
A comprehensive solution designed to harmonize and standardize master data management throughout businesses is SAP Master Data Governance (MDG). It provides a strong framework for setting up workflows, regulations, and standards for data in order to maintain data integrity, consistency, and regulatory compliance. Businesses can improve data quality, operational efficiency, and decision-making skills by using SAP MDG to expedite the production, management, and control of master data.
1. What’s SAP MDG, and what are its main factors?
Ans:
SAP MDG is a master data operation result from SAP that ensures associations have a single, accurate view of their master data across enterprise systems. The main factors include the Data Model, which defines the structure of master data realities; the UI Framework for configuring user interfaces; the Workflow, which defines and manages data blessing processes; and the Data Replication Framework, which ensures data thickness across different systems.
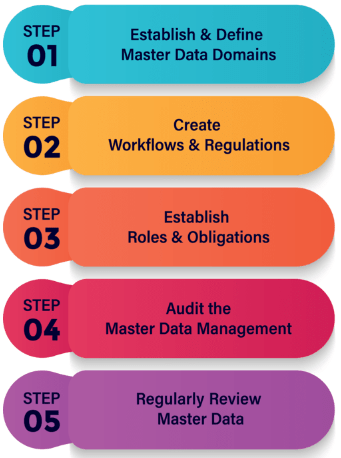
2. Explain the part of the Data Model in SAP MDG?
Ans:
The Data Model in SAP MDG is vital as it defines the structure and attributes of master data realities similar to guests, suppliers, or accouterments. It’s customizable and determines how data is validated, stored, and replicated. The data model is pivotal for ensuring that all data adheres to specific norms and obediences set by the association, easing effective data governance.
3. How does SAP MDG handle data replication?
Ans:
SAP MDG uses the Data Replication Framework( DRF) to manage and cover the distribution of master data across various consuming systems, whether they are SAP or non-SAP systems. This frame supports different replication styles, including IDOC, web service, and RFC, ensuring that data is harmonious and up-to-date across all platforms, which is pivotal for maintaining functional effectiveness and data integrity.
4. What’s the significance of workflow in SAP MDG?
Ans:
- Workflow in SAP MDG is critical for managing data blessing processes.
- It ensures that only validated and approved data is entered into the system, maintaining data delicacy and thickness.
- The workflow is largely customizable, allowing associations to define specific rules and blessing processes that align with their internal controls and compliance conditions, therefore enhancing data governance.
5. How does SAP MDG support data quality operation?
Ans:
SAP MDG provides several features that support data quality operation, including duplication check, data confirmation, and enrichment functionalities. It integrates with SAP Data Services to further enhance data quality through advanced sanctification, matching, and de-duplication processes. These capabilities ensure that the data isn’t only harmonious but also accurate and secure, which is vital for making informed business opinions.
6. What challenges might be faced while enforcing SAP MDG, and how could they be addressed?
Ans:
- Challenges in enforcing SAP MDG frequently include handling complex system geographies, ensuring users’ relinquishment, and achieving data thickness.
- It’s also important to engage stakeholders beforehand in the process to ensure alignment with business requirements and to give comprehensive training to end-users to ease smooth relinquishment.
- Also, using SAP’s stylish practices and guidelines can help in effectively managing these challenges during perpetration.
7. What’s SAP MDG, and how does it integrate with ERP systems?
Ans:
- AP MDG( Master Data Governance) ensures the uniformity, delicacy, and responsibility of an association’s enterprise data.
- MDG centralizes data governance and uses business processes and structure to ensure that data norms are maintained.
- Its integration capabilities with ERP systems are robust. It uses standard data replication methods and service-acquainted architecture to ensure that master data is harmonious across all systems, therefore enabling better decision-making and nonsupervisory compliance.
8. Discuss the differences and benefits of SAP MDG over other data operation results.
Ans:
| Aspect | SAP MDG | Other Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized Governance | Central platform for master data management, ensuring consistent control. | Lack centralized governance, leading to fragmented data management. |
| Standardization and Harmonization | Establishes standardized models, rules, and workflows for data consistency. | Lack standardized approaches, resulting in errors and inconsistencies. |
| Workflow Automation | Automates governance processes, reducing manual effort and accelerating data processing. | Often rely on manual processes, slowing down data handling. |
| Data Quality Management | Includes tools for data accuracy and integrity, enabling proactive monitoring. | May lack robust data quality management, compromising decision-making. |
9. How to handle data quality in SAP MDG?
Ans:
In SAP MDG, data quality is managed through several layers of confirmation, duplication checks, and standardization processes. MDG allows the configuration of data quality rules directly within the data models to ensure compliance with business rules as data is entered or imported. Integration with SAP Information Steward enhances these capabilities, furnishing deep perceptivity into data quality criteria and ongoing monitoring.
10. Explain the conception of a connection and central governance in SAP MDG.
Ans:
- Connection and central governance are two crucial functionalities in SAP MDG. Connection refers to the process of collecting and harmonizing master data from various sources to produce a best-record script.
