- Introduction to Blockchain
- Why Understanding Blockchain Types Matters
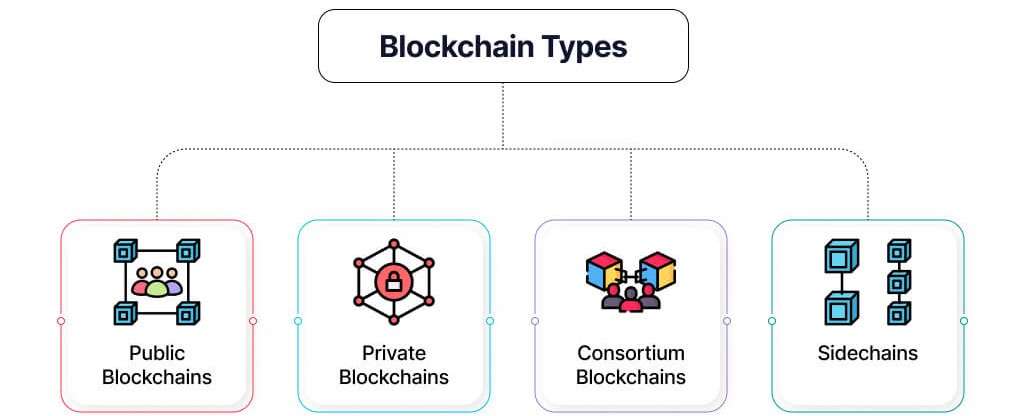
- Public Blockchains
- Private Blockchains
- Consortium (Federated) Blockchains
- Hybrid Blockchains
- Comparison Table: Blockchain Types at a Glance
- Use Cases Based on Blockchain Types
Introduction to Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, making it secure, transparent, and tamper-proof. Originally developed as the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain technology has evolved far beyond digital currencies. There are different types of blockchain, including public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchains, each designed to meet varying needs of transparency, control, and scalability. One of the core advantages of blockchain is real-time transaction tracking, allowing users to verify data and ownership without intermediaries. Blockchain training is key for mastering this technology, enabling individuals to securely manage and verify transactions in a decentralized system. This feature is especially valuable in industries like finance, supply chain, and even healthcare. In fact, blockchain technology in healthcare is emerging as a powerful tool to improve data security, ensure patient privacy, and streamline the sharing of medical records across providers without compromising confidentiality. By offering a tamper-resistant system, it helps reduce fraud and ensures the integrity of sensitive information. As organizations continue to explore its potential, blockchain is proving to be more than just a buzzword it’s becoming a foundational technology for secure, transparent, and efficient digital systems across various sectors.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Blockchain Certification? Sign Up For Our Blockchain Training Course Today!
Why Understanding Blockchain Types Matters
- Choosing the Right Blockchain System: Different use cases require different blockchain systems. Public blockchains are ideal for transparency, while private ones are better for controlled environments like enterprises.
- Optimizing Blockchain Programming: Each blockchain type comes with unique technical requirements. Understanding this helps developers tailor blockchain programming approaches, ensuring compatibility, efficiency, and scalability especially when exploring concepts like What Is DAO Blockchain.
- Security in Blockchain Wallets: The type of blockchain influences how blockchain wallets store and manage keys and assets. A public blockchain may require more robust wallet security compared to private networks.
Understanding the different types of blockchain is essential for anyone looking to explore or work within the blockchain ecosystem. Whether you’re a developer, investor, or business leader, knowing how various blockchain structures function can help you make informed decisions, build better solutions, and navigate this fast-evolving space with confidence. Here are six reasons why understanding blockchain types truly matters:
- Building Efficient Blockchain Networks: A solid grasp of blockchain types allows businesses to build or join the most suitable blockchain network, optimizing speed, decentralization, and security.
- Understanding Blockchain Mining Mechanisms: Public blockchains often rely on blockchain mining, whereas private and consortium blockchains use alternative validation methods. Knowing the differences is key for energy efficiency and performance.
- Supporting Better Integration: By understanding how various blockchain types work, organizations can more effectively integrate blockchain with existing systems, ensuring smoother adoption and better ROI.
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are one of the most well-known types of blockchain, designed to be completely open and decentralized, allowing anyone to join, read, and write to the network without needing permission. They operate on consensus mechanisms like proof-of-work or proof-of-stake, ensuring security and transparency across all users. One of the key advantages of public blockchains is the ability to track blockchain transactions in real time, as all activity is recorded on a distributed ledger that is visible to anyone. This level of transparency not only builds trust but also makes public blockchains ideal for applications that benefit from openness, such as cryptocurrency and global supply chains a key consideration when discussing The Future of Blockchain Technology. Interestingly, even blockchain technology in healthcare can benefit from the public blockchain model in certain areas like verifying the authenticity of medical research or tracking drug provenance, though data privacy regulations often require a hybrid or permissioned approach for patient information. Still, the inherent openness of public blockchains sets a strong foundation for innovation across industries, proving especially valuable where accountability, traceability, and decentralization are critical. As organizations and developers explore the broader types of blockchain, understanding the unique role and potential of public blockchains remains a vital step in harnessing the power of distributed ledger technology.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Blockchain Certification? Sign Up For Our Blockchain Training Course Today!
