
SAP EHS, which stands for Environment, Health, and Safety, is a comprehensive software solution developed by SAP SE, a global leader in enterprise application software. SAP EHS is designed to assist organizations in effectively managing their environmental, health, and safety processes and compliance requirements. This software suite encompasses a wide range of functionalities and modules tailored to address various aspects of environmental sustainability, occupational health, industrial hygiene, and workplace safety.
1. Describe Product Safety in SAP EHS.
Ans:
SAP Product Safety, formerly known as SAP EHS Management, is a software program that assists businesses in guaranteeing the security and conformity of their goods throughout their whole lifecycle. With the aid of the Specification Information System, companies can monitor chemicals, substances, materials, and other items through the SAP EHS submodule Product Safety.
2. Describe the Management of Dangerous Goods.
Ans:
Monitor hazardous goods data in SAP and also describe various inspections that ought to have been carried out during the offering, delivery, and handling of dangerous goods with the help of the EHS Dangerous Goods Management module.
3. Describe Safety and Industrial Hygiene.
Ans:
Classify their work zones using SAP EHS’s Industrial Hygiene and Safety submodule. The anticipation, identification, assessment, and management of health risks resulting from the use of chemical and physical agents, including the assessment of indoor air quality, are the main objectives of EH&S industrial hygiene activities.
4. What Do Business Health Centers Entail?
Ans:
Organizational well-being emphasizes treating those who are not employees of the organization and working with outside partners on a regular basis. External parties and business partners are recorded in the SAP section Central Business Partner.
5. What are the various components of an organization’s EHS consultant?
Ans:
The various components of the Environment, Health and Safety (EH&S) are as follows:
- Safety of Products
- Waste Management;
- Occupational Health;
- Global Label Management
6. Define the main elements that makeup Earth.
Ans:
There are four categories of fundamental elements on Earth:
- The lithosphere, or outer layer of the Earth, is made up of rocks and minerals.
- The atmosphere, which is the vapour or gas envelope that surrounds the world,
- The hydrosphere is the fluid portion of the globe that includes the water vapour found in the surrounding air, as well as water from lakes, streams, seas, and rocks.
- The biosphere is the universe of living things that are audible on land, in water, and everywhere else.
7. What does SAP EHS’s waste administration mean?
Ans:
The Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS) field provides help for managing business activities pertaining to environmental and human health and safety. With the help of environment management, you may schedule the tasks necessary to oversee your company’s adherence to environmental standards pertaining to emissions.
8. What are the means of disposing of waste?
Ans:
Waste transportation refers to the movement of waste across a certain area using trucks, barges, trains, tankers, or other types of vehicles. Wastes that can be carried include hazardous or radioactive materials as well as municipal trash. It is possible to transport hazardous waste for disposal, storage, or treatment.
9. What is the behavior of headers and footers when you use incorporates?
Ans:
When incorporates are added to the ace format, their headers and footers are ignored. Included content is not allowed in the headers or footers of integrates.
The top and bottom portions of the document are called headers and footers, respectively. Footnotes, page numbers, titles, and other information that are not part of the main text are frequently kept in these distinct sections.
10. Explain the Different Hypotheses about Earth’s origin?
Ans:
| Hypothesis | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nebular Hypothesis | Proposes that the Sun and planets formed from a rotating disk of dust and gas (a nebula) that condensed and accreted over billions of years. |
| 2 | Planetesimal Hypothesis | Suggests that small, solid bodies called planetesimals collided and merged to form larger bodies, eventually leading to the formation of planets like Earth. |
| 3 | Capture Hypothesis | Posits that the Earth formed elsewhere in the solar system and was later captured by the gravitational pull of the Sun. |
| 4 | Giant Impact Hypothesis | Proposes that the Moon formed from the debris ejected during a collision between the early Earth and a Mars-sized body, leading to the current Earth-Moon system. |
| 5 | BinaryStar Hypothesis | Speculates that the Sun was once part of a binary star system and that the planets, including Earth, formed from the debris around one of the stars. |
11. List a Few Typical PPE for Construction Sites.
Ans:
Some of the PPE used in development sites include caps, fall capture technology, highly deceivable clothes, and eye protection.