- This is pivotal for associations with fractured data geographies. Central governance, on the other hand, involves the creation and conservation of master data records across business operations.
- It ensures that all data adheres to certain governance rules before it’s distributed to transactional and logical systems.
11. What are the typical places involved in an SAP MDG perpetration?
Ans:
An SAP MDG perpetration involves various places similar to Data servants, who ensure the quality and thickness of data; MDG Consultants, who design and configure the result; Technical Developers, who customize functionalities; and Project directors, who oversee the design to ensure it meets business conditions and timelines. Also, places like System directors are essential for maintaining the result post-implementation.
12. How does SAP MDG grease nonsupervisory compliance?
Ans:
- SAP MDG facilitates nonsupervisory compliance by furnishing a transparent, auditable system for managing master data across the enterprise.
- It ensures that all data handling processes from creation to omission are compatible with internal and external programs and regulations.
- The capability to trace any changes made to data, who made them, and when is necessary for meeting strict compliance conditions similar to GDPR or SOX.
- MDG’s strong governance capabilities help associations not only misbehave with regulations but also prepare reports fluently and directly, reducing the threat of compliance breaches and associated penalties.
13. What’s the purpose of using SAP MDG in an association?
Ans:
- SAP MDG (Master Data Governance) is enforced in associations to ensure the quality, thickness, and governance of critical data across business systems.
- It acts as a central mecca where master data can be created, modified, and distributed in a controlled manner, ensuring compliance with both internal norms and external regulations.
- MDG enhances functional effectiveness by reducing crimes and disagreement in data, which in turn minimizes expensive business processes and adaptations.
- By maintaining clean and accurate master data, associations can ameliorate their logical capabilities, performing in better decision- making processes.
14. How does interpretation operation work in SAP MDG?
Ans:
Version operation in SAP MDG is pivotal for tracking changes and maintaining literal data integrity. Whenever master data is modified, a new interpretation of that data record is created, allowing users to track the elaboration of data over time. This is particularly important in surroundings where data delicacy and traceability are necessary for compliance and auditing purposes.
15. Describe the process of data replication in SAP MDG.
Ans:
Data replication in SAP MDG is managed through its Data Replication Framework( DRF), which enables accompanied data distribution to various target systems, ensuring that all systems use up-to-date and harmonious data. The DRF configures and monitors data replication jobs, exercising different technologies similar to IDocs, web services, or RFC, depending on the target system’s capabilities and conditions.
16. Explain how SAP MDG supports data migration systems.
Ans:
SAP MDG plays a vital part in data migration systems by serving as a platform to cleanse, validate, and govern master data before it’s moved to a new system. During migration, MDG can be used to regularize data formats, remove duplicates, and enrich data. . MDG’s strong governance capabilities ensure that the migrated data adheres to predefined business rules and regulations, reducing the threat of crimes and data inconsistencies post-migration.
17. How to manage the master data lifecycle in SAP MDG?
Ans:
- Managing the master data lifecycle in SAP MDG involves several crucial phases: creation, blessing, replication, and archiving or omission.
- Blessing processes are rigorously controlled through workflows that ensure only the authorized labor force can authorize changes.
- Eventually, data is either replicated to other systems or archived and deleted in a controlled manner, clinging to compliance conditions and data retention programs.
18. What are the main functionalities of SAP MDG?
Ans:
- SAP MDG provides comprehensive functionalities to handle all aspects of master data operation, including data modeling, data confirmation, data enrichment, and data replication.
- It enables users to manage, cleanse, and maintain master data across different business areas, such as finance, material, supplier, and client data.
- MDG supports a workflow-grounded governance process, which helps ensure that all data complies with business rules and regulations before being approved for use.
- It integrates seamlessly with both SAP and non-SAP systems, enhancing data delicacy and thickness across the enterprise.
19. How does SAP MDG support different data disciplines?
Ans:
SAP MDG is a protean and supports multiple data disciplines, including fiscal data, material data, supplier data, and client data. Each sphere is equipped with standard models that can be extended or customized based on specific business conditions. MDG provides technical governance tools and workflows for each sphere, ensuring that sphere-specific data governance challenges are addressed effectively.
20. Discuss the integration of SAP MDG with S/4HANA.
Ans:
SAP MDG integrates easily with SAP S/ 4HANA, using the advanced capabilities of the HANA database to enhance data recycling pets and analytics. When enforced with S/ 4HANA, MDG can handle large volumes of data more efficiently, making use of HANA’s in-memory technology for faster data confirmation and replication. This integration is particularly helpful during high data volume transfers, where performance is pivotal.
21. What’s the part of Data servants in SAP MDG?
Ans:
- Due to their primary responsibility for preserving the quality and integrity of master data throughout its lifecycle, data servants are essential to the SAP MDG framework.
- They apply data governance programs, oversee data sanctification, and manage data blessing processes to ensure compliance with organizational norms and nonsupervisory conditions.
