
CICS, which stands for Customer Information Control System, is a software program engineered to streamline the operational activities of companies. Think of it as a pivotal nexus that fosters seamless communication among various applications. CICS serves as the underlying software infrastructure that connects vital systems within an organization. In the banking sector, CICS plays a pivotal role in integrating bank account with the ATM network.
1. What is CICS?
Ans:
The acronym for Customer Information Control System is CICS. It is a software program designed to assist companies in running their day-to-day operations. Consider it as a central hub that facilitates communication between different apps. CICS is the software that, for instance, links bank account to the ATM and manages the money withdrawal process when use one.
2. What are CICI’s primary duties?
Ans:
| Aspect | CICS Transaction Server (CICS TS) | CICS Web Support |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Functionality | Provides a runtime environment for executing transactional applications written in languages like COBOL, PL/I, C, and Assembler. | Enables CICS applications to interact with web browsers and serve web-based clients. |
| Protocol Support | Supports traditional communication protocols such as SNA (Systems Network Architecture) and TCP/IP for communication with terminals and other systems. | Supports modern web protocols such as HTTP and HTTPS for communication with web browsers and web-based clients. |
| Application Interface | Typically used for running traditional mainframe applications that handle transactions, batch processing, and backend processing tasks. | Allows CICS applications to expose their functionality as web services and integrate with web-based user interfaces. |
| Client Interaction | Primarily interacts with terminal-based or client/server applications, often using 3270 terminal emulation or proprietary communication protocols. | Interacts with web browsers and other web clients, providing HTML-based user interfaces and supporting technologies like JavaScript and CSS. |
3. Describe TCT and RCT.
Ans:
Terminal Control Table (TCT): Each terminal linked to the CICS system has its own set of data stored in this table. This data includes the type of terminal device, device address, and current status. CICS uses the TCT to control terminal activities, including screen display management and transaction routing to the appropriate terminal.
Resource Control Table (RCT): Files, programs, and transactions are only a few of the resources in the CICS system that are detailed in the RCT table. Name, location, status, and other characteristics of the resource are included in this information.
4. What constitutes a CICS system’s principal parts?
Ans:
A CICS system is made up of a number of essential parts that cooperate to handle system resources and execute transactions. Among the key elements are:
- CICS Region: Terminals, software, and files are all logically grouped as CICS resources in a CICS region. It is in charge of overseeing the system.
- Terminal Control Program (TCP): TCP is in charge of overseeing user terminal and CICS system communication. It supervises screen displays, performs input and output functions, and responds to user requests.
5. What distinguishes a program from a transaction of CICS?
Ans:
A collection of instructions written in a high-level language, such as PL/I or COBOL, is called a program in CICS. It is processed, connected, and run in the context of CICS. Software can carry out a specific function, such as creating a report or updating a file. Employ a range of strategies to converse with one another and share information. Once the task is finished, CICS releases the resources allotted to it and gives the transaction back control.
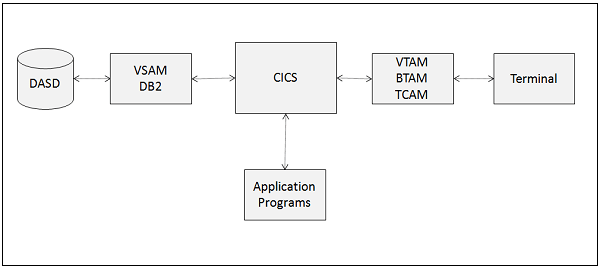
6. What CICS command is used to get the time and date right now?
Ans:
To obtain the current date and time, use the ASKTIME CICS command. The CICS time-of-day clock (EIBTIME) and date (EIBDATE) entries in the EIB are updated by ASKTIME. The task’s first start date and time are initially entered in these two parameters. CICS issues an MVS STACK macro and updates it by a local time difference in response to an ASKTIME instruction.
7. How are CICS transactions handled?
Ans:
- User starts the transaction: Through a terminal or other input device, a user sends a request to start a transaction. A transaction code linked to a program or group of programs that carry out the desired activity is entered by the user.
- Transaction identification and routing: After receiving a transaction request, the CICS system determines which program or programs to execute. Additionally, the system chooses the resources, including databases and files, that the transaction must access.
- Program execution: In order to complete the transaction, the CICS system loads and runs the necessary programs. The programs carry out the required action, like creating a report or changing a file.
