
A peer-to-peer computer process, Blockchain mining is used to secure and verify bitcoin transactions. Mining involves Blockchain miners who add bitcoin transaction data to Bitcoin’s global public ledger of past transactions. In the ledgers, blocks are secured by Blockchain miners and are connected to each other forming a chain.
When we talk in depth, as opposed to traditional financial services systems, Bitcoins have no central clearing house. Bitcoin transactions are generally verified in decentralized clearing systems wherein people contribute computing resources to verify the same. This process of verifying transactions in called mining. It is probably referred to as mining as it is analogous to mining of commodities like gold—mining gold requires a lot of effort and resources, but then there is a limited supply of gold; hence, the amount of gold which is mined every year remains roughly the same. In the same manner, a lot of computing power is consumed in the process of mining bitcoins. The number of bitcoins that are generated from mining dwindles over time. In words of Satoshi Nakamato, there’s a limited supply of bitcoins—only 21 million bitcoins will ever be created.

At its core, the term ‘Blockchain mining’ is used to describe the process of adding transaction records to the bitcoin blockchain. This process of adding blocks to the blockchain is how transactions are processed and how money moves around securely on Bitcoins. This process of Blockchain mining is performed by a community of people around the world called ‘Blockchain miners.’
Anyone can apply to become a Blockchain miner. These Blockchain miners install and run a special Blockchain mining software that enables their computers to communicate securely with one another. Once a computer installs the software, joins the network and begins mining bitcoins, it becomes what is called a ‘node.’ Together, all these nodes communicate with one another and process transactions to add new blocks to the blockchain which is commonly known as the bitcoin network. This bitcoin network runs throughout the day. It processes equivalent to millions of dollars in bitcoin transactions and has never been hacked or experienced a downtime since its launch in 2009.
How can you mine bitcoins?
You can buy and trade for bitcoins, or you can mine them. For mining bitcoins, users are rewarded in bitcoins. This mechanism forms the pivot around which the bitcoin economy revolves. While the cost and difficulty of mining bitcoins individually continues to increase, several cloud-based mining services have gradually emerged. These services allow individual users to lease the processing power of mining equipment and mine bitcoins remotely. However, you can mine bitcoins in person too.
There are two ways to mine bitcoins.
- Mining bitcoins on cloud
- Mining bitcoins on your own
Mining Bitcoins on Cloud
- Obtain a bitcoin wallet: Bitcoins are stored in digital wallets in an encrypted manner. This will keep your bitcoins safe.
- Secure the wallet: Since there is no ownership on bitcoins, anyone who gains access to your wallet can use it without any restriction. So, enable two-factor authentication and store the wallet on a computer that does not have access to the Internet or store it in an external device.
- Choose a cloud mining service provider: Cloud mining service providers allow users to rent processing or hashing power to mine bitcoins remotely. Popular cloud mining service providers are Genesis Mining and HashFlare.
- Choose a cloud mining package: To choose a package, you will need to decide on how much you are willing to pay and keep your eyes open to the hashing power the package will offer. Cloud mining companies will mostly envisage the Return on Investment (ROI) based on the current market value of Bitcoins.
- Pick a mining pool: This is the best shot you can get to earn bitcoins easily. There are many mining pools which charge a mere 2 percent of your total earnings. Over here, you will have to create workers which are basically sub accounts that can be used to track your contributions to the pool.
- Put your earnings in your own secure wallet: Whenever you witness an ROI, simply withdraw your earnings and put them in your own secure wallet.