- Data servants also collaborate closely with IT and business units to understand data operations and apply governance practices that support business objects.
- Their work is vital in reducing data-related crimes and ensuring that stakeholders have access to dependable and over-to-date information for their functional and logical requirements.
22. How can businesses ensure successful SAP MDG perpetration?
Ans:
- A successful SAP MDG perpetration hinges on several factors, including a clear description of data governance objects, strong design operation, and deep engagement from all stakeholders.
- It’s pivotal to conduct thorough demand-gathering sessions to knit MDG functionalities to specific business requirements.
- Training and change operations are essential to promote user relinquishment and to ensure that users are comfortable with the new system.
- Regular monitoring and conservation of the system post-implementation ensure continued compliance with data governance norms.
23. Explain the significance of change requests in SAP MDG.
Ans:
Change requests in SAP MDG are vital for tracking and managing any changes to master data. They serve as a formal medium for requesting, approving, and establishing changes, which helps maintain data integrity and traceability. Each change request goes through a rigorous workflow process, ensuring that only an authorized labor force can make or authorize changes.
24. How does SAP MDG handle security and user access?
Ans:
SAP MDG incorporates robust security measures and detailed access controls to cover sensitive master data. It utilizes SAP’s standard authorization generalities, which can be finely tuned to control access in veritably grainy situations, ensuring that users only have the necessary warrants needed for their places. MDG supports part- grounded access control( RBAC), which helps in managing who can view, produce, edit, or authorize master data.
25. What are some crucial performance pointers( KPIs) used to measure the effectiveness of SAP MDG?
Ans:
- Crucial performance pointers for SAP MDG focus on data quality, process effectiveness, and compliance.
- Common KPIs include the delicacy of master data, the chance of indistinguishable data entries, the average time taken for data blessing, and the rate of rework due to data crimes.
- Monitoring these KPIs helps associations identify areas for enhancement in their data governance processes, ensuring that they can maintain high norms of data quality and effectiveness in their operations.
26. Explain how SAP MDG supports business rules confirmation.
Ans:
- SAP MDG employs an important frame for validating business rules across all stages of the master data lifecycle.
- It uses active and unresistant rule sets to check data thickness and compliance with predefined business sense ahead and after data is entered into the system.
- MDG allows for the customization of confirmation rules specific to business requirements, which can be applied automatically during the creation or revision of master data.
- This ensures that only correct and complete data enters the governance workflow, significantly reducing crimes and enhancing overall data quality.
27. Discuss the impact of poor master data operation and how MDG addresses these issues.
Ans:
Poor master data operation can lead to significant functional inefficiencies, inaccurate reporting, compliance pitfalls, and potentially large fiscal losses. Issues similar to indistinguishable data entries, incorrect data, and deficient data records are common in surroundings with shy data governance. SAP MDG addresses these challenges by furnishing a centralized platform to manage master data across various disciplines effectively.
28. How do advancements and upgrades in SAP MDG affect configurations?
Ans:
Enhancements and upgrades in SAP MDG are designed to be minimally disruptive but bear careful planning and testing to ensure comity with being configurations. SAP generally maintains backward comity with former performances, which means that utmost customizations and configurations should continue to work after an upgrade. Still, it’s critical to completely test the system in anon-production terrain to identify any implicit impacts.
29. Describe a typical workflow in SAP MDG for creating new master data.
Ans:
- The data also undergoes original confirmation checks against predefined business rules to ensure compliance and accuracy.
- Depending on the governance model, multiple situations of blessing might be needed. Once approved, the data is replicated to applicable functional and logical systems.
- Throughout this process, MDG maintains a detailed log of all conduct for inspection and compliance purposes.
30. What part does SAP MDG play in the environment of digital metamorphosis?
Ans:
- SAP MDG is vital in digital metamorphosis enterprise as it ensures the quality and integrity of the data at the core of these metamorphoses.
- Accurate and timely data is pivotal for using ultramodern technologies similar to AI, machine literacy, and IoT, which are integral to digital metamorphosis strategies.
- This enables associations to acclimatize more snappily to changing request conditions and introduce and maintain competitive advantage while reducing pitfalls and costs associated with poor data operation.
31. Explain the difference between SAP MDG and SAP MDM?
Ans:
SAP MDG and SAP MDM (Master Data Management) both end up managing master data but differ in their compass and perpetuation. SAP MDM was designed to attend master data across miscellaneous IT geographies, primarily fastening on the integration and adjustment of master data coming from various sources. SAP MDG focuses on the governance aspect of master data operation, furnishing strong workflow-grounded tools.
32. Discuss how SAP MDG can be integrated with other systems.
Ans:
- Integration is generally achieved through standard data replication ways similar as IDocs, RFC, and web services.
- SAP MDG also supports train-grounded, XML, and SOA-grounded replication, making it protean for different integration scripts.
- Fornon-SAP systems, SAP provides APIs and standard middleware tools like SAP PI/ PO to ease the integration.
- This ensures that all systems within the enterprise geography can pierce harmonious, validated, and approved master data.
