
- Introduction to DApps
- Key Characteristics of DApps
- How DApps Work
- DApps vs Traditional Apps
- Types of DApps
- Benefits of DApps
- Challenges and Limitations
- Conclusion
Introduction to DApps
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain and decentralized technology, the term DApp, short for Decentralized Application, has become a central concept driving innovation. Unlike traditional applications that rely on centralized servers and authorities to operate, DApps run on blockchain networks, which are distributed and maintained by a community of nodes. This fundamental difference makes DApps autonomous, transparent, and resistant to censorship or single points of failure. Because their code and data reside on a decentralized ledger, DApps ensure that no single entity controls the application, enhancing security and trust among users. DApps cover a wide range of use cases and industries. Financial services are among the most prominent, with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms enabling lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management without intermediaries, driving demand for Blockchain Training to navigate and leverage these technologies effectively. Beyond finance, DApps have expanded into gaming, where players can truly own digital assets; social media, providing censorship-resistant communication channels; file storage solutions that protect privacy and data integrity; and governance systems that allow token holders to participate in decision-making processes transparently. Each of these applications leverages the benefits of decentralization to solve problems inherent in traditional centralized models. As blockchain ecosystems continue to mature, the development and adoption of DApps are accelerating. This growth is supported by advances in smart contract platforms such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana, which provide the infrastructure to build increasingly complex and scalable applications. With their ability to promote user empowerment and reshape digital interactions, DApps are becoming key players in driving decentralization across diverse sectors, paving the way for new business models and digital experiences.
Interested in Obtaining Your PMP Certificate? View The PMP Certification Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Key Characteristics of DApps
To be considered a true decentralized application, or DApp, an application must meet several essential criteria that set it apart from traditional centralized apps. First and foremost, a DApp operates on a decentralized blockchain network rather than relying on centralized servers. This ensures that the application’s data and logic are distributed across many nodes, reducing the risk of censorship, downtime, or control by a single entity. The application must also be open-source, allowing anyone to inspect, verify, and contribute to the codebase, which promotes transparency and trust within the community, exemplifying What is Blockchain Technology & How Does It Work. Another important characteristic of true DApps is the use of smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code and deployed on the blockchain. Smart contracts automate key functions within the app, eliminating the need for intermediaries and ensuring that transactions and processes are executed exactly as programmed. This automation increases security, reliability, and efficiency. A significant number of DApps also issue their own native tokens. These tokens serve multiple purposes such as incentivizing user participation, enabling decentralized governance, and powering the internal economy of the app. For example, tokens might be used to reward users who contribute valuable resources or content, or to give holders voting rights on future updates and decisions affecting the platform.
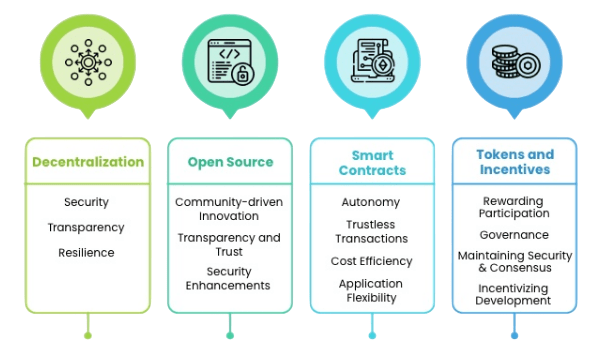
Tokenization creates economic incentives aligned with the interests of the community, encouraging active engagement and long-term sustainability. In summary, a true DApp combines decentralization, open-source development, smart contract functionality, and often tokenization to offer a transparent, autonomous, and community-driven application experience that challenges the norms of traditional software.
How DApps Work
- Decentralized Network: DApps run on blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, which consist of many distributed nodes. These nodes collectively maintain the ledger and execute the application logic without relying on a central server.
- Smart Contracts: The core functionality of DApps is implemented through smart contracts self-executing code stored on the blockchain. Smart contracts automatically enforce rules and conditions, enabling trustless and transparent transactions.