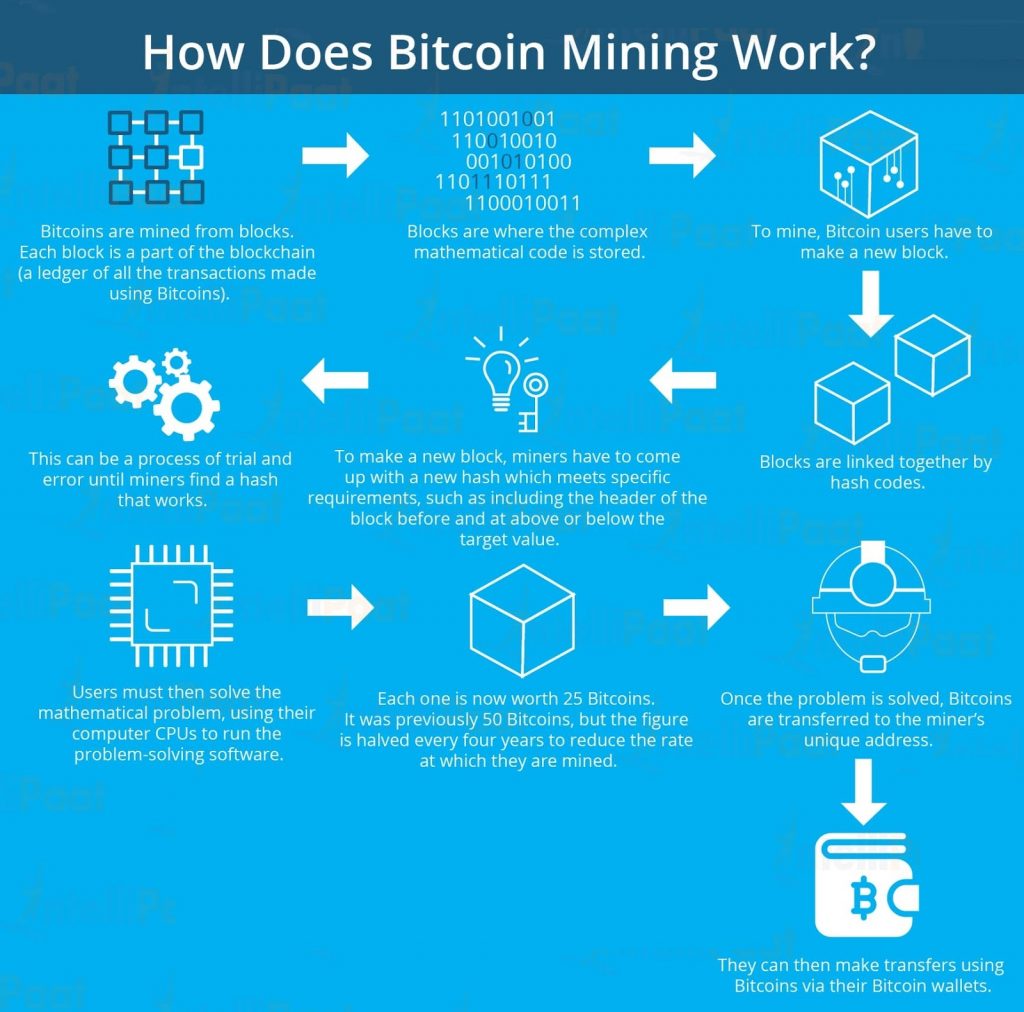
Mining Bitcoins on your own:
- Purchase a custom mining hardware: You need to purchase an Application-specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) miner to mine bitcoins. While purchasing an ASIC Blockchain miner, you should consider its efficacy in hashing power and take a note of its pricing policies.
- Purchase a power supply: Blockchain miners consume a lot of power. So, get a dependable power supply which is compatible with the ASIC miner that you purchase.
- Obtain a bitcoin wallet: Bitcoins are stored in digital wallets in an encrypted manner. This will keep your bitcoins safe.
- Secure the wallet: Since there is no ownership on bitcoins, anyone who gains access to your wallet can use it without any restriction. So, enable two-factor authentication and store the wallet on a computer that does not have access to the Internet or store it in an external device.
- Pick a mining pool: This is the best shot you can get to earn bitcoins easily. There are many mining pools which charge a mere 2 percent of your total earnings. Over here, you will have to create workers which are basically subaccounts that can be used to track your contributions to the pool.
- Connect the power supply to the ASIC Blockchain miner.
- Connect the ASIC Blockchain miner to your router.
- Boot up your ASIC miner.
- Enter your router’s IP address in a web browser.
- Find ‘connected devices’ in the router miner page.
- Find your ASIC miner and click on it to display the device information.
- Copy and paste the IP address of your ASIC miner into your web browser.
- Log in to the ASIC miner with the default username and password that are ‘Root’ and ‘Root.’
- Select ‘Miner Configuration’ to set up the miner according to your preferences.
- Enter the URL, username, and password for your mining pool on the Miner Configuration page of the ASIC Miner.