8. How is the CICS Resource Definition Online (RDO) used, and what is its purpose?
Ans:
The CICS Resource Definition Online (RDO) is a facility within the Customer Information Control System (CICS) that allows administrators to define and manage resources dynamically while CICS is running. Its primary purpose is to streamline the administration of CICS resources such as files, programs, transactions, and terminals. RDO enables administrators to define these resources through an online interface, eliminating and restart CICS.
9. How to read a VSAM file in CICS?
Ans:
Typically consisting of four alphanumeric characters, a “TransID” is specified in the CICS system definition (CSD) file. A user selects the Transid of the program they wish to run when they start a transaction, and CICS then calls that application. In CICS, “TransIDs” are widely used to start transactions and carry out transaction programs. Program-to-program communication is another usage, where a program can transfer control to another program by utilizing.
10. How to define the word “deadlock”?
Ans:
A deadlock occurs when conflicting demands or interests prevent two or more parties from reaching an agreement or finding a solution. It illustrates a scenario in computing when multiple processes are waiting on resources that are shared by one another, making it impossible for them to proceed. A deadlock, in its simplest form, is an instance where additional action is not practical without outside support.
11. How does CICS Handle Errors?
Ans:
Return codes: Depending on whether an operation is successful or unsuccessful, CICS programs may return different return codes. The calling software can take corrective action by examining and handling these return codes appropriately.Condition handling: To handle abnormal termination (ABEND) circumstances that arise during runtime, CICS applications can utilize the EXEC CICS HANDLE ABEND command. This command enables the application to handle unexpected exceptions by taking corrective action.
12. What are the advantages of COMMAREA?
Ans:
- Data can be passed between applications running in the same CICS task using COMMAREA, which provides several benefits.
- It facilitates quick and easy data transfer between applications without requiring the overhead of writing information to a file or database.
- Its uniform data interchange format throughout programs guarantees dependable and consistent communication.
13. What kinds of DFHMDF are included in the CICS Set?
Ans:
A tool for defining maps in CICS applications is the CICS Map Definition Facility (DFHMDF). The numerous forms of DFHMDF serve distinct purposes in defining various CICS application elements, including files, programs, terminals, and maps. Every kind of DFHMDF is specifically designed to streamline the creation and administration of CICS applications, guaranteeing appropriate communication with users and resources.
14. What distinguishes CICS from other systems for processing transactions?
Ans:
- Flexibility in application: It offers excellent application versatility and supports a number of programming languages, including Assembler, C, C++, PL/I, COBOL, and C. Because of this adaptability, developers may create and manage complex systems that need to be written in many programming languages with ease.
- Scalability: It can manage both extensive and sophisticated settings for transaction processing and can grow to accommodate the needs of big businesses. It can manage millions of users and thousands of transactions per second.
- Reliability: With features like backup, recovery, and automated restart, it is a highly dependable transaction processing system. Errors and system breakdowns can be swiftly and effectively recovered from.
15. Describe some popular CICS features?
Ans:
- EXEC CICS LINK: This command allows to launch a program in the same CICS region from within another program.
- EXEC CICS XCTL: This command is used to move control within a task from one program to another.
- EXEC CICS RETURN: This command returns control to the caller program after another program has executed it.
- EXEC CICS SEND: This command is used to send information to a different terminal or application.
- EXEC CICS RECEIVE: This command is used to accept input from a terminal or other application.
16. How should every CICS program be categorized?
Ans:
CICS programs can be divided into the following categories:
- Non-discursive programs
- Interactive Programs
- Concealment-Based Programs
17. In a CICS program, how is data integrity ensured?
Ans:
Employ Sync Points for CICS: A sync point is a transactional checkpoint where CICS ensures that every modification made to the resources is either committed or reversed. By utilizing sync points, we can ensure that updates are only committed when they are all successful and are rolled back when any of them fail. This guarantees the consistency and dependability of the data.
18. How does the CICS Program Handle Dynamic Memory Allocation?
Ans:
Managing dynamic memory allocation in CICS programs requires the use of CICS dynamic storage allocation services. These services guarantee effective use of system resources by enabling programs to dynamically create and deallocate memory during runtime. CICS offers a range of dynamic storage allocation services to accommodate different programming requirements.
19. Enumerate a few strategies that use to maximize CICS performance.
Ans:
- To maximize performance, we can develop effective code by selecting suitable data structures and algorithms.
- Caching is an option, and Discuss RCT and TCT.
