
What is Cyber Security?
Cyber Security :It refers to the set of techniques used to protect the integrity of networks, programs, and data from attack/damage (or) unauthorized access.Cybersecurity is essential for a country’s military, hospitals, large corporations, small businesses, and other organizations and individuals since data is now the cornerstone of any organization. If that data is exploited, then there are a lot of risks. Now, we have understood what cybersecurity is, let’s see what the CIA triad is and how it is related to cybersecurity.According to the research, the cyber security market is expected to reach by 170 billion by 2020. So we need cyber security to protect the system from the attacks. This includes the application attacks, malware attacks, running somewhere, phishing, exploit kits. Today cyber adversaries have automated these tactics at lower and lower costs.
Cybersecurity is a popular topic, but do you know why it is essential? We are living in a digital era where data is everything. We must understand that private information is much more vulnerable than ever before. We often hear about data breaches and cases of identity theft that affect millions of consumers. Two years ago, WannaCry ransomware encrypted millions of computers. All companies and institutions are fighting to protect their data against hackers and cybercriminals, and you can also play a role in it. Cybersecurity is not involved only in organizations, but even personal computers, mobile phones, and tablets.

CIA Triad:
The security of any organization starts with three principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability. This is called the CIA, which has served as the industry standard for computer security since the time of first mainframes.
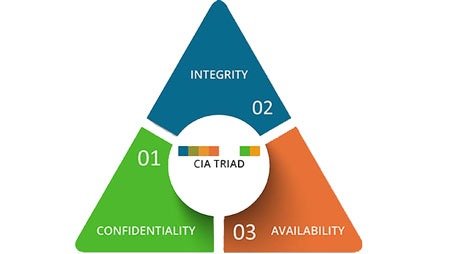
- Confidentiality: The principles of confidentiality assert that only authorized parties can access sensitive information and functions. Example: military secrets.
- Integrity: The principles of integrity assert that only authorized people and means can alter, add, or remove sensitive information and functions. Example: a user entering incorrect data into the database.
- Availability: The principles of availability assert that systems, functions, and data must be available on-demand according to agreed-upon parameters based on levels of service.
Let’s look at the areas in cybersecurity to understand the space better.
Specialties in Cybersecurity:
To pursue your career in cybersecurity, it is essential to know about the areas of specialization in it. There are nine:
- Access control systems and methodology: This deals with protecting critical system resources from unauthorized modification.
- Telecommunications and network security: This focuses on communications, protocols, and network services, and the potential vulnerabilities associated with each.
- Security management practices: This area deals effectively with catastrophic systems failures, natural disasters, and other types of service interruptions.
- Security architecture and models: This focuses mostly on having security policies and procedures in place. This particular security domain involves policy planning for just about every type of security issue.
- Law, investigation, and ethics: This handles the legal issues associated with computer security.
- Application and system development security: This person covers things like database security models and the implementation of multilevel security for in-house applications.
- Cryptography: Designed to help you understand how and when to use encryption.
- Computer operations security: This covers all those things that happen while your computers are running.
- Physical security: This primarily addresses questions about physical access to your servers and workstations.
Basic Terminologies:
These are some of the terms that you must be familiar with before learning anything about cybersecurity. These terms derive from networking concepts and will be useful to understand.
Network
A network is a connection between two or more computers so that they can communicate with each other. For example:

Internet
The Internet is a means of connecting a computer to any other computer anywhere in the world via dedicated routers and servers.
Internet Protocols
The data that is transferred or received cannot follow any path. There are a set of rules that are followed to control the flow of the internet. These rules are called internet protocol.
IP Address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is an address assigned to all devices that connect to a computer network and uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address looks like this: 168.192.10.3
MAC Address
This is a unique identification number that every device has that connects to the internet. Traditional MAC addresses are 12-digit hexadecimal numbers. MAC address looks like this: D8-FC-93-C5-A5-EO.
