
SAP Global Trade Services (SAP GTS) is a sophisticated global trade management software solution that enhances international commerce by consolidating customs compliance, logistics management, and documentation tasks into a unified system. This advanced technology seamlessly integrates with ERP and CRM systems, enabling efficient oversight of trade transactions across the entire enterprise. With SAP GTS, businesses can streamline operations and easily monitor trade performance, leveraging robust reporting and analytics tools to drive continuous improvement in their global trade processes.
1. What are Sap Gts?
Ans:
With the help of the Global Trade Services (GTS) system, you can handle a sizable number of business partners and documents, automate international trade transactions, and make sure your organization always conforms with rapidly evolving international legal laws.
2. What are SAP GTS’s main features?
Ans:
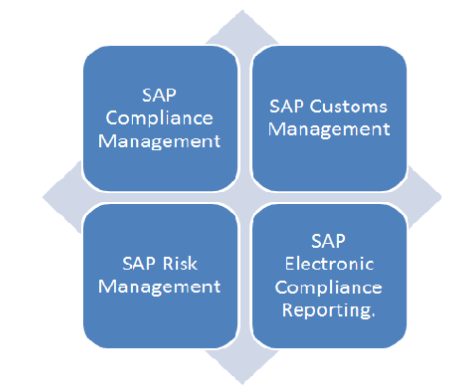
3. How do Sap Global Trade Services (GTS) and Ecc Foreign Trade compare?
Ans:
Scope:
- It is a standalone application that provides comprehensive functionality for managing global trade processes, including Compliance Management, Customs Management, Risk Management, and more.
ECC Foreign Trade:
- Foreign Trade is a module within SAP ECC that focuses on handling basic export and import processes, such as creating export/import documents, managing legal control, and basic customs declarations.
4. What Benefits Come With Using SAP GTS?
Ans:
- Using automated methods to save time
- Discount on expenditure
- Less concern for human paintings
- Automatically detecting noncompliance and prohibited vendors
- Can maintain the organization’s logo and accept it as true in order to avoid penalties and repercussions
- Quick exchange handling and customer satisfaction
5. What Is The Connection Between Sap GTS And R/three?
Ans:
The connection between SAP Global Trade Services (GTS) and SAP R/3, which is the predecessor of SAP ECC (Enterprise Central Component) and SAP S/4HANA, lies in the integration of GTS with the broader SAP ERP landscape. SAP GTS can be integrated with R/3, ECC, or S/4HANA systems to enhance and extend the capabilities of global trade management within the SAP environment
6. Which Functionalities Are Included in Sap GTS?
Ans:
- Compliance Management: To assess issues with worldwide exchange compliance
- Customs Management: Handles transactions pertaining to customs.
- Risk management: To lessen the dangers associated with financial dealings.
- Electronic Compliance Reporting: For the purpose of filing reports on changes made inside Europe
- System Administration: Manages the GTS feeder system’s configuration and tracking.
7. What Constitutes The Main Elements Of Sap GTS?
Ans:
- SAP Compliance Management
- SAP Customs Management
- SAP Risk Management
- SAP Electronic Compliance Reporting
8. What Advantages Does Sap GT Offer?
Ans:
- Assure strict adherence to trade regulations
- Reduce the possibility of severe fines and penalties
- Prevent costly freight delays at customs and border crossings.
- Swift execution
- Cheaper costs for IT protection
- Quicker Contact with Customs
- High return on investment
9. Explain Compliance Management?
Ans:
Import and export control restrictions are addressed by compliance management functions. With the help of this tool, one may keep an eye on processes that need to be licensed and adhere to international laws that forbid or restrict trade with specific individuals, groups, or nations.
10. What is Risk Management Function In Sap Gts?
Ans:
Processing Letters of Credit, determining preferences, and managing Long Term Vendor Declarations all involve risk management. enabling you to reduce the financial risk connected to international trade.
11. What Kind of Results Can Be Obtained With Sap Gts?
Ans:
- Less chance of fines and penalties from the trade.
- Controlling expenses while exporting.
- Increased output and the simplification of all trade procedures for better global operations.
- The complete elimination of manual labor with the use of automated technologies. In turn, this also eliminates the time spent on these manual chores.
- Reliable and seamless integration across all international supply chains.
12. Difference between Tally software and SAP software?
Ans:
Target Market:
- Tally: Primarily targets small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). It is widely used for accounting, financial management, and basic business operations.
