
SAP PP, or SAP Production Planning, is an integral module within the SAP ERP system designed to streamline and enhance manufacturing processes in organizations. At its core, SAP PP facilitates the planning and management of production activities, aiming to optimize efficiency and ensure timely product delivery. The module relies on essential components such as master data, encompassing details about products, materials, work centers, and production resources. Central to its functionality is the Bill of Materials (BOM), defining the structure of components needed for production. Work centers represent the physical locations where manufacturing occurs, and routing outlines the sequence of operations and associated work centers. SAP PP supports diverse production planning strategies, including make-to-order and make-to-stock, while Material Requirements Planning (MRP) ensures timely availability of necessary materials. Capacity planning helps balance workloads and identify constraints, and the module integrates seamlessly with other SAP modules, enabling a cohesive business process. With features for shop floor control, reporting, and analytics, SAP PP empowers organizations to gain visibility, control, and efficiency in their manufacturing operations.
Q1. Explain SAP PP?
Ans
The SAP Production Planning (PPP) process is associated with the company’s production planning and includes all related activities such as Material Requirement Planning (MRP), Bills of Material (BOM), Routing, Capacity Planning, and so on. However, its two main segments are Material Planning and Execution Planning.
Q2. what are the production process in SAP?
Ans:
- Discrete Manufacturing
- Repetitive Manufacturing
- Production- Process Industries
Q3. List out activities carried out in Production Planning?
Ans:
- Processing material master
- Creation of Bill of Material
- Displaying work center and routing
- Maintaining planning calendar
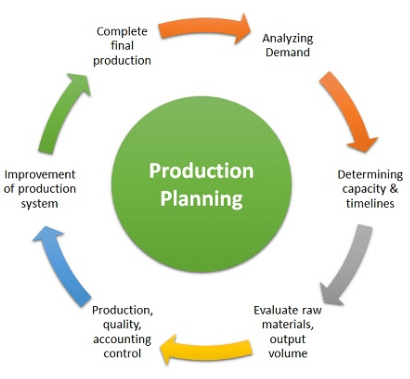
Q4. what is Routing in SAP PP?
Ans:
Routing in SAP PP is referred to the list of activities which are required to produce any material. For example when does cost estimation for material, the system triggers a relevant routing and activity rates for all described in the routing. Which will helpful to evaluate the processing cost in product costing.
Q5. What are steps of Production Execution Process?
Ans:
- Converting planned order to the production order
- Releasing production order
- Goods issue for a production order
- Confirmation of a production order
- Goods receipt against production order
Q6. What reports are generated in product cost controlling information system?
Ans:
- Product cost planning
- Cost object controlling with the subcomponents
- Product cost by period
- Product cost by order
Q7. what is work center in SAP PP and what is use of Data in Work Centers?
Ans:
In SAP PP, a work center is a location or resource where manufacturing activities occur, encompassing both human and machine elements. Work center data in SAP PP includes information about the capabilities, capacity, and scheduling constraints of the work center. This data is crucial for production planning, enabling organizations to optimize resource utilization and ensure efficient manufacturing processes by balancing workloads and coordinating activities.
Q8. What is use of MRP PP evaluations?
Ans:
This contains the function for evaluating the MRP result. This function can be used to determine an information about availability of material and to identify any material shortage situation.
Q9. what is purpose of using Capacity Planning?
Ans:
- Long term rough cut planning
- Medium term planning
- Short term planning
Q10. How should create production order without routing and BOM?
Ans:
Without BOM and routing can create a production order by changing a config in OPL8 ( order type dependent parameters) as a routing optional. When try to create an order using the C001 it may ask for the sales order.
Q11. what could happens to planned after it converted into production order?
Ans:
Planned orders are offset by production orders when they are converted to production orders.
Q12. Distinguish difference between stock transport order and stock transfer order?
Ans:
| Aspect | Stock Transport Order (STO) | Stock Transfer Order (STO) | |
| Purpose |
Inter-company transfers |
Intra-company transfers | |
| Document Type | STO typically involves document type NB (stock transport order) in SAP. | STO uses document type UB (stock transfer order) in SAP. | |
| Delivery Process | Involves a delivery document (NL) | Direct transfer, no delivery process |
Q13. Define PRT (Production Resource Tools) in SAP PP?
