
- Introduction to Axios
- Why Use Axios in React?
- Installing Axios
- Sending GET Requests
- Sending POST Requests
- Handling Responses
- Error Handling in Axios
- Cancelling Requests
- Secure API Calls
- Conclusion
Introduction to Axios
Axios is a promise-based HTTP client for the browser and Node.js. It is used to make asynchronous HTTP requests to REST endpoints and can be a powerful tool when working with APIs in modern web development. Axios supports all the major HTTP methods including GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and PATCH. Its syntax is clean, easy to use, and includes many built-in features like interceptors, request cancellation, and automatic JSON data transformation. Axios works on both the client side (browser) and the server side (Node.js), making it extremely flexible for full-stack applications. Developers prefer Axios over the native Fetch API due to its automatic transformation of JSON data, better error handling, and simpler syntax. It is also highly customizable, allowing headers and timeouts to be easily configured.One of the best-selling JavaScript libraries for building user interfaces is React, which supports integration with a variety of data-pulling technologies. Among those tools, one of the best and easiest libraries to use for sending HTTP requests in React is Axios. This article will cover how to use Axios in a React app, such as how to send requests, handle responses, and handle failure.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer Certification? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Certification Courses Today!
Why Use Axios in React?
Axios is widely used because it simplifies the process of sending asynchronous HTTP requests. Unlike the native Fetch API, Axios automatically converts the response data to JSON, handles timeouts, and allows intercepting both requests and responses globally. One of its greatest strengths is its consistency across browsers, which is especially useful when working with older browsers that might not fully support Fetch.Due to its functionality, ease of use, and broad browser support, Axios is a popular JavaScript library for making HTTP requests. It is a pragmatic choice for client-side (browser) and server-side (Node.js) development as it simplifies activities like automatic handling of JSON data, request/response conversion, and error handling. Axios also includes built-in CSRF protection support, request cancellation, and transformation of request and response data. These features make it the preferred choice for many developers when dealing with web development. Additionally, Axios provides built-in support for client-side request timeout and automatic conversion of request and response data formats.

Installing Axios
Installing Axios is straightforward. If you’re using Node.js or a JavaScript bundler like Webpack, you can install it via npm or yarn: npm install axios or yarn add axios
If you’re working with a front-end project and prefer to use a CDN, you can add Axios using a Now you're ready to start making API requests using Axios.
Sending GET Requests
Sending GET requests are used to retrieve data from a server. With Axios, sending a GET request is simple and requires only the URL as a parameter:
- axios.get('https://api.example.com/data')
- .then(response => {
- console.log(response.data);
- })
- .catch(error => {
- console.error(error);
- });
Excited to Obtaining Your web developer Certificate? View The web developer course Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Sending POST Requests
Sending POST requests are used to send data to the server. Axios makes this easy by passing the data as the second parameter to the .post() method:
- axios.post('https://api.example.com/users',{
- name: 'John Doe',
- email: 'john@example.com'
- })
- .then(response => console.log(response.data))
- .catch(error => console.error(error));
- axios.post('https://api.example.com/users', userData, {
- headers: {
- 'Content-Type': 'application/json'
- }
- });
Handling Responses
When a request is successful, Axios returns a response object. The response typically contains:
- Data: The payload returned from the server
- Status: HTTP status code (200, 201, etc.)
- StatusText: HTTP status text (OK, Created, etc.)
- Headers: HTTP headers
- Config: The Axios config object used for the request
- axios.get('https://api.example.com/nonexistent')
- .catch(error => {
- if (error.response) {
- // Server responded with a status code outside 2xx
- console.log('Error Data:', error.response.data);
- console.log('Error Status:', error.response.status);
- } else if (error.request) {
- // Request was made but no response received
- console.log('No response:', error.request);
- } else {
- // Something else caused the error
- console.log('Error:', error.message);
- }
- });
- axios.get('https://api.example.com/data', { signal: controller.signal })
- .then(response => console.log(response.data))
- .catch(error => {
- if (axios.isCancel(error)) {
- console.log('Request canceled:', error.message);
- } else {
- console.error('Error:', error);
- }
- });
- // Cancel the request
- controller.abort();
- Use authentication tokens (JWT, OAuth) and send them in the Authorization header.