- SAP: Targets a broad range of enterprises, from small businesses to large multinational corporations. SAP provides comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions that cover various business functions.
13. Difference Between (a/c Payable / Receivable ) And ( Bills Payable / Receivable )?
Ans:
| a/c Payable / Receivable | Bills Payable / Receivable |
|---|---|
| Accounts Payable: Sums owed to creditors, vendors, and suppliers. Another name for the accounting company is Sundry Creditors. Current Liability is this. | Bills Payable: These are Current Liabilities that are drawn out with the assistance of Creditors or Suppliers on the agency. |
| Accounts Receivable Amounts owed to creditors or customers are referred to as accounts receivable. The accounting company is sometimes referred to as Sundry Debtors. The current asset is this. | Bills Receivable: These are Current Assets that are drawn by a business from its Customers or Debtors. |
14. What does the SAP GTS electronic compliance reporting function entail?
Ans:
Reporting on Electronic Compliance: For intra-European trade between EU member states, the ECR permits the routine filing of Intrastat declarations to the authorities. The logistical methods are used to obtain pertinent information, which is then periodically provided to the government responsible for nationwide records.
15. Why some transformers without a breather?
Ans:
- In SAP GTS, the absence of a breather on some transformers might be attributed to specific operational or environmental considerations.
- Transformers without breathers are typically utilized in sealed environments where the exchange of air with the external atmosphere is not required.
- Sealed transformers help prevent the entry of contaminants, such as moisture and dust, into the insulating oil, reducing the risk of insulation breakdown
16. In R12 What are the PO types in Purchasing and Invoices in AP?
Ans:
- In Oracle E-Business Suite R12, Purchasing supports various Purchase Order (PO) types to cater to different procurement scenarios. Common PO types include Standard Purchase Order, Blanket Purchase Agreement, Contract Purchase Agreement, and Planned Purchase Order.
- In Accounts Payable (AP), R12 supports various invoice types, including Standard Invoice, Debit Memo, Credit Memo, and Prepayment Invoice. These invoice types enable users to accurately reflect different financial transactions within the system.
17. What is SPL screening in SAP GTS?
Ans:
- SPL (Sanctioned Party List) screening in SAP GTS involves checking business partners against lists of sanctioned individuals, entities, or countries to ensure compliance with trade regulations.
- This screening helps prevent illegal transactions with restricted parties.
18. How does SAP GTS handle customs processes?
Ans:
SAP GTS Customs Management automates customs declaration processes by providing tools for managing import and export declarations, electronic communication with customs authorities, and ensuring compliance with local customs regulations.
19. Explain the concept of Preference Management in SAP GTS.
Ans:
- Preference Management in SAP GTS allows businesses to manage and utilize preferential agreements, such as free trade agreements, to optimize duty rates and reduce costs associated with international trade.
- It involves determining the origin of goods to qualify for preferential treatment.
20. How does SAP GTS contribute to supply chain visibility?
Ans:
- SAP GTS enhances supply chain visibility by providing real-time tracking of goods, monitoring customs processes, and ensuring compliance with trade regulations.
- This visibility helps businesses optimize their supply chain processes and respond quickly to changes in international trade conditions.
21. What is the purpose of the Legal Control functionality in SAP GTS?
Ans:
Legal Control in SAP GTS helps businesses manage the legal aspects of international trade, including embargo checks, compliance with export control laws, and adherence to licensing requirements. It ensures that trade activities comply with legal regulations to avoid penalties.
22. How does SAP GTS handle restricted party screening?
Ans:
SAP GTS uses SPL screening to perform restricted party checks. It compares business partners against lists of sanctioned individuals, organizations, or countries, helping businesses avoid engaging in trade activities with entities that are subject to legal restrictions.
23. Explain the integration points of SAP GTS with other SAP modules.
Ans:
- SAP GTS integrates with various SAP modules, including SAP ERP (for order and delivery information), SAP SCM (for supply chain visibility), and SAP S/4HANA (for end-to-end business processes).
- Integration ensures seamless information flow across different business functions.
24. What is Risk Management in SAP GTS?
Ans:
SAP GTS Risk Management is concerned with identifying and reducing financial and legal risks involved with global commerce. It assists firms in identifying and managing possible risks, as well as assuring compliance with trade legislation and reducing financial vulnerabilities.
25. How does SAP GTS handle denied party screening?
Ans:
- Denied party screening in SAP GTS involves checking business partners against lists of denied or restricted entities.