Ans:
In SAP PP, PRT (Production Resource Tools) refers to equipment or resources required during production processes but are not directly consumed. PRT includes tools, jigs, fixtures, and gauges essential for manufacturing. These resources are linked to operations in the Bill of Materials (BOM) or routing, aiding in the accurate execution of production steps. PRT in SAP PP enhances production efficiency by ensuring the availability and proper utilization of tools necessary for the manufacturing process.
Q14. How to create PRT master records?
Ans:
To create PRT (Production Resource Tool) master records in SAP PP, navigate to the transaction code CR01. Enter the PRT category and the relevant details such as the PRT group, description, and unit of measure. Specify additional information like costs and storage details if necessary. Save the master record to complete the creation process.
Q15. what is t-code for changing production order and to display production order?
Ans:
- T-code to change a production order = C002
- T-code to display a production order = C003
- REPORT Z_DISPLAY_PROD_ORDER.
- PARAMETERS: p_prod_order TYPE AUFNR OBLIGATORY.
- START-OF-SELECTION.
- CALL FUNCTION ‘CO_ZPP_DISPLAY’
- EXPORTING
- PRODUCTIONORDER = p_prod_order.
Q16. Define PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) in SAP PP and what is use?
Ans:
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) in SAP PP is a holistic approach to overseeing the entire lifespan of a product, from conception to disposal. It encompasses processes such as design, manufacturing, and data management. In SAP PP, PLM ensures efficient coordination, collaboration, and documentation throughout the product lifecycle. Its use enhances control and visibility, fostering innovation, quality, and streamlined time-to-market for products.
Q17. In SAP-PP what are costing parameters?
Ans:
- Work Center
- Activity types and formulas
- cost center
- Routing
Q18. Does the cost-controlling information system specify the fields shown on the report’s list screen?
Ans:
Yes, the specification of fields on a report’s list screen in a cost-controlling information system is typically determined by system configuration and user customization options. System administrators and users may configure or customize the fields based on organizational needs, roles, and permissions.
Q19. What is the purpose of SAP Material View and its applicable parameters?
Ans:
SAP Material View serves to manage and display detailed material information in the SAP system. It applies to diverse parameters like material type, industry sector, and plant, enabling comprehensive material data control. This feature is crucial for organizations to efficiently handle and track their materials.
Q20. what are the types of Master Views for a Production and Planning?
- SAP MRP1 View
- SAP MRP2 View
- SAP MRP3 View
- SAP MRP4 View
- SAP Work Scheduling View
Q21. How MRP (Material Requirement Planning) types are classified?
Ans:
- Materials for a consumption based planning
- Planning based on a demand
Q22. what are keyfields found in MRP View 1?
Ans:
The key fields in MRP (Material Requirements Planning) View 1 in SAP typically include essential parameters for material planning. These may encompass the material type, plant, and MRP group, which categorizes materials for planning purposes. Additionally, fields such as the planning strategy, lot-sizing procedure, and reorder point may be present, providing critical information for determining when and how much material to procure.
Q23. List out basic procedure for dispatching operations in a capacity leveling?
Ans:
In the dispatching operations for capacity leveling, the basic procedure involves reviewing the available work centers, identifying the operations to be dispatched, and considering the current capacity load. Prioritization of operations based on deadlines, constraints, or other criteria is then performed. The dispatch list is generated, detailing the sequence of operations for execution.
Q24. what is need of MRP list if the stock requirement list is already given?
Ans:
MRP list displays a result of the last planning run, changes that occurred between the planning runs are ignored in MRP list. On the other hand, the system displays all changes made to the stock, issues, and receipts in the requirement list or stock.
Q25. what are t-codes for creating, changing and summarizing BOM?
Ans:
- Creating BOM= CS01
- Changing BOM= CS02
- Summarized BOM=CS13
Q26. what is use of t-code CS20 in BOM?
Ans:
- Change an item data
- Creating a new material
- Replacing it with the another material
Q27. Distinguish difference between SAP PP with Oracle?
