
An enterprise’s IT infrastructure can more easily exchange information and services with the help of IBM WebSphere Enterprise Service Bus (ESB), an integration solution. Serving as a platform for middleware, it links various systems, applications, and services to provide effective data exchange and communication. Complex integration scenarios are well-suited for WebSphere ESB because of its extensible and flexible architecture, which supports many communications patterns such as publish-subscribe and point-to-point. It makes interoperability across many technologies possible by supporting a large number of protocols and standards. In addition, WebSphere ESB comes with tools for managing, implementing, and creating integration solutions, which help businesses increase agility, optimise business processes, and boost overall operational effectiveness.
1. Describe Web-Sphere ESB in detail.
Ans:
IBM’s WebSphere ESB is the integration middleware for a seamless communication between the applications and services, offering mediation, transformation, and routing capabilities.
2. Name a few functions present in the WebSphere?
Ans:
The WebSphere tools can be used to deploy and manage web applications, enterprise Java applications, and components of service-oriented architecture (SOA).
3. How can Protocol Transformation be handled by WebSphere ESB?
Ans:
For handling protocol transformation, WebSphere ESB does it as follows:
- Message Transformation
- Protocol Adapters
- Data Mapping
- Error Handling
4. Describe WebSphere ESB’s service mediation concept works?
Ans:
The WebSphere ESB’s service mediation module manages communications between services and apps, facilitating data transformation, protocol mediation, and service coordination to guarantee smooth system integration and communication.
5. Describe operation of WebSphere or other application-server cluster?
Ans:
An application server cluster consists of multiple server instances, managed by cluster manager. A load balancer distributes the requests for high availability, scalability, and resource use. Requests are forwarded to be healthy servers for service availability.
6. Describe WebSphere ESB mediation flows and subflows?
Ans:
The most important parts of ESB are the mediation flows and subflows, which describe the message path, translation, and processing and let developers graphically define the operations and transformations.
7. Describe a function of ESB primitives used in mediation, such as Filter, Aggregate, and Splitter?
Ans:
Let’s examine the roles played by three typical ESB primitives in mediation:
- Filter
- Aggregate
- Splitter
8. How is content-based routing implemented?
Ans:
The Filter primitive in the WebSphere Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) enables a content-based routing, enabling messages to be sent to the specific locations and actions based on an incoming content.
9. Describe asymmetric clustering?
Ans:
Asymmetric clustering, used in the WebSphere Application Server, offers the flexibility and specialization by combining the distinct node types.
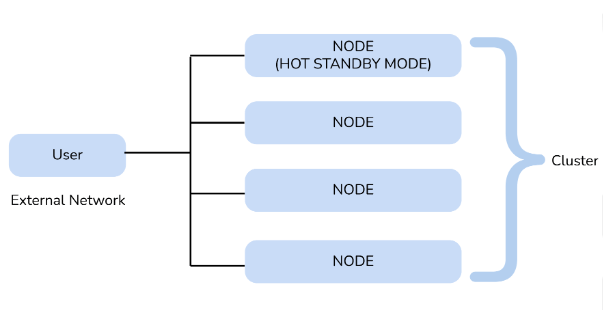
10. What difficulties are frequently encountered when implementing the WebSphere ESB, and how does one overcome them?
Ans:
Data transformation, protocol mediation, and service orchestration are streamlined when different apps and systems are integrated utilizing ESB mediation processes.
11. Explain WebSphere ESB endpoint lookup concept?
Ans:
WebSphere ESB endpoint lookup concept uses a service registry to dynamically locate and obtain endpoint data for services, enabling flexible endpoint resolution without hardcoding addresses in mediation flows.
12. What function do mediation primitives provide in WebSphere ESB?
Ans:
The message processing logic, content-based routing, enrichment, error handling, and protocol mediation are made possible by WebSphere ESB’s mediation primitives, which improve integration and communication across the diverse systems.
13. How does IBM WebSphere ESB differ from the other integration solutions?
Ans:
IBM WebSphere ESB is the flexible middleware platform based on the SOA principles, offering reusability, standardization, and adaptability for enterprise-level integration problems.
