
The soaring demand for logistics management has led SAP to come up with several modules that streamline sales and distribution. Companies are in pursuit of specialists who can seamlessly deal with SAP Logistics. One such SAP Logistics module is SAP SD. To help individuals crack SAP SD job interviews, we have prepared a set of most frequently-asked interview questions on this topic. This page contains a list of top 20 on-demand SAP SD interview questions. Learn SAP S/4HANA Sales and Distribution from Intellipaat SAP SD Training Certification Courseto fast-track your career now.
1. What does SAP SD?
Ans:
One of the primary modules, sales, and distribution, abbreviated as a SD, is developed by a SAP. To manage the billing, selling, shipping, and transportation of a several products are they own. This module registers the consumers’ data, along with product they have purchased.
2. What does primary function of SAP?
Ans:
The primary function of SAP is to run and grow businesses and services in the numerous large companies. It is top Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software.
3. What does areas use SAP?
Ans:
Initially developed by IBM, SAP was made to resolve a software application problems. Later, it came up with SAP R/3 application software, where R stands for a real-time data processing and 3 represents Application, Presentation, and Database Leaders.
SAP became famous in no time. It was adopted by a giant enterprises that resulted in adding many other SAP modules, are finance and accounting, production and planning, controlling, materials management, and more, to cover a specific areas in a business.
4. What does key components of SAP SD?
Ans:
- Contract Handling and Management
- Customer and Vendor Master Data
- Transportation of products
- Credit Management
- Shipping of Material
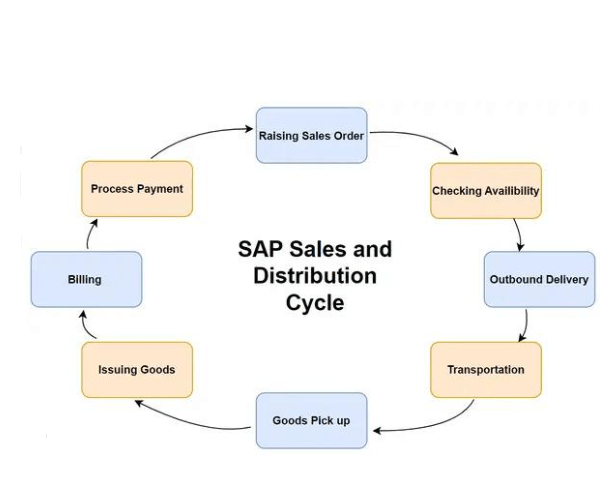
5. Explain organizational structure in SAP SD.
Ans:
Components in SAP, like sales areas, divisions, distribution channels, sales offices, and sales groups, and follow two steps within organization:
- Create an organization element in SAP system
- Link every element according to requirement
6. Describe material management in SAP ERP system.
Ans:
Material management is one of the most significant modules in SAP ERP systems, linked with the other SAP R/3. All these other modules are interlinked with the each other. The primary function of material management is to keep a record and monitor everyday business requirements and operations in an inventory.
7. Give an example of Material Management integration with Sales and Distribution?
Ans:
Multiple links are between the SAP SD and SAP MM. The Material management is used to generate the inbound and outbound sales and distribution updates. Likewise, MM is used to find out price details and availability of a product but is controlled by sales and distribution module.
8. What does SAP SD modules?
Ans:
SAP SD modules contain all customer data and related information about their services. It is one of important modules in the SAP ERP that deals with the billing, selling, and transportation of goods and services of an organization. SAP SD also contains the several sub-modules for a seamless functioning of software.
9. Name the sub-modules of SAP SD?
Ans:
- SAP SD-BF (Basic Functions)
- SAP SD-MD ( Master Data)
- SAP SD-SLS (Sales)
- SAP SD-TBA (Transportation)
- SAP SD-SHP (shipping)
- SAP SD-FTT (Foreign trade)
- SAP SD-CAS (Sales support)
- SAP SD-BIL (Billing)
10. Explain about sales support.
Ans:
A sales support is one of the complex components of SAP SD. The primary function of module is assist companies and large organizations in building a new sales, tracking existing and old sales, and maintaining the record of performance along with the sales. It is a helpful module to look up work progress and make changes in procedures, if necessary. Gathering information on an interested customers can be done through the emails, which helps business to be great extent.
