaction
- Operational Efficiency
- Reduced Errors
53. How Comfortable Are You with SQL? Can You Write a Basic SQL Query?
Ans:
- SELECT FirstName, LastName, City
- FROM Employees
- WHERE Department = ‘Sales’
- ORDER BY LastName;
This query retrieves the first name, last name, and city of employees working in the ‘Sales’ department, ordered by last name.
54. Explain the Difference Between a Left Join and an Inner Join.
Ans:
Inner Join:
Retrieves rows from both tables that satisfy the specified join condition.
Excludes rows from both tables if they do not meet the join condition.
Commonly used for matching records between two tables.
- SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName
- FROM Orders
- INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID;
Left Join (or Left Outer Join):
Retrieves all rows from the left table and the matching rows from the right table.
If there is no match in the right table, NULL values are returned for columns from the right table.
Useful for situations where you want to include unmatched rows from the left table.
- SELECT Customers.CustomerID, Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID
- FROM Orders
- LEFT JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
55. What Is a Data Warehouse, and How Does It Differ from a Transactional Database?
Ans:
Data Warehouse:
- A data warehouse is a centralized repository that stores large volumes of historical and aggregated data.
- Optimised for reporting and analytical queries.
- Focuses on providing a comprehensive and consolidated view of business data.
Transactional Database:
- A transactional database is designed for handling day-to-day transactional operations.
- Stores current and frequently changing data.
- Normalised to reduce redundancy and maintain data integrity.
56. Explain the Concept of Star and Snowflake Schema in Data Warehousing.
Ans:
Star Schema:
- Star schema is a data warehouse schema where a central fact table is connected to multiple dimension tables.
- Offers simplicity and ease of query performance.
Snowflake Schema:
- Snowflake schema is an extension of the star schema where dimension tables are normalized into multiple related tables.
- Provides improved data integrity and reduced redundancy at the cost of increased complexity.
57. What Is Data Modeling, and How Does It Relate to Business Objects Universe Design?
Ans:
Data Modeling:
- Data modeling is the process of defining the structure of a database to represent the relationships between different data elements.
- Provides a blueprint for database design and supports efficient data retrieval.
Business Objects Universe Design:
- Business Objects Universe design involves creating a semantic layer that abstracts the complexity of underlying database structures.
- The universe acts as an intermediary between reports and databases, simplifying the reporting process for end-users.
58. How Do You Handle Slowly Changing Dimensions in Data Modeling?
Ans:
Slowly changing dimensions (SCD) in data modeling involves handling changes to dimension data over time. Common strategies include:
Type 1 (Overwrite): Overwrite the existing data with new values, discarding historical information.
Type 2 (Add New Row): Add new rows for changes, preserving historical data with effective start and end dates.
Type 3 (Add Columns): Introduce additional columns to capture changes while maintaining original values.
Hybrid Approaches: Combine strategies based on the nature of data changes.
59. Explain the purpose of ETL.
Ans:
- ETL processes are crucial in data warehousing and business intelligence.
- The primary purpose is to extract data from various sources, transform it into a consistent format, and load it into a data warehouse for analysis and reporting.
60. What is the importance of data visualization in Business Intelligence?
Ans:
Data visualization is essential in business intelligence as it helps users understand complex data through graphical representation. It enhances decision-making by providing insights and trends that may not be apparent in raw data.
61. Write down the principles of Effective Data Visualization.
Ans:
Simplicity: Keep visualizations simple and easy to understand.
Relevance: Focus on relevant data for the audience.
Clarity: Ensure clarity in conveying the intended message.
Interactivity: Allow users to interact with and explore data.
Consistency: Maintain consistency in design and terminology.
62. Explain about the business Objects in Healthcare.
Ans:
Business Objects can be applied in healthcare for analyzing patient data, monitoring treatment outcomes, and managing healthcare resources efficiently.
63. Explain Business Intelligence in Retail.
Ans:
In retail, business intelligence can help optimize inventory management, analyze customer purchasing behavior, forecast demand, and improve overall decision-making for sales and marketing strategies.
64. What is real-time data processing with business objects?
Ans:
Business Objects supports real-time data processing through features like real-time data connectors and event-based triggers, enabling users to access up-to-the-minute information.
65. What are the challenges and benefits of real-time BI?
Ans:
Challenges: Increased system complexity data consistency issues.
Benefits: Timely decision-making and faster response to market changes.
66. Discuss the integration of Business Objects with the Cloud.
Ans:
Business Objects can be integrated with cloud-based solutions using connectors and APIs, allowing organizations to leverage the scalability and flexibility of cloud platforms.