14. How does WebSphere ESB handle message enrichment?
Ans:
WebSphere ESB implements message enrichment using mediation flows and primitives to add data from the multiple sources.
15. Could you explain the integration between IBM MQ and WebSphere ESB?
Ans:
WebSphere ESB and IBM MQ integration ensures a seamless message transmission across applications and systems.
16. Describe process of WebSphere’s edge server caching proxy.?
Ans:
WebSphere’s Edge Cache, also called IBM Edge Components Cache, reduces load on origin servers, guarantees material availability, and increases the performance of web applications by caching frequently accessed content at the edge of the network.
17. How message routing and content-based routing are handled by WebSphere ESB?
Ans:
The message routing features of WebSphere ESB make use of mediation primitives for rules and expressions, such as Filter, Router, and Dynamic Router.
18. Describe WebSphere ESB concept of dynamic endpoint resolution.?
Ans:
Service registry stores endpoint information for a dynamic resolution, ESB queries for most recent addresses during message processing. Dynamic resolution simplifies the reconfiguration of service endpoints without altering mediation logic, enabling quick adjustments in service locations or systems.
19. Explain Various Administrator Benefits Using Web Sphere?
Ans:
Web sphere almost reduces the work of server administrator as he can manage load on the servers efficiently without any hassles. It also gives flexibility to divide the load and applications among the different server farms.
20. Describe a service register in an ESB and how it works?
Ans:
ESB Service Register manages data on available services, endpoints, enabling dynamic discovery and resolution.
21. What does Websphere’s Sync function perform?
Ans:
A connected pool is the collection of pre-established connections to backend resources, reducing overhead and improving the application performance by keeping connections open and available for an instant usage.
22. What does connected pool mean?
Ans:
A connected pool is the collection of pre-established connections to backend resources, reducing overhead and improving the application performance by keeping connections open and available for an instant usage.
23. Describe variations between Websphere and Weblogic?
Ans:
| Aspect | IBM WebSphere | Oracle WebLogic | |
| Vendor |
IBM |
Oracle | |
| Licensing | Typically more expensive | Generally less expensive | |
| Java EE Version | Java EE (now Jakarta EE) | Java EE (now Jakarta EE) | |
| Administration |
WebLogic Server Administration Console |
WebLogic Server |
24. What is Ripple start?
Ans:
To restart the WAS cluster, use ripplestart. JVM is started after it has been stopped. By using ripplestart, you can make sure that only one JVM is unavailable at once, which prevents application outages.
25. What would do when a JVM is consuming 100% CPU & Memory on a server?
Ans:
First of all, identify which JVM has a high utilization. Take the thread dump of identified JVM for investigation and restart JVM as a workaround to cool down CPU/Memory.
26. What is node sync?
Ans:
IBM WAS stores an entire configuration in a central repository called the Master repository,and every node will have a local repository.
27. Does the application run without any issue if DMGR is down?
Ans:
Yes, DMGR down doesn’t impact an existing running application. However, if need to make any changes or deployment through the DMGR, then that would be affected./p>
28. How can I deploy an application in WebSphere?
Ans:
There are three possible ways to deploy.
- Hot deployment
- DMGR
- Scripts
29. Why does JVM come up automatically though stop/kill the process manually?
Ans:
There could be two things.
- Automatic restart is enabled for JVM which is default settings and available under the JVM>>Monitoring policy.
- If above is not the case then, there might be a script in cron, which checks for the process, and if not found then starts it.
30. Explain Network Deployment Feature Present In Was?
Ans:
It will eliminate the need to manage singletons and offer a hot recovery feature that eliminates the need to worry about GC collected singletons. The shared file system is a possible location for transaction logs.
31. What is a virtual host?
Ans:
Virtual host contains the multiple URLs (IP or FQDN based) on a single application and configuration is done through the WAS administrative console.
32. What is the functionality of Fan-in and Fan-out?
Ans:
Fan-out: can use the Fan Out primitive to fire output terminal once (with the input message) or fire an output terminal multiple times.
Fan-In: Fan-In is always partnered with the Fan-Out in the same flow and acts as decision point for when to continue flow execution.