Ans:
SAP PP :
It has latest features on guiding a planning processes for production
Routing is possible in all modules in SAP PP
The latest version has been released
Oracle:
Not all but the few features are outdated
Routing is not possible in all modules
No update on release of a next version
Q28. What is mean by term production?
Ans:
It is basically a manufacturing of goods and services or shaping them in the form that is required by the users. A product or service must go through a number of steps, each of which strives to improve the product or service from the last. Production can be done internally or externally.
Q29. What is batch production, and is SAP PP reliable for it?
Ans:
Building a project is not always simple for organisations. As a result, they accumulate it in small sections, referred to as batches. Every component of the product is constructed by a distinct team with a shared goal. Simply put, batch production ensures that errors are eliminated when they should be. It is among the most effective and extensively used production techniques. With the aid of SAP PP’s features specifically designed for this purpose, users can monitor every batch.
Q30. What are the key steps in the production execution process?
Ans:
The very first thing is converting a planned order into the production one. The next thing about which users are should pay attention to is releasing the production order post which goods are issued. The receiver then acknowledges a same and finally, the receipts are matched.
Q31. Why is SAP PP a reliable tool for effective production planning?
Ans:
SAP PP (Production Planning) is considered reliable for effective production planning due to its comprehensive features. It offers integrated modules for material planning, capacity management, and shop floor control, streamlining the entire production process. The tool enables real-time visibility into production data, facilitating informed decision-making.
Q32. What does factors can help in preparing the Production Budget?
Ans:
Factors influencing the production budget include sales forecasts, existing inventory levels, production capacity, lead times, market demand, seasonal variations, resource availability, technology efficiency, quality standards, and budget constraints. Balancing these factors ensures a production plan aligned with demand, resource optimization, and financial goals.
Q33. Does SAP PP is useful when it comes to getting authorization of product?
Ans:
Yes, it is more beneficial in this matter. It simply makes sure of all standards are followed during pre and post-production. This is the precise moment when it helps companies to more reliably ensure a product’s authorization.
Q34. Is it possible to get product ready for inspection through SAP PP?
Ans:
The most potent tool is SAP Production Planning. It merely offers guidance to users on how to implement the many tactics and techniques that aid in appropriate production without sacrificing quality. SAP PP tool help eliminating the various errors and bugs that affect the quality. Therefore, it contributes the lot to proper production planning and getting product ready and friendly with inspection process in the reliable manner.
Q35. What is mean by term planning horizon?
Ans:
Planning horizon refers to the specific period of time over which an organization or individual plans and makes decisions. It is critical concept in the various fields are business, project management, economics, and finance.
Q36. Does Resource allocation have role in proper implementation of Product planning approach?
Ans:
Allocating resources is one of the most important requirements for a same. It simply makes sure right employees and human resources are assigned for a tasks that are complex and need additional attention. With the proper resource allocation, it is possible for an organizations to avoid several hassles that declare their presence in production.
Q37. What does SAP PP’s productive capacity mean, and how can it benefit the company?
Ans:
In essence, it is a feature of the SAP Production Planning tool that informs users of the maximum production level they are able to manage given their total resource availability. It simply helps to determine an organizations about the exact time, resources, planning, investment, and the other needs they have to accomplish production process easily.
Q38. Compare in-house and out-house production processes?
Ans:
When a company uses its own resources—tools, expertise, and technology—to develop its goods or services in-house, it’s known as in-house production. In-house production needs a huge costs in the initial stage but it offers the large-scale benefits for the long run. Out-house production means getting product or a service ready by an organization from the third-party source. This is also known as outsourcing.
Q39. What are some tactics that can improve product planning without requiring further financial outlays?
Ans:
Improving product planning without additional financial outlays can involve tactics such as optimizing existing inventory, enhancing communication with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, implementing efficient production schedules to minimize overtime costs, and leveraging technology for better demand forecasting. Streamlining internal processes, cross-training employees, and fostering collaboration between departments can also enhance overall production planning without significant financial investments.
Q40. How mass production is good approach ?
Ans:
It is basically a manufacturing or production of a very large amount of the units. Actually, not all products—aside from those with higher demand—need to be produced in large quantities. Through this production method, users can simply ensure favourable outcomes because bulk production always aids in cost-cutting.