- The Terminal Control Table, or TCT for short, is an index of each terminal.
- The Resource Control Table, or RCT for short, is a list of DB2 plan names and the transaction ID.
20. What is an operating system’s CICS job priority?
Ans:
CICS, often known as a batch task, runs at a high priority in the operating system. CICS, also called a batch job, runs in the operating system middleware with high priority when an application requests it. It specializes in securely and swiftly handling high numbers of online transactions, guaranteeing effective transaction performance and management.
21. What is the difference between FCT and PCT?
Ans:
- Functional Communication Training, or FCT, is a behavioral intervention that teaches people how to communicate more effectively to replace difficult or inappropriate behaviors. Its main goal is to assist people in expressing their wants and requirements in ways that are acceptable to society.
- Parent-Child Training, or PCT, teaches parents useful skills to enhance their relationships with their kids. It usually consists of techniques for encouraging good relationships between parents and children, managing behavior, and communicating.
22. What does a CICS task entail?
Ans:
A CICS task is a specific CICS transaction that is executed once. This procedure begins when the enter key is pushed, and the key is input into the transaction. The program’s execution ends once it gives CICS back control. A unique license known as a CEMT (Conference of European Ministers of Transport) authorization enables companies to transport goods between nations within a group of nations known as CEMT countries.
23. What is meant by CEMT?
Ans:
- Master Terminal Transaction is referred to as CEMT. It’s an ID for a system transaction that asks what’s going on and modifies the resources’ state.
- Permission issued by the Conference of European Ministers of Transport, or CEMT, is a unique license that permits companies to transfer commodities between nations within a group of nations known as CEMT countries.
- It makes it simpler to transport items across borders without requiring a number of separate licenses, much like a passport for goods.
24. Define COMMAREA?
Ans:
COMMAREA serves as a temporary storage facility, it is frequently referred to as a communication area. It serves as a data transfer medium for several programs that are loaded by a single transaction or a group of related transactions. The name of a data area sometimes referred to as a communication area, where data is sent to a transaction or program is specified by the COMMAREA. It is a command-line option for XCTL, RETURN, and LINK.
25. What are a few commonly used CICS programs?
Ans:
Usually use the CICS programs Task Control, Storage Control, Terminal Control, and File Control in our different applications. Use the linkage options section to instruct EGL on how to construct the call statement correctly. Can set a callLink element’s type property to any of the following values in the linkage options section of the CICS environments: localCall.
26. How does SEND MAP MAPONLY differ from SEND MAP DATA ONLY?
Ans:
- SEND MAP MAPONLY: This command sends only the map definition not any associated data to the terminal. The screen layout is refreshed, but the fields stay blank and do not display any data from the software.
- SEND MAP DATA ONLY: This command only sends the data to the terminal; it does not convey the map definition. This is typically done when the map is already displayed and wish to update the field contents without making any layout changes.
27. What are the requirements for a CICS-integrated translator?
Ans:
Among the crucial criteria are a properly installed CICS environment, appropriate programming language support, availability of the necessary libraries and resources, and precise configuration settings. The specifications for the application program and the necessary data definitions must also be worked with by the CICS translator. Some components must exist for integration to work and be effective.
28. What is the primary purpose of the extra- and intra-partition TDQs?
Ans:
CICS includes several batch areas, and some datasets are mostly used as communication conduits between CICS and the batch regions that are not under its purview. Extra-partition TDQs support the previously described procedure. Conversely, intra-partition TDQs are lines of communication inside the CICS area. These channels have several queues.
29. Each map contains multiple fields, with three standard working storage fields in each. What are they?
Ans:
- In CICS, the three most often used working storage fields are output/input field, length, and attribute.
- These three fields are necessary in order to categorize the maps.
- CICS includes several batch areas, and some datasets are mostly used as communication conduits between CICS and the batch regions that are not under its purview.
- Extra-partition TDQs support the previously described procedure.
30. How does EIBCALEN fit into CICS?
Ans:
The value given in the LENGTH option of a LINK, XCTL, or RETURN command will always be included by EIBCALEN, regardless of the size of the program’s data area. It is imperative to confirm that the transaction accesses data in that specific region appropriately and that the number in EIBCALEN accurately matches the value provided in the program’s DSECT.