33. How can I take WAS configuration backup without stopping the DMGR
Ans:
Go to the DMGR profile and bin folder Execute ./backupConfig.sh -nostop to take the backup
34. What are all Primitives used in Mediation?
Ans:
- Message Filter
- Type Filter
- Endpoint Lookup
- Service Invoke
- Fan-out
- Fan-in
35. How to check the installed WAS version?
Ans:
- WAS – Network Deployment
- WAS – Developers
- WAS – z/OS
- WAS – Hypervisor
- WAS – Express
36. How to check the installed WAS version?
Ans:
- Go to the profile and bin folder
- Execute ./versionInfo.sh
37. How do I know if JVM is up or not?
Ans:
There are multiple ways to confirm this.
- Login to the server and grep for JVM by ps -ef | grep vmname
- Check if can access the JVM URL
- Check if can telnet JVM URL and port
- Check if JVM port is listening on a server
38. What are log files generated by WebSphere?
Ans:
IBM WebSphere Application Server generates several log files to assist in troubleshooting and monitoring. Common logs include SystemOut.log and SystemErr.log for standard output and errors, trace.log for detailed tracing, ffdc logs for capturing failure data, native_stdout.log and native_stderr.
39. How to generate thread dump?
Ans:
There are three possible ways to generate a thread dump. Through DMGR console: Go to the Troubleshooting >>Select a JVM and click on Java core Kill -3 PID of JVM
40. Explain Caching Proxy Of Ibm Web Sphere Edge Sphere?
Ans:
A caching proxy can be configured in a forward direction or as a proxy. Content requested by the user is cached by edge before sending or adhering to a query.
41. What is garbage collection?
Ans:
Garbage collection (GC) in the context of IBM WebSphere, or any Java-based application server, refers to an automatic memory management process within the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
42. How do you disable security in WebSphere?
Ans:
Can disable security by executing the security off through wsadmin.sh. DMGR must be restarted after switching off security. Disabling security features can pose serious risks to a system and compromise its integrity.
43. How to enable verbose garbage collection?
Ans:
Verbose GC is not enabled by default; however, it can be activated if necessary by going to Servers >> Server Type >>WebSphere Application Server.
44. How can I set up WebSphere to launch automatically upon server reboot?
Ans:
IBM WebSphere automatically starts when a server reboots, and can use the operating system’s service management tools. The specific steps might vary based on the operating system we are using.
45. How to increase heap size of JVM?
Ans:
To increase JVM heap size, use -Xms for initial size and -Xmx for maximum size. For instance, java -Xms256m -Xmx1g -jar YourApp.jar sets the initial heap to 256MB and the maximum to 1GB. Adjust as needed.
46. Can Sync the node when the node agent is down?
Ans:
IBM WebSphere Application Server, node synchronization process typically involves Node Agent (nodeagent) communicating with the Deployment Manager to ensure that configuration and application changes are propagated to all nodes in the cell.
47. What’s the command to stop and start DMGR, Nodeagent &JVM?
Ans:
To stop
- JVM – stopServer.sh JVMNAME
- Nodeagent – stopNode.sh
- DMGR – stopManager.sh
To start
- JVM – startServer.sh JVMNAME
- Nodeagent – startNode.sh
- DMGR – startManager.sh
48. What is new in WAS 8.5.5?
Ans:
- On the high level:
- Java SE 7 support
- HPEL logging
- Inbuilt health management
- Liberty profile
- Intelligent routing
- Dynamic clustering
- JDBC 4.1 clustering
- Web 2.0 support
49. What does it mean by node federation?
Ans:
Node federation in the WebSphere Application Server refers to a process of integrating multiple WebSphere nodes into a single administrative domain.
50. What is FFDC?
Ans:
During the WebSphere runtime, errors and events are captured by FFDC (First Failure Data Capture). When contacting IBM support for assistance, they frequently inquire about FFDC data, which can be useful in analyzing the problem.