33. What’s the impact of SAP MDG on business process effectiveness?
Ans:
SAP MDG significantly enhances business process effectiveness by furnishing clean, accurate, and up-to-date master data that are essential for effective operations and accurate decision- timber. By automating data governance processes, MDG reduces homemade crimes and streamlines the data blessing cycles, therefore accelerating the time-to-request for new enterprises.
34. Discuss the part of artificial intelligence in enhancing SAP MDG functionalities?
Ans:
Artificial intelligence significantly enhances SAP MDG functionalities by automating complex processes and furnishing prophetic perceptivity into data operation practices. AI can be integrated within MDG to automate data matching and de-duplication processes, making data sanctification brisk and more accurate. AI models can dissect literal data governance patterns to prognosticate implicit data quality issues.
35. What are some stylish practices for maintaining the performance of SAP MDG?
Ans:
- Maintaining optimal performance in SAP MDG involves several stylish practices, including regular monitoring of system health and data processes.
- It’s pivotal to keep the data model as streamlined as possible to avoid performance lags, especially when dealing with large volumes of data.
- Enforcing archiving and purging strategies for old data requests and inactive data also helps in maintaining system effectiveness.
- Also, optimizing workflow designs to minimize backups and using SAP HANA’s in- memory computing capabilities for briskly data processing can significantly enhance MDG performance.
36. Explain the conception of connection and Mass Processing in SAP MDG.
Ans:
- In SAP MDG, connection refers to the process of incorporating and harmonizing data from various sources to produce a golden record’ — a single, unified view of master data that’s accurate, complete, and free of duplicates.
- Mass Processing, on the other hand, allows for handling large volumes of master data changes or creations contemporaneously.
- This is particularly useful for bulk updates needed during system connection systems or periodic updates to master data attributes across the board, enhancing effectiveness and thickness.
37. What’s part of SAP Fiori in SAP MDG, and how does it enhance users’ experience?
Ans:
SAP Fiori plays a pivotal part in SAP MDG by enhancing users’ experience through its clean, ultramodern, and user-friendly interface. Fiori simplifies commerce with MDG functionalities, making it more accessible and intuitive for users across different places in the association. This includes streamlined navigation, responsive design suitable for various biases, and part-grounded access that presents users with task-specific data and conduct.
38. How does SAP MDG handle integration with non-SAP systems?
Ans:
- SAP MDG is designed to handle integration withnon-SAP systems effectively through its flexible frame that supports various integration styles.
- SAP MDG can also work with middleware similar to SAP Process Orchestration( PO) to grease communication between MDG and external systems, ensuring that data thickness and integrity are maintained across the enterprise geography.
- This capability is critical for associations that operate a miscellaneous blend of IT systems and bear robust data governance across all platforms.
39. Explain the significance of the Data Model in SAP MDG?
Ans:
- The Data Model is at the core of SAP MDG and is pivotal for defining how master data is structured, governed, and managed within the system.
- It determines the attributes, connections, and metadata that are essential for master data realities similar to guests, suppliers, accouterments, and fiscal data.
- A well-designed Data Model is imperative because it ensures that all data conforms to needed norms and business rules, easing effective data governance.
- Customizing the Data Model to fit the specific requirements of an association is one of the primary tasks in an MDG perpetration, ensuring that the system supports all applicable business processes efficiently.
40. How does SAP MDG support data remediation processes?
Ans:
SAP MDG facilitates data remediation by furnishing tools and workflows that help identify, correct, and help issues with data quality. It includes functionality for covering data quality, detecting anomalies, and driving remediation workflows that involve the applicable data servants or directors. The system can apply remediation processes through its governance capabilities, ensuring that any changes to data are totally reviewed and approved.
41. How does SAP MDG help in achieving data thickness across multiple systems?
Ans:
SAP MDG plays a critical part in achieving data thickness by serving as a central mecca where all master data is created, modified, and distributed. This centralized approach ensures that the same confirmation rules and business processes are applied slightly across all data points before they’re replicated in other systems. MDG uses various data replication ways to attend data across SAP and non-SAP systems effectively, ensuring that all downstream systems.
42. What’s the difference between active and unresistant duplication checks in SAP MDG?
Ans:
- In SAP MDG, an active duplication check involves real-time scanning of data entries against being records to identify implicit duplicates as soon as the data is entered into the system.
- An unresistant duplication check is generally run as a batch process, surveying the entire database periodically to find and resolve duplicates that weren’t caught at the time of entry.
- Both styles are pivotal in maintaining the cleanliness of data in MDG, but the active system provides a more immediate remedy at the point of data entry.
43. How does SAP MDG support the lifecycle operation of master data?
Ans:
- It provides a robust frame for defining and managing the stages of data lifecycle, including original data creation, blessing processes, periodic reviews and updates, and eventual archiving or omission.
- MDG’s interpretation operation capabilities insure that changes to master data are tracked over time, furnishing a clear inspection trail.