Private Blockchains
- Enhanced Control Over the Blockchain System: In a private blockchain system, only authorized nodes can participate, ensuring stricter control over data and access, which is critical for internal business operations.
- Secure Blockchain Wallet Integration: Private blockchains offer enhanced security for blockchain wallets by limiting access to known participants, reducing the risk of unauthorized transactions or wallet breaches an important factor to consider when Choosing the Best Ethereum Wallets.
- Custom Blockchain Programming: Developers can tailor blockchain programming to meet specific enterprise needs, integrating smart contracts, data privacy rules, and workflows unique to the organization.
- Efficient Blockchain Network Performance: A private blockchain network generally has fewer nodes and uses lighter consensus mechanisms, leading to faster transaction speeds and better scalability compared to public networks.
- Limited or No Blockchain Mining: Since participants are pre-approved, blockchain mining is often unnecessary, reducing energy consumption and improving efficiency within the network.
- Streamlined Business Operations: Private blockchains support seamless data sharing, automated processes, and secure collaboration among trusted entities, making them ideal for supply chain management, finance, and healthcare industries.
- Flexible Blockchain System Design: A hybrid blockchain system allows organizations to keep sensitive data private while enabling public verification for selected transactions, ensuring both security and transparency.
- Custom Blockchain Programming Options: Developers can design specific modules through blockchain programming to define which data stays private and what is shared publicly, offering tailored solutions for different industries.
- Secure and Selective Blockchain Wallet Access: In hybrid models, blockchain wallets can be designed to interact with both private and public components, offering users controlled access to data and assets based on permissions a practical approach often highlighted when Exploring Blockchain in Banking.
- Efficient Blockchain Network Performance: Hybrid blockchain networks often use limited nodes for validation, improving transaction speed and scalability while still maintaining a layer of decentralized trust.
- Reduced Need for Blockchain Mining: While public elements may still use blockchain mining or similar validation, private segments typically rely on faster, permission-based consensus mechanisms, improving efficiency.
- Ideal for Enterprise and Government Use: Hybrid blockchains offer the privacy control of private blockchains and the integrity of public ones, making them suitable for industries that handle both sensitive and public data.
Private blockchains are permissioned networks where access is restricted to selected participants, making them ideal for enterprises that require confidentiality, control, and efficiency. Unlike public blockchains, private blockchains operate under a centralized authority, providing faster performance and more predictable governance. Here’s why private blockchains are important and how they relate to key blockchain concepts:
Consortium (Federated) Blockchains
Consortium (federated) blockchains are a hybrid model that combine features of both public and private blockchains, offering a balanced approach to decentralization and control. In this blockchain system, the network is governed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity, making it ideal for industries that require collaboration but also need to maintain confidentiality and efficiency. This setup allows for a more scalable and secure blockchain network, where pre-selected nodes validate transactions, reducing the risks associated with open participation. Unlike public blockchains, blockchain mining is typically unnecessary in consortium models, as consensus is achieved through trusted validators, which also makes the network more energy efficient a concept often emphasized in Blockchain Training programs. Developers working on blockchain programming for consortium networks can build custom smart contracts and applications tailored to the needs of participating institutions. Blockchain wallets used in these systems are often enterprise-grade, offering robust security features for managing digital assets and credentials across multiple organizations. Consortium blockchains are widely used in sectors like banking, supply chain, and healthcare, where data sharing among trusted partners is crucial. By combining decentralization with governance, consortium blockchains represent a powerful and practical blockchain system for real-world business applications.
Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains blend the best features of both public and private blockchains, creating a flexible blockchain system that offers controlled access while maintaining some level of transparency. These blockchains are ideal for businesses and governments that need to keep certain data confidential while still benefiting from the openness and auditability of a public network. Here are six key points about hybrid blockchains and how they interact with core blockchain concepts:
Hybrid blockchains provide a smart middle ground, balancing privacy, control, and transparency within a single, adaptable blockchain system.
Comparison Table: Blockchain Types at a Glance
Understanding the different types of blockchain is essential for choosing the right solution based on your needs, whether it’s transparency, control, or performance. A comparison table: blockchain types at a glance helps quickly highlight the key differences between public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchains. Public blockchains are fully decentralized and allow anyone to participate, making them ideal for open systems where users need to track blockchain transactions openly. Private blockchains, on the other hand, are controlled by a single entity, offering higher speed and privacy, which is beneficial for businesses requiring restricted access and internal use cases. Consortium blockchains, governed by a group of organizations, balance decentralization with efficiency, making them perfect for industries where collaboration is key but full public access isn’t practical a structure that also relies on understanding the Basics of Hashing in Blockchain for secure and efficient data handling. Hybrid blockchains combine public transparency with private control, offering flexibility for complex use cases like supply chain or blockchain technology in healthcare, where some data must remain confidential while still allowing verification and interoperability. By comparing these blockchain types side by side, organizations can better evaluate which model aligns with their goals, operational needs, and compliance requirements, especially in sectors that depend on both data security and trust, such as finance, logistics, and healthcare.