11. What does main functions of sales order processing?
Ans:
- e-Transfer of a documents and printing them
- Checking availability of purchased articles
- Checking for the incomplete data
- Scheduling a goods delivery dates
- Checking status updates of sales transactions
- Calculation of a prices and taxes
12. Name the type of sales order related to SD.
Ans:
- Availability Check
- Tax Determination
- Sales Order
- Link Points
- Credit Check
- Costing
13. What does sales area in SAP SD?
Ans:
The sales area in SAP SD helps to find what marketing strategy has been adopted by a one particular division for improving the sales.It collecting the sales organization, divisions and distribution channels.
14. What does distribution channel in SAP SD?
Ans:
Distribution channels in SAP SD consist of a details and information on the distributed products.It keeps the log of all services and products provided to the user by an organization.
15. Explain division in SAP SD.
Ans:
The product and service lines of a product in an organization are shown by the division in SAP SD.
16. What does partner function?
Ans:
SAP SD counts all steps within organization through partner functions.These functions are allow the organizations to keep record of which partner is linked to particular customer,performance record and details of customers or partners with the whom business is to be carried out.
17. List the types of a partner functions in SAP SD.
Ans:
- Partner Function
- Partner Type
- Vendor
- Customer
- Shipping
- Forwarding agent
- Selling
- Human resource
- Sales personnel
18. Explain sales activity in SAP SD.
Ans:
A Sales activity is one of the activities that take place in SAP SD.They are tasks that sales personnel are undertake to be improve the sales.
19. Name and describe types of pre-sales activities.
Ans:
Pre-sale activities are activities that occur before a product’s sales to customers. Inquiries and quotations from vendors are a few of pre-sale activities.
20. List some of general data control elements.
Ans:
To find the types of item categories, data control elements are can be used. Chances in an existing item categories can also be taken, or new ones can be created using data control elements.
21. What does outline agreement?
Ans:
An outline deal or agreement is a long-term purchasing agreement signed with the vendor. Numerous terms and conditions are mentioned in agreement stating the materials are supplied by vendors. There are two types of the outline agreements under the SAP SD- scheduling agreement and contract.
22. What does contract in outline agreement?
Ans:
The contract is the formal agreement signed between vendor and the customer for a period of time.There are two types of a contracts – value and quantity.
23. Describe the types of contracts are.
Ans:
There are the two types of contracts:
- Quantity contracts: In this type of a contract, the vendor has to write a terms and conditions of contract according to material quantity being supplied.
- Value contracts: In this, vendor has to pay the value for services and mention the same in contract.
24. Explain the process of creating scheduling agreement?
Ans:
A scheduling agreement is external agreement that applies to customers and contains a product details, delivery dates, and services.
25. What does schedule line categories?
Ans:
In sales document, all the items are divided into the schedule lines, which are assigned to the multiple control elements. The scheduled lines mention all the details, like quantity, delivery dates, inventory availability, and more.
26. What does schedule line categories in different sales documents?
Ans:
According to item category and sales document type, scheduled lines are be categorized. All these control elements are related to the shipping and general data, which are used to categorize a schedule lines.
27. Explain copy control?
Ans:
It is known as a copy control when all the crucial data, like transaction details, are copied from one document to the another.
- The SAP system consists of copy routines, which keep record of how the systems copy data from a one source to another target document.
- Such type of an information helps create additional routines that will meet business requirements.
28. How is pricing done in SAP SD?
Ans:
Pricing in SAP SD is done to figure out prices of external customers or vendors. There is some predetermined set of the conditions when the pricing is calculated.
29. How do copy controls work in the SAP systems?
Ans:
There are the three different levels in a sales order, which are as follows:
- Header level: Used when system copies a data from the header source to target header document.
- Item level: Used to find out a line item status.
- Schedule line level: Used when copying sales order is done from billing document.
30. What does condition table and record?
Ans:
To identify the individual condition record, a combination of keys is required. This is known as condition table. The system stores the related information in a particular format and specific condition, which is called the condition record.
31. What does manual pricing?
Ans:
During a sales order process, manipulation of prices can be done manually on item level as well as the header level. The manual manipulation is dependent on the individual conditions to find the price. The set of the activities goes as follows:
- Enter the additional pricing elements
- Delete pricing element
- Change condition
32. What does pricing by item category?
Ans:
All items are not suitable for pricing. The item is kept empty/blank if found it is not suitable or relevant for pricing. Item category is used to find the prices of such items.
- The system search order path can be determined to retrieve a data.
- An access sequence consists of the more than one access sequence that is used to search for valid record relevant to conditions until it’s found successfully.