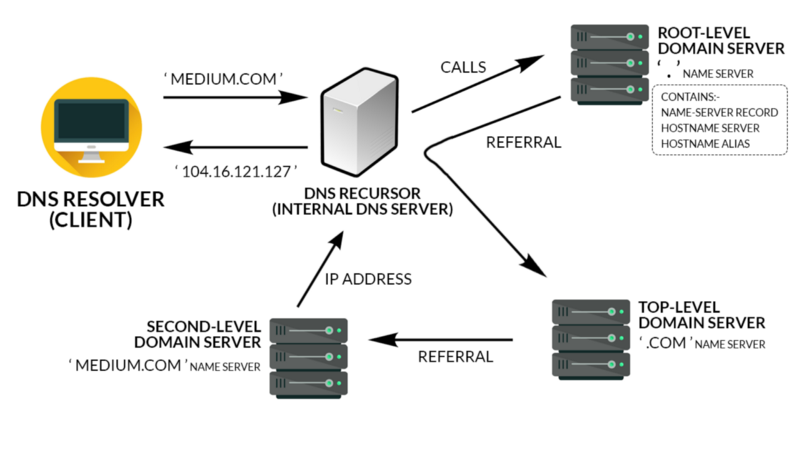
Domain Name Server(DNS)
Consider DNS as the phonebook of the internet. All the IP addresses and the name of the links are saved in it. For example, you want to go to google.com. You type this on your web application. Then, this name goes to the DNS server, and the DNS server finds the IP address of google.com. Then, the DNS server returns it to your computer with the IP address.
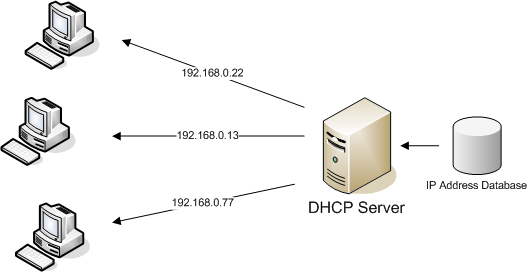
DHCP(Dynamic host configuration protocol)
Dynamic host configuration protocol is a protocol that assigns an IP address to any device that wants to connect to the internet.
Router
This is a device that routes the data that comes to it and then sends that data to the destination to ensure that it is on the appropriate path.
Bots
Bots are computer programs that control your computer without your knowledge. They automatically send emails, retrieve web pages, and change computer settings.
Common Types of Attacks:
Before we get into the types of attacks, we should know why these attacks happen. There is always a motive behind every attack; the main reason for attacks is money. Hackers penetrate the system and then demand ransom from the victims. There are other reasons like a financial loss to the target, achieving a state’s military objective, damaging the reputation of the target, or political maneuvering.
