
- Introduction – What is Linear Search?
- Use Cases and Applications
- How Linear Search Works – Step-by-Step Explanation
- Pseudocode for Linear Search
- Linear Search in Arrays
- Linear Search in Linked Lists
- Time Complexity Analysis
- Conclusion
Introduction – What is Linear Search?
Linear Search, also known as Sequential Search, is a fundamental and straightforward searching technique used in computer science. It is employed to find a specific element within a data structure, such as an array or a list. This algorithm works by checking each element in the list one by one from the beginning until the target element is found or the end of the list is reached. Due to its simplicity, linear search is often used in situations involving small or unsorted data sets. Though considered inefficient compared to more advanced searching algorithms like binary search or hash-based searches, linear search holds its importance in programming and algorithmic education. It is a building block that helps beginners understand the essence of iteration, conditional logic, and complexity analysis.Linear search, also known as sequential search, Web Designing & Development Training is a simple algorithm used to find a specific element within a list or array. It works by checking each element in the list one by one, starting from the first element and moving sequentially toward the last, until the target value is found or the end of the list is reached. If the target element is found, the algorithm returns its position (index); otherwise, it indicates that the element is not present in the list. Linear search is easy to implement and does not require any sorting of the data, making it a useful method for small or unsorted datasets. However, its major drawback is its inefficiency with large datasets, as its time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of elements in the list. This means that in the worst case, the algorithm may need to check every single item in the list. Despite its simplicity, linear search is foundational in computer science and often serves as an introductory concept in algorithm and data structure courses. It is particularly useful when dealing with short lists or in situations where performance is not a critical concern.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Use Cases and Applications
- Unsorted Data Searching: Ideal for searching in unsorted lists where sorting is not feasible or necessary.
- Small Datasets: Efficient and simple for small-sized arrays or lists due to low overhead.
- Presence Check: Used to check if a specific element exists in a dataset (e.g., checking if a user input matches any item in a list).
- Single Occurrence Search: Useful when the goal is to find the first occurrence of an element, not all instances.
- Data Validation: Helps validate if an input value exists in a predefined set of valid entries Minimum Spanning Tree.
- Real-Time Systems: Applied in systems where data is streamed or constantly updated, and sorting isn’t possible in real-time.
- Educational Tools: Commonly used in teaching basic algorithm design and analysis in computer science.
- Low-Resource Environments: Useful in embedded systems or simple applications where minimal resources are available.
- String or Character Search: Can be used to find a specific character in a string or a word in a list of words.
- Basic Search in Spreadsheets or Databases: Applied in scripts/macros for basic lookup tasks when no indexing is implemented.
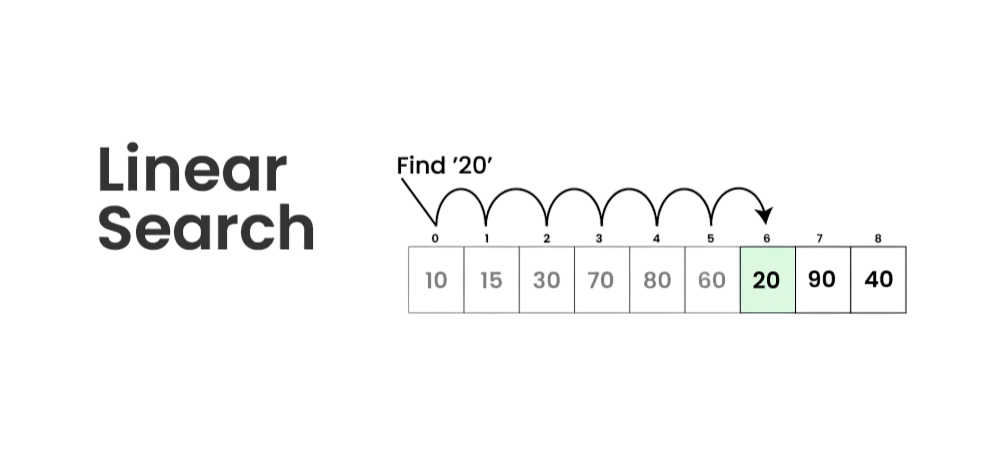
How Linear Search Works – Step-by-Step Explanation
Linear search works by checking each element in a list one by one to find a target value. Here is a step-by-step explanation of how the algorithm functions:
- Start at the Beginning: Begin with the first element of the list or array.