33. What does access sequence?
Ans:
An access sequence is the search procedure used to find a data for one particular type.
- The system search order path can be determined to retrieve a data.
- An access sequence consists of the more than one access sequence that is used to search for valid record relevant to conditions until it’s found successfully.
34. Name the pricing and types.
Ans:
Condition type is defined as specific features of daily pricing activities in SAP system. Using condition type you can also put different condition types for each pricing, discounts on goods, tax and surcharge that occurs in business transactions.
35. Explain SAP SD product proposals.
Ans:
A top-notch strategy to improve the any company’s sales performance is proposing a new product. These products can be more expensive, cheap, or similar to the products requested by a customer.
- The system uses the power tool to market products online.
- This tool is known as automatic product proposal, which is capable of matching market requirement.
- Anyone can make such proposal types by using SAP CRM module.
36. What does quota arrangement?
Ans:
The materials to manufacture the product are taken from several local vendors. In quota arrangement, a quota is assigned to every supply source. The one who drops lowest quota pricing will represent a product production.
37. What do you understand by surcharge and discount?
Ans:
The relationship between the different products is cross-selling. Its a rules suggest up-selling, down-selling, leading, and sub-associated products.
38. Explain the types of sales orders.
Ans:
Different transactions are define different sales document types. Business transactions are grouped into the sales documents categories as follows:
- Sales orders
- Inquiries and quotations
- Post-sale documents
- Outline agreement
39. What does features that project proposal supports?
Ans:
- The relationship between the different products is cross-selling. Its a rules suggest up-selling, down-selling, leading, and sub-associated products.
- Generating a product proposals, proposing accessories, and top N product list with the respect to specific promotions.
40. Explain consignments processing.
Ans:
A few products are owned by a company that are located at client’s location. These products are known as a consignments.
41. Explain shipping in SAP SD.
Ans:
Shipping activity is tracked to be ensure logistics are running smoothly and customer service and distribution are going seamlessly. Shipping is used to do outbound delivery and the other activities like packing goods and picking them to transfer to destination.
42. What does Customer Material Info Record In SAP SD?
Ans:
- A customer material info record in the SAP SD is a master data record that links specific material to a specific customer.
- It contains information like customer’s material number, description, and pricing details.
43. What does Consignment Process In SAP SD?
Ans:
The consignment process in the SAP SD involves the delivering goods to a customer but retaining ownership until goods are actually used or sold.It helps in managing inventory at customer’s location while still maintaining a control.
44. What does mapping an enterprise structure in SAP SD?
Ans:
An enterprise structure is explained by several organizational units, like a distribution channels, clients, company code location, and more, which represent a corporate world’s business structure.
45. How can customize a rebate processing in SAP SD?
Ans:
A special agreement is granted to user on a specific sales volume over the particular time, known as a rebate agreement. To customize a rebate processing, follow these steps:
- Define a rebate agreement types.
- Create a condition type groups to group different condition types in order to calculate rebate
- Create a new condition types
- An Account determination is done
- Follow the procedure to add pricing to newly created condition.
- GL accounts are configured based on the customer group/material group/account key combination.
46. Describe transfer order.
Ans:
A transfer order contains all information related to transferring the materials in and out of the warehouse. It also contains the data related to storage to execute a logical stock transfers within allotted time frame.
47. What does shipping points?
Ans:
One delivery is only processed by a one shipping point, independent organizational entities. In the shipping point, processing and monitoring of all the deliveries and goods are carried out.
48. How can we close the backorders?
Ans:
- Create the accurate account estimate of demand using the past purchasing patterns.
- Work with supplier to track when back-ordered items are available
- Increase the stocking capacity
- Diversify the suppliers, if possible
- Be proactive about communicating with the customers
- Partner with the professional fulfillment company
49. Why should select SAP over others?
Ans:
SAP helps the outsource a business’s security, infrastructure, and continuity at a lower costs. Customers prefer a several SAP platforms for real-time analytics because of quick processing and solution capability. SAP is localized in over the 120 countries and operates in 37 languages, which makes it versatile to collaborate with the various companies.
50. How can explain the access sequence for a header conditions?
Ans:
There is no determination at header level, so one cannot change access sequence for header conditions in SAP. Use a group condition at item level to access the sequence. Even though condition is entered manually on header, it is still distributed to item level as that’s where a pricing applies.