- Click ‘Save and Apply’ to save your credentials for future use.
- Start mining and in periodic intervals check your profitability.
- Put your earnings in your own secure wallet: Whenever you witness an ROI, simply withdraw your earnings and put them in your own secure wallet.
What are Blockchain smart contracts with respect to Bitcoins?
- On an evening when Nick Szabo was wondering about the purpose of security around bitcoins, he thought of incorporating software-based protocols to facilitate, verify, and enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. These software models later were referred to as ‘blockchain smart contracts.’ The basic purpose behind the inception of Blockchain smart contracts was to allow the performance of credible transactions without involving third parties. Although these transactions are trackable, they are irreversible. The aim of blockchain smart contracts is to provide security that is superior to the traditional contract law and in the meanwhile reduce other transaction costs that are associated with contracting.
- Szabo defined blockchain smart contracts as computerized transaction protocols that execute terms of a contract. He further wanted to extend the functionality of electronic transaction methods, such as POS to the digital landscape.
- In 2018, a US Senate report said: ‘While smart contracts blockchain might sound new, the concept is rooted in basic contract law. Usually, the judicial system adjudicates contractual disputes and enforces terms, but it is also common to have another arbitration method, especially for international transactions. With smart contracts blockchain, a program enforces the contract built into the code.’
- Considering the flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and robustness that smart contracts blockchain have introduced in the realm of bitcoins, they are undoubtedly at the epitome of their adaptability and popularity.
Byzantine fault-tolerant algorithms are the algorithms that allow digital security through decentralization to form smart contracts blockchain. Certain programming languages with various degrees of Turing completeness as a built-in feature of some blockchains make the creation of custom sophisticated logic possible. Some notable implementations of smart contracts blockchain are:
- For Bitcoins: This cryptocurrency provides a Turing incomplete script language that allows to customize the creation of situation-specific smart contracts blockchain.
- For Ethereum: Ethereum implements a nearly Turing-complete language on its blockchain as a prominent smart contract framework.
- For Ripple: Ripple’s Codius was another smart contract framework the development of which got halted in late 2015.
Have a peek at the image below to understand how exactly smart contracts blockchain function.
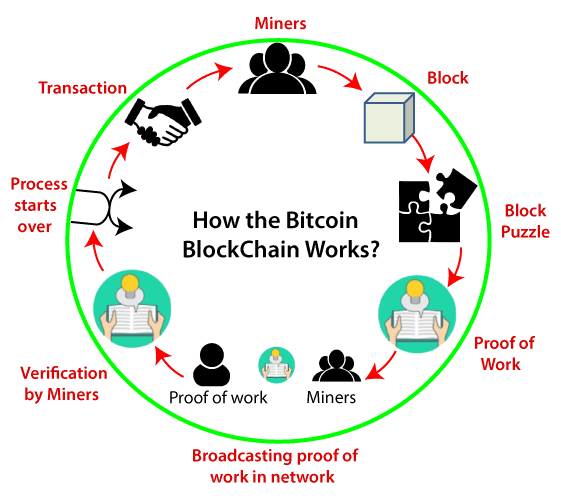
There are several types of blockchain smart contracts. They are listed as follows:
- Assurance Contracts: These contracts assure both sending and receiving parties guaranteed returns on their respective investments.
- Smart Properties: With smart properties, ownership is controlled by the blockchain and a smart contract. They can be leveraged for digital properties like company shares and ‘access rights’ to an online service.
- Transferable Virtual Properties: These properties have single ownership at a time. They cannot be controlled by a central authority.
- Autonomous Agents: Autonomous agents reduce costs by cutting out any middle man. They also discard human interactions and the liabilities that tag along with these interactions.
- Distributed Markets: These are used for trading securities like stocks and bonds with no centralized clearinghouse.
Blockchain Applications Overview
Blockchain is a software product that allows storage and conversion of data via the Internet, in a secure and transparent way without a central governing body.
Blockchain is:
- a platform that completes transactions without involving a third party;
- a system of distributed consensus and trust;
- an infrastructure that provides authentication and notarization.