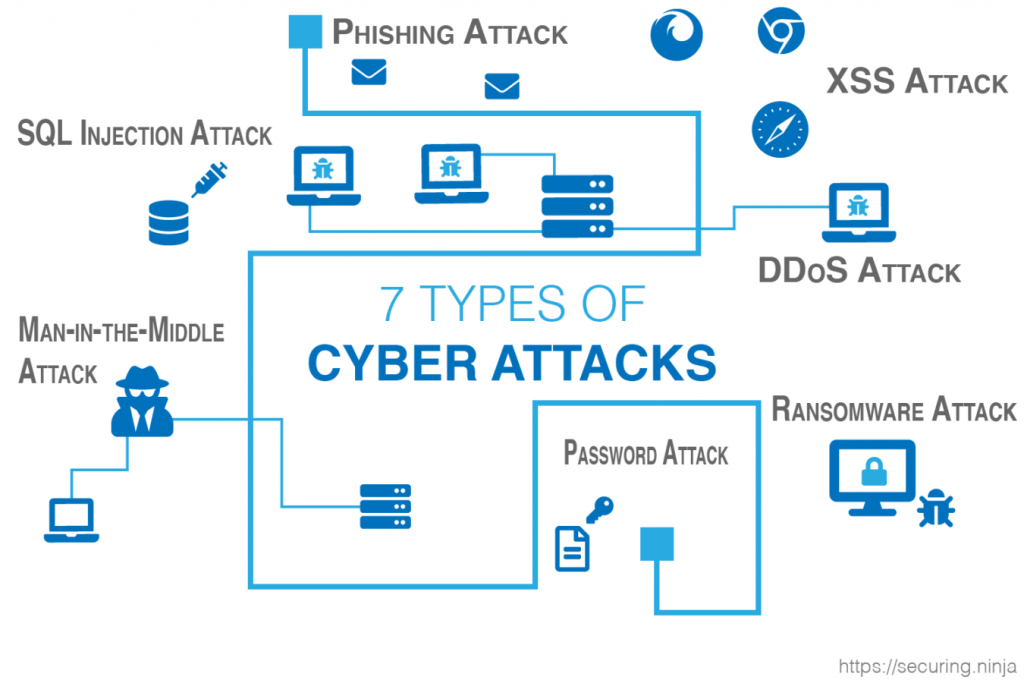
The five main types of attacks are as follows:
- Distributed denial of service(DDoS)
- Man in the middle
- Email attacks
- Password attacks
- Malware attack
Let’s look at them in detail:
Distributed Denial of Service
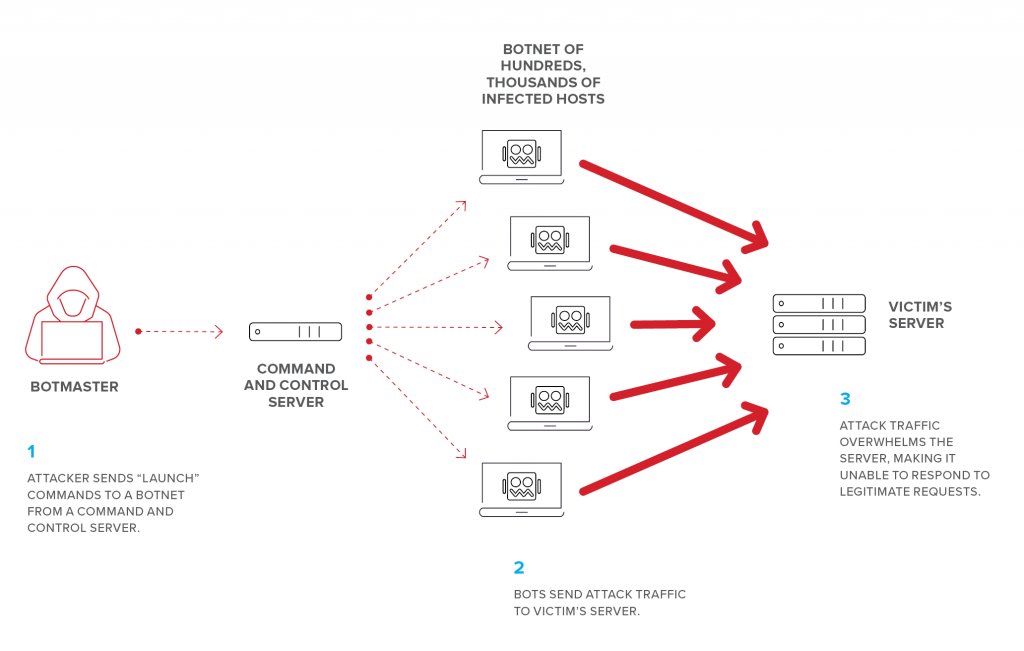
It is an attack used to restrict a user from accessing the resources by flooding the traffic that is used to access resources. A botnet controller controls all the bots that are under it. The attacker sends a command to the botnet controller that tells all bots to attack a server so that the server will be flooded. When a user wants to access a website, he will not be able to, as the traffic on the website will be at full capacity.
Man in the Middle Attack
Let’s look at an example to understand this better. Suppose you want to do an online transaction and you connect to your bank and make the payment.
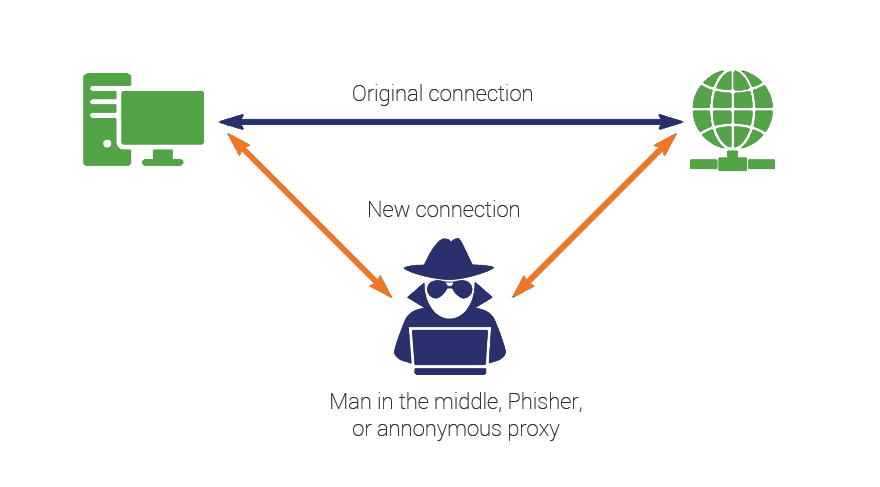
Now, while you are completing the transaction, you have to put in credit card details and the PIN. The attacker can spoof you and monitor your transaction. As soon as you put in your details, he will see them.