51. How does Process A Return In SAP SD?
Ans:
To process a return in the SAP SD, follow these steps:
- Navigate to SAP Easy Access Menu
- Choose the Sales and Distribution > Sales > Sales Document > Returns (VA01)
- Enter required details like a return quantity, reason, etc
- Save return order
52. When use SAP Return Order and SAP Credit Memo?
Ans:
SAP Return Order is carried out when a customer returns any previously purchased products and requires the credit or money back. While credit memo is when a customer is credited without returning the any goods
53. How does Set Up A Consignment Process In SAP SD?
Ans:
Setting up a consignment process in the SAP SD involves configuring a special consignment types, pricing procedures, and agreements.It also requires a defining relevant master data records for the customers and materials.
54. Explain Copy control is and when Copy Control transition can be done?
Ans:
In SAP SD, the process of copying data from a source document to the target document is done by a Copy Controls. A Copy control can be done in the following manner:
- Sales document by sales document
- Billing document by sales document
- Sales document by delivery
- Sales document by billing document
- Delivery by billing document
55. How are the three tiers of copy controls put up? What are the transaction codes that allow for this to be done?
Ans:
At three levels of a sales order copy controls are set up at Header level, Item level and Schedule line level
- VTAA: from a sales order to sales order
- VTLA: from a sales order to delivery
- VTAF: from billing document to the sales order
- VTFA: from a sales order to billing document
- VTFL: from delivery to the billing document
- VTFF: from billing document to the billing document
56. How can we include condition type in the pricing procedure
Ans:
To include the condition type in pricing procedure have to follow the pathway Basic Functions >Pricing >Pricing Control >Define and Assign a pricing procedure and then select “ Maintain a pricing procedures” after that select pricing procedure and then “Control Data” and add the condition type to pricing system.
57. Explain Proforma Invoice and what are types of it?
Ans:
Proforma invoice is the reference doc for import and export negotiations. A standard proforma invoice doc types are:
- With reference to order – F5
- With reference to delivery- F8
58. Mention the transaction code used to create a return delivery?
Ans:
Transaction code is used to create the return delivery is T/C VA01 with the standard order type RE, while return delivery is T/C VL01 with a return delivery doctype LR
59. What are the purpose of billing document in SAP SD?
Ans:
A billing document in the SAP SD is used to generate a invoices for goods/services provided to a customer. It contains all necessary information like prices, quantities, taxes, and payment terms. It serves as legal document for both seller and the buyer.
60. Distinguish difference between rush order and cash sales?
Ans:
| Aspect | Rush Order | Cash Sales | |
| Purpose |
Urgent customer requests |
Immediate payment at the point of sale | |
| Customer Relationship | Existing customers | Various, including one-time buyers | |
| Order Creation | Formal sales order process | Direct transaction, no formal order | |
| Payment |
Flexible payment terms |
Immediate payment (cash or electronic) |
61. List out five features can control for the sale document type?
Ans:
For a sale document type five features can control is:
- Text
- Partner
- Pricing
- Taxes
- Output
- Delivery
62. Mention the techniques available in delivery Scheduling?
Ans:
The techniques are available in the delivery Scheduling are
- Backward Scheduling: The system calculates the requested delivery date
- Forward Scheduling: The system calculates earliest possible date based on material available date
63. What does various Customer account groups can create in the SAP SD module?
Ans:
A Customer account groups that can be created in the SAP SD are:
- One time customers
- Export customers
- Domestic customers
64. What is the significance of delivery document in SAP SD?
Ans:
A delivery document in SAP SD is crucial as it confirms a physical shipment of goods to a customer. It contains an information about the items being shipped, quantities, delivery dates, and shipping details.
65. Explain the primary functions of Sales order processing?
Ans:
The wholesale side of organization is the main area to be concerned for sales order. Its main functions are:
- Verifying purchased items are available
- E-transferring documents and printing them
- Verifying insufficient data
- Verifying a sales transactions status updates
- Scheduling delivery dates of the goods
- Calculating a price and taxes
66. What are the various sales activities that can be performed in the SAP SD?
Ans:
Sales activities in SAP Sales and Distribution module are divided into the pre-sales and post-sales activities:
- Pre-sales activities: The activities that take place before selling product to customers are called Pre-sales activities. Examples for a Pre-sales activities are inquiry, quotation.etc
- Post-sales activities: The activities that take place after selling product to customers are called Post-sales activities. Examples of the Post-sales activities are support, relationship management
67. How does a sales activity differ from a sales document?
Ans:
Sales activities in SAP Sales and Distribution module are divided into the pre-sales and post-sales activities. It includes activities when sell material instead of making a sales preparation with the customer. Example: Sales letter, sales calls, post-sales activities are support and relationship, etc. Sales documents are regarded as a sales when sell the materials to the clients and are created within SAP system to handle the sales process. Examples: quotations, sales orders, etc.