- Compliance Management utilizes denied party screening to prevent transactions with entities that are prohibited or restricted by international trade laws.
26. Explain the role of SAP GTS in export control?
Ans:
SAP GTS plays a crucial role in export control by managing and enforcing compliance with export regulations. It includes checks for licensing requirements, embargoes, and other legal aspects to ensure that exported goods adhere to international trade laws.
27. What is the significance of embargo checks in SAP GTS?
Ans:
- Embargo checks in SAP GTS are critical for screening business partners against embargoed countries or regions.
- Compliance Management performs embargo checks to prevent transactions that may violate trade restrictions imposed on specific countries.
28. How does SAP GTS handle dual-use goods?
Ans:
SAP GTS addresses the management of dual-use goods through Compliance Management. It ensures that businesses comply with regulations related to goods that can have both civilian and military applications, requiring careful monitoring and control.
29. What is the purpose of SAP GTS Preference Determination?
Ans:
- SAP GTS Preference Determination is responsible for identifying the preferential origin of goods based on trade agreements.
- It helps businesses determine eligibility for preferential treatment, optimizing duty rates and ensuring compliance with trade agreements.
30. How does SAP GTS assist in managing trade licenses?
Ans:
- SAP GTS supports the management of trade licenses by tracking and validating the required licenses for specific transactions.
- It ensures that businesses obtain and maintain the necessary licenses for compliant international trade.
31. Explain SAP GTS Intrastat Reporting?
Ans:
SAP GTS Intrastat Reporting handles the reporting of goods movement statistics within the European Union. It helps businesses comply with EU regulations by providing accurate and timely reporting of intra-community trade statistics.
32. How does SAP GTS handle trade document management?
Ans:
- SAP GTS manages trade documents through the creation and storage of electronic documents related to international trade transactions.
- It enables the efficient handling of documents such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
- Trade document management ensures compliance with documentation requirements for customs and regulatory purposes.
33. Explain the concept of SAP GTS Customs Management.
Ans:
- Customs Management in SAP GTS automates and streamlines customs declaration processes.
- It includes functionalities for managing import and export declarations, ensuring compliance with local customs regulations.
- SAP GTS Customs Management facilitates electronic communication with customs authorities, reducing manual efforts in customs documentation.
34. How is SAP GTS involved in managing preferential trade agreements?
Ans:
- SAP GTS handles preferential trade agreements through the Preference Management component.
- It determines the preferential origin of goods based on trade agreements to optimize duty rates.
- The system ensures that businesses can claim preferential treatment when eligible, enhancing cost savings in international trade.
35. What challenges face when implementing SAP GTS, and how can they be addressed?
Ans:
Challenges in SAP GTS implementation may include data integration issues and user adoption. To address these problems, careful planning, comprehensive training programmes, and coordination between IT and business teams are required to guarantee a seamless transition and maximize the system’s benefits.
36. How does SAP GTS assist in managing trade licenses and permits?
Ans:
- SAP GTS supports the tracking and validation of trade licenses required for specific transactions.
- It ensures that businesses obtain and maintain the necessary licenses for compliant international trade.
- Trade license management in SAP GTS helps organizations stay in line with regulatory requirements.
37. How can SAP GTS contribute to reducing trade-related costs for businesses?
Ans:
SAP GTS contributes to cost reduction by tracking and calculating additional costs associated with international trade. It allows businesses to optimize costs, including customs duties and taxes, providing a comprehensive view of the true cost of imported goods.
38. Explain SAP GTS in managing controlled goods and technologies?
Ans:
- SAP GTS manages controlled goods and technologies through Compliance Management.
- It helps ensure compliance with export control laws, particularly for items with dual-use applications.
- The system provides mechanisms to control and monitor the movement of controlled goods.
39. How does SAP GTS handle Intrastat reporting, and in which scenarios is it required?
Ans:
- SAP GTS Intrastat reporting handles the reporting of goods movement statistics within the European Union.
- It is required for scenarios involving the movement of goods between EU member states.
- Intrastat reporting in SAP GTS ensures compliance with EU regulations for intra-community trade statistics.
40. How does SAP GTS ensure compliance with changing global trade regulations?
Ans:
SAP GTS maintains compliance by regularly updating its content with the latest trade regulations. The system provides automated checks against these regulations, ensuring that businesses are informed about and adhere to the ever-evolving international trade requirements. This proactive approach enables organizations to mitigate the risk of non-compliance and stay aligned with the dynamic nature of global trade laws.