67. What are the considerations for Migrating Business Objects to the Cloud?\
Ans:
Data security, integration with existing systems, compliance with regulations, and performance are critical considerations.
68. Explain about Agile BI and self-service BI.
Ans:
Agile BI: Emphasises flexibility and responsiveness in BI development.
Self-Service BI: Empowers users to create their reports and analyze data without heavy dependence on IT.
69. What is self-service BI with business objects?
Ans:
Business Objects provides self-service capabilities through tools like Web Intelligence, allowing users to create and modify reports without IT intervention.
70. What are the predictive analytics in business objects?
Ans:
- Data Collection
- Data Preprocessing
- Feature Selection
- Model Training
- Validation and Testing
- Integration with BI Tools
- Dashboard Creation
- Real-Time Monitoring
- Actionable Insights
- Evaluation and Iteration
71. Give the example of Predictive Analytics in BI.
Ans:
Predicting customer churn based on historical data and customer behavior patterns.
Implement real-time monitoring to assess customer churn predictions continuously. As new data becomes available, the predictive model can be updated to improve accuracy and adapt to changing patterns.
72. Define the collaboration in business objects.
Ans:
Business Objects allows collaboration through features like shared folders, annotations, and comments within reports.
BusinessObjects, a business intelligence (BI) platform developed by SAP, provides collaborative features to facilitate communication and interaction among users in the context of data analysis and reporting.
73. Explain the business objects broadcast agent.
Ans:
The Broadcast Agent is designed to automate distributing reports, dashboards, and other BusinessObjects documents to a targeted audience. This automation helps ensure that relevant information is delivered to users promptly without manual intervention.
Business Objects supports mobile BI through responsive design and dedicated mobile apps, allowing users to access reports and dashboards on mobile devices.
74. What are the challenges faced in mobile BI implementation?
Ans:
- Device Fragmentation
- Screen Size and Resolution
- Data Security
- Network Connectivity
- Data Visualization: Integration with Device Features
- User Training and Adoption
- Data Governance
- Performance Optimization
- Offline Access
- Cost of Implementation
- Cost of Implementation
75. Discuss the licensing model for business objects.
Ans:
Business Objects typically uses a user-based licensing model, where organizations pay for the number of users accessing the system.
Software licensing models can evolve, and it’s crucial to refer to the most recent documentation or contact SAP directly for the latest information.
76. Explain the cost considerations for business object implementation.
Ans:
The cost considerations for implementing SAP BusinessObjects or any business intelligence (BI) solution can vary based on several factors, including the scale of deployment, features required, licensing models, and implementation approach.
Licensing costs, implementation services, training, infrastructure, and ongoing support are factors to consider when estimating the costs of implementing Business Objects.
77. Discuss the contribution of business objects and data governance.
Ans:
Business Objects contributes to data governance by providing tools for metadata management, access control, and auditing. It helps ensure that data is accurate, accessible, and complies with organizational policies.
BusinessObjects, developed by SAP, is a business intelligence (BI) platform that provides reporting, querying, analysis, and data visualization tools.
78. Ensure data quality and integrity in BI.
Ans:
Steps include data profiling, validation rules, regular data cleansing, and establishing data quality metrics. Business Objects allows for implementing these steps through its data profiling and cleansing capabilities.
79. Explain the BI Tools for collaboration.
Ans:
BI tools facilitate collaboration by providing shared dashboards, collaborative features within reports, and enabling data sharing across different departments.
Business Intelligence (BI) tools with collaboration features enable users to share insights, discuss findings, and collaborate on data-driven decision-making.
80. What is aligning marketing and sales with BI?
Ans:
BI can be used to analyze customer demographics, purchasing behavior, and marketing campaign effectiveness, enabling alignment between marketing and sales strategies based on data-driven insights.
81. Ensure the data privacy in business objects.
Ans:
Compliance with data privacy regulations involves implementing access controls, encryption, and auditing features in Business Objects. Organizations should also have clear policies on data handling and user training on compliance.
82. What is the role of Encryption in Business Objects?
Ans:
Encryption secures sensitive data in transit and at rest, preventing unauthorized access. Business Objects supports encryption mechanisms to protect data during transmission and storage.
83. How can you manage the changes in Production?
Ans:
Changes to reports or universes in a production environment should follow a version control system, with proper testing and approval processes in place to avoid disruptions. Backup strategies should be implemented.
84. What are the communication changes to end-users?
Ans:
Effective communication involves documentation, training sessions, and clear communication channels. Announcements and user guides can help end-users understand changes and adapt to new features.