31. How does the error-handling system in CICS operate?
Ans:
Error management in CICS is managed by condition handlers, which also catch and handle other exceptions, such as abends (abnormal ends). Programs can use the HANDLE ABEND command to specify recovery steps. CICS logs errors for diagnostic and troubleshooting purposes. Additionally, applications might include special error-handling techniques to maintain data integrity and provide users feedback while a transaction is in progress.
32. What’s the key difference between the INTO and SET options in the EXEC CICS RECEIVE MAP command?
Ans:
The primary distinction between the INTO and SET options of the EXEC CICS RECEIVE MAP command lies in how they handle the data received from a terminal. When using the INTO option, the received map data is copied directly into a user-defined data area specified by the INTO option. This method involves physically moving the data from the CICS internal storage to the user-defined storage area.
33. What is the Executive Interface Block (EIB), and what are its key features?
Ans:
An EIB stays connected to a task until it is finished. Throughout the assignment, the EIB does not change as it moves through the program. We can access EIB fields by examining COBOL program in reading mode. The CICS loads the Execute Interface Block (EIB), a control block, automatically for each program. The EIB is specific to a job and is there for the whole task lifecycle. It includes a collection of task-related system-related data.
34. What’s the point of a “TransID,” and where is the definition found?
Ans:
Each CICS transaction is given a unique code known as a TransID, or Transaction Identifier, which makes processing and identification easier. Its main goals are to efficiently handle user interactions and direct user requests to the relevant transaction processes. The CICS resource definition tables describe TransIDs and include information on a variety of features, including associated programs, input/output requirements, and transaction logic.
35. What distinguishes TCT from RCT in particular?
Ans:
In CICS, there are two types of control tables: terminal control table (TCT) and resource control table (RCT). To make user interactions easier, TCT controls terminal parameters including communication settings and device type. Databases and files related to CICS transactions are managed by RCT. RCT prioritizes resource allocation and control, assuring effective operation inside the CICS environment, whereas TCT concentrates on terminal management.
36. In CICS, how may one access a CSAM file?
Ans:
Use particular CICS file control commands to open a CSAM (Component Sequential Access Method) file in CICS. Make sure the file is defined in the CICS resource definitions first. Next, operate on the file using program’s READ, WRITE, or DELETE commands. Make sure the error is correctly handled and implemented to manage any I/O errors during file access.
37. Explain MRO.
Ans:
The term multi-region operation is MRO. It is a system that permits data sharing, communication, and resources between the same CPU’s CICS address areas.”MRO is an acronym for maintenance, repair, and operations, or overhaul in certain situations. It encompasses all activities required for facility maintenance and to maintain the production process without interfering with it directly.
38. What does CICS stand for in full, and why is it used?
Ans:
- CICS, which stands for Customer Information Control System.
- This kind of system control software oversees IBM management’s online transactions and monitors the company’s interactions.
- IBM offers two mainframe operating systems: batch and time-sharing.
- A single request is often used to start CICS processing, which may also impact one or more objects.
39. What does PPT refer to in CICS, and what information does it contain?
Ans:
The acronym for Processing Programming Table is PPT. Within the CICS, PowerPoint includes crucial data such as the name of the program, Mapset names, task use counter, language, size, primary storage location, map, and so forth. The Processing Programming Table (PPT) in CICS contains data that includes program names, Mapset names, task utilization counters, sizes, languages, and primary storage addresses, among other things.
40. What is CICS main feature?
Ans:
Online application development and execution are the main uses of CICS. Its primary goal is to make databases and the files they are connected with extremely accessible. CICS ensures effective communication by facilitating organized data transmission and reception. Additionally, it provides a communication channel through the terminal, enabling users to easily engage with data and apps.
41. In CICS, what separates a temporary dataset from a permanent dataset?
Ans:
In CICS, transient datasets are short-lived, existing just during a transaction, and are commonly employed for intermediate data storage. On the other hand, permanent datasets store data that must be kept for access in the future and continue after the transaction has ended. This distinction has an impact on application architecture by managing, retrieving, and deleting data in the CICS environment.
42. In CICS, what is the distinction between a call and a link?
Ans:
In CICS, the primary distinction between a call and a link is that, in the case of a call, any modifications made to the called program also require the calling program to be compiled. When it comes to a link, it’s not necessary. When using LINK, the program can be called in the same region, or it can be statically or dynamically routed to another area. CICS has little interaction with a CALL, and the processing remains in the exact location.
