
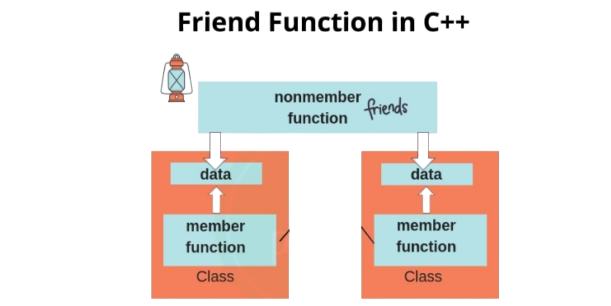
- Introduction to Friend Function in C++
- Syntax and Usage
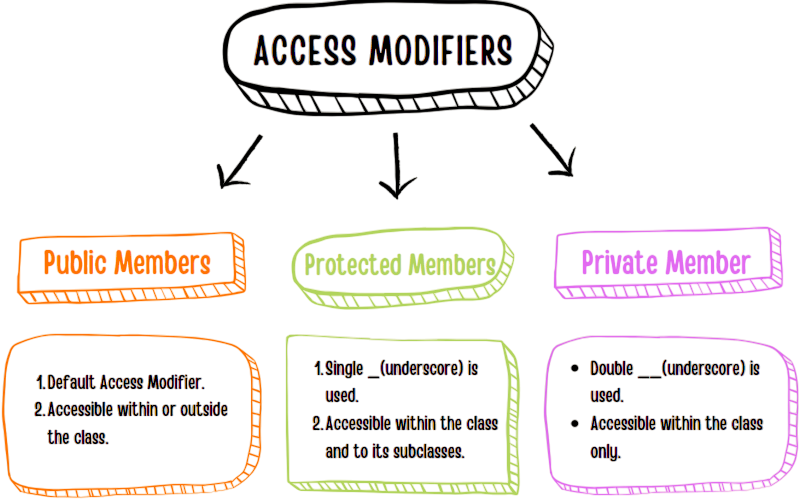
- Accessing Private Members
- Friend Classes
- Friend vs Member Functions
- Use in Operator Overloading
- Security and Design Implications
- Practical Examples
- Friend Functions in Inheritance
- Rules and Limitations
- When Not to Use
- Summary
Introduction to Friend Function in C++
A Friend Function in C++ is a function that is not a member of a class but is allowed access to the class’s private and protected members. This concept provides flexibility when two or more classes need to work closely together. Declaring a function as a friend breaks the traditional encapsulation concept but is justified in cases where internal data access by an external function simplifies implementation or enhances efficiency. To understand how such trade-offs apply in distributed environments, exploring Cloud Computing Course reveals how architectural decisions like access control, modularity, and service exposure impact scalability, security, and performance in cloud-native systems. A Friend Function in C++ is defined outside the class but declared within it using the keyword friend. This design pattern helps build relationships between classes and functions that require tighter coupling than member functions can provide.
To Earn Your Cloud Computing Course Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cloud Computing Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cloud Computing Course Today!
Syntax and Usage
To declare a friend function, use the friend keyword inside the class. This declaration allows the external function to access the class’s private and protected members. Here’s an example: in collaborative development environments, understanding Git and Version Control is equally essential ensuring that changes to such class structures are tracked, merged, and maintained efficiently across teams and repositories.
- class Box {
- private:
- int width;
- public:
- Box() : width(0) {}
- friend void setWidth(Box &b, int w);
- };
- void setWidth(Box &b, int w) {
- b.width = w;
- }
Here, the setWidth function, although not a member of the Box class, can access and modify its private member width because it’s declared as a friend.
Accessing Private Members
The primary use of friend functions is to allow access to private and protected members from outside the class. This is especially useful when implementing functions that require intimate access to a class’s internal data, such as utility functions or operations involving two different classes.
Friend functions are called like regular functions, not through class objects, as they are not members of the class. To understand how such tightly coupled logic contrasts with modern architectural patterns, exploring What are Microservices reveals how loosely coupled services communicate through APIs promoting modularity, scalability, and independent deployment across distributed systems.
Would You Like to Know More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Now!
Friend Classes
In Friend Class functions, entire classes can be declared as friends of another class. When this is done, all the member functions of the friend class can access the private and protected members of the target class. This is commonly used when one class acts as a utility or helper to another. To contrast this with dynamic and flexible paradigms, exploring What is Python Programming reveals how Python emphasizes simplicity, readability, and loose coupling making helper functions and modular design more intuitive and less reliant on access modifiers.
Example:
- class B;
- class A {
- private:
- int value;
- public:
- A() : value(10) {}
- friend class B;
- };
- class B {
- public:
- void displayAValue(A &obj) {
- std::cout << “A’s value: ” << obj.value << std::endl;
- }
- };
In this case, class B can access all members of class A, including the private ones, due to the friend declaration.
Friend vs Member Functions
Member functions are part of the class and can access all its members directly. Friend functions, on the other hand, are not part of the class but can access private and protected members due to the friend declaration. While member functions can be overridden and inherited, friend functions cannot. Also, friend functions are defined outside the class and do not require an object to be called using dot or arrow operators.