- Compare with Target: Compare the current element with the target value you are searching for.
- Check for Match: If the current element matches the target, GUI Tkinter Module return its position (index) and end the search.
- Move to Next Element: If the current element does not match, move to the next element in the list.
- Repeat the Process: Continue comparing each element one by one with the target value.
- End of List Condition: If the end of the list is reached and no match is found, conclude that the element is not present.
- Return Result: Return a value (often -1 or a message like “Not Found”) to indicate the target is not in the list.
- for i from 0 to length of array – 1:
- if array[i] == target:
- return i
- return -1
- array: The list of elements you want to search through.
- target: The value you are searching for.
- The loop starts at index 0 and goes through each element one by one Web Designing & Development Training .
- If the target is found, the function returns its index.
- If the loop completes without finding the target, it returns -1 to indicate the value is not in the array.
- int linearSearch(int arr[], int n, int target) {
- for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- if (arr[i] == target)
- return i;
- }
- return -1;
- }
- int linearSearch(Node* head, int target) {
- int index = 0;
- Node* current = head;
- while (current != NULL) {
- if (current->data == target)
- return index;
- current = current->next;
- index++;
- }
- return -1;
- }
- The target element is found at the first position.
- Only one comparison is needed.
- Example: Searching for 3 in [3, 5, 7, 9].
- The target element is expected to be somewhere in the middle of the list.
- On average, about n/2 comparisons are made, Data Structures & Algorithms which simplifies to O(n).
- Example: Searching for 7 in [1, 3, 5, 7, 9].
- The target element is at the last position or not in the list at all.
- Every single element must be checked.
- Example: Searching for 9 in [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] or searching for 10 (which isn’t there).
- Linear search uses a constant amount of extra space.
- No additional data structures are needed—just a few variables for indexing and comparisons.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Pseudocode for Linear Search
Unordered_map:
Here is a simple pseudocode for the linear search algorithm:
LinearSearch(array, target):
Explanation:
Linear Search in Arrays
Arrays allow index-based data access, Paging in Operating Systems which makes them ideal for linear search implementation. Here’s a practical example in C++:
This method scans each element and returns the position where the target is found.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Linear Search in Linked Lists
Unlike arrays, linked lists don’t allow direct access by index. Instead, linear search in linked lists requires traversal using pointers Reverse C++ Vector :
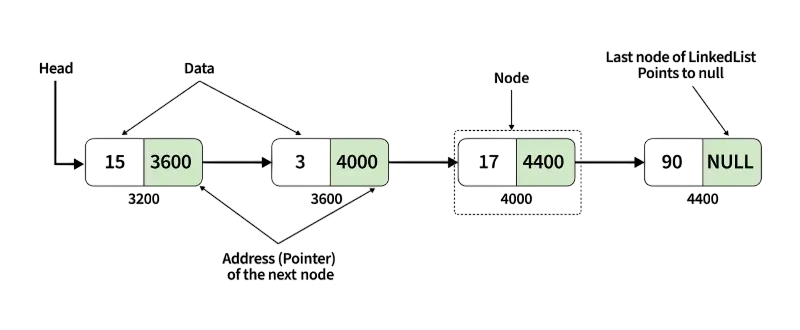
Each node is evaluated one after another until the target is found.
Time Complexity Analysis
Linear search has a straightforward time complexity analysis because it checks each element in the list one by one.
Best Case: O(1)
Average Case: O(n)
Worst Case: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Conclusion
Linear search is one of the most fundamental and straightforward search algorithms in computer science. It works by sequentially checking each element in a list until the desired value is found or the list ends. While it may not be the most efficient method for large datasets due to its O(n) time complexity, Web Designing & Development Training its simplicity, ease of implementation, and constant O(1) space usage make it highly useful in many practical scenarios, especially with small or unsorted data. Linear search also plays an important role in developing logical reasoning skills and serves as a foundational concept in algorithm learning. Understanding Pseudocode for Linear search is essential for anyone beginning their journey in programming or preparing for competitive exams and technical interviews.