51. Which scripting language is default in WebSphere? JACL or Jython?
Ans:
WebSphere Application Server versions 6.x and earlier, default scripting language was JACL However, starting from the WebSphere Application Server version 7.0.Jython is a Python implementation for a Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
52. How can I apply a fix pack in WebSphere 8.5.x?
Ans:
- Stop WebSphere
- Download Fix Pack
- Extract Fix Pack
- Run Installation Manager
- Select the Fix Pack
- Review and Confirm
53. What is environmental support?
Ans:
Development supporting the following.
- CIT
- SIT
- UAT
- DEMO
- Pre-production
54. What is session affinity?
Ans:
Session affinity in the other word is persistence session. Having a session affinity allows a request to bind with a single JVM.
55. Can deploy more than one application in a single JVM?
Ans:
Yes, it is possible to deploy more than one application in a single JVM (Java Virtual Machine). In Java-based application servers, multiple applications can run within the same JVM.
56. Which database do you use with Websphere?
Ans:
Most of the organization uses the Oracle database but WebSphere supports the following database as well.
- DB2
- Oracle Database
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Sybase
57. How do I connect Web Server to WAS?
Ans:
Using plugin – this is a recommended method to install the WAS plugin on a web server.
Using ProxyPass – if using Apache and don’t want to use a plugin then can connect to WAS JVM by a ProxyPass directive.
58. Do I need a Web Server in front of WAS?
Ans:
The decision to use a web server in front of WebSphere Application Server (WAS) depends on specific requirements and complexity of deployment.
- Security
- Load Balancing
59. What is Cell?
Ans:
A cell is the logical group of nodes, which can have one or more nodes; clusters and all administered from a single administrative console.
60. What is the default session timeout for an administrative console?
Ans:
In IBM WebSphere Application Server (WAS), default session timeout for an administrative console is typically set to 60 minutes (or 3600 seconds).
61. What is a fix pack?
Ans:
A fix pack, short for “fix package,” is the collection of software updates, bug fixes, security patches, and enhancements provided by a software vendor to address issues in products.
62. What registry or repository is supported in WebSphere?
Ans:
- Federated repository
- Local operating system
- Standalone LDAP registry
- Standalone custom registry
63. What are shared libraries?
Ans:
Shared libraries, also known as dynamic-link libraries (DLLs) in Windows or shared objects (SO) in the Unix-based systems, are files that contain compiled code and data multiple programs can use simultaneously.
64. What is the context root?
Ans:
The context root refers to the base URL under which a web application is accessed. It represents the starting point in URL hierarchy for resources within the web application.
65. What is the WAS plugin configuration file name?
Ans:
In IBM WebSphere Application Server (WAS), configuration file for web server plugin is typically named plugin-cfg.xml.
66. Is it possible to modify the deployed application’s context root?
Ans:
Yes, it’s doable. To do this through the administrative console, go inside the application and click Context root for a web module to change the context root.
67. What is PMT?
Ans:
PMT stands for Profile Management Tool. The Profile Management Tool (PMT) is a graphical user interface (GUI) tool provided by IBM to create, manage, and modify WebSphere Application Server profiles.
68. How can I use Nikto Scanner to identify Web Server Vulnerabilities?
Ans:
Nikto is the popular open-source web server vulnerability scanner that can help to identify potential security issues in the web servers, including those running IBM WebSphere.
- Prerequisites
- Target Web Server
69. What is the difference between Application Server and Portal Server ?
Ans:
Application servers allow a web server to create a dynamic, personalized response to a client request, extending the web server’s capacity to handle Web application queries.
70. What steps involved in deploying themes and skins in websphere portal environments ?
Ans:
- Export a WebSphere wps.ear (Portal EAR) using ws admin.
- Use the EarExpander tool to expand an exported wps.ear file.
- Copy updated themes and skins into ../themes/html, ../skins/html folder.
71. How to find Web Server Vulnerabilities with Nikto Scanner ?
Ans:
- Install the portlet using the portal administration page using the Web Modules portlet.
- Install portlet using xmlaccess tool.
- Pre-deploy a portlet as standard EAR by installing the portlet WAR file in the WAS console and then registering the portlet using xmlaccess.
72. What is the purpose of the Export.xml and ExportRelease.xml XMLAccess configuration files? What is the distinction?
Ans:
Export.xml exports a complete portal configuration and is useful when transferring the configurations between development installations.