85. Explain the challenges in data migration.
Ans:
Challenges may include data mapping issues, system compatibility, data format discrepancies, and downtime during migration. Thorough planning and testing are essential to mitigate these challenges.
86. How can you ensure data integrity in migration?
Ans:
Data integrity can be maintained through data validation checks, reconciliation processes, and accurate data mapping between source and target systems.
87. How is data mining involved in business objects? Explain.
Ans:
Data mining involves uncovering patterns and relationships in large datasets. In Business Objects, this can be applied to analyze customer behavior, identify market trends, and make predictions.
88. Give an example of Data Mining in BI.
Ans:
Analysing customer purchase history to identify cross-selling opportunities and predict future purchasing patterns.
Data mining in Business Intelligence (BI) involves various techniques to discover patterns, relationships, and insights from large datasets.
Example: Customer Segmentation for a Retailer
89. Compare the business objects with other BI tools.
Ans:
Business Objects is known for its robust reporting and query capabilities. Unlike Tableau, Business Objects may have a steeper learning curve but offers more extensive data integration options.
It’s important to note that the BI landscape evolves, and new features or changes in existing tools may occur.
90. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of business objects vs. Tableau.
Ans:
Strengths of Business Objects include its powerful reporting and ad-hoc query capabilities, while weaknesses may consist of a less intuitive user interface than Tableau.
91. How can I stay Updated on Business Objects?
Ans:
Stay updated through official documentation, forums, online courses, and user group participation. Regularly checking for updates and attending relevant conferences can also be beneficial.
Participate in the SAP Community forums related to BusinessObjects. Engage with other users, ask questions, and share your knowledge. The community is a valuable resource for staying informed about common issues, solutions, and updates.
92. How can you improve your skills in the past year?
Ans:
Improving skills is a continuous process that involves intentional effort and a commitment to learning and development.
Examples could include:
- Completing relevant online courses.
- Participating in workshops.
- Attending webinars.
- Working on real-world projects to apply and reinforce learned concepts.
93. Explain how you can meet tight deadlines in a BI project.
Ans:
Prioritise tasks, collaborate closely with the team, and utilize agile methodologies to adapt to changing requirements. Effective communication and regular updates can also help manage expectations.
94. Discuss handling conflicting priorities.
Ans:
Prioritise tasks based on strategic goals, communicate with stakeholders to set expectations and work collaboratively to find solutions that align with overall project objectives. Adaptability and flexibility are vital in handling conflicting priorities.
95. Give a suitable example of successful collaboration with a cross-functional team.
Ans:
In a previous project, I collaborated with IT, marketing, and finance members to implement a comprehensive BI solution. We conducted regular cross-functional meetings to gather requirements, ensure alignment with business goals, and address any challenges promptly. This collaboration resulted in a successful BI implementation that met the needs of all departments.
96. How can you handle last-minute changes to a critical report?
Ans:
I would assess the impact of the requested change on the report and project timeline. If the difference is critical and feasible within the given timeframe, I prioritize it, communicate the potential implications to stakeholders, and work closely with the team to implement the modification efficiently while maintaining data accuracy.
97. Explain the troubleshooting of complex performance issues in business objects.
Ans:
I would follow a systematic approach in a scenario where a Business Objects system faced performance issues. This might include analyzing server logs, identifying bottlenecks in database queries, optimizing report design, and collaborating with administrators to fine-tune the underlying database. Regular monitoring and performance testing would be conducted to validate the effectiveness of the implemented solutions.
98. What is your experience in handling user dissatisfaction with the performance of business objects?
Ans:
- Performing a thorough performance analysis, identifying the root causes, and implementing optimizations would be a priority.
- Clear communication with users about the steps to address the performance issues and providing training or guidance on optimizing queries or report design could help manage dissatisfaction.
- Additionally, setting realistic expectations about the system’s capabilities and timelines for improvements is crucial. Ongoing monitoring and proactive communication would be maintained to ensure user satisfaction.
99. Explain the differences between a Universe and a Report in SAP BusinessObjects.
Ans:
A Universe in SAP BusinessObjects is a semantic layer that acts as an intermediary between the database and the end-user tools. It simplifies the complexity of database structures by providing a business-oriented view of the data. A Report, on the other hand, is a document created using a BusinessObjects reporting tool (e.g., Web Intelligence) that uses a Universe to access and present data.
100. Can you explain the concept of aggregate awareness in SAP?
Ans:Aggregate awareness is a feature in SAP BusinessObjects that enhances query performance by allowing the system to intelligently choose between aggregated and detailed data based on the level of granularity needed in a report or query.