Q41. Name important activities that are part of any production process?
Ans:
- Processing a material master and creating a bill
- Displaying a work center
- Defining the MRP
- Range of coverage
Q42. While manufacturing the product, what exactly factors to be of significant importance?
Ans:
During manufacturing, key factors of significance include ensuring product quality through rigorous quality control measures, optimizing production efficiency to minimize costs, adhering to production schedules to meet demand, maintaining workplace safety for employees, and managing inventory levels effectively. Additionally, factors like sustainable practices, regulatory compliance, and technological integration contribute to successful and responsible manufacturing.
Q43. How Production planning is related to material requirement?
Ans:
The material requirement is actually one of the important principles of a production planning. The planners have to make sure that entire raw material remains available all the time. Generally, have to make sure of the availability of at least 10 days of a stock depending on the type of production. All orders about the raw material should be placed on a time.
Q44. What are prime requirements for production planning?
Ans:
- Right equipment
- Workforce
- Technology
- Controls
- Processes
Q45. What are various factors to pay attention to in order to avoid errors from production?
Ans:
Every time they are traced, the problems must be formulated. Verifying inventory in relation to time is the first step that can help prevent them. Organisations need to know the real returns on their investment in quality, and all suppliers need to be qualified. These remedial measures make it possible to address problems that frequently surface during a production.
Q46. What is role of data which is present in work centers in SAP PP?
Ans:
They are packed with some crucial information that merely verifies pricing and related aspects. Furthermore, they ensure that everything is scheduled appropriately. This is helpful in figuring out an object’s total duration. It also ensures easy and manual performance of operation maintenance and capacity planning.
Q47. What is Product analysis?
Ans:
It is basically approach to testing the product after its development and before its delivery to customers. Product analysis makes sure of quality and better customer relations. In addition to this, it enables an organizations to save cost which they have to bear for faulty or a wrong product delivery.
Q48. How production cost can be eliminated? Can SAP PP help in this matter?
Ans:
There are the several methods of cutting the overall cost from the development or a production process. The first thing could be outsourcing a specific or an entire project to the another company or an organization that has specialization for same. Purchasing a raw material in bulk and making sure everything is running well is another strategy. Investing in technology that yields positive outcomes is another way that can assist in this situation.
Q49. What are different phases of planning in SAP PP users can make use of?
Ans:
These are Extensive. both short- and medium-term planning. Users are free to decide for themselves which module and which phase they want to think about. However, in the SAP PP this largely depends on data and an information availability.
Q50. Without BOM and Routing, is it possible in SAP PP to create production order?
Ans:
AP PP (Production Planning) module, Bill of Materials (BOM) and Routing are the essential components for creating production order. The BOM provides the list of materials, components, and sub-assemblies required to produce the finished product, along with quantities and relationships. The Routing specifies the sequence of operations or work centers involved in a production process.
Q51. What are different type of manufacturing/production processes in SAP?
Ans:
SAP encompasses diverse manufacturing processes, such as discrete, process, repetitive, make-to-order, make-to-stock, and engineer-to-order. These are facilitated by modules like SAP PP, MM, and PM, addressing industry-specific production needs. Discrete manufacturing involves distinct units, while process manufacturing suits formula-based production. Repetitive manufacturing is ideal for high-volume, repetitive production. Make-to-order caters to customized products based on customer orders, and make-to-stock produces goods based on forecasted demand.
Q52.Difference between discrete and repetitive production?
Ans:
Discrete production creates unique, individual units with customized specifications, suitable for varied products. Repetitive production, geared for efficiency, involves the continuous manufacturing of standardized products in high volumes on assembly lines. Discrete suits industries with diverse offerings, while repetitive is optimal for mass production, such as in automotive or electronics.
Q53. What is mean by gaps in project implementation? Have found any gap during implementation?
Ans:
A gap during project is referred to as “space between where are and where want to be.” Gap analysis is undertaken as means of bridging that space. There is a GAP analysis during the Blue Print phase. It seeks to ascertain what can be accomplished with standard SAP and how the client really desires a specific scenario to be handled.