- Frontend Interface: While the backend logic lives on the blockchain, DApps usually have a user-friendly frontend interface accessible via web browsers or mobile apps, making it essential to learn How to Start a Career in Blockchain Technology.
- Token Integration: Many DApps issue their own native tokens used to incentivize users, facilitate governance, or fuel the app’s internal economy. Tokens are transferred and managed through smart contracts.
- User Wallets: Users access DApps via cryptocurrency wallets such as MetaMask or Trust Wallet, which manage private keys and enable secure transaction signing. Wallets connect users to the blockchain without exposing sensitive data.
- Consensus Mechanism: Transactions and smart contract executions on DApps are validated and recorded through the blockchain’s consensus protocol, ensuring security and immutability of data.
- Open Source and Transparency: Most DApps are open source, allowing developers and users to audit the code. This transparency fosters trust and community involvement, promoting rapid innovation and security improvements.
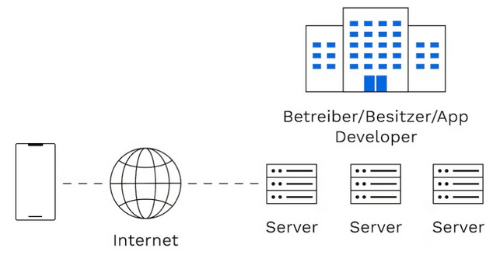
- Centralization vs Decentralization: Traditional apps are hosted on centralized servers controlled by a single entity, while DApps run on decentralized blockchain networks managed by multiple nodes, reducing reliance on any one party.
- Control and Ownership: DApps give users more control, often making users stakeholders in the ecosystem, increasing the relevance of Blockchain Training for understanding and building these decentralized systems.
- Censorship Resistance: Traditional apps can be censored or shut down by authorities or companies. DApps are censorship-resistant because no single entity can easily alter or remove the application from the blockchain.
- Transparency: DApps operate with open-source smart contracts, allowing anyone to verify the rules and transactions. Traditional apps generally operate behind closed doors with proprietary code.
- Security: DApps benefit from blockchain’s cryptographic security and immutability, making data tampering difficult. Traditional apps can be vulnerable to hacks if centralized servers are compromised.
- Performance and Scalability: Traditional apps usually offer faster response times and handle more users efficiently, while many DApps face challenges related to blockchain scalability and higher transaction costs.
- User Experience: Traditional apps often provide more polished and user-friendly interfaces. DApps, being newer and more complex, sometimes struggle with usability, requiring users to manage wallets and understand blockchain concepts.
- Decentralization: DApps run on blockchain networks without a central authority, reducing risks of censorship, downtime, and single points of failure, ensuring continuous availability.
- Transparency: The code and transactions of DApps are often open source and recorded on public ledgers, allowing anyone to audit, verify, and trust the application’s operations.
- User Control: Users maintain control over their data and assets through private keys and wallets, minimizing reliance on intermediaries and reducing risks of data misuse.
- Security: DApps benefit from the cryptographic security of blockchain, making them highly resistant to hacking, fraud, and data tampering, which underscores the importance of Blockchain Security.
- Incentivization: Many DApps integrate native tokens to incentivize user participation, governance, and contribution, creating active and engaged communities.
- Censorship Resistance: Because no single entity controls DApps, they are less vulnerable to government or corporate censorship, preserving freedom of access and expression.
- Innovation: The open-source and composable nature of DApps enables developers to build on existing protocols, rapidly creating new and diverse applications across industries.
To Earn Your PMP Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s PMP Certification Training Today!