43. In CICS, how are transactions carried out?
Ans:
In CICS, transactions are carried out either by application software or by a user entering a command at a terminal. Using the TransID as a guide, the CICS dispatcher routes the request and initiates the related transaction program. After it is started, CICS handles input/output processing, resource management, program execution control, and control to make sure transactions are completed.
44. In CICS, what distinguishes a program from a transaction?
Ans:
A program in CICS is a collection of executable code created to carry out particular operations, including logic processing or data manipulation. On the other hand, a transaction is an operational instance that, upon receiving input from the user or system, calls and runs a program. As a result, although a program describes behavior, a transaction is an instance of that behavior.
45. Which parts constitute the core of a CICS system?
Ans:
Transaction programs (TPs), which manage application logic, transient and permanent datasets for data management, control tables for system setup, and communication facilities for inter-region connectivity, are some of the essential parts of a CICS system. It also consists of the CICS region, which holds all operational procedures and allows reliable transaction processing and resource management.
46. In CICS, what is meant by the term “BMS”?
Ans:
- The abbreviation for BMS is Basic Mapping Support. BMS is made available by CICS to specify and format the screen.
- The MAP is the screen defined by the BMS. The Mapset is a compilation of all the screens.
- An application programming interface (API) that connects terminal devices with CICS programs is known as essential mapping support or BMS.
- For this purpose, there are two sets of commands: BMS and COM. Terminal control describes the other one. In numerous applications, BMS offers innumerable benefits.
47. Which CICS control tables are crucial?
Ans:
Certain IBM-supplied CICS control tables must be updated with the application information for CICS application programs to be executed successfully. A list of several significant control tables is provided below: TCT is an abbreviation for Table of Terminal Control. It is required to be entered when logging into a CICS terminal. The terminal IDs associated with the active CICS area are listed in this table.
48. How is COMMAREA used to achieve its objectives?
Ans:
COMMAREA is a term frequently used to refer to a communication area. Information is exchanged or transmitted between various programs within this data space. The main purpose of this temporary storage space primarily utilized as a mean to transport data between different programs that are loaded by a single transaction or by a collection of linked transactions.
49. What are the core services that CICS offers?
Ans:
The primary capabilities that CICS offers are database access for data storage and retrieval, communication services to facilitate interaction with other systems, resource management to efficiently handle system resources, and transaction management to coordinate program execution. Together, these features enable high-volume transaction processing, guaranteeing performance and dependability while handling intricate application contexts.
50. What distinguishes a system-controlled task in CICS from a program-controlled task?
Ans:
The application program starts and controls a program-controlled task, which enables customized logic and flow control according to particular needs. On the other hand, CICS manages a system-controlled task completely, taking care of transaction flow and resource allocation automatically. This difference affects how tasks are carried out, with program-controlled tasks providing greater adaptability.
51. What tactics can be used to improve the performance of CICS?
Ans:
Use techniques like optimizing application design to reduce resource contention and I/O activities to improve CICS performance. Employ performance monitoring instruments to pinpoint obstructions and adjust parameters. Utilize load balancing throughout CICS zones to effectively manage transactions, and think about using caching techniques to shorten database access times.
52. In CICS, what is a transaction, and what role do transactions play within the system?
Ans:
- A transaction initiates or completes a specific task. It serves as a unique identification.
- A transaction can be started concurrently from several systems but from different systems.
- A transaction is a four-character entry type that prohibits any transaction name duplication.
- A transaction can map to the program one to one or multiple times. When the transaction trigger occurs, it is carried out.
53. Which varieties of DFHMDF are there in the CICS set?
Ans:
- POS: The position in the CICS is abbreviated as POS. The row and column positions in the field with respect to the upper left corner of the map position are indicated by the POS parameter.
- Attrib: The field attribute’s abbreviation is ATTRB. The BMS usually uses the default values for the auto-skip protection, average intensity, and the modified value.
- Initial: The BMS does not require the initial type either. It is only utilized in the title and label fields, which in the BMS already have a fixed value.
54. What are some of the critical fields in the CICS EIB block named?
Ans:
The CICS Execute Interface Block (EIB) contains several critical fields that provide vital information about the current task and the execution environment within a CICS program. Some of the key fields include EIBDATE and EIBTIME, which record the date and time the task started, essential for timestamping and logging purposes. EIBTRMID stores the terminal identifier, which is useful for identifying the terminal from which the transaction originated.
