
- Introduction to C Language
- Hello World Program
- Variables and Data Types
- If-else and Switch Cases
- Loops: for, while, do-while
- Arrays and Strings
- Functions and Recursion
- Conclusion
Introduction to C Language
The C programming language is one of the most influential and widely used programming languages in the history of computer science. Developed in the early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie at Bell Labs, C was originally designed to develop the UNIX operating system. Since then, it has become a foundational language for system programming, embedded systems, and application development. C Language is a procedural, structured programming language that provides low-level access to memory through the use of pointers while still offering high-level programming features. Its simplicity, efficiency, and portability make it ideal for writing operating systems, compilers, and other performance-critical applications. One of the key strengths of C is its ability to work closely with hardware. It allows direct manipulation of bits, bytes, and addresses, Web Designing & Development Training . which is essential for systems-level programming. Despite being a powerful low-level language, C includes features like functions, loops, conditionals, and data structures, making it suitable for writing complex programs. C has influenced many modern languages such as C++, Java, C#, and Python, and understanding C provides a strong foundation for learning them. Its standardized syntax and extensive use in academia make it a common choice for teaching programming fundamentals. Programs written in C are compiled, which means they are translated into machine code before execution, resulting in fast and efficient performance. The language’s portability allows code to run on various platforms with minimal changes, as long as a compatible compiler is available. In summary, C is a powerful, efficient, and versatile programming language that continues to play a crucial role in software development. Whether you’re working on embedded systems, operating systems, or learning programming basics, mastering C is a valuable skill for any software developer.
Hello World Program
The “Hello, World!” program is the simplest way to get started with C and test your development environment.
Example:
- #include
- int main() {
- printf(“Hello, World!\n”);
- return 0;
- }
Explanation:
- #include
: Includes the standard input/output library. - main(): Software Engineering Prototype The entry point of every C program.
- printf(): Prints text to the console.
- return 0: Ends the program.
Output:
Hello, World!
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Variables and Data Types
- Definition: A variable is a named memory location used to store data that can be modified during program execution.
- Declaration: Must be declared before use with a specific data type.
- Naming Rules: Must begin with a letter or underscore (_). Can contain letters, digits, and underscores. What is Software Engineering Cannot use keywords or special characters.
- Initialization: Variables can be assigned a value at the time of declaration.
- Scope: Determines the part of the program where the variable can be accessed (local, global, etc.)