- Its integration capabilities allow for flawless updates across all connected systems, ensuring that data remains harmonious and applicable throughout its lifecycle, therefore supporting effective business operations and compliance.
44. What’s the difference between SAP MDG and traditional styles?
Ans:
SAP MDG differs from traditional styles of master data operation primarily in its integration within SAP surroundings and its focus on governance rather than bare data operation. Traditional styles frequently involve managing master data through distant systems that can be error-prone and hamstrung. SAP MDG provides a centralized, rule-grounded workflow that ensures data delicacy, thickness, and compliance before the data is replicated.
45. What’s the material master in SAP MDG?
Ans:
In SAP MDG, the material master refers to a centralized depository that manages all information related to accouterments within an association. This depository includes detailed information on each material, similar to descriptions, specifications, and related attributes like size, weight, and material type. SAP MDG ensures that this data is constantly maintained across all business processes and systems.
46. What’s sphere-specific master data governance?
Ans:
- Sphere-specific master data governance refers to managing master data with a focus on specific disciplines, such as finance, supplier, client, or material data within an association.
- SAP MDG facilitates this by furnishing technical functionalities and fabrics acclimatized to the unique conditions and norms of each data sphere.
- This approach ensures that data governance practices are optimized for the specific types of data, perfecting data delicacy, compliance, and functional effectiveness.
- Sphere-specific governance in MDG includes confirmation rules, workflows, and blessing processes that are specifically designed to handle the complications and nonsupervisory conditions of each sphere effectively.
47. What’s the advantage of creating master data centrally in the SAP MDG system?
Ans:
- Creating master data centrally in the SAP MDG system offers significant advantages, including enhanced data quality, thickness, and control.
- The centralized operation allows for a single point of verity for master data within the association, reducing data duplication and disagreement.
- Likewise, centralized data creation in MDG streamlines processes facilitates easier and more accurate reporting and improves functional edge by barring the need to attune data across different systems or databases.
48. When is it necessary to spark business functions in SAP MDG?
Ans:
Cranking business functions in SAP MDG is necessary when associations need to enable fresh features or customize functionalities to meet specific business conditions. Business functions in MDG can include new data models, enhanced workflows, integration capabilities, or support for new nonsupervisory conditions. Activation is generally done during the original setup and configuration of MDG or to take advantage of new features handed by SAP.
49. What’s the foundation business function in the SAP MDG frame?
Ans:
The foundation business function in the SAP MDG frame refers to the introductory enabling functionalities that support the governance of master data across various disciplines. It includes the underpinning structure that allows for data modeling, UI configuration, process modeling, and rule-ground workflow operation. The business function as it provides the necessary tools and technologies for creating, maintaining, and validating master data.
50. What’s the difference between Mecca and law deployment in SAP MDG?
Ans:
- In SAP MDG, mecca deployment refers to installing MDG on a separate garçon, distinct from the SAP ERP system.
- This setup is salutary for associations wanting to polarize governance across multiple ERP surroundings, minimizing the impact on ERP operations.
- Co-deployment, on the other hand, involves installing MDG directly on the same garçon as the being SAP ERP system.
- This option can reduce structure costs and simplify integration but might impact ERP system performance due to the fresh cargo.
51. What’s a config Gomorrah in SAP MDG systems?
Ans:
- In SAP MDG, a config Gomorrah refers to a medium or system setup used to attend configuration settings across different systems in an SAP geography.
- This conception is pivotal when MDG is stationed in a mecca mode and needs to ensure harmonious configuration across connected systems.
- The config Gomorrah serves as the philanthropist for configuration data from a central source( the config mecca), effectively” sinking” the incoming settings to maintain uniformity.
- This ensures that all connected systems cleave to the same configuration rules and parameters, which is essential for maintaining harmonious data governance practices and system geste.
52. What’s the TCO( Total Cost of perpetration) in SAP MDG systems?
Ans:
The Total Cost of perpetration( TCO) in SAP MDG systems encompasses all charges related to planting, configuring, and maintaining the MDG system over its lifecycle. This includes tackle and software costs, licensing freights, costs for professional services like advisers for setup and customization, training for end-users and directors, and ongoing support and conservation costs.
53. What’s the purpose of the staging area in SAP MDG?
Ans:
- The staging area in SAP MDG serves as a temporary holding and processing zone for master data before it’s validated, approved, and distributed into the functional systems.
- This area is pivotal for ensuring data quality and governance as it allows data to be checked for delicacy, absoluteness, and compliance with business rules without impacting the live product data.
- The staging area supports the collaboration of various stakeholders involved in the data governance process, enabling them to review, edit, and authorize changes before they become part of the sanctioned master data set.
54. Mention the differences between master data, metadata, and sale data.
Ans:
Master data represents the core information used across an association to support operations, similar to data about guests, products, workers, and merchandisers. It’s fairly stationary and is essential for deals and reporting. Metadata, on the other hand, is data about data; it describes and gives information about other data, which helps in understanding and using the factual data effectively (e.g., data length, type, and constraints in a database).