55. What does MDT mean? What functions do FRSET and FSET serve in MDT?
Ans:
- Modified Data Tag is what the abbreviation MDT stands for. During an input operation, MDT is employed. If the field on the screen is changed,
- For Flag Reset, use FRSET. It is employed to turn off the modified data tag in the attribute bytes for each field on the screen and to reset MDT.
- A changed data tag that has been turned on, either by the user or the program, remains on until it is expressly turned off, even after many screen transmissions. Conversely, FSET activates the updated data tag.
56. What category does a CICS program fall under?
Ans:
- Talk-based programs
- Not in dialogue
- Programs ostensibly conversational
57. What does the phrase “conversational programs” mean?
Ans:
Conversational programs require human intervention to execute. Put another way, a conversational program asks the user for input before processing the data and displaying the results on the screen. Sending messages to the terminals and getting responses from the users who are actively using them is the primary function of the conversational programs.
58. What does the phrase “non-conversational programs” mean?
Ans:
Applications that don’t require human input to run are known as non-conversational applications. When we begin the execution of the program, it has access to all necessary inputs. Stated differently, non-conversational applications are those that are utilized to display reports or messages. Non-conventional programs operate in batch mode and are very similar to batch programs. Their primary function is to periodically display a sequence on the screen.
59. How is the allocation of dynamic memory in a CICS program managed?
Ans:
Programs can request memory while they are running in a CICS program by using the GETMAIN command, which controls dynamic memory allocation. CICS manages memory allocation and deallocation, guaranteeing effective resource utilization. Using the FREEMAN command to correctly free memory is crucial after preventing memory and maintaining system performance.
60. What steps can be taken in a CICS application to guarantee data integrity?
Ans:
Use task management units and the COMMIT and ROLLBACK commands to maintain transaction atomicity to guarantee data integrity in CICS applications. Use appropriate locking techniques to stop data corruption when many users are accessed concurrently. Furthermore, incorporate error handling and validation checks into the design of apps to detect discrepancies early on, guarantee proper data processing, and help recover from mistakes.
61. CICS control tables can be accessed by which CICS service transaction?
Ans:
Transaction CSN1 is the CICS service transaction that provides access to CICS control tables. Through this transaction, users can see and edit several control tables, including crucial resource definitions and configuration files required for CICS to operate correctly. To maintain the overall dependability of the CICS environment and efficiently monitor system performance, system administrators need access to these vital data.
62. What does the phrase pseudo-conversational programs mean?
Ans:
Conversation-emulating programs respond to the user’s actions or circumstances. As a subset of conversational programs, they can only be called or launched by other programs. Interaction requires user activities, such as clicking buttons or pressing Enter. These programs are also known as event-based programs, which highlights how reactive they are to user input and how they are made to offer a responsive experience.
63. Describe the process for initiating a CICS transaction.
Ans:
- TCP, or transmission control protocol, generates entries in TCT, or total cost technology, based on data stored in TIOA or terminal input/output.
- After obtaining the transaction identity from TIOA, the Task Control Program (KCP) verifies that it is present in PCT.
- Task Control Area (TCA), where KCP generates task control data, is acquired by SCP.
- Next, KCP searches for the application.
- Programs listed in PPT that are loaded from PCT.
64. What is MDT specifically?
Ans:
- The character of one attribute is retained.
- Its two values are 1. and 0.
- The terminal operator has not modified this field if it is 0.
- The terminal operator has modified this field if the value is 1.
- Data from the field is sent from the terminal to the host computer if MDT is set to 1.
65. Is Quasi-reentrancy defined?
Ans:
Each EXEC CICS instruction precedes and follows a quasi-reentrant program that enters and exits in the same state. A program is deemed quasi-reentrant upon transfer of control if it retains the same state at the entrance and before and after every EXEC CICS command. For the program to be able to manage concurrent executions without experiencing problems with data integrity, this consistency is essential.
66. What variations of DFHMDF are there in the CICS?
Ans:
- POS: The acronym for “position” in the CICS is POS. The row and column positions in the field surrounding the upper left corner of the map are indicated by the POS parameter.
- Length: The length invariably indicates how many characters are in the field. Each length will require one more column than its length value as the attribute bytes are absent from length.
- ATTRIB: The field attribute is shortened to ATTRIB. Most of the time, the field attribute is not required in the Basic Mapping Support (BMS). This is a result of the BMS constantly using auto-skip protection, average intensity, and personalized tag default settings.