Password Attack
To crack a password or find a password, we use this technique. There are five types of password attacks:
- Dictionary attack: In this method, we handle every password that is possible through the dictionary.
- Brute force: This is a trial and error method used to decode the password or data. This attack takes the most amount of time.
- Keylogger: As the name suggests, a keylogger records all keystrokes on a keyboard. Most hackers use keyloggers to get passwords and account details.
- Shoulder surfing: The attackers observe the user’s keyboard by looking over the user’s shoulder.
- Rainbow table: There are rainbow tables that contain precomputed hash values. Attackers use this table to find the password of the user.
Email Attacks
First, let’s see how an email works. Suppose John is sending an email to Jack. The email first goes to the email server. Then it goes to the DNS server to find the IP address of the destination. From the source email server, the email goes to the destination server. From there, the email is sent to the IP address on which Jack is working. It is illustrated in the picture below.
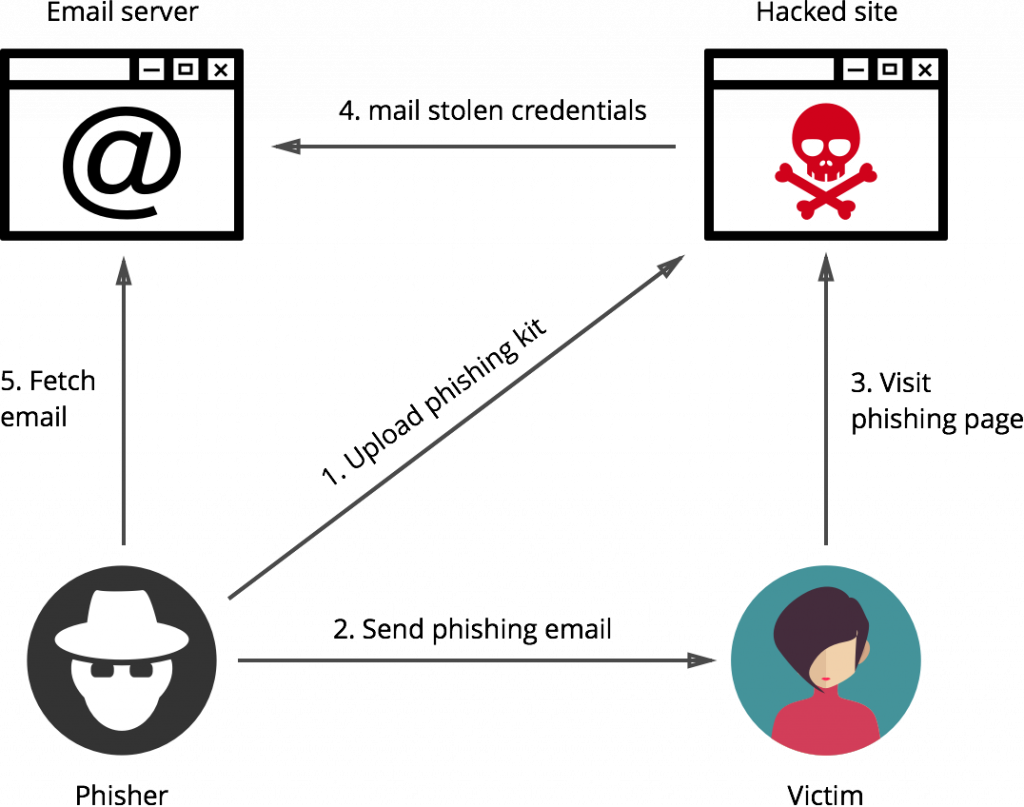
There are three types of email attacks
- Phishing: The attacker sends bait, often in the form of an email. It encourages people to share their details. For example, you receive an email like this: If someone is a customer of ABC bank, he would probably open the link and give the details. But these kinds of emails are always phishing; banks do not send emails like this.