41. Explain integrating SAP GTS with other SAP modules for seamless information flow?
Ans:
- SAP GTS integrates with various SAP modules, such as SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA.
- Integration ensures seamless information flow across different business functions.
- It enables a consolidated view of data and processes, promoting efficiency and accuracy in global trade management.
42. How does SAP GTS handle landed costs in international trade scenarios?
Ans:
- SAP GTS facilitates the management of landed costs by tracking additional costs associated with international trade.
- It includes expenses such as customs duties, taxes, and freight charges in the overall cost calculations.
- Handling landed costs in SAP GTS provides a comprehensive view of the true cost of imported goods.
43. How does SAP GTS contribute to reducing trade-related costs for businesses?
Ans:
SAP GTS contributes to cost reduction by optimizing trade processes and minimizing the risk of penalties. Through functionalities like Preference Management and landed cost calculations, the system helps businesses leverage preferential trade agreements, reduce duty rates, and accurately account for additional costs. This holistic approach to cost management in international trade positions SAP GTS as a valuable tool for enhancing the overall efficiency and financial performance of businesses engaged in cross-border transactions.
44. What does SAP GTS support businesses in managing complex supply chains?
Ans:
- SAP GTS supports businesses in managing complex supply chains by providing real-time visibility into global trade activities.
- The system tracks goods throughout the supply chain, monitors customs processes, and ensures compliance with trade regulations.
45. How does SAP GTS handle the classification of products for customs purposes?
Ans:
SAP GTS facilitates product classification by assigning Harmonized System (HS) codes based on characteristics. It streamlines customs declarations by ensuring accurate classification, supporting compliance with customs regulations.
46. Explain SAP GTS in managing Intrastat reporting within the European Union?
Ans:
SAP GTS Intrastat reporting manages the reporting of goods movement statistics within the EU. It ensures compliance with EU regulations, providing accurate and timely reporting of intra-community trade statistics.
47. What does SAP GTS play in supporting businesses in navigating export control regulations?
Ans:
- SAP GTS supports businesses in navigating export control regulations by automating compliance checks.
- It ensures that exported goods adhere to legal requirements, including licensing and embargo restrictions.
48. How does SAP GTS handle the identification and management of dual-use goods?
Ans:
- SAP GTS manages dual-use goods by incorporating Compliance Management features.
- It ensures compliance with regulations governing goods with both civilian and military applications, providing control and visibility
49. What is SAP GTS Customs Management in cross-border transactions?
Ans:
SAP GTS Customs Management automates customs declaration processes and facilitates electronic communication with customs authorities. This ensures compliance with local customs regulations and reduces manual efforts, enhancing efficiency in international trade.
50. What does SAP GTS play in managing trade licenses and permits?
Ans:
SAP GTS supports the tracking and validation of trade licenses necessary for specific transactions. It ensures businesses obtain and maintain the required licenses for compliant international trade, contributing to regulatory adherence.
51. How does SAP GTS streamline trade document management processes for businesses?
Ans:
SAP GTS simplifies trade document management by offering tools for creating, managing, and storing electronic trade documents. This enhances efficiency in handling essential documentation for customs and compliance purposes in international trade.
52. Explain SAP GTS Risk Management in mitigating trade-related risks?
Ans:
- Risk Management in SAP GTS assesses and mitigates financial and legal risks associated with global trade.
- It identifies potential risks, such as compliance issues or financial exposures, allowing proactive risk mitigation.
- SAP GTS Risk Management enhances decision-making and helps organizations navigate the complexities of international trade.
53. FTO in SAP GTS: what is it?
Ans:
Essentially, mapping a company to a foreign trade organization is completed in the SAP GTS system configuration area by navigating to the Global Trade Services–>Organizational Framework –>FTO to Company Code Mapping
54. What is SAP GTS Compliance Management in international trade?
Ans:
- Compliance Management ensures adherence to global trade regulations and laws.
- It includes features like embargo checks, restricted party screening, and export control to prevent legal violations.
- SAP GTS Compliance Management minimizes the risk of penalties and legal consequences associated with non-compliance
55. Explain SAP GTS in denied party screening ?
Ans:
SAP GTS conducts denied party screening by checking business partners against lists of restricted entities. This ensures businesses avoid engaging in transactions with denied or restricted parties, mitigating the risk of legal consequences and promoting compliance with international trade laws.