Used in construction in PPE:
- Gloves,
- Protective clothes,
- Respirators,
- Hard helmets,
- Safety glasses,
- and earplugs.
12. What Is a Permit For Safe Work?
Ans:
In basic terms, a protected work permit is a report that authorizes the work to be done, identifies the risks involved, and specifies the safety precautions that must be taken to avoid those risks.
A document that contains information about the job that needs to be done, the risks associated, the safety measures to take, the necessary authorizations, and other components.
13. What is the SAP EHS?
Ans:
SAP EHS makes it possible for ERP consultants to abide by legal requirements pertaining to health and safety. Waste management, basic data applications, product management, coverage, and safety management are just a few of the industries that employ SAP EHS applications. SAP EHS assists businesses in applying cutting-edge technology, adhering to laws and regulations, and smartly handling safety compliances.
14. What are the duties and functions of consultants for SAP EHS?
Ans:
In their capacity as environment engineers for health and safety, they are in charge of overseeing initiatives that shield people everywhere from potential risks in the workplace and the Environment. Defend the Environment against risks caused by humans.
15. Describe the EHS policies.
Ans:
The EHS rules set minimal standards for organizations in certain situations. Written health and safety policies in a robust and efficient setting are seen to be the cornerstone of successful and long-lasting environmental health and safety programs.
16. What are SAP EHS’s primary functionalities?
Ans:
The primary functionalities of the SAP EHS are as follows:
- SAP EHS helps companies to keep their employee health and safety features operational.
- Product functionality related to safety and stewardship.
- Functionality for managing environmental compliance.
- Functionality for Reach and Product compliance.
- SAP best practices for sustainability analytics packages.
17. Why is SAP EHS necessary?
Ans:
The following are a few advantages of SAP EHS that will clarify why SAP EHS is necessary for any industry:
- The accountability, commitment, and leadership of management.
- Risk management and evaluation.
- Construction management and design of facilities and equipment.
- Development of documents and information.
- Individual and instruction.
- Evaluation, criticism, and development.
- Stewardship of the supply chain and products.
- Emergency services and community awareness.
18. What does risky product management entail?
Ans:
SAP EHS’s dangerous products management module enables businesses to handle pertinent data about hazardous materials in SAP and specify the different inspections that must be carried out during the handling, shipping, and sales of hazardous materials.
19. What does SAP EHS mean by industry hygiene and safety?
Ans:
The SAP EHS sub-module for industry hygiene and safety enables businesses to identify work zones, evaluate the risk of a given exposure and task, and keep track of exposures. SAP Product Safety, formerly known as SAP EHS Management, is a software program that assists businesses in guaranteeing the security and conformity of their goods throughout their whole lifecycle.
20. In SAP EHS, what is incident management?
Ans:
An enterprise-wide platform that controls and supports the business processes for event recording, corrective action triggers, reporting, monitoring, and investigation for safe and healthy environments is one of the benefits of using an incident management system in SAP EHS.
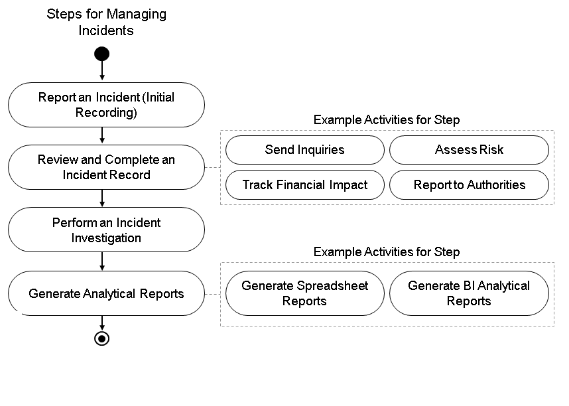
21. What does SAP EHS’s product safety mean?
Ans:
A submodule of SAP EHS called “product safety” aids in the management of chemicals, substances, materials, etc., for businesses. An information system for specifications can aid with product safety.
22. What are the various theories on the origin of the Earth?
Ans:
Man has been curious about the look of things since the beginning of the cosmos and the Earth. All of the early municipal establishments developed their explanations and modifications of the universe’s and the world’s origins due to this natural curiosity.