55. What’s Netweaver?
Ans:
SAP NetWeaver is an intertwined technology platform that can host and connect various SAP business operations. It acts as the specialized foundation that facilitates the integration of information and processes from distant sources both within and outside an enterprise. NetWeaver supports various calculating platforms and databases, offering tools and technologies for main data operation, operation development, and integration.
56. List some benefits of SAP MDG.
Ans:
- SAP Master Data Governance( MDG) offers a comprehensive result for ensuring the delicacy, thickness, and governance of enterprise data.
- Benefits include bettered data quality through formalized and streamlined processes for data entry and confirmation, enhanced functional effectiveness by automating data governance tasks, and stronger compliance with nonsupervisory conditions due to traceable inspection trails and transparent data changes.
- SAP MDG also supports centralized data operation, which reduces redundancy and enhances the integrity of information across the enterprise.
57. List some downsides of Sap MDG.
Ans:
- The complexity of original setup and configuration can be a significant hedge, frequently taking technical chops and substantial time investment.
- Also, the severity in some predefined workflows and models may not fit every association’s unique processes without custom development, which can add to the expenditure.
- User relinquishment can be another challenge, as the system demands a shift in how data is handled, challenging comprehensive training and change operation sweats.
58. What’s birth data in SAP AR and AP?
Ans:
In SAP Accounts Receivable( AR) and Accounts Payable( AP), birth date is a critical term used for determining the due dates for payment deals. This data is used as the reference point from which payment terms( like net 30 days, 60 days, etc.) are applied to calculate the factual due date for checks. In practice, the birth date can be the document date, the advertisement date, or a date agreed upon by the parties.
59. What’s the difference between online logical processing and data mining?
Ans:
In Data analysis, online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining have various functions. OLAP is a technique for multi-dimensional analysis of business data, offering insights via drill-down, slicing, and dicing features, among other characteristics. With the help of these tools, customers may quickly and interactively summarize data and efficiently investigate patterns and trends in their business environments.
60. What’s the part of ODS in BIW?
Ans:
- In a Business Information Warehouse, a functional Data Store plays a pivotal part by acting as a central storehouse area for data that’s in the process of being gutted, converted, and loaded into further endless data storehouse layers.
- The ODS allows for fresh operations on the data, similar to sanctification, resolving redundancy, and integrating data from different sources.
- This subcaste is particularly useful for detailed reporting and analysis because it maintains grainy data that are frequently added up in further processing layers.
61. What is Batch Data Communication?
Ans:
Batch Data Communication is a traditional data transfer fashion in SAP used to transfer data fromnon-SAP systems to SAP systems. BDC works by bluffing users’ inputs in defenses of SAP deals to perform data entry tasks automatically. It’s substantially used for mass input of data where direct database inserts aren’t possible due to the complexity of the data or the need for data confirmation that’s bedded in the sale canons.
62. How do the SET and GET parameters differ?
Ans:
- SET and GET parameters in SAP are used for passing data between programs and defenses.
- The SET parameter is used to assign a value to a global SAP memory variable, making it accessible across deals during a session.
- GET parameter is used to recoup the value of a parameter from the global SAP memory. This allows different programs or deals to partake information efficiently without demanding a database call or external storehouse medium.
63. What is meant by one-time merchandisers?
Ans:
One- time merchandisers in SAP relate to seller accounts that are created for single use to handle deals involving occasional or occasional merchandisers without maintaining their complete information in the system. These accounts are generally used for merchandisers from whom a company doesn’t plan to buy regularly and therefore doesn’t warrant maintaining a full seller master record.
64. Explain what internal tables, tables with values, and translucent tables are.
Ans:
In SAP ABAP, internal tables are used to store temporary data in a structured manner during program prosecution, analogous to arrays in other programming languages. They’re used considerably for various data manipulations within a program. Tables with values( value tables) are defined in the Data Dictionary and are used to circumscribe and check the data entered in a table for a specific field grounded on the values present in another table.
65. What are the standard way for enforcing SAP Payment Run?
Ans:
- The due checks are named grounded on the payment parameters defined in the payment run configuration.
- The system checks for payment styles, terms, and other conditions assigned in the seller master and tab records.
- Payment proffers are also generated and reviewed for any disagreement or blocks. Following the blessing, factual payment documents are created, and the corresponding entries are posted in the tally.
- Payment mediums like checks or electronic transfers are executed. These ways help maintain fiscal delicacy and timely payments.
66. What’s the difference between SAP Base and ABAP?
Ans:
- SAP Base refers to the administration of the SAP system that includes conditioning like installation, configuration, and conservation of the SAP waiters and terrain.
- It’s primarily concerned with managing the specialized armature and ensuring optimal performance and trustability of the SAP system.
- ABAP, or Advanced Business Application Programming, on the other hand, is the programming language that SAP uses to create operations and modify workflows.