56. How can I contribute to optimizing duty rates through preference determination?
Ans:
- SAP GTS optimizes duty rates by determining the preferential origin of goods based on trade agreements.
- This enables businesses to leverage preferential trade agreements, reduce duty rates, and comply with specific requirements, supporting cost-effective international trade.
57. How does SAP GTS handle the reconciliation of data discrepancies between different systems?
Ans:
SAP GTS reconciles data discrepancies through standardized interfaces and data exchange mechanisms. This ensures consistency and accuracy in trade data across various systems, reducing errors and enhancing the reliability of information in a global enterprise.
58. How does SAP GTS contribute to the optimization of duty drawback processes in global trade scenarios?
Ans:
- Duty Drawback Calculation: SAP GTS calculates duty drawbacks, considering factors like import duties paid on raw materials.
- Automated Processes: The system automates duty drawback processes, reducing manual efforts and minimizing errors.
- Compliance Checks: SAP GTS ensures that duty drawback claims adhere to legal requirements and regulations.
- Reporting and Analytics: The system provides reporting tools for analyzing duty drawback utilization and optimizing processes.
- Traceability and Transparency: SAP GTS enhances traceability, enabling businesses to track the origin and sustainability of products.
- Compliance with Regulations: The system supports compliance with environmental and social responsibility regulations.
59. Which SAP GTS is preferred?
Ans:
Preference Processing: SAP GTS’s identity-based preference processing helps exporters identify their commodities as eligible for preferential treatment and complete all regulatory requirements for customs preferences. At the identification level, users are able to ascertain the preference status of production and process orders.
60. How does SAP GTS handle the integration of trade data with external partners in the supply chain?
Ans:
- EDI Integration: SAP GTS supports Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) for seamless communication with external partners.
- API Connectivity: The system allows API-based integrations, ensuring real-time data exchange with supply chain partners.
- Collaboration Platforms: SAP GTS integrates with collaborative platforms, enhancing communication and data sharing.
- Secure Data Transmission: The system ensures secure transmission of trade data, maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
61. What strategies can organizations employ to ensure data security and confidentiality in SAP GTS implementations?
Ans:
- Role-Based Access Control: Role-based access controls can be used by organizations to restrict data access based on user roles.
- Data Encryption: Employing encryption methods ensures that sensitive trade data is transmitted and stored securely.
- Audit Trails: Implementing comprehensive audit trails helps track and monitor user activities for data security.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conducting regular security assessments and updates safeguards against potential vulnerabilities.
62. Explain SAP GTS on cross-border e-commerce transactions ?
Ans:
- Automated Compliance Checks: SAP GTS automates compliance checks, addressing challenges in varying e-commerce regulations.
- Customs Integration: The system seamlessly integrates with customs processes, reducing delays in e-commerce shipments.
- Global Trade Visibility: SAP GTS provides visibility into cross-border transactions, ensuring transparency in e-commerce operations.
- Adaptability to Regulatory Changes: The system adapts to evolving e-commerce regulations, ensuring ongoing compliance in dynamic online markets.
63. How does one handle the reconciliation of data discrepancies between different systems in global enterprise?
Ans:
SAP GTS reconciles data discrepancies through standardized interfaces and data exchange mechanisms. This ensures consistency and accuracy in trade data across various systems, reducing errors and enhancing the reliability of information in a global enterprise.
64. How does SAP GTS contribute to the automation of export control processes?
Ans:
- Batch Processing: SAP GTS facilitates batch processing for high-volume export transactions, optimizing efficiency.
- Automated Compliance Checks: The system automates export control compliance checks, reducing manual efforts.
- Bulk Document Generation: SAP GTS can generate export-related documents in bulk, streamlining documentation processes.
- Performance Optimization: Continuous performance optimization ensures swift processing in high-volume export scenarios.
65. Elaborate on the features of SAP GTS Collaboration Portal?
Ans:
SAP GTS Collaboration Portal facilitates secure communication and collaboration between trading partners. It enables real-time data exchange, document sharing, and collaborative workflows, promoting transparency and efficiency in global trade relationships.
66. How does SAP GTS support businesses in managing and monitoring restricted party screening for global transactions?
Ans:
SAP GTS conducts restricted party screening by checking business partners against denied party lists. The system automates this process, ensuring that organizations avoid engaging in transactions with restricted entities and comply with international trade laws.
67. What is SAP GTS in managing and optimizing duty drawback processes for businesses engaged in global trade?
Ans:
- SAP GTS calculates duty drawbacks, automates related processes, and ensures compliance with legal requirements.