68. What does invoice correction?
Ans:
Invoice correction is the type of sales document.This is a documented process that introduces new approach to dealing with complaints and issuing debit and credit memos
- It enables users to modify the quantity and price for any faulty items that are present on invoice.
- The request for each invoice is made by invoice. In every invoice correction request, there are the two items.
- Quality and value is the first thing that is copied from invoices. A debit item is another thing that gives correct quality and value.
69. What are the types of sales orders?
Ans:
Various transactions in SAP system indicate various sales document types. The business transactions are categorized into the sales documents in different categories, which include the following:
- Inquiries and quotations
- Outline agreement
- Sales order
- Post-sale document
70. What does mean by pricing in a SAP Sales and distribution?
Ans:
Structure of Sales order: A customer inquiry may involve the one or more items which include a service or material quality included in order. Sales order quality is divided into the business lines, and it is made up of various subsets and delivery dates. The items in sales order are clubbed in a hierarchy and enable to distinguish between the batches or for using combinations of materials. An item can be split into the several billing plan deadlines, and every billing plan indicates time while a fixed amount of items should be billed.
- Creating the sales order – VA01 (t-code)
- Editing the sales order – VA02 (t-code)
- Displaying the Sales order – VA03 (t-code)
71. What is the Purpose of Debit Memo Request In SAP SD?
Ans:
A debit memo request in the SAP SD is used to request a credit from customer. It is sent when a customer has overpaid or when adjustment is needed due to an error.
72. How to create a quotation in SAP sales and distribution
Ans:
A quotation is the legal document to the clients about the delivery of the products and services. Usually, this is given after inquiry from the client.In SAP R/3 Menu, VA21 – t-code
73. Explain the structure of sales order in SAP SD.
Ans:
Structure of Sales order: A customer inquiry may involve the one or more items which include a service or material quality included in order. Sales order quality is divided into the business lines, and it is made up of various subsets and delivery dates. The items in sales order are clubbed in a hierarchy and enable to distinguish between the batches or for using combinations of materials. An item can be split into the several billing plan deadlines, and every billing plan indicates time while a fixed amount of items should be billed.
- Creating the sales order – VA01 (t-code)
- Editing the sales order – VA02 (t-code)
- Displaying the Sales order – VA03 (t-code)
74. What is availability check in SAP SD?
Ans:
An availability check in SAP SD is the process that determines whether requested quantity of a product is available in stock before confirming sales order. It considers factors like an existing stock, incoming goods, and production.
75. What are the factors that must be considered when define various item categories?
Ans:
The factors that must be considered when define the various item categories are:
- A A General data control elements
- Billing data control elements
- Shipping a data control elements
76. Explain outline agreement?
Ans:
A long-term purchase agreement signed with the provider is referred to as online agreement.SAP SD includes the two types of outline agreements they are:
- Scheduling agreement
- Contract
77. What is a product proposals in SAP SD?
Ans:
Coming up with the new product is always a great strategy to enhance sales performance of an organization. The recommended products can be cheaper, costly or the same as a products that are demanded by the customer. Automatic Product Proposal is the powerful tool that is used by system to market the products online.
78. What is mapping an enterprise structure?
Ans:
Enterprise structure is a structure of the business in real life. Different organizational units are defined by requirements like a company code location, client, distribution channel, etc.
79. What is the use of SAP FI in SAP Sales and Distribution?
Ans:
In case of a standard sales order, create an outbound goods delivery to customer. Here movement 601 takes place. This movement is configured in MM and movement of goods hit the some G/L account in FI.
80. What does use of partner function in SAP Sales and Distribution?
Ans:
Partner function allows to identify which functions partner has to be perform in a business process. Consider a simplest case, where all customer functions are performed by a partner customer. As these are mandate functions they has to be defined as an obligatory functions in SD system.
81. How to assign a sales organization to delivering plant?
Ans:
- SPRO-IMG-Enterprise Structure-Assignment-SD-Assign Plant to Sales Organization/Dist.Channel.
