
- Overview of Inheritance in OOP
- Definition of Hierarchical Inheritance
- Syntax and Code Structure
- Example Program in C++
- Advantages of Hierarchical Inheritance
- Access Modifiers (public, private, protected)
- Virtual Functions and Hierarchical Inheritance
- Conclusion
Overview of Inheritance in OOP
Inheritance is a cornerstone of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and plays a critical role in the design and development of maintainable, scalable, and reusable software systems. Inheritance allows one class to acquire the properties and behaviors (methods and data members) of another class. It models real-world relationships and fosters a hierarchy between entities.Inheritance is one of the core principles of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), enabling the creation of a new class based on an existing class. This mechanism allows a derived (or child) class to inherit attributes and behaviors (data members and member functions) from a base (or parent) class, promoting code reusability, scalability, and maintainability. Inheritance models a real-world “is-a” relationship, such as a Car being a type of Vehicle. The derived class can use, extend, or override the functionality of the base class, allowing Web Designing & Development Training to build more specialized classes without rewriting existing code. There are several types of inheritance in OOP, including single inheritance, multiple inheritance, multilevel inheritance, hierarchical inheritance, and hybrid inheritance. Each type supports a different structure and relationship among classes. For example, in hierarchical inheritance, multiple derived classes inherit from a single base class, which helps in organizing related functionalities efficiently. Inheritance also promotes polymorphism, particularly when combined with virtual functions, allowing objects of different derived classes to be treated as objects of the base class while invoking the correct overridden methods at runtime. Access modifiers like public, private, and protected play a crucial role in controlling how the base class members are accessed in derived classes. Proper use of inheritance leads to cleaner code architecture and easier debugging, while improper use may lead to tightly coupled and complex class hierarchies. Most modern programming languages like C++, Java, Python, and C# support inheritance, though implementation details may vary. In C++, inheritance is explicitly declared using a colon followed by the access specifier and base class name. Overall, inheritance simplifies the development of complex systems by enabling code reuse, promoting logical class hierarchies, and enhancing program organization through abstraction and encapsulation.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Definition of Hierarchical Inheritance
Hierarchical inheritance is a type of inheritance in object-oriented programming (OOP) where multiple derived (child) classes inherit from a single base (parent) class. In this model, the parent class contains common attributes and behaviors, which are shared by all child classes. Each child class can then extend or override these inherited features to implement its own specific functionality. This structure promotes code reusability and logical organization by allowing related classes to share common functionality without duplicating code StringBuilder . For example, consider a base class Animal that has general methods like eat() and sleep(). Derived classes such as Dog, Cat, and Bird can inherit from Animal, gaining access to these common methods while also defining their own unique behaviors like bark(), meow(), or fly() respectively. This setup demonstrates hierarchical inheritance, as multiple subclasses share a common ancestry.
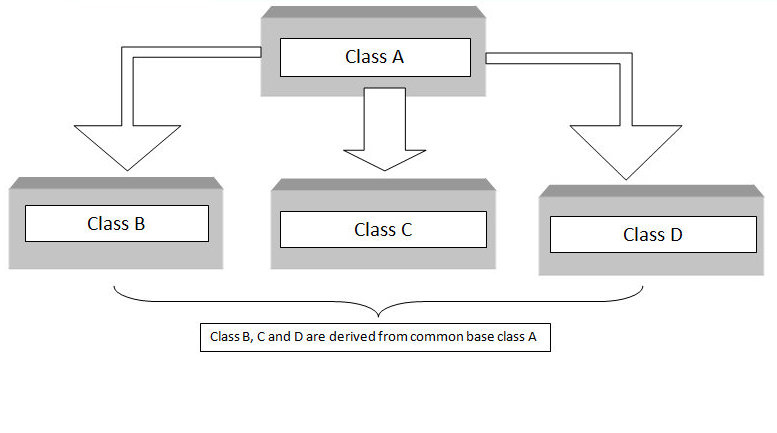
Hierarchical inheritance is widely used in real-world software development to model systems where multiple specialized entities share a common foundation. It also supports the principles of abstraction and polymorphism, allowing programs to handle different objects through a common interface. Most OOP languages like C++, Java, and Python support hierarchical inheritance, with syntax varying slightly across languages.
Syntax and Code Structure
In C++, Pointers in C hierarchical inheritance can be implemented using the following structure:
- class Base {
- public:
- void commonFunction() {
- cout << "Function in Base class." << endl;
- }
- };
- class Derived1 : public Base {
- public:
- void specificFunction1() {
- cout << "Function in Derived1 class." << endl;
- }
- };
- class Derived2 : public Base {
- public:
- void specificFunction2() {
- cout << "Function in Derived2 class." << endl;
- }
- };
Each derived class has access to the members of the base class unless those members are private. This setup facilitates code reuse and maintains consistency across related classes.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Example Program in C++
Let’s consider a more practical example involving animals:
- #include
- using namespace std;
- class Animal {
- public:
- void eat() {
- cout << "This animal eats food." << endl;
- }
- };
- class Dog : public Animal {
- public:
- void bark() {
- cout << "The dog barks." << endl;
- }
- };
- class Cat : public Animal {
- public:
- void meow() {
- cout << "The cat meows." << endl;
- }
- };
- int main() {
- Dog d;
- d.eat();
- d.bark();
- Cat c;
- c.eat();
- c.meow();
- return 0;
- }
In this program, Linux Operating System Dog and Cat classes inherit the eat() function from the Animal class, while defining their own unique behaviors.