- Avoid hardcoding API keys in client-side code.
- Use environment variables to manage sensitive data.
- Validate all inputs before sending them to the API.
- axios.get('https://api.example.com/secure-data', {
- headers: {
- 'Authorization': `Bearer ${yourToken}`
- }
- });
This structured response allows developers to easily work with the returned data and perform additional actions based on status codes or headers.
Interested in Pursuing web developer certification Program? Enroll For Web developer course Today!
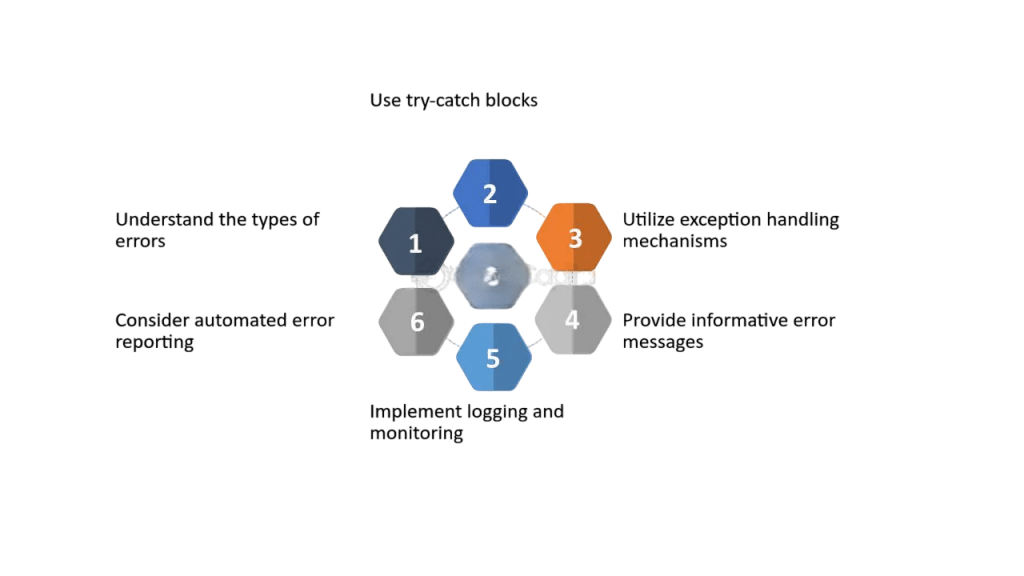
Error Handling in Axios
Error handling is crucial when dealing with HTTP requests. Axios uses .catch() to capture errors, which can be due to a failed request, network issues, or incorrect API endpoints. Axios provides a detailed error object that contains useful information:
Cancelling Requests
Axios supports cancellation of requests using the AbortController or legacy CancelToken API. This is especially useful for avoiding unnecessary API calls when a component unmounts: const controller = new AbortController();
Secure API Calls
Security is critical when making API calls. Some best practices include: Always use HTTPS to encrypt data in transit.
Conclusion
Use axios in react is a powerful and flexible HTTP client that greatly simplifies making API calls in modern web development. With its rich set of features such as interceptors, automatic JSON parsing, and request cancellation, Axios stands out as a reliable alternative to the native Fetch API. It integrates well with popular front-end frameworks like React and Vue, making it a go-to choice for developers worldwide. By learning how to send GET and POST requests, handle responses and errors, and use advanced features like interceptors and secure headers, developers can build robust and secure web applications. Whether you're building a single-page app, integrating third-party services, or managing large-scale APIs, Axios provides all the tools needed to succeed.