The field of research known as COSMOLOGY oversees the evolution of ideas on the origin of the Earth, how it is related to the nearby planetary group, and how it is connected to the Earth itself. Before the invention of the telescope, man had to persevere. All of the more powerful telescopes were developed after a few centuries.
23. What six categories of dangers are there in the workplace?
Ans:
The six categories of dangers that are present in the workplace are as follows:
- Risks to safety
- Dangers from biological sources
- Workload dangers, financial hazards, and physical hazards.
- Molecular hazards.
24. List the essential elements of the SAP EHS.
Ans:
The main elements of the SAP EHS are as follows:
- Management of hazardous substances.
- Management of dangerous commodities.
- Product safety oversight.
- Handling of waste.
- Management of occupational health.
- Safety and hygiene in the workplace.
- Fundamental reporting and data.
25. What are the company’s health centers called?
Ans:
The main elements of the SAP EHS are company health centres, which frequently collaborate with outside partners and occasionally provide care for individuals who are not employees of the company. Business partners and external partners are included in the SAP component’s central business partners.
26. How would you describe industrial safety and hygiene?
Ans:
The SAP EHS additionally includes an industrial hygiene and safety sub-module. It helps companies to describe the work areas, track exposure, and measure risk associated with particular tasks and exposures. SAP Product Safety, formerly known as SAP EHS Management, is a software program that assists businesses in guaranteeing the security and conformity of their goods throughout their whole lifecycle.
27. What does SAP EHS Squander Administration entail?
Ans:
SAP EHS’s Trash Administration gives staff members the authority to manage and organize contemporary rubbish while adhering to local, national, and worldwide waste standards. The Environment and sustainability are the four main components of the EHS policy. Promote EHS Integration and Business Excellence among Compliance Workers and Stakeholders (Clients, Suppliers, Contractors, and Government).
28. Which kinds of EHS are there?
Ans:
The five most prevalent categories of Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) regulations are as follows: Regulations pertaining to product safety, transportation safety, fire safety, environmental protection, and occupational safety and health.
29. Which SAP programs are compatible with SAP EHS integration?
Ans:
The SAP EHS integrates with the following SAP modules, including SAP Material Management (SAP), with success. SAP PM (Product maintenance) and SAP FI (Finance).
- Human resources, or SAP HR.
- The SAP system for managing documents.
30. What does industrial safety and hygiene mean?
Ans:
The SAP EHS sub-module for industrial hygiene and safety enables the company to identify:
- Work area,
- Evaluate potential risk factors, and
- Keep track of exposures.
31. What are the many facets of an organization’s SAP EHS consultant?
Ans:
The components of an SAP environment, health, and safety consultant in an organization are as follows:
- Product Security
- Management of labels worldwide.
- Health at work.
- Handling of waste.
32. What does SAP EHS waste management entail?
Ans:
The SAP EHS, waste management component, helps businesses manage and get rid of industrial waste while following local, national, and international waste regulations. The SAP EHS Environment Management solution enables activities including cost allocation and tracking of waste disposal costs in addition to assisting customers in making sure their waste management procedures are compliant from generation to disposal.
33. What functions and duties do SAP EHS consultants perform?
Ans:
In their capacity as environment engineers for health and safety, they are in charge of overseeing initiatives that shield people everywhere from potential risks in the workplace and the Environment. (Defend the Environment against risks caused by humans).
34. Describe the SAP EHS product safety.
Ans:
SAP EHS is feasible. It’s one of the EHS’s submodules; product safety gives firms control over substances, materials, and chemicals, as well as system-related data. SAP Environment, Health, and Safety (SAP EHS) Product Safety is a comprehensive solution designed to help organizations ensure compliance with global product safety regulations and standards while managing product-related risks effectively. This module within the SAP EHS suite enables businesses to streamline their product safety processes, from product formulation and testing to regulatory compliance and product stewardship.
With SAP EHS Product Safety, companies can efficiently manage product safety data, including substance properties, hazard classifications, and safety data sheets (SDS).
35. How would you define the management of dangerous goods?
Ans:
The SAP EHS includes a subcomponent called dangerous products management. Its activities include the following: monitoring critical SAP information on dangerous items.
Outline various checks, such as placing orders, making offers, delivering goods, and tending to dangerous goods.