This external access simplifies certain operations but must be balanced with design clarity. To explore how data structures are handled in a more dynamic language, exploring Know About Python List reveals how Python lists offer flexible indexing, slicing, and built-in methods making them ideal for rapid development and clean, readable code. Use member functions when behavior belongs strictly to the class, and friend functions when behavior involves interaction between multiple classes or functions.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cloud Computing by Enrolling in Our Cloud Computing Master Program Training Course Now!
Use in Operator Overloading
Friend functions are commonly used to overload operators when two different classes or objects are involved, especially for binary operators. For instance: when designing systems that require tight interaction between components, understanding What Is a Software Developer reveals how professionals apply such principles to build efficient, maintainable code balancing encapsulation with performance across diverse programming tasks.
- class Complex {
- private:
- float real, imag;
- public:
- Complex(float r, float i) : real(r), imag(i) {}
- friend Complex operator+(Complex c1, Complex c2);
- };
- Complex operator+(Complex c1, Complex c2) {
- return Complex(c1.real + c2.real, c1.imag + c2.imag);
- }
Here, the + operator is overloaded as a friend function to allow direct access to the private members of Complex objects.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cloud Computing Course? Sign Up For Our Cloud Computing Course Today!
Security and Design Implications
Friend functions compromise encapsulation, one of the cornerstones of object-oriented design. Therefore, their use should be minimal and only when absolutely necessary. Overusing friend functions may indicate poor class design. It’s advisable to use friend functions when alternative solutions like getter/setter methods increase complexity or reduce clarity. To understand how such design decisions scale in distributed systems, exploring Cloud Computing Course reveals how modular architecture, service boundaries, and controlled access patterns are essential for building secure, maintainable cloud-native applications. Always assess whether a friend function is the most appropriate solution or if refactoring might be a better option.
Preparing for Cloud Computing Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cloud Computing Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Practical Examples
Friend functions prove useful in many real-world scenarios, such as input/output stream handling, operator overloading, and classes that tightly integrate. To understand how different languages approach such integrations, exploring Kotlin vs Java reveals how Kotlin emphasizes conciseness and null safety, while Java offers mature tooling and widespread adoption helping developers choose the right language for tightly coupled or modular system design.
- class Rectangle;
- class AreaCalculator {
- public:
- static int calculateArea(Rectangle &);
- };
- class Rectangle {
- private:
- int length, breadth;
- public:
- Rectangle(int l, int b) : length(l), breadth(b) {}
- friend int AreaCalculator::calculateArea(Rectangle &);
- };
- int AreaCalculator::calculateArea(Rectangle &r) {
- return r.length * r.breadth;
- }
This example demonstrates the use of a friend function to compute the area of a rectangle while accessing its private data members.
Friend Functions in Inheritance
Friendship is not inherited. If class A declares class B as a friend, class C derived from B does not inherit this privilege. Similarly, if class B is a friend of base class A, it does not automatically gain access to members of classes derived from A. Friendship is explicitly declared and is not subject to the rules of inheritance. To understand how access control and design boundaries are handled in modern object-oriented systems, exploring What is Abstraction in Java reveals how abstraction hides internal implementation details while exposing only essential interfaces promoting modularity, security, and clean architecture. This helps in maintaining controlled access and avoiding security risks.
Rules and Limitations
Friend functions and classes must follow certain rules:
- Friendship is neither inherited nor transitive.
- Declaring a friend function does not make it a member of the class.
- Friend functions can be declared in any section (public, private, or protected).
- A single function can be a friend to multiple classes.
- Friendship cannot be revoked once granted.
Understanding these limitations is critical to using the feature responsibly and effectively.
When Not to Use
Friend functions should be avoided in the following scenarios: when they compromise encapsulation, introduce tight coupling, or bypass intended access controls. These risks can lead to fragile code and maintenance challenges. To understand how structural integrity is preserved in modern programming, exploring Important Data Structures and Algorithms reveals how thoughtful design using stacks modularity, and scalable problem-solving.
- When standard accessors and mutators can perform the required functionality.
- When their use undermines the encapsulation of class members.
- When they lead to tightly coupled code that is hard to maintain or extend.
- When alternatives like inheritance or interfaces could offer a cleaner solution.
Instead of overusing friend functions, strive for clean, modular code that adheres to the principles of object-oriented programming. Use friend functions as a last resort when no better solution exists.
Summary
Friend functions are a powerful feature in C++ that allow non-member functions and other classes to access the private and protected members of a class. While they can facilitate cleaner operator overloading and close collaboration between classes, they must be used judiciously. Misuse can lead to tight coupling and reduced modularity. To understand how such design choices scale in distributed systems, exploring Cloud Computing Course reveals how abstraction, decoupling, and service orchestration are essential for building scalable, resilient cloud-native applications. Overuse can violate encapsulation and indicate design flaws. Proper understanding of when and how to use friend function in C++ can lead to cleaner, more maintainable, and efficient code. With correct usage, friend functions offer a robust mechanism for extending class functionalities without compromising code quality.