Q54. What are different documents are prepare in all phases during sap implementation?
Ans:
During SAP implementation, various documents are prepared across phases. In the planning phase, a Project Charter outlines objectives. The Blueprint phase involves creating Business Process Documents and Functional Specifications. In the Realization phase, Configuration Documents detail system setup.
Q55. What are steps of production execution process? in short paragraph
Ans:
The production execution process involves several key steps. It begins with order creation, specifying the details of the production run. Next, materials are issued, and the production order is released for manufacturing. During the production process, work centers and machines are utilized, and labor resources are deployed as needed. After completion, goods are confirmed and recorded, and any variances are analyzed.
Q56. What are basic difference between MTS and MTO?
Ans:
Make-to-Stock (MTS) and Make-to-Order (MTO) are production strategies with key differences. MTS involves producing goods in anticipation of forecasted demand, leading to stocked inventory. MTO, on the other hand, initiates production in response to specific customer orders, allowing for customization but without pre-produced inventory. MTS is efficient for high-volume, standardized items, while MTO is suitable for customized or low-volume products, offering greater flexibility but potentially longer lead times.
Q57. In SAP project the customization comes under which phase?
Ans:
Customization activities are performed during the “Realization” phase.: Realization: This phase is where a system configuration and customization take place. Configurations are made in the SAP based on requirements gathered in the Business Blueprint phase. Customization involves the setting up the SAP system to meet specific needs of the organization.
Q58. What Is customized Reports?
Ans:
When standard reports provided by the SAP does not meet the Business requirements, then develop a customized reports as per user requirements, often called Z reports. Developing the reports can be done through the ABAP custom reports / through Report Painter / ABAP Query.
Q59. What is Master data in production planning ?
Ans:
In production planning, master data refers to the foundational information that remains relatively constant and is essential for the planning and execution of production processes. This includes data such as product details, bills of materials (BOM), work centers, routing information, and production versions. Master data provides a standardized and consistent reference for planning activities, ensuring accurate and efficient production operations.
Q60. Describe different types of a scrap.
Ans:
Scrap in manufacturing refers to materials deemed unusable for the intended product. There are two primary types: planned scrap, a predetermined quantity factored into production calculations to account for expected material losses, and unplanned or incidental scrap, which arises unexpectedly due to variations in production processes. While planned scrap helps in efficient resource planning, minimizing waste, unplanned scrap often results from unforeseen issues and requires continuous process improvement to reduce its occurrence.
Q61. What is difference between by-product and co-product and how do differentiate them in a BOM?
Ans:
Co-Product – A co-product is the product that is produced in conjunction with the other products. The system creates the separate order item in the production order for an each co-product.
By Product – An output from the production process that may be valuable or marketable, or it may occasionally be waste.The System Does not create separate order item for the each by-Product.
BOM Settings- Negative sign is used for a co-products and also co-product indicator should be active in the BOM. And the byproduct has only -ve quantity in BOM component.
Q62. Difference between BOM group and group BOM?
Ans:
BOM Group – It is the collection of bills of material that lets describe the product or a number of similar products.
Group BOM – It is the BOM wherein do not assign any plant while its creation. This means this BOM can be later assigned to the any plants as per requirement.
Q63. What is super BOM?
Ans:
The BOM which maintain for Configurable materials is called as a Super BOM. It contains all possible components that are required to be manufacture the material. Both components that are utilised in every variant and those that are exclusive to a particular variant (variant parts) are found in the BOM (non-variable parts). This is why BOMs for configurable materials are known as a super BOMs.
Q64. What is mean by variant BOM?
Ans:
Several similar materials which have the common parts can be created as a SAP variant BOM. SAP variant BOM will have a BOM technical type V. BOM group for all variant bills of materials will be same. This helps the business users to simplify a BOM maintenance.
Q65. How many numbers of alternative BOM can be created?
Ans:
There is no specific predefined limit on maximum number of alternative BOMs (Bill of Materials) that can be created. The number of alternative BOMs can create depends on version of SAP using and the configuration settings in specific SAP system. The actual limit, if any, would be determined by a hardware resources, database constraints, and specific SAP configuration in an organization’s system.