36. How may the Squander transporter be modified?
Ans:
The following navigation is used to modify the Squander transporter:
- Usually, hazardous materials are used to transfer hazardous material on public roads. Very little is moved by air or by inland waterways, and very little is moved by rail.
- Apply the code WAA20 and go to the alternate waste transporter.
37. How Can Dangerous Substances Be Changed?
Ans:
Use the following Tcode if the activity is less troublesome.
- Code HSMD:
- Find the appropriate option if you need to change the ACE (hazardous material.
- Modify the procedure to reduce exposure to dangerous chemicals.
- Shut down or contain the process.
- Reduce the production of dust and other pollutants by using wet procedures.
38. In SAP EHS, what is incident management?
Ans:
The following advantages of using an incident management solution in SAP EHS are available:
An enterprise-wide platform for overseeing and assisting the business procedures for documenting events, identifying triggers for remedial action, reporting, keeping an eye on things, and looking into safe and healthy settings.
39. What is the objective of SAP EHS’s Incident Management component?
Ans:
When it comes to workplace safety, environmental problems, or occupational health concerns, incidents or accidents are reported, looked into, and tracked using SAP EHS’s Incident Management component.
SAP Incident Management Solman
Resolving issues brought up by end users, system alerts from monitoring services, or key users is the responsibility of the incident management process.
40. What is the aim of the SAP EHS’s Substance Management component?
Ans:
Material safety data sheets (MSDS), chemical composition, and handling guidelines are only a few of the details concerning hazardous compounds that are utilized in the company that are managed and tracked by SAP EHS’s Substance Management component.
41. What is the goal of SAP EHS’s Occupational Health component?
Ans:
Processes connected to employee health, including medical surveillance, physicals, exposure monitoring, and health-related paperwork, are managed by SAP EHS’s Occupational Health component. To offer a repository for tracking employees’ history of occupational health issues and implement a risk-based occupational health approach that integrates with central HR data.
42. How does SAP EHS handle exposure control?
Ans:
- Organizations may monitor and control employee exposure to dangerous materials or working conditions with SAP EHS.
- It has tools for gathering and analyzing data, as well as for monitoring exposure.
- Software known as SAP EHS was developed to address industrial hygiene, occupational health, and general worker, product, and organizational safety effectively and efficiently.
43. What is the purpose of the Agent Assignment in SAP EHS?
Ans:
Individuals or organizational units can be given responsibility for particular EHS-related duties or activities using SAP EHS’s Agent Assignment feature. It aids in guaranteeing responsibility and appropriate EHS process execution.
44. How are other SAP modules integrated with SAP EHS?
Ans:
SAP Environmental, Health, and Safety (SAP EHS) interfaces with multiple SAP modules, including:
- Materials Management (MM),
- Plant Maintenance (PM),
- Production Planning (PP),
- and Quality Management (QM),
- to guarantee that environmental, health, and safety factors are considered inside the company.
45. In SAP EHS, what is a specification?
Ans:
- In SAP EHS, a specification is a collection of attributes or features that characterize a material, a product, or a procedure.
- It contains details on the physical characteristics, chemical makeup, and regulatory information.
- Value assignment assigns values to specifications utilizing several value assignment kinds of value assignment categories (e.g., Property, Composition, and Listing).
46. What is the objective of SAP EHS’s Waste Management component?
Ans:
The generation, packaging, transportation, and disposal of waste items, as well as their disposal, are all managed and tracked by SAP EHS’s Waste Management component. Guarantees that participants comprehend the entire process, from knowing the legal requirements for trash disposal to classifying waste according to its characteristics.
47. What is the objective of SAP EHS’s Environmental Compliance component?
Ans:
Organizations may guarantee compliance with environmental standards and laws by utilizing SAP EHS’s Environmental Compliance components. It has tools for tracking emissions, handling licenses, and compiling environmental information.
48. In what ways is regulatory compliance managed by SAP EHS?
Ans:
SAP EHS offers tools to track and guarantee adherence to safety, health, and environmental laws. It has tools for handling permits, keeping track of regulatory obligations, and producing compliance reports.