73. What are steps involved in building a release in WebSphere Portal ?
Ans:
If have a completely new installation of staging server and the production server:
- Install staging server, then install production server.
- Develop a release on a staging server.
- Build release on the staging server.
74. What is the purpose of the Release Builder tool in WebSphere Portal ?
Ans:
When staging subsequent WebSphere portal releases, ReleaseBuilder makes it possible to handle release configurations independently of user configurations. Artifacts and configurations must be transferred across the systems.
75. What are steps involved in editing WebSPhere Member Manager (wmm.xml) files on federated nodes ?
Ans:
On the primary node of a WebSphere Portal cluster, check out files using ./WPSconfig.sh check-out-wmm-cfg-files-from-dmgr task. Make any changes to Member Manager files. The files can be edited in a portal_server_root/wmm directory on WebSphere Portal node.
76. What is LDAP realm support and why would you want to use it?
Ans:
Horizontal partitioning, also known as grouping users from one or more LDAP trees of a single user registry, is made possible by a realm and makes them available to WebSphere Portal as a cohesive user population.
77. What is the Application group ?
Ans:
A database user registry can construct user groups with members (users or groups) that are part of the configured LDAP user registry by using the idea of application groups.
78. What portal resources are scoped for a virtual portal ?
Ans:
- Portal pages
- Portlet instances
- Portal Search Engine search services and search collections
79. What portal resources cant be separated for virtual portals ?
Ans:
- Themes and skins
- Vault segments and vault slots.s
- Supported clients and markups.s
- Composite applications and templates.s
- Policies
80. How do enable temporary and extended trace logging for WebSphere Portal ?
Ans:
Using the IBM WebSphere Application Server administrative console, the administrator portlet Enable Tracing, or the Enable Tracing portlet on a portal administration page, temporary traces can be set for a limited time.
81. What are different states of the syndication process ?
Ans:
Idle: No syndication is occurring.
Pending: A request has been made to the syndicator, but it has yet to initiate a request to the syndication application.
Queued: Although syndication is not yet active, the syndicator has submitted a request to the application for syndication.
Active: Syndication is an occurring between syndicator and subscriber.
Disabled: Syndication is currently disabled.
82. What are two types of rendering portlets ?
Ans:
Full Page Refresh (FPR) Portlets: FPR portlets, also known as a traditional or non-ajax portlets, trigger the full page refresh when any interaction occurs within portlet.
Partial Page Refresh (PPR) Portlets: PPR portlets, also known as the Ajax portlets, use asynchronous techniques to refresh only the portion of the web page without reloading the entire page.
83. Explain Web Sphere Commerce?
Ans:
IBM web sphere commerce has a single platform which offers the complete ecommerce solutions to developers. It can be productive if planning to do business with consumers, business and indirectly through the channel partners.
84. Explain Architecture Of Web Sphere?
Ans:
Web Sphere is a built on the three main components they are:
- Database
- J2EE application server
- A web server
The databases which it supports:
- DB2
- Oracle
- Cloudscape
85. What are t Application server in IBMWAS and supported web servers ?
Ans:
- IBM server
- Microsoft IIS
- Sun web server.
86. What portal resources can’t be seperated for virual portal ?
Ans:
- Order management
- A Web sphere commerce accelerator
- Analytical and business intelligence
- Open standards are Java, EJB, etc
87. Explain Ibm Web Sphere Edge Server?
Ans:
A web sphere edge server is used to enhance web-based system performance. It is a forwarding and proxy server.
88. Explain Extended Deployment?
Ans:
Web sphere application server extended deployment increases the functionality of the server in the two main areas they are manageability and performance.
89. Explain Security Features Present In Was?
Ans:
The Java EE security model serves as the foundation for most web sphere security models. Additionally, the operating system has an impact. The WAS also has capabilities for user permission and authentication.
90. Explain Asymmetric Clustering?
Ans:
Asymmetric clustering applications are primarily used in electronic trading systems employed in the banks. Among the characteristics are the ability to declare partitions during runtime and the typical one-cluster operation. Work specific to the particular can be routed to that cluster.