- Initial: An initial is also not necessary in the BMS. The only initial that can be used is the one that already has a constant value in the BMS for the label and title fields.
67. In the CICS, what are the main uses for the transaction?
Ans:
A transaction is a unique identifier that is mainly utilized to carry out or start a specific task. Four-character input is referred to as a transaction, and duplication is not allowed, especially in transaction names. Multiple systems may simultaneously initiate a transaction, but not from the same system. Most of the time, a transaction will have one or more mappings to the program that need to be executed when the transaction trigger occurs.
68. What is the primary purpose of TDQs, both extra- and intra-partition?
Ans:
There are several batch areas in CICS, and some datasets are mainly used as a means of communication between batch regions that are not within CICS’s control. Extra-partition TDQs enable contact with other regions, whilst intra-partition TDQs act as channels for communication within the CICS area. The numerous queue structure of these channels facilitates effective data transfer and interaction between batch operations and CICS applications.
69. Describe re-entry in terms of CICS.
Ans:
After the operating system interrupts itself, it performs other OS activities, including OS chores of the same program. A reentrant program does not change itself to reenter itself and continue processing. It is a “reusable” or “reentrancy” application. In the context of CICS, a reentrant program is a quasi-reentrant program. To state it differently, A quasi-reentrant program is a CICS program that stays true to itself, allowing it to return and carry on processing.
70. Why are CICS translators needed?
Ans:
- When used from the compiler option, the Integrated CICS translator is necessary for the COBOL compiler to operate.
- The compiler uses the integrated CICS translator to communicate with CICS statements in the source program.
- After modifying the CICS statements, the translator returns and instructs the compiler on what native language statements should be generated.
- In contrast to a Separate translator, Integrated Translator does not impose any limitations on the management of native Cobol statements in the Source Program or CICS statements.
71. What do the Skipper and Stopper fields’ attribute values mean?
Ans:
The Skipper field in CICS helps manage screen flow by indicating how many lines to skip before processing output. The Stopper field defines the end of a data block or display region by indicating where output processing should stop. These parameters are essential for controlling screen layouts and guaranteeing that CICS applications have understandable and intuitive user interfaces.
72. What distinguishes the command EXEC CICS XCTL from the command EXEC CICS LINK?
Ans:
The XTCL command transfers control to an application that resides at the same logical level and does not expect to control it back, whereas the LINK command passes the power to an application program to the next logical level and expects control back. One of the definitions of the field CHG is the picture, which tells the BMS what kinds of images are often used to produce the fields.
73. What function does the Table of Terminal Control provide?
Ans:
For terminal devices connected to the CICS region, the Terminal Control Table (TCT) in CICS specifies characteristics and control settings. It controls parameters like user capabilities, communication protocols, and terminal types. The TCT enables consistent user interactions, guaranteeing accurate transaction processing based on the attributes of the terminal being used, thus enhancing the overall user experience.
74. What is meant by the phrase “multi-region operation”?
Ans:
The term “multi-region operation” describes CICS’s capacity to run several CICS regions simultaneously, providing load balancing and high availability. Each region can process transactions independently while sharing resources and data. Because failures in one zone may be isolated without affecting others, this architecture enhances system resilience and performance and maintains service availability in critical contexts.
75. What does “reentry into the program” mean?
Ans:
The capacity of a program to run repeatedly simultaneously without causing data corruption or inconsistencies is known as program reentrance. This is accomplished by making sure that shared data is only accessible through regulated methods, like temporary storage, or is read-only. In multitasking settings like CICS, where many transactions may invoke the same resource, reentrant programs are crucial.
76. What role do extrapartition and intrapartition TDQs play?
Ans:
Within a single CICS area, there are intrapartition TDQs (Transient Data Queues) that facilitate effective data processing and transmission. On the other hand, extra partition TDQs cover several CICS regions, allowing data sharing and inter-regional connectivity. This distinction affects design choices and performance improvements in multi-region CICS setups, making it important for applications that call for coordination across regions.
77. What are the constraints of CCOMMAREA, and what is the rationale behind them?
Ans:
The 32 KB size limit of CCOMMAREA limits the amount of data that may be sent between programs. The purpose of this restriction is to prevent larger data structures from causing more overhead and slower processing times, which would compromise CICS’s ability to manage resources and communicate effectively. Respecting this boundary guarantees peak efficiency and dependability.