49. What is the purpose of SAP EHS’s Phrase Management function?
Ans:
Users can create and manage standard phrases or texts that can be used in a variety of EHS procedures and documentation, including labels, SDSs, and reports, using SAP EHS’s Phrase Management feature.
50. How are incident reports and investigations handled by SAP EHS?
Ans:
SAP EHS users may investigate, take corrective action, and record and track problems. In order to guarantee that events are appropriately handled, it offers processes, notifications, and reporting features. SAP EHS provides tools for organizations to effectively track and ensure adherence to safety, health, and environmental laws. It offers functionalities to manage permits, monitor regulatory obligations, and generate compliance reports, thus aiding businesses in meeting their regulatory requirements efficiently.
SAP EHS’s Phrase Management feature serves to streamline the creation and management of standard phrases or texts used across various EHS procedures and documentation. These phrases can be utilized in labels, Safety Data Sheets (SDSs), reports, and other documentation, ensuring consistency and accuracy in communication and compliance efforts.
51. In SAP EHS, what is a Safety Data Sheet (SDS)?
Ans:
- In SAP EHS, a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) serves as a comprehensive document that provides essential information about the risks associated with handling, storing, and responding to emergencies related to hazardous materials or products.
- Often mandated by regulatory organizations, the SDS ensures that users have access to critical safety information to mitigate risks effectively.
- In SAP EHS, a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is a document that offers details on the risks associated with handling, storing, and responding to emergencies for hazardous materials or products. Usually, regulatory organizations demand it.
52. How does SAP EHS handle occupational health management?
Ans:
With the ability to collect employee health data, administer medical surveillance programs, keep track of exposures, and preserve health-related records, SAP EHS facilitates occupational health management.
- Collects employee health data.
- Administers medical surveillance programs.
- Tracks exposures to occupational hazards.
- Preserves health-related records for employees.
53. Describe the Hazardous Goods Master.
Ans:
Information on hazardous materials, products, or chemicals is contained in a SAP EHS hazardous goods master. This information includes handling guidelines, transit laws, labelling, and classification. Any object or agent (chemical, biological, radioactive, or physical) that poses a risk to people, animals, or the environment is considered a hazardous material.
54. How is risk assessment handled by SAP EHS?
Ans:
By offering instruments to recognize and assess hazards related to workplace activities, substances, or procedures, SAP EHS facilitates risk assessment. It supports the management of risk mitigation initiatives and the selection of suitable control mechanisms.
55. How does SAP EHS handle compliance reports?
Ans:
- SAP EHS offers reporting capabilities to provide compliance reports that are needed by internal stakeholders or regulatory bodies.
- Users can gather, examine, and produce personalized reports using EHS data. Product-related environmental rules, such as the REACH chemicals of Very High Concern in articles and
- The EU Directive for the Restriction of Hazardous Chemicals (EU RoHS), are made easier for discrete manufacturers to comply with by the product compliance business model.
56. What does SAP EHS’s Waste Transfer Document serve as?
Ans:
- Documents the transfer of waste from one party to another.
- Includes details such as type of waste, quantity, mode of transportation, and associated paperwork.
- Ensures proper documentation and tracking of waste transfers for regulatory compliance and accountability.
The transfer of waste products from one party to another is documented in SAP EHS using the Waste Transfer Document. It contains details regarding the kind, amount, and mode of transportation of the garbage, as well as any associated paperwork.
57. How does SAP EHS handle chemical management?
Ans:
- Handles and monitors chemical data.
- Provides handling directions and labeling specifications.
- Defines hazardous property standards.
- Ensures regulatory compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
- Safeguards the health and safety of employees handling chemicals.
Organizations may handle and monitor chemical data, including handling directions, labeling specifications, hazardous property standards, and regulatory compliance, with SAP EHS to safeguard the health and safety of employees who handle chemicals, maintain chemical data, and guarantee regulatory compliance.
58. How does SAP EHS handle classification and labeling?
Ans:
- SAP EHS facilitates the classification and labeling of products and substances in accordance with legal requirements.
- It offers features for creating labels, controlling label templates, and ensuring compliance with labeling regulations.
- This functionality ensures that products and substances are appropriately classified and labeled, enhancing safety and regulatory compliance efforts.
- SAP EHS facilitates product and substance labeling and classification in compliance with legal requirements. It has features for creating labels, controlling label templates, and guaranteeing labeling compliance.
