
- Introduction to Abstraction
- Definition and Syntax of Abstract Classes
- Pure Virtual Functions
- Why Use Abstract Classes?
- Abstract Class vs Interface
- Inheriting from Abstract Classes
- Object Slicing and Abstract Classes
- Conclusion
Introduction to Abstraction
Abstraction is one of the fundamental concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP) and serves as the foundation for building complex and scalable systems. In essence, abstraction means hiding the implementation details from the user and exposing only the relevant parts. For example, when you drive a car, you don’t need to understand the internal combustion engine, you just use the steering wheel and pedals. Similarly, in programming, abstraction allows users to interact with objects at a higher level without worrying about how they work internally. In C++, abstraction is achieved through classes, particularly abstract classes, which act as blueprints for derived classes Web Designing & Development Training . These classes define interfaces and set rules that must be followed by subclasses, ensuring consistency and promoting reuse. Abstract classes are crucial for designing flexible and extensible software, especially when implementing polymorphic behavior.Abstraction is a fundamental concept in computer science and software engineering that focuses on simplifying complex systems by hiding unnecessary details and highlighting only the essential features. It allows developers to manage complexity by breaking down large problems into smaller, more manageable parts. By using abstraction, programmers can create general models or interfaces that represent real-world entities without exposing the inner workings or implementation details. In object-oriented programming, abstraction is often achieved through abstract classes and interfaces, which define methods and properties that must be implemented by derived classes. This ensures a clear separation between what an object does and how it does it, promoting modularity and reusability of code. For example, a “Vehicle” interface might specify methods like start() and stop(), but it doesn’t dictate how these methods are implemented in a car or a bike. Abstraction not only helps in managing complexity but also improves maintainability, as changes to the internal implementation do not affect the external interface. It encourages a focus on high-level design, making it easier to collaborate, debug, and scale software systems. Ultimately, abstraction serves as a bridge between raw data and meaningful information, enabling developers to build efficient, flexible, and robust applications.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Definition and Syntax of Abstract Classes
An abstract classes in C++ is a class that cannot be instantiated on its own. It is designed to serve as a base class for other classes. Abstract classes typically contain at least one pure virtual function, which forces derived classes to implement the function.Abstraction is the process of hiding the complex implementation details of a system and exposing only the essential features Web Designing & Development Training or functionalities to the user. It helps in managing complexity by focusing on what an object or system does, rather than how it does it.
Syntax of an abstract class:
- class AbstractBase {
- public:
- virtual void display() = 0; // Pure virtual function
- };
When a function is declared with = 0, it becomes a pure virtual function, and the class becomes abstract. Such classes are useful when you want to provide a generic interface while deferring the implementation to the subclasses.
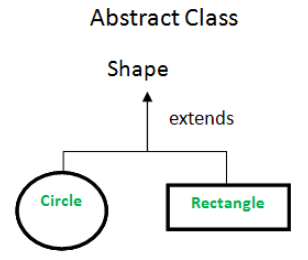
Pure Virtual Functions
A pure virtual function is a virtual function that is declared within a base class but does not have a definition in the base class. Instead, it must be defined by derived classes. It is used to define an interface in a base class.
- class Shape {
- public:
- virtual void draw() = 0; // Pure virtual
- };
In the example above, Shape defines a common interface for all derived classes, such as Circle, Square, or Rectangle C++ Vectors. Each of these classes must implement the draw() function. Pure virtual functions ensure that subclasses adhere to the contract defined by the abstract base class.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Why Use Abstract Classes?
- Define a common interface: Abstract classes allow you to define methods that must be implemented by all subclasses, ensuring a consistent interface.
- Encourage code reuse: You can provide shared code and default behavior in the abstract class, which subclasses can reuse or override.
- Enforce design contracts: By forcing subclasses to implement abstract methods, you ensure that specific functionality is provided Backtracking Programming .
- Promote modularity: Abstract classes help break down complex systems into smaller, manageable components.
- Support polymorphism: Objects of different subclasses can be treated as objects of the abstract class type, enabling flexible and interchangeable code.
- Prevent direct instantiation: Abstract classes cannot be instantiated on their own, which avoids creating incomplete or generic objects.
- Facilitate future extensions: New subclasses can be added without modifying the abstract class, making the system easier to extend.
- Improve maintainability: Changes in shared code can be made in the abstract class, automatically benefiting all subclasses.
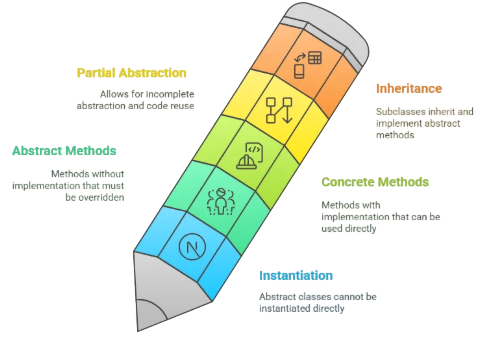
- Definition: A class that cannot be instantiated and may include both pure virtual (abstract) and concrete (implemented) methods.
- Method Implementation: Can have both abstract and fully implemented methods.
- Member Variables: Can contain data members (variables).
- Constructor: Can have constructors to initialize member variables.
- Use Case: Ideal when multiple classes share common behavior or implementation.
- Inheritance: Supports single or multiple inheritance (in C++), usually extended by subclasses.
- Flexibility: Less flexible than interfaces when dealing with multiple unrelated types.
- Definition: A completely abstract type that contains only pure virtual functions Web Designing & Development Training (no implementation or data members).
- Method Implementation: All methods must be pure virtual (no implementation allowed).
- Member Variables: Interfaces do not have member variables (in C++).
- Constructor: Interfaces cannot have constructors.
- Use Case: Best for defining a contract for unrelated classes to follow.
- Inheritance: Supports multiple inheritance, allowing classes to implement multiple interfaces.
- Flexibility: More flexible for designing loosely coupled, scalable systems.
- class Animal {
- public:
- virtual void sound() = 0;
- };
- class Dog : public Animal {
- public:
- void sound() override {
- cout << "Bark" << endl;
- }
- };
- int main() {
- Dog d;
- d.sound();
- return 0;
- }
- Animal* a = new Dog();
- a->sound(); // Polymorphic behavior
Abstract Class vs Interface
Abstract Class
Interface
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Inheriting from Abstract Classes
When a class inherits from an abstract class, it must override all pure virtual functions to become a concrete class. If it fails to do so, Height of a Tree it remains abstract and cannot be instantiated.
In the example above, Dog is a concrete class because it provides an implementation for the pure virtual function sound().
Object Slicing and Abstract Classes
C Programming Examples Object slicing occurs when a derived class object is assigned to a base class object, and the derived-specific attributes are lost. Abstract classes help avoid object slicing because they are used via pointers or references.
This approach ensures that the correct overridden function is called at runtime, supporting polymorphism without slicing.
Conclusion
Abstract classes in C++ are a cornerstone of object-oriented programming. They allow you to define interfaces and enforce behavior across different derived classes. By using abstract classes effectively, you can build systems that are modular, flexible, and maintainable. Whether you’re designing plugins, frameworks, or large software systems, abstract classes help you define clear contracts between components Web Designing Training. Combined with other OOP principles like inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation, abstract classes form the bedrock of clean C++ architecture. Understanding and mastering abstract classes is essential for writing robust and scalable C++ programs. They not only help with code reuse and interface definition but also promote best practices in software design.