- Spoofing: The attacker pretends to be another person or organization and sends you an email stating that it is a legitimate email. For example: After seeing this email, you might share the password to your computer. Always ask the person from whom you received the email one more time to confirm that he is the right person.
- Email attachments: You can send files through emails. These files may be images, documents, audio, or videos. Attackers send you an email, and you are encouraged to open the attached file. For example: Download these attachments only if you are sure that it is a legitimate email.
Malware Attack
- Malware: This is a malicious program or software that disrupts or damages the computer. There are three types of malware.
- Virus: A computer virus is a malicious code that replicates by copying itself to another program or document and changes how a computer works. The virus requires someone to knowingly or unknowingly spread the infection without the knowledge or permission of a user or system administrator. An example of a virus is the Melissa virus.
- Worms: These are standalone programs that run independently and infect systems. For example, W32.Alcra.F is a worm that propagates through network share devices.
Functions of Malware
- Overwhelming system resources: Malware, especially worms, can spread around and overwhelm a system or network. Some malware creates so many folders that no memory is left and slows a computer down.
- Creating a backdoor: Let’s look at an example: Microsoft sends updates every Sunday on all Windows platforms. How do these updates reach your Windows OS? They create backdoors from where they can send updates. Similarly, hackers create backdoors from where they can continuously send viruses after getting into a system.
- Disabling security functions: Some malware can disable antivirus software, as well as security updates. This malware tends to last longer because there is no security to stop it. They tend to keep the system vulnerable to other malware.
- Creating botnets: Hackers make botnets by purely coding. A botmaster controls botnets, and they are usually used to crash websites. Botmaster tells all botnets to flood the website by accessing the website at the same time.
Sources of Malware
- Removable media: Removable media, like Pendrive, CDs, DVDs, and flash drives, may be used to send viruses to your system.
- Documents and executable files: Viruses can be hidden in document files with the .exe extension. As soon as you open them, the virus activates.
- Internet downloads: Download files only from trusted websites. If you download from untrusted websites, there may be chances that those files will contain viruses, and as soon as you open them, the hacker might get access to your system.
- Network connections: Be sure that your service provider is genuine. If the network is unsecured, then it can be accessed by anyone.
- Email attachments: Never open email attachments unless the sender can be trusted. These files may contain viruses to create backdoors.
- Malicious advertisements: Never click on ads that you don’t trust. They are created so that you can click on them, and hackers will receive details about you.
Job Roles and Salary:
Here are some roles in the cybersecurity field:
- Chief Information Security Officer: Manages the IT security division of an organization.
- Forensic Computer Analyst: Looks for evidence after the breach or attack on an organization.
- Information Security Analyst: Protects the computer systems and networks of an organization.
- Penetration Tester: Penetration testers are highly skilled security specialists that spend their days attempting to breach computer and network security systems.
- IT Security Engineer: Plan to carry security measures to monitor and protect data and systems from hackers and cyber attacks.
- Security Architect: Maintain the network security of an organization.
- Security Systems Administrator: Install, administer, maintain, and troubleshoot a computer, network, and data security systems are their responsibilities.
- IT Security Consultant: Protect the organization’s sensitive data.
Certifications:
To start your career in the cybersecurity field, you must know the certifications that you need to clear to get into this field. Top three certifications are:
- CEH (Certified Ethical Hacker): The Certified Ethical Hacking (CEH V10) Course will train you in reverse engineering so that you can better protect corporate infrastructures from data breaches.
- CompTIA Security+: The CompTIA Security+ Certification is a globally trusted platform to validate foundationally, vendor-neutral IT security knowledge and skills.
- CND (Certified Network Defender): The Certified Network Defender (CND) Certification Covers protecting, identifying, and responding to network security, and teaches an arsenal of tools to provide real-world experience on current network security methodologies.
Conclusions:
More attention to both the capacity and capability of the U.S. cybersecurity workforce is needed. All organizations need to understand their threat environment and the risks they face, address their cybersecurity problems, and hire the most appropriate people to do that work.Hope you have found all the details that you were looking for, in this article.