59. What is SAP EHS’s Exposure Profile used for?
Ans:
SAP EHS’s Exposure Profile is utilized to establish and manage exposure limits, thresholds, and guidelines for hazardous substances or work circumstances. This feature supports organizations in evaluating and managing worker exposures to potentially harmful substances, thereby promoting a safe and healthy work environment. To establish and manage the exposure limits, thresholds, and guidelines for hazardous substances or work circumstances, utilize SAP EHS’s Exposure Profile.
60. How does SAP EHS handle environmental reporting?
Ans:
The feature of SAP EHS enables the collection, analysis, and reporting of environmental data that is needed for internal reporting needs or regulatory agency requirements. It has tools for keeping an eye on resource usage, waste production, and emissions.
61. What is the SAP EHS Control Measure’s purpose?
Ans:
A preventative or protective measure used to lessen risks or hazards connected to workplace activities, substances, or processes is called a control measure in SAP EHS. Engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment are some examples of it.
62. What is the objective of SAP EHS’s Medical Surveillance Program?
Ans:
Employee health examinations, follow-ups based on work-related exposures or risks, and medical examinations are tracked and managed by SAP EHS’s Medical Surveillance Program. Policy for environmental health and safety. An organization’s formal EHS policy should be defined, documented, and endorsed by top management through established procedures.
63. How is waste tracking managed by SAP EHS?
Ans:
The Organizations may monitor and control waste materials throughout the disposal process with SAP EHS. It has functions for tracking garbage disposal documents, packaging, transportation, and waste generation recording.
64. What does SAP EHS’s Environmental Compliance Calendar serve as?
Ans:
Activities linked to compliance, like permit renewals, inspections, and reporting deadlines, are tracked and monitored using SAP EHS’s Environmental Compliance Calendar. It assists in guaranteeing prompt adherence to regulatory obligations.
65. What is the purpose of the Chemical Substance Report from SAP EHS?
Ans:
- A chemical substance’s attributes, dangers, classification, regulatory status, and related documentation are all covered in depth by the Chemical Substance Report in SAP EHS.
- Waste streams are generated at the product level linked to the waste material, while transporters and disposers are assigned at the waste material level.
66. How does SAP EHS handle training management?
Ans:
Through the provision of tools to create and manage staff training programs pertaining to environmental, health, and safety subjects, SAP EHS supports training management. It aids in guaranteeing that workers have sufficient training and competence.
67. What is SAP EHS’s Waste Profile used for?
Ans:
- Information about waste products, such as waste codes, packaging specifications, transportation limitations, and disposal techniques, can be found in SAP EHS’s Waste Profile.
- It aids in guaranteeing appropriate waste management and disposal. The Waste Profile feature in SAP EHS serves as a central repository for information related to waste products.
- It includes details such as waste codes, packaging specifications, transportation limitations, and disposal techniques.
- By consolidating this information in one place, the Waste Profile facilitates efficient and effective waste management and disposal processes.
68. How are incident notification and escalation handled by SAP EHS?
Ans:
The ability to alert and escalate incidents to the appropriate parties, such as emergency response teams, supervisors, or EHS managers, is provided by SAP EHS. Workflows and notifications are integrated to guarantee that the right actions are executed on time.
69. How are substance registration and compliance handled by SAP EHS?
Ans:
Organizations can handle substance registration and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) compliance using SAP EHS. It has tools for monitoring the status of substance registrations, organizing paperwork, and making sure reporting regulations are followed.
70. What is the SAP EHS Industrial Hygiene Survey’s objective?
Ans:
To measure and track occupational exposures to chemical, physical, and biological hazards, SAP EHS uses the Industrial Hygiene Survey. It is beneficial in that it aids in recognizing and reducing dangers to occupational health.
71. How does SAP EHS handle audits and inspections?
Ans:
EHS audits and inspections can be planned, carried out, and tracked with SAP EHS. It has tools for creating checklists, allocating responsibilities, documenting discoveries, and monitoring remedial measures. Examine the information associated with this business object, look into the occurrence, and report occurrences in accordance with internal guidelines.