- T-Code − OVX6
82. What are the different activities under consignment stock in SAP SD?
Ans:
Consignment stock management includes the four key activities in the system:
- Creating the Consignment Fill-Up (Stock is fill up at warehouse)
- Creating a Consignment Issue (Stock issued from warehouse)
- Creating the Consignment Pick-Up (Stock return to manufacturer)
- Displaying the Consignment Returns (Stock return from customer)
83. Explain delivery block is in SAP SD.
Ans:
A delivery block in the SAP SD is a status set on a sales order or delivery document that prevents a further processing or shipping of associated goods. It’s often used for the quality checks, credit limit issues, or other reasons to temporarily halt delivery process.
84. Any example of using the condition technique and type?
Ans:
Condition type allows to define the discount for a special material.This can be specified in system to calculate discount as an amount or it can calculate the discount in terms of a percentage.In case have to use both the discount types, two separate a condition types has to be defined in the system.
85. In sales order how system does picks up plant?
Ans:
Can assign the particular material master to particular plant and it picks up from there.
86. Distinguish Difference between milestone and periodic billing?
Ans:
- Milestone: Incomplete amount in each bill till full amount is billed
- Periodic: Full amount in every bill till the agreement period
87. Define Cross company stock transfer?
Ans:
Cross-company Stock Transfer is a technique of delivering the sales order via new company code. Moreover, it is also indispensable for providing a material from a plant having one business code to the plant in another business code.
88. What is alternative condition base value?
Ans:
This indicates the classically a formula obligatory for condition category to support an alternative base value needed for computation of a value.
89. What is Item Category?
Ans:
In SAP, the sales item category is measured to more significant. A company requires it to organize a sales document flood while impacting timetable line category. The item category put influence n delivery and billing process
90. What is R/3? ?
Ans:
R/3 is there as three-tiered architecture, which is used by a scheme. There are three tiers mentioned as:
- Database server
- Application server
- Presentation server
91. Define Cross company stock transfer?
Ans:
In SAP, the sales item category is measured to more significant. A company requires it to organize a sales document flood while impacting timetable line category. The item category put influence n delivery and billing process
92. What is the use of Sales support function in SD module?
Ans:
A Sales support is one of the key component in the Sales and Distribution SD module. This module helps the organizations to create a new sales, tracking of existing sales, and performance and eventually help in improving the marketing and sales in an organization.
93. What does surcharge and discount? What does predefined discount type in SAP system?
Ans:
A standard SAP system includes the variety of common discount types and can also define the customize discounts and surcharges as per business requirement.
94. Why does the customer master have different views?
Ans:
The main purpose of customer views is for each determine the roles effectively in the customer
- GENERAL DATA– deals with all details regarding the customer
- COMPANY CODE DATA– deals with the financial aspects
- SALES AREA DATA– deals with the sales; billing; shipping details along with partner determination
95. How to manage discounts in Condition record?
Ans:
While creating the condition records, can use any of standard discount types:
- While doing an automatic pricing, system checks for a discount that satisfies a certain condition and it checks for valid condition records.
- If a discount refers to the group like a material group or price groups, that group must be assigned to the relevant customer or material master record before automatic pricing is done in system.
96. Can we extend material and customer to the other sales area in SAP Sales and Distribution?
Ans:
Sales area is the combination of sales organization and distribution channel and Division. Division is the logical grouping of products, hence can’t extend material to the other sales areas. But can extend customer to the other sales areas through common Distribution channel & division.
97. What is the use of customer group?
Ans:
Customer group is used for generating a statistics and also used to give the group pricing, and discounts etc…
98. What is backorder in SAP SD?
Ans:
A backorder in the SAP SD occurs when there is insufficient stock to fulfill customer’s order at a specific point in time. The order is recorded, but delivery is delayed until required items are available. It’s a way to ensure the customers receive their products even if there are temporary shortages.
99. What does Rebate Agreement In SAP SD?
Ans:
A rebate agreement in the SAP SD is a special pricing arrangement between seller and a customer. It offers a rebate or discount based on predefined conditions, like achieving sales targets over a specified period. Rebates are settled periodically, often monthly or be quarterly.
100. How to transfer data from legacy code to sap Legacy Code?
Ans:
It should be legacy data to the SAP. What it means is want to transfer all the customer and materials and all other information from the Older (legacy system) to new SAP system. And can do it using many tools, most noticeably MDMs.