DApps vs Traditional Apps
Types of DApps
DApps cover a wide range of industries and use cases, with decentralized file and data storage being one of the most important categories. Traditional file storage relies heavily on centralized servers controlled by companies, which can raise concerns about privacy, censorship, data loss, and security vulnerabilities. Decentralized storage DApps address these issues by distributing data across a network of nodes, ensuring greater resilience, transparency, and user control over their information. Two prominent examples of decentralized storage DApps are Filecoin and Arweave. Filecoin operates as a decentralized marketplace where users can rent out unused hard drive space to store files, and in return, earn Filecoin tokens. This incentivizes participants to contribute storage resources and creates a robust and scalable network for data storage that is resistant to censorship and centralized control, showcasing the Power of Tron Blockchain. Users benefit from enhanced security and privacy, as their data is encrypted and fragmented across multiple locations. Arweave offers a slightly different approach, focusing on permanent and immutable data storage through its “permaweb” concept. This allows users to store data and applications indefinitely, with a one-time upfront payment covering perpetual storage fees. Arweave’s blockchain-based storage provides a new way to preserve important records, websites, and digital content without the risk of deletion or tampering. These decentralized storage DApps exemplify how blockchain technology is transforming industries by providing alternatives to traditional centralized infrastructure. By distributing data and incentivizing network participation, they increase reliability and empower users with greater ownership of their digital assets. As demand for secure and censorship-resistant storage grows, decentralized file storage DApps like Filecoin and Arweave are poised to play a critical role in the future of data management.
Want to Pursue a PMP Master’s Degree? Enroll For PMP Master Program Training Course Today!
Benefits of DApps
Challenges and Limitations
While decentralized applications (DApps) hold great promise for transforming industries by offering transparency, security, and user control, they are still in a relatively early stage of development and face several significant challenges. One major hurdle is the regulatory uncertainty surrounding many DApps, particularly those operating in the financial sector. Since these applications often deal with digital assets, lending, trading, and investments without traditional intermediaries, they exist in legal gray areas. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are still formulating how to apply existing laws to these new technologies, and evolving regulations could impose compliance requirements or restrictions that impact the growth and operation of many DApps. This uncertainty creates risks for developers and users alike, making legal clarity a critical factor for widespread adoption in the context of Industries That Blockchain Will Disrupt in Future. From a technical perspective, building a robust DApp is complex and demands expertise in multiple areas. Developers need a strong understanding of blockchain technology and smart contract programming, as well as experience with frontend frameworks and decentralized system architecture. Unlike traditional applications, DApps must handle issues such as transaction costs (gas fees), network latency, and data immutability, which can affect user experience and scalability. Furthermore, the immutability of smart contracts means bugs or vulnerabilities can have serious consequences, necessitating rigorous testing and auditing. Usability and scalability also remain challenges. Many DApps have interfaces and workflows that can be confusing to new users, limiting mainstream adoption. Scalability solutions are still evolving to handle large volumes of users and transactions efficiently. Despite these hurdles, the ongoing innovation and growing ecosystem around DApps suggest they will continue to mature and overcome these obstacles, shaping the future of decentralized digital services.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s PMP Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
Decentralized applications, or DApps, are changing how we think about software, digital ownership, and online interactions. Unlike traditional applications that depend on centralized servers and authorities, DApps run on blockchain networks, giving users direct control over their data and digital assets. This shift empowers individuals by removing intermediaries who usually manage or monetize user information, creating a more transparent and fair online environment. By enabling decentralized governance and token-based incentives, DApps transform users from passive consumers into active participants who help shape the platforms they use. Although the benefits are clear, challenges still exist in areas like user experience, scalability, and regulation, highlighting the importance of Blockchain Training to address and overcome these issues. Many DApps have complicated interfaces that can discourage widespread use. Additionally, blockchain networks face difficulties in processing a high number of transactions quickly and affordably. Legal uncertainty around decentralized platforms, especially in finance, creates risks that might affect their growth. Nevertheless, ongoing improvements in blockchain technology, scaling solutions, and clearer regulations are steadily addressing these problems. Whether you are a developer creating the next generation of decentralized software, an investor exploring new opportunities, or simply an interested internet user, understanding DApps is important for grasping the larger Web3 movement. DApps are more than just apps. They represent a new way of designing digital ecosystems. From banking and gaming to social media and governance, decentralized applications will change many aspects of daily life. As blockchain technology gains wider use, DApps will play a major role in shaping the future of the internet by offering more freedom, security, and opportunity to users everywhere.