72. What is SAP EHS’s EHS Dashboard used for?
Ans:
- Provides an overview of key EHS metrics, indicators, and performance measurements.
- Presents information visually through charts, graphs, and other visualizations.
- Supports tracking EHS performance and identifying areas requiring improvement.
- Enables stakeholders to monitor progress and make informed decisions regarding EHS initiatives.
73. How does SAP EHS manage emergency response planning?
Ans:
- The Software is made to handle industrial hygiene, worker and product safety, and occupational health in the workplace effectively and efficiently.
- By offering resources for creating and managing emergency response plans, protocols, and contact lists, SAP EHS facilitates emergency response planning. It facilitates readiness and efficient action.
71. What does SAP EHS’s Incident Investigation Report serve as?
Ans:
The SAP EHS (Environment, Health, and Safety) Incident Investigation Report serves as a crucial tool for organizations to meticulously document and analyze incidents occurring within their premises. Its primary function is to record intricate details surrounding incidents, including time, location, and descriptions, encompassing various types such as workplace accidents, environmental spills, and safety breaches. Through this report, organizations conduct thorough investigations, identifying contributing factors and delving into underlying causes to comprehend the root of the incident.
72. How does SAP EHS handle permit management?
Ans:
Organizations may handle environmental licences and permits with SAP EHS. It has tools for monitoring to permit Requirements, Organizing permit paperwork and making sure provisions of the permission are followed.
73. What is the SAP EHS Exposure Limit used for?
Ans:
- Represents the maximum permitted concentration or degree of exposure to a hazardous material or work condition.
- Aids in establishing suitable control mechanisms for managing exposure risks.
- Ensures compliance with safety regulations and standards.
- Helps in safeguarding worker safety and health.
74. What does SAP EHS’s Waste Disposal Approval serve as?
Ans:
To get permission from waste management facilities or regulatory bodies for the disposal of waste materials, Use SAP EHS’s Waste Disposal Approval feature. It aids in guaranteeing adherence to disposal guidelines.
75. How does SAP EHS handle radiation safety management?
Ans:
By offering resources to monitor and control radiation sources, exposures, and safety precautions, SAP EHS facilitates radiation safety management. It aids in guaranteeing adherence to radiation safety guidelines. Features including product compliance, occupational health, incident management, and sustainability reporting,
76. What is the SAP EHS Risk Matrix used for?
Ans:
The SAP EHS Risk Matrix serves as a valuable tool for evaluating and prioritizing risks within an organization. By visually representing risks based on their probability and severity, the Risk Matrix enables stakeholders to identify high-risk areas that require immediate attention. This facilitates the establishment of risk mitigation strategies and priorities, helping organizations allocate resources effectively to address potential hazards.
77. How does SAP EHS handle regulatory reports?
Ans:
- Permits the preparation and submission of regulatory reports that are needed by environmental, health, and safety regulatory agencies.
- Streamlines the processes of obtaining data, validating it, and producing reports.
- Guarantees adherence to legal reporting specifications.
- Assists companies in adhering to regulations and fulfilling their legal responsibilities.
78. Define how many types of ECS elements.
Ans:
The Three Foundations of Superb Customer Service:
- Intelligence: This involves understanding customer needs, preferences, and expectations. It includes gathering and analyzing data, actively listening to customers, and using insights to provide personalized and effective solutions.
- Persistence: This refers to the commitment and dedication to resolving customer issues and delivering excellent service, even in challenging situations.
- Personalization: This involves tailoring the customer experience to meet individual preferences and requirements. It includes recognizing and acknowledging customers by name, remembering their past interactions and preferences, and offering customized recommendations or solutions.
79. Define the Types of ECS.
Ans:
ECS comes in two flavours: ECS (Credit) and ECS (Debit).
A single debit, such as a dividend, interest, or salary payment, is made to an account using ECS (Credit), which allows credit to be extended to a large number of beneficiaries.
80. How does SAP EHS manage product compliance?
Ans:
Organizations can manage product compliance with rules like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), REACH, and other product-related directives by using SAP EHS. It has tools for organizing documentation, keeping track of compliance requirements, and guaranteeing product conformance.
81. What is ECS architecture?
Ans:
- Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing is what SAP stands for. SAP created the enterprise resource planning (ERP) software industry standard worldwide.