Are You Preparing for Blockchain Developer Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Blockchain Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
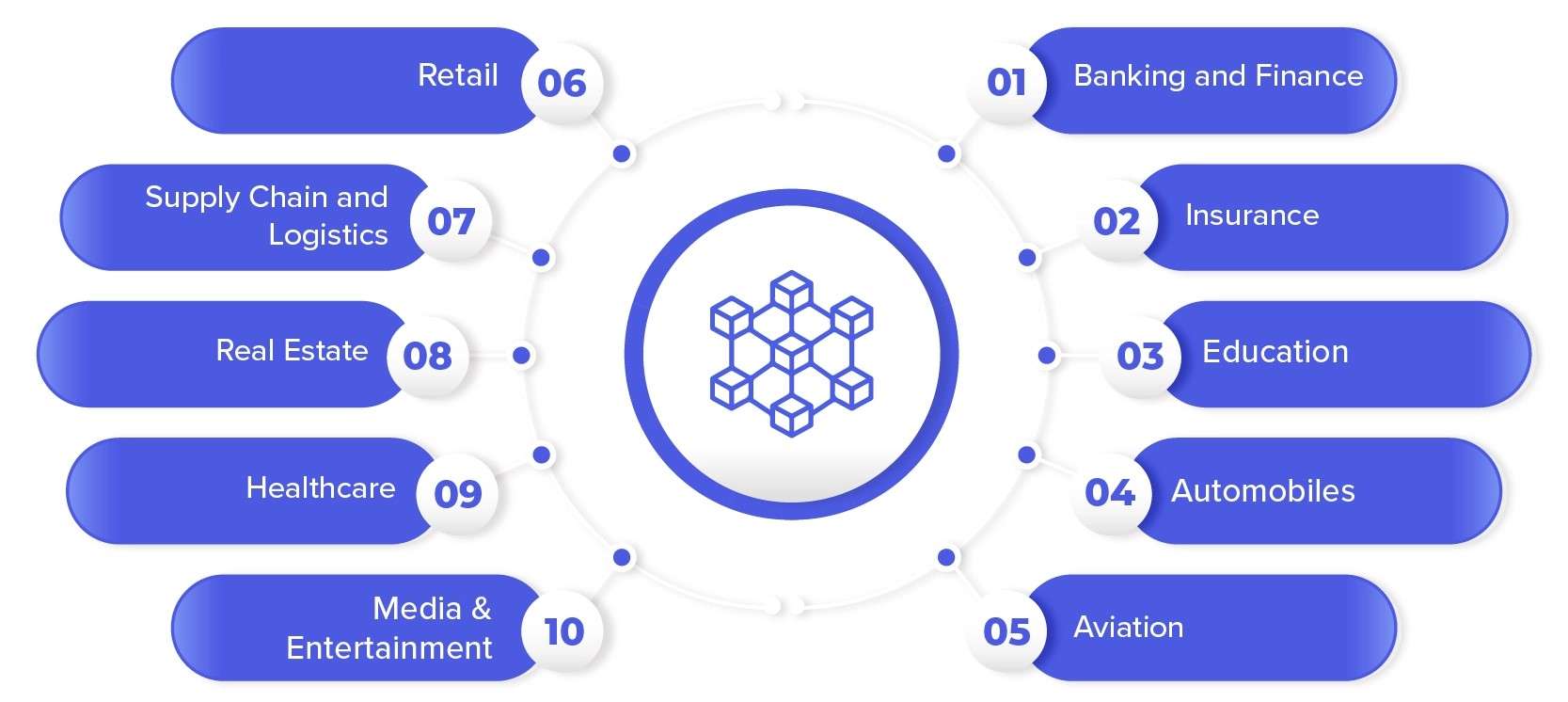
Use Cases Based on Blockchain Types
Different types of blockchain serve different industries and use cases, each offering unique strengths based on their level of decentralization, transparency, and access control. Public blockchains, for instance, are ideal for cryptocurrency, voting systems, and digital identity platforms due to their transparency and ability to track blockchain transactions in real time. Private blockchains, with their restricted access and high efficiency, are commonly used by enterprises for internal data management, supply chain tracking, and secure financial transactions. Consortium blockchains, which are governed by a group of trusted entities, work well in collaborative environments such as banking, trade finance, and logistics, where controlled transparency is crucial making them a key focus in many Blockchain Training programs. Hybrid blockchains blend public and private features, making them suitable for complex systems that need both privacy and public verification, like government records or smart city infrastructure. A growing application is blockchain technology in healthcare, where hybrid and private blockchains help securely store patient data, improve interoperability among providers, and enable secure sharing without compromising privacy. These diverse use cases highlight the importance of selecting the right blockchain type to meet specific needs, whether it’s for transparency, speed, or data confidentiality in critical sectors like finance, healthcare, and beyond.