- By optimizing duty drawback processes, businesses can minimize financial burdens and enhance their competitiveness in global trade.
68. How does SAP GTS handle the integration with customs processes for streamlined operations?
Ans:
SAP GTS integrates with customs processes to automate documentation and clearance. It provides real-time visibility into customs procedures, ensuring that businesses can efficiently navigate through regulatory requirements for cross-border transactions.
69. Explain SAP GTS Collaboration Portal in global trade operations?
Ans:
The SAP GTS Collaboration Portal facilitates secure communication and collaboration between trading partners. It enables real-time data exchange, document sharing, and collaborative workflows, promoting transparency and efficiency in global trade relationships
70. Explain SAP GTS on managing sustainability and corporate social responsibility (CSR) in global trade.
Ans:
- SAP GTS enhances traceability, enabling businesses to track the origin and sustainability of products.
- The system supports compliance with environmental and social responsibility regulations, aligning global trade operations with organizational CSR values.
71. How can SAP GTS assist businesses in adapting to changes in international trade regulations?
Ans:
SAP GTS regularly updates its content to reflect changes in international trade regulations. The system supports scenario planning, allowing businesses to evaluate the impact of potential regulatory changes and adapt proactively to dynamic geopolitical landscapes.
72. Explain SAP GTS Risk Management in identifying and mitigating global trade risks?
Ans:
SAP GTS Risk Management identifies potential financial and legal risks associated with global trade. It assesses the impact of these risks, enabling businesses to implement proactive measures and make informed decisions to mitigate challenges in global trade operations.
73. How does SAP GTS handle automated export and import processes?
Ans:
- SAP GTS automates export and import processes by streamlining documentation, compliance checks, and customs procedures.
- The key benefits include increased efficiency, reduced manual errors, and enhanced compliance with international trade regulations
74. Explain SAP GTS in managing and optimizing duty rates through preference determination?
Ans:
- SAP GTS optimizes duty rates by determining the preferential origin of goods based on trade agreements.
- This enables businesses to leverage preferential trade agreements, reduce duty rates, and comply with specific requirements, supporting cost-effective international trade.
75. What strategies can organizations employ to leverage SAP GTS for continuous improvement?
Ans:
Organizations can conduct regular audits of SAP GTS configurations, implement continuous user training programs, establish feedback mechanisms for user insights, and ensure the regular update of the SAP GTS system with the latest patches and enhancements.
76. How does SAP GTS contribute to managing and monitoring the utilization ?
Ans:
- SAP GTS employs rule-based logic to determine the eligibility of goods for preferential treatment.
- The system provides tools for tracking and analyzing patterns in preferential trade agreement use, produces notifications for approaching expirations, and provides reporting capabilities for informed decision-making.
77. Describe SAP GTS’ capabilities in managing strategic trade control scenarios ?
Ans:
SAP GTS supports strategic trade control by identifying and managing goods with strategic importance. It conducts embargo checks, screening business partners against restricted lists to ensure compliance. The system provides visibility into the movement and status of controlled goods, aiding compliance.
78. Explain SAP GTS on trade finance processes and its role in mitigating financial risks?
Ans:
SAP GTS contributes to trade finance by providing accurate landed cost calculations, optimizing duty rates, and assessing financial risks in international transactions. It supports informed financial decision-making and helps mitigate risks associated with global trade.
79. How can SAP GTS assist businesses in preparing for customs audits effectively?
Ans:
- SAP GTS streamlines customs audits by facilitating quick document retrieval, maintaining detailed audit trails, generating automated compliance reports, and providing tools for communication with customs authorities.
- These features ensure efficient preparation and cooperation during customs audits.
80. What is managing trade preferences ?
Ans:
- SAP GTS determines preferential trade agreements, allowing businesses to optimize duty rates based on the preferential origin of goods.
- It ensures compliance with trade preferences, reduces duty costs for eligible transactions, and supports efficient international trade operations.
89. What does SAP’s GTS check mean?
Ans:
Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) verifies if an outgoing consignment may be delivered to a particular goods receiver by using the compliance check and letter of credit check provided by SAP Global Trade Services (SAP GTS).
90. What does GTS mean?
Ans:
In addition to any other existing commercial agreements, these General Terms and Conditions of Supply and Payment (GTS) exclusively apply to all business transactions between us and the buyer, principal, or customer, hereby referred to as the Customer.