- According to this article, Entities, Components, and Systems (ECS) constitute the three first-class components of a software architecture pattern.
- However, because of ambiguities in the English language, the term “ECS” is commonly understood to mean “a system made up of entities and components.”
82. Define FX valuation.
Ans:
FX valuation, short for foreign exchange valuation, refers to the process of assessing and documenting the impact of changes in foreign exchange rates on various financial elements within an organization. This includes assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, gains, and losses denominated in foreign currencies. For businesses operating across international borders or engaging in transactions involving multiple currencies, fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly affect the value of their financial holdings and transactions.
83. Define PPP FX valuation.
Ans:
According to PPP theory, changes in inflation or exchange rates should cause pricing gaps between nations to gradually close (which also has some implications for exchange rate movements). Long-term focus on the FX market shows that currencies tend to trend in the direction of their “fair value.”
The primary objective of SAP EHS’s Health Surveillance Plan is to define and administer employee health surveillance programs. These programs encompass various activities such as physical examinations, medical testing, and follow-ups to monitor and maintain the health and well-being of employees. By implementing the Health Surveillance Plan, organizations aim to ensure compliance with laws and regulations governing employee health and safety.
84. How does SAP EHS handle incident trend analysis?
Ans:
Incident trend analysis, SAP EHS provides tools and functionalities to analyze event data and identify patterns over time. This involves utilizing statistical analysis tools, data visualization tools, and reporting tools to spot trends in incident occurrences and their associated factors. By identifying trends, organizations can take proactive measures to prevent future incidents and improve overall safety performance. This analysis helps in making data-driven decisions, implementing targeted interventions, and continuously improving health, safety, and environmental management practices within the organization.
85. What is the SAP EHS Health Surveillance Plan’s objective?
Ans:
The objective of the SAP EHS Health Surveillance Plan is to effectively manage and administer employee health surveillance programs within an organization. This includes the definition and implementation of protocols for conducting various health assessments such as physicals, testing, and follow-ups. The primary goal is to ensure the health and well-being of employees while also ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations pertaining to health and safety in the workplace.
86. How does SAP EHS facilitate the identification of incident trends.
Ans:
- Examines event data and identifies patterns over time.
- Utilizes statistical analysis tools to spot trends.
- Employs data visualization tools for easy interpretation.
- Provides reporting tools for comprehensive analysis.
- Enables proactive measures to address emerging trends and prevent incidents.
87. What role does SAP EHS play in waste management processes within organizations?
Ans:
- Obtains permission from waste management facilities or regulatory bodies for waste disposal.
- Ensures compliance with disposal guidelines and regulations.
- Facilitates proper and legal disposal of waste materials.
- Helps in maintaining environmental compliance and sustainability initiatives.
88. What does SAP EHS’s Waste Disposal Record serve as?
Ans:
Waste disposal information, including waste type, quantity, disposal method, and disposal location, is tracked and recorded using the Waste Disposal Record in SAP EHS. SAP EHS’s Agent Assignment feature allows individuals or organizational units to be assigned specific responsibilities for EHS-related duties or activities. By assigning agents, the system ensures accountability and facilitates the proper execution of EHS processes, contributing to effective management of environmental, health, and safety tasks within the organization.
89. How do I change a dangerous substance Ace?
Ans:
- Identify the unsafe substance: Determine the specific substance or material that is deemed unsafe within your workplace environment. This could include hazardous chemicals, materials, or products.
- Assess the risks: Evaluate the potential risks and hazards associated with the unsafe substance. Consider factors such as toxicity, flammability, reactivity, and potential health effects on workers.
- Determine necessary changes: Decide on the alterations or modifications needed to make the substance safe for use or handling. This may involve dilution, substitution with safer alternatives, or implementing engineering controls to minimize exposure.
90. What Is A Permit To Work Safely?
Ans:
A Safe Work Permit is a formal document issued by an organization or employer that authorizes specific work activities to be carried out in a controlled and safe manner. It serves as a means to ensure that potential hazards associated with the work are identified, evaluated, and effectively managed to prevent accidents, injuries, or incidents.Key features of a Safe Work Permit typically include:
- Work Description
- Hazards Identification
- Control Measures