Q66. How can attach drawing to BOM?
Ans:
To attach a drawing to a Bill of Materials (BOM), organizations commonly use document management systems or software integrated with their Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. In these systems, users can link the drawing file directly to the corresponding BOM item, ensuring that the relevant documentation is easily accessible to users involved in production planning and execution. This integration streamlines the management of engineering documents and enhances collaboration across different departments involved in the manufacturing process.
Q67. Why does need of production version ?
Ans:
Production versions are vital for specifying manufacturing details like routing and BOM. They ensure consistency and accuracy in production planning. By managing changes effectively, they prevent disruptions to existing processes. Production versions aid in controlling variations in product manufacturing, and they are essential for efficient resource allocation.
Q68. What is Difference between TECO and CLSD?
Ans:
TECO means Technically complete. By setting the status TECO; the order from logistics point of view is set as a complete. However, can carry out Variances, settlements on order.
CLSD Once the order is TECO and all settlements are completed then order will be set to Close. Until unless all settlements are done on order; the order cannot be closed.
Q69. What is phantom assembly ?
Ans:
Phantom assemblies are the assemblies that have own product structure, but whose assembly does not a physically exist. The components of phantom assembly are incorporated directly in superordinate product. The product structure of a superordinate product contains the reference to phantom assembly. In simple words SAP, phantom assembly is the special non-stock material that has its own components.
Q70. What is Backflush and places where backflush is used?
Ans:
Backflush is a manufacturing process where the system automatically issues materials and records production upon the completion of a finished product, without the need for explicit, real-time material transactions. It is commonly used in repetitive or high-volume production settings where material consumption is predictable and follows a standard formula. Backflushing is efficient in environments where real-time tracking of material usage for each product is not practical or necessary, such as in assembly line production.
Q71. What is movement type for Goods issue reversal?
Ans:
SAP PP the movement type used for a goods issue reversal is 262. Movement type 262 is specifically used to cancel the goods issue .When goods are issued from stock, the corresponding entry is made in system using a specific movement type (e.g., 261 for a standard goods issue).
Q72. What is MRP profile?
Ans:
SAP and materials planning, an MRP (Material Requirements Planning) profile is configuration setting that defines how MRP process should work for a specific material or group of materials. It contains the set of parameters and options that influence behavior of MRP for those materials. MRP profiles are important part of SAP’s Material Requirements Planning functionality and are used to the tailor the planning process to a specific needs of different materials or groups of materials within organization.
Q73. Difference between MRP and MPS ?
Ans:
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and Master Production Scheduling (MPS) are components of production planning. MRP focuses on detailed material planning, calculating quantities and timings for materials needed in production. In contrast, MPS addresses the broader production schedule, determining when and how much to produce to meet overall demand. MRP deals with inventory levels and order releases, while MPS is concerned with the timing and volume of finished goods production.
Q74. What is MRP controller ?
Ans:
The MRP Controller in the SAP, Material Requirements Planning Controller, is the mandatory field in Material Master. It represents a person, or group, that will be responsible for controlling a workflow scheduling.
Q75. What is planned cost, Actual cost and target cost?
Ans:
- Planned cost = A Planned qty X Planned cost
- Actual cost = An Actual qty X Actual cost
- Target cost = An Actual qty X Planned cost
Q76. What are different standard MRP types in SAP PP?
Ans:
In SAP PP, standard MRP types include PD for customer requirements, NETPL for network components, VB and V1 for consumption-based planning, and VM for reorder point planning. These MRP types cater to various production scenarios, offering flexibility and customization in material requirements planning.
Q77. What are the key fields in MRP1 View?
Ans:
- General Data
- MRP Procedure
- Lot Size data
Q78. What are the key fields in MRP3 View?
Ans:
- Forecast Requirement
- Planning
- Availability Check
Q79. Difference between Customer Independent requirement and Planned Independent requirement ?
Ans:
Customer Independent Requirements (CIR) are external demands driven by customer orders or forecasts, influencing production planning. Planned Independent Requirements (PIR), on the other hand, are internal projections derived from the company’s sales and operational planning, serving as a basis for production planning. CIR is customer-driven and directly impacts the production schedule, while PIR is an internal estimate used for capacity and resource planning, helping to align production with anticipated demand.