67. What’s the donation operation and Database Garçon in the SAP R/3?
Ans:
The SAP R/ 3 system is grounded on a three-league armature conforming to the donation, operation, and database layers. The donation subcaste is where the users interact with the system, generally through the SAP GUI( Graphical Users Interface) or via web cybersurfers. The operation subcaste hosts the factual SAP software and handles the processing of deals, executing business sense, and managing user requests.
68. What are the common transport crimes?
Ans:
Common transport crimes in SAP systems generally occur during the movement of data and configurations across different system surroundings. These crimes can range from missing objects and authorization issues to conflicts in object performances. A frequent error is the failure of significance due to shy prerequisites or dependencies in the target system.
69. Explain the system to reuse consumer data in SAP MDG?
Ans:
- In SAP MDG, recycling consumer data involves several crucial ways to ensure data delicacy and compliance with data protection laws.
- Originally, consumer data is collected and entered into the system, where it’s validated to insure it meets predefined norms and business rules.
- This data also goes through a governance workflow for blessing or rejection, frequently involving multiple stakeholders. After blessing, the data is replicated to downstream systems.
- SAP MDG also provides tools for data anonymization and pseudonymization to ensure consumer sequestration.
70. What’s the dispatcher?
Ans:
- The dispatcher is a core element in the armature of the SAP NetWeaver operation Garçon. It plays a pivotal part in managing the processing of requests in the SAP system.
- The dispatcher’s main function is to admit requests from users, which can include deals, reports, or HTTP requests, and distribute them to available work processes for prosecution.
- It maintains a line for these requests and manages the distribution grounded on process vacuity and cargo balancing.
71. List two distinct types of communication services.
Ans:
In the environment of enterprise networks and services, two distinct types of communication services are” coetaneous” and” asynchronous” communication services. Coetaneous communication requires the sender to stay for the receiver’s response, thereby maintaining a harmonious connection during the communication session. This is typical in telephone exchanges or real-time data services.
72. What are pooled tables?
Ans:
Pooled tables are a type of table in the SAP database used primarily to store control data and small volumes of critical data that can be grouped together. These tables are stored in a pooled database table on the database position to save space and reduce operation outflow. Each pool table in the ABAP Dictionary corresponds to multiple pooled tables in the database.
73. List some of the benefits of Business storehouse reporting over R/3.
Ans:
- It consolidates data from various sources, not just SAP R/3, furnishing a comprehensive view across the enterprise.
- BW provides important data modeling tools to manage data confines and scales, easing further perceptive analysis.
- It also includes data warehousing functionalities similar to data birth, metamorphosis, and loading (ETL), which enhance data cleanliness and integrity.
- Incipiently, BW supports a high degree of robotization and scheduling of reports, adding effectiveness in data operation and reporting processes.
74. What’s the difference between a sphere name and a data element?
Ans:
- In SAP, a sphere name defines the specialized attributes of a field, similar to its data type, length, and possible value range.
- On the other hand, a data element is more specific and is used to describe a field in business terms, including its business sense.
- It links to a sphere for its underpinning data type parcels but also includes semantic information similar to field markers and attestation.
75. How does SAP MDG handle client data management?
Ans:
In SAP Master Data Governance, customer data processing refers to the internal management and upkeep of customer-related data. Client records must be created, updated, and validated to guarantee correctness and consistency across systems. With the help of SAP MDG’s data governance solutions, businesses can effectively manage changes, establish workflows, and enforce data quality guidelines.
76. What’s the difference between residual payment and partial payment in accounts receivable?
Ans:
- In SAP,” residual payment” and” partial payment” are two styles used to handle deficient payments from guests.
- A partial payment is recorded when a client pays only a part of the total tab quantum, leaving the original tab complete and creating a new open item for the remaining balance.
- Again, a residual payment also involves an deficient payment but differs in that the original tab is cleared and a new tab is issued for the remaining quantum.
- Therefore, partial payments keep the original tab active, whereas residual payments replace the original tab with a new residual item.
77. List out the different types of source systems in SAP.
Ans:
In SAP, source systems relate to the various systems that give data inputs for processing in another system. Types of source systems can include SAP ERP systems, where data is frequently uprooted for use in SAP BI;non-SAP relational databases like Oracle or SQL Garçon; flat lines similar to CSV or Excel; and external systems, which can include web services or third-party data providers.
78. What’s Extractor?
Ans:
In SAP systems, an Extractor refers to a data reclamation medium used primarily in SAP Business Warehouse( BW) to cost data from various source systems, including SAP ERP systems. Extractors can be database views, function modules, or reports that understand how to efficiently prize defined sets of data. They’re pivotal for enabling the effective and effective transfer of data from functional databases into the logical terrain of SAP BW.
79. What’s extended star schema?
Ans:
- The extended star schema is an adaption of the classic star schema used specifically in SAP Business Warehouse for optimizing data storehouse and reclamation.
- What makes it extended’ is the addition of external SAP-specific structures like the Dimension ID tables and the use of Persistent Staging Area( PSA) and master data tables that are regularized.