- Lifetime: The duration during which a variable exists in memory.
- int – Integer numbers (e.g., 1, -10)
- float – Single-precision decimal numbers (e.g., 3.14)
- double – Double-precision decimal numbers
- char – Single character (e.g., ‘A’)
- Arrays
- Pointers
- Structures
- Unions
- Enumeration (enum): Used to define a set of named integer constants
- Void Type: Reverse C++ Vector Represents “no value”; used for functions that return nothing
- Type Modifiers: short, long, signed, unsigned – used to change the size or sign of data types
- #include
- int main() {
- int marks = 70;
- if (marks >= 90)
- printf(“Grade: A\n”);
- else if (marks >= 75)
- printf(“Grade: B\n”);
- else
- printf(“Grade: C\n”);
- return 0;
- }
- #include
- int main() {
- int choice = 2;
- switch (choice) {
- case 1: printf(“Start\n”); break;
- case 2: printf(“Stop\n”); break;
- default: printf(“Invalid\n”);
- }
- return 0;
- }
- for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
- printf(“%d “, i);
- }
- int i = 1;
- while (i <= 5) {
- printf(“%d “, i);
- i++;
- }
- int i = 1;
- do {
- printf(“%d “, i);
- i++;
- } while (i <= 5);
- #int nums[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
- for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
- printf(“%d “, nums[i]);
- }
- char name[] = “Alice”;
- printf(“Hello, %s\n”, name);
- int add(int a, int b) {
- return a + b;
- }
- int main() {
- printf(“Sum: %d\n”, add(3, 4));
- return 0;
- }
- int factorial(int n) {
- if (n == 0) return 1;
- return n * factorial(n – 1);
- }
- int main() {
- printf(“Factorial: %d\n”, factorial(5));
- return 0;
- }
Example: int age;
Example: int age = 25;
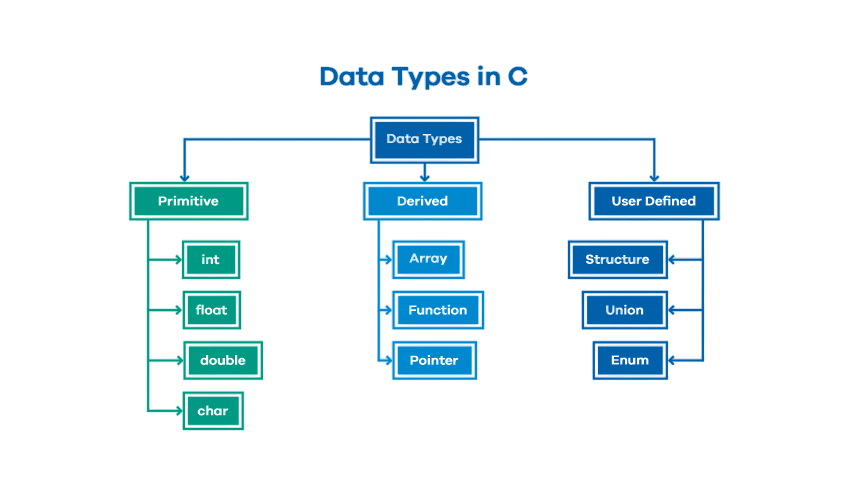
Data Types in C
Basic (Primitive) Data Types:
Derived Data Types:
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
If-else and Switch Cases
Web Designing & Development Training Conditional statements control the flow based on conditions.
If-else Example:
Switch Case Example:
Loops: for, while, do-while
Loops repeat blocks of code.
For Loop:
While Loop:
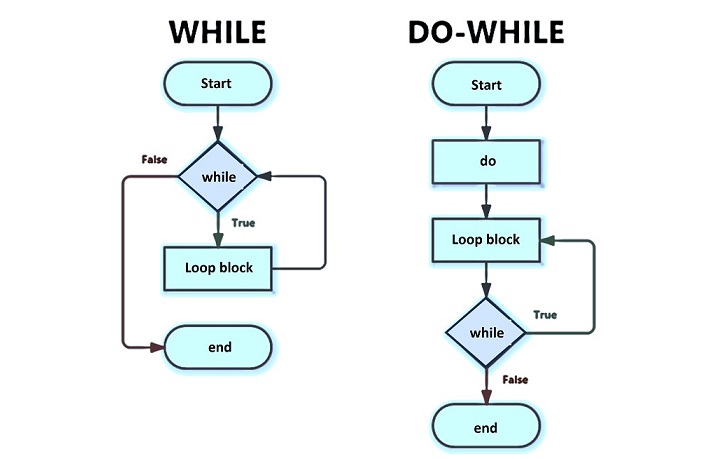
Do-While Loop:
Output for all:
1 2 3 4 5
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Arrays and Strings
C Programming Examples Arrays store multiple values of the same type.
Array Example:
String Example:
Strings are arrays of characters terminated with \0.
Functions and Recursion
Functions and Recursion modularize code for reusability and clarity Backtracking Programming .
Function Example:
Recursion Example:
Conclusion
The Flood Fill algorithm is a powerful tool in computer graphics, from simple shape coloring to complex region analysis. While the recursive approach is easy to implement, the iterative method is preferred for robustness and performance. Understanding the principles of neighborhood traversal, color replacement, Web Designing & Development Training and boundary handling equips you to use this algorithm in a wide range of applications from gaming to image analysis. Whether you’re building a paint application or a grid-based puzzle solver,Pseudocode mastering flood fill gives you a strong foundation in both graphics and algorithmic logic.