Q80. Difference between NETCH,NETPL & NEUPL?
Ans:
In SAP PP, NETCH, NETPL, and NEUPL are indicators related to the availability check during material requirements planning (MRP). NETCH considers only the available stock and incoming planned orders, NETPL considers both stock and dependent reservations, and NEUPL includes stock, reservations, and incoming orders. NETCH is suitable for scenarios with no dependent requirements, NETPL is used when reservations are relevant, and NEUPL is employed when both dependent reservations and incoming orders need consideration for the availability check in the MRP process.
Q81. What is Schedule Margin key?
Ans:
Schedule Margin Key is the configuration setting that determines a amount of time by which a planned order or production order is brought forward or pushed back during scheduling process. It helps in managing scheduling of production operations by considering the various factors such as lead times, processing times, and safety margins.
Q82. What is availability check?
Ans:
Availability check is the crucial functionality in SAP and the other enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems that helps to organizations manage their inventory and ensure timely delivery to the customers. It involves the verifying the availability of materials, components, and resources needed to fulfill customer orders or a production requirements.
Q83. What is planning fence time?
Ans:
Planning fence time, also known planning fence is a term used in the production planning and scheduling. It represents the specific time period before the start of production order within which changes to order can be made without affecting a current production schedule.
Q84. What is difference between MD04 and MD05 t-codes?
Ans:
In SAP, MD04 and MD05 are transaction codes related to material requirements planning (MRP). MD04 displays stock/requirements lists for a specific material, providing an overview of its current status. On the other hand, MD05 is used to display a planning run, showing the results of an MRP run with detailed information on planned orders, purchase requisitions, and stock/requirements lists. While MD04 focuses on a specific material, MD05 gives a broader view of the MRP run results for multiple materials.
Q85. What are different Planning strategies?
Ans:
In SAP Production Planning (PP), various planning strategies determine how the system plans and manages production. Examples include Make-to-Stock (10), Make-to-Order (20), and Configure-to-Order (25). These strategies define how and when production orders are created based on demand or customer orders. The choice of planning strategy depends on factors like production environment, customer requirements, and industry characteristics. Each strategy aligns with specific business needs, providing flexibility in production planning within the SAP PP module.
Q86. What is COGI report/error?
Ans:
COGI stands for a Controlling Goods Issued and is a standard SAP transaction which shows the report of automatic goods movement errors. Automatic Goods Issues are carried out by a production confirmation if the Backflush indicator is set on MRP1 View.
Q87. What are all steps involved in Variant Configuration?
Ans:
Variant Configuration in SAP involves several steps. Firstly, configure the characteristics and classes relevant to the product. Then, define dependencies and conditions to govern how characteristics interact. Create a configuration profile to link the product model with the configuration. Assign the configuration profile to the material master. During sales order creation, the system uses the configured profile to generate a Bill of Material (BOM) and a Routing.
Q88. Dependency types in variant configuration?
Ans:
In Variant Configuration in SAP, dependency types define the relationships and constraints between characteristics. There are two main types: Preceding Dependency, where one characteristic’s value determines the possible values for another, and Action Dependency, which triggers actions or changes based on the values of certain characteristics. Preceding Dependency includes Value-Dependent and Fixed Value, while Action Dependency involves Default, Copy, and Check.
Q89. Difference between PP and MM Module?
Ans:
Bill of Materials (BOM) – Once define the BOM for Header material (such as the finished good), can get the exact requirement for the quantity of inventory.
Material Requirement Planning for an External Procurement (MRP) – Once maintain the MRP views in Material Master, can generate the automatic reservation and Purchase Requisition after running t MRP.
Stocks Determination – when issue and receive material to the production order.
Q90. Difference between PP and QM Module?
Ans:
In process inspection during Production – This is used when required to check the product at a regular intervals. Need to activate Inspection type 03 in the material master Quality management view. Inspection after Goods Receipt for a Production order – This is used when it’s required to check product after completion of production process. select Inspection Type 04 in quality management view in material master.