- This schema improves query performance by minimizing the number of joins demanded during data reclamation, thereby enhancing the overall effectiveness of the data storehouse.
80. Mention the major benefits of reporting with BW over R/3.
Ans:
- Reporting with SAP Business Warehouse over SAP R/3 (now part of SAP ECC) offers several significant advantages.
- Originally, BW allowed for data connection from multiple sources, furnishing a comprehensive view of the data, which is frequently necessary for strategic decision- timber.
- Secondly, BW optimizes data reclamation for reporting through its data warehousing capabilities, including effective data modeling and indexing.
- Also, BW can handle large data volumes more efficiently than R/3 by unpacking the data storehouse and processing tasks.
81. Mention the two types of services that are used to deal with communication.
Ans:
- In the environment of IT and dispatches, the two primary types of services are coetaneous and asynchronous communication services.
- Coetaneous communication requires that both the sender and receiver be present and available at the same time for the communication to take place, similar to telephone calls or videotape conferencing.
- Asynchronous communication doesn’t bear contemporaneous presence; dispatches can be transferred and entered at different times, similar to emails or textbook dispatches.
- Both types play pivotal places in business surroundings, enabling effective and effective communication grounded on the nature of the information exchange and the proximity with which a response is needed.
82. What’s an update type with reference to a match law ID?
Ans:
In SAP, a match law ID refers to a specific type of hunt help that assists users in chancing records within the database. An update type in this environment relates to how these match canons are refreshed or streamlined in the system. Update types are important because they determine how the underpinning data of a match law ID is kept current with the changes in the database.
83. What’s meant by “ Business Content ” in SAP?
Ans:
In SAP systems,” Business Content” refers to pre-configured and ready-to-use reports, queries, word cells, crucial performance pointers( KPIs), places, and other rudiments that are designed to hot-start the perpetration of specific business scripts in SAP surroundings. This content is completely integrated and can be used incontinently upon activation.
84. How does SAP MDG grease compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR?
Ans:
- SAP MDG is necessary for helping associations misbehave with data protection regulations similar to GDPR by furnishing tools to manage and cover particular and sensitive data.
- It enables the setup of specific governance rules to control data access, processing, and storehousing, ensuring data is handled according to legal conditions.
- MDG supports data anonymization and pseudonymization processes that are essential for GDPR compliance.
- It also offers comprehensive inspection trails and change logs, allowing associations to demonstrate responsibility and translucency in data handling practices.
85. What’s the significance of the reality-type conception in SAP MDG?
Ans:
In SAP MDG, the reality Type conception is pivotal as it defines the structure of data objects within the data model. Each reality type represents a specific type of master data, similar to guests, merchandisers, or accouterments, and specifies the attributes, connections, and metadata for these data objects. This structural description is vital for ensuring that all data within the system conforms to the same specifications, easing thickness and interoperability.
86. How can SAP MDG be optimized for performance in large enterprises?
Ans:
- Optimizing SAP MDG for performance in large enterprises involves several strategies. It’s pivotal to knit the data model to reduce complexity and ameliorate responsiveness.
- Exercising SAP HANA as the underpinning database can enhance performance due to its in- memory technology.
- Enforcing effective data replication and synchronization styles minimizes the impact on system performance.
- Regular system checkups and updates also contribute to maintaining optimal performance situations.
87. What’s Parametric Import?
Ans:
- Parametric Import is a point used in various software operations, including CAD systems and data operation tools, which allows users to import data where parameters can be stoutly defined and acclimated during the import process.
- In the environment of data operation, similar to SAP MDG, Parametric Import might relate to the capability to import data grounded on specific parameters set by users, enabling a more controlled and acclimatized data integration process.
88. How does SAP MDG grease the operation of custom objects?
Ans:
SAP MDG allows for comprehensive operation of custom objects by enabling associations to extend the standard data model to include custom-defined data types and attributes. Businesses that need to manage unique data that does not fit into predefined orders like guests. Users can define these custom objects within MDG using its flexible frame, which supports the creation of specific attributes, setting confirmation rules, and configuring workflows.
89. What strategies can be used to enhance users’ relinquishment of SAP MDG?
Ans:
- Enhancing users’ relinquishment of SAP MDG involves strategic planning around user training, system usability, and nonstop support.
- Effective training programs that are acclimatized to different users’ places within the association are pivotal, as they help users understand how MDG processes and benefits align with their diurnal tasks.
- Perfecting system usability through substantiated interfaces and dashboards can also significantly enhance user engagement.
- Furnishing robust support and quick resolution of issues encourages users to calculate on the system, thereby adding relinquishment rates.
90. What are the crucial challenges in planting SAP MDG in a pall terrain, and how can they be overcome?
Ans:
Planting SAP MDG in a pall terrain presents several challenges, including data security, integration complexity, and maintaining data governance norms. Ensuring data security in the pall is consummate; thus, enforcing robust encryption ways and access controls is essential. Integration with on-premise systems and other pall operations frequently involves complex synchronization and data thickness challenges.