Certainly, one of the greatest advantages of blockchain is traceability. The technology was built as an open ledger, filled in chronological order, distributed, verified, and protected against forgery by means of a distributed trust system, thanks to which everything registered there is accessible for tracking, and cannot be deleted. Thus, we can apply this principle of traceability in a variety of areas, for example, products, medicines, works of art, and precious metals.
Below, we will review blockchain applications examples in various spheres. All of these applications have something in common: almost absolute protection of transmission and archiving of information.
Energy
Electric power is not the main reason for the hype around the blockchain, but this, of course, is the industry in which the number of blockchain applications is growing steadily.
For instance, with the support of New York leadership, the TransActive Grid joint venture decided to combine energy and a decentralized economic system. A micro-network was created consisting of two enterprises: L03 Energy which develops solar energy networks, and ConsenSys, which specializes in the blockchain. In this case, the goal is to enable citizens to regain the production of electricity by creating energy mini-communities. For this purpose, sensors record the history of energy creation at a particular point and transmit the data to the airspace blockchain. Smart contracts can then regulate the rules for using this energy as well as the pricing set by producers.
The main advantage of this blockchain application is that it will not only reduce dependence on state energy but will also encourage users to produce renewable electricity and invest in it independently.
There are some other prospective projects in this sphere. In France, Air Products and Engie launched an innovative blockchain technology partnership to certify the traceability of green electricity. Engie conducts similar experiments, in particular in the field of tracing flows (water, gas, and electricity), and has done so since 2015.
In July 2016, Ponton, a start-up from Germany, developed the Enerchain platform, the first European power market based on the blockchain. Enerchain allows the anonymous sending of orders. Partners click on a button on the screen to complete a transaction, and everything is done directly, without intermediaries. As of 2018, the company has worked with 39 power and gas traders, developing their peer-to-peer platform.
These initiatives are not just experiments. In fact, the use of micro-energy projects around the world could generate more than $40 billion annually by 2020.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain Applications
The main advantage of blockchain is automation of control over transactions security. Blockchain prevents fraud and abuse and can solve many other problems, depending upon the implementation method and use.
Here are some advantages of blockchain applications:
- Resistance to failures, since the vulnerable point of failure, is distributed within numerous nodes, making the system more failure-resistant.
- Invulnerability to network censorship, since there is no central authority that any party could address and demand the removal of data. Parties cannot even block the domain or IP addresses of the application, because a decentralized application does not need specific addresses or domains. Of course, they can track an individual network user by IP address and disable them. But if the peer-to-peer network is large enough, completely disconnecting the application becomes an impossible task, especially if the nodes are scattered across different countries.
- Users are more likely to trust an application that is not controlled by one governing body capable of deceiving them for their own benefit.
Of course, every system has both merits and drawbacks. Consider the disadvantages of blockchain applications:
- Difficulties with updating and eliminating errors. The application must be updated on each node of the peer-to-peer network or forked if parts of nodes don’t accept amendments.
- Robustness of network for dedicated purposes. Any application has some business logic behind it. In general, this logic defines how new application must work in terms of business requirements. Blockchain, by nature, employs strict logic that doesn’t allow redesign without loss of benefits, which leads to the need for logical business changes to be acceptable to the blockchain solution.
- Sometimes, applications need to verify the identity of the user. Since there is no central authority that assures the identity of the user, the development of certain decentralized apps can become a serious problem.
- Difficulty of development. It is necessary to apply very complex protocols for achieving consensus and allow for scaling from the very beginning. One cannot hastily implement an idea, hoping sometime later to add new features and expand the application without forking or redeployment of the network.
- Normally, applications do not need third-party APIs to store or retrieve data. Your decentralized application (Dapp) should not depend upon the API of centralized applications, but they can depend on other Dapps. In theory, this sounds good, but it may cause difficulties in practice.
A Concluding Note on Blockchain smart contracts
In a paper that he published in 1994, Szabo proposed the execution of a contract for synthetic assets including derivatives and bonds. He referred to the sale and purchase of derivatives with complex terms.
‘These new securities are formed by combining securities and derivatives in a wide variety of ways. Very complex term structures for payments can now be built into standardized contracts and traded with low transaction costs, due to computerized analysis of these complex term structures,’ he wrote.
Further, check our online Blockchain course for certification and prepare yourself with our free Blockchain interview questions listed by the experts.