78. Can dynamic calls be used in CICS?
Ans:
Indeed. The calling program must utilize the CALL identifier, and the call function must be specified in a PPT in order to use dynamic calls in CICS. But have to make sure the COB PATH environment variable is set correctly. Additionally, need to confirm that the called module is named correctly.
79. What is meant by “quasi-reentrant” and “reentrant”?
Ans:
Programs that are “reentrant” can be securely called by numerous tasks at once without sharing any data that might cause problems. Conversely, “quasi-reentrant” systems are capable of supporting several concurrent executions, although they could need exclusive access to specific data locations. Designing reliable CICS programs that guarantee data integrity in multi-user settings requires an understanding of these differences.
80. What is CICS in its entirety? What is its primary purpose?
Ans:
- The phrase Customer Information Control System is abbreviated as CICS.
- It is a system control program that oversees IBM management’s online transactions.
- It evaluates IBM’s communications as well. IBM’s mainframe operating system mainly uses batch and time-sharing.
- CICS is a processing type that was primarily developed using a single request that one or more objects can fulfill.
81. Which capability makes it easier for CICS and DB2 to connect?
Ans:
The CICS-DB2 interface is the feature that joins CICS with DB2. Through this interface, CICS programs can run SQL queries against DB2 databases, facilitating the retrieval and manipulation of data inside of CICS transactions. By utilizing DB2’s robust database, the integration facilitates effective data processing and transaction management, improving the functionality of CICS applications.
82. Which AID will the ANYKEY option of the HANDLE AID command not accept?
Ans:
The PA1 key will not be recognized when using the ANYKEY option of the HANDLE AID command in CICS. This is important to keep in mind because the PA1 key is typically used for a specific purpose, such as initiating or terminating an operation. Eliminating it from the ANYKEY option helps programs that require key input handling from exhibiting unexpected behavior.
83. In what way would START be distinguished from XTCL?
Ans:
In the CICS system, the START command is especially useful for starting a new task. It is made especially for interval management, making sure that things are planned out and done correctly. The XCTL command is mainly used for program control, but it may also be used to transfer control to another program running within the same job, which makes resource and process management more effective.
84. How may a transaction be terminated?
Ans:
To terminate a transaction, release associated resources, and end the transaction process, use the CICS ENDTRANS command. Alternatively, can use the TERMINATE command to end the transaction programmatically. Making sure that all cleanup tasks are finished before terminating is vital. To maintain data integrity and system stability during transaction processing.
85. What are the CICS commands ENQ and DEQ used for?
Ans:
Data integrity is ensured in CICS by locking a resource using the ENQ (enqueue) command, which stops concurrent access from other transactions. On the other hand, the lock is released by the DEQ (dequeue) command, granting access to the resource for additional transactions. When used in tandem, these commands efficiently handle resource contention, preserving ordered access and guarding against data corruption in contexts with multiple users.
86. Under what circumstances does CICS require a NEWCOPY?
Ans:
When a program or transaction specification needs to be updated without pausing the CICS area as a whole, a NEWCOPY is needed in CICS. Updates to the resource setups, data definitions, and program logic fall under this category. Running a NEWCOPY enables the program’s upgraded version to be utilized while minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous service availability.
87. What does it mean to set the BMS length of a field to 0?
Ans:
It is indicated that a field is hidden or not displayed on the screen when its BMS length is set to 0. This feature, which permits changes to program logic without notifying the user, is frequently used to manage control flow. This feature ensures more seamless application-user interaction in CICS systems by simplifying user interface design and improving data flow control.
88. In CICS, how would tasks be distinguished from transactions?
Ans:
In the context of CICS, a task and a transaction are primarily distinguished by the fact that a task needs user initiative, but a transaction can be initiated by numerous users at once. Multiple people can start the same transaction at the same time, which makes processing speedy. Nonetheless, a job is usually started by a single user at a time, highlighting the interpersonal communication required for task completion in the CICS context.
89. Which CICS programs are some of the most popular ones?
Ans:
- Programs for Storage Control
- Programs for task control and file control
- Program for Terminal Control
90. What does the phrase “mapset” mean?
Ans:
A load module made up of linked and altered maps that specify how users are shown data is called a map set. To manage these maps, a Program Processing Table (PPT) needs to be provided. One to seven characters can be used in a name. We call the configuration of the displays a map. For efficient functioning, maps must be made for both physical (mostly used by CICS) and logical or symbolic (mainly used by application programs) purposes.