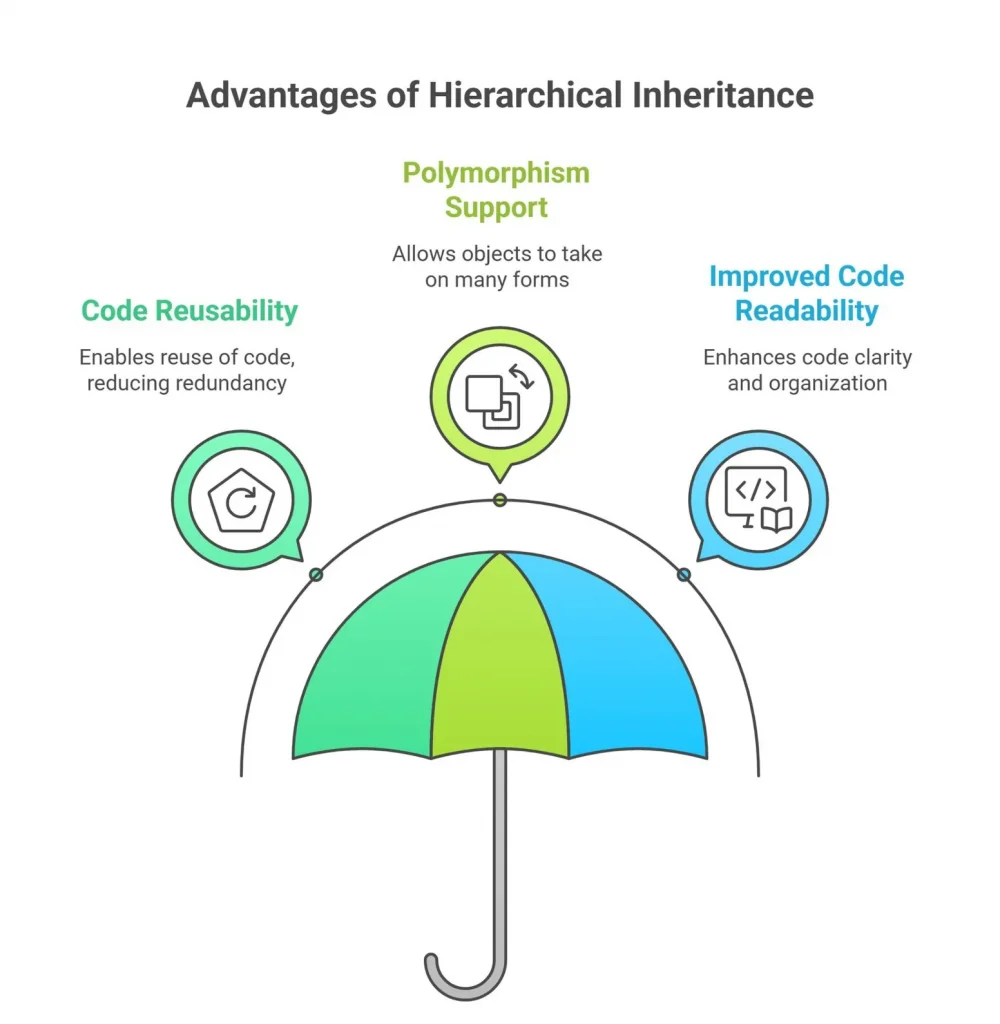
Advantages of Hierarchical Inheritance
- Code Reusability: Common properties and methods defined in the base class can be reused by all derived classes, reducing code duplication.
- Improved Organization: It helps organize classes in a logical hierarchy, making the codebase easier to understand and maintain.
- Scalability: New derived classes can be added without modifying the base class, Web Designing & Development Training supporting easy expansion of the system.
- Consistency: Shared behavior across multiple subclasses ensures consistent implementation of common functionalities.
- Reduces Development Time: Since derived classes inherit existing functionality, developers can focus on writing only the specialized code.
- Supports Polymorphism: Objects of different subclasses can be treated as objects of the base class, React Hooks enabling dynamic method dispatch.
- Encourages Modularity: Each class handles its own specific behavior while relying on the base class for shared logic, promoting modular design.
- Easier Maintenance and Updates: Changes in the base class (like fixing a bug or updating logic) automatically reflect in all derived classes, reducing maintenance effort.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Access Modifiers (public, private, protected)
Access modifiers play a significant role in inheritance. They control the visibility of base class members in derived classes:
- Public inheritance: Base class public and protected members retain their accessibility in derived class.
- Protected inheritance: Base class public and protected members become protected Break and Continue In C
- Private inheritance: All inherited members become private.
- class A {
- public:
- int x;
- protected:
- int y;
- private:
- int z; // Not inherited
- };
- class B : public A { // x and y accessible // z is not accessible
- };
- class Base {
- public:
- virtual void greet() {
- cout << "Hello from Base class." << endl;
- }
- };
- class Derived1 : public Base {
- public:
- void greet() override {
- cout << "Hello from Derived1 class." << endl;
- }
- };
- class Derived2 : public Base {
- public:
- void greet() override {
- cout << "Hello from Derived2 class." << endl;
- }
- };
Virtual Functions and Hierarchical Inheritance
Virtual functions are a key feature in C++ that support runtime polymorphism. In hierarchical inheritance, virtual functions allow derived classes to override the base class method behavior Become an IT Engineer:
If you use a base class pointer to point to a derived class object and call greet(), the correct version will be executed due to virtual dispatch.
Conclusion
Hierarchical inheritance in C++ is a powerful and elegant feature that simplifies the representation of systems where multiple entities share common behaviors. It not only helps in reducing code duplication but also enhances maintainability and scalability. By understanding how constructors, destructors, access modifiers, and virtual functions work in this context, Web Designing & Development Training can write more efficient and robust object-oriented applications. The key to Advantages of Hierarchical Inheritance lies in thoughtful class design identifying shared functionalities early, properly applying inheritance hierarchies, and making use of access specifiers and polymorphism. With practice and real-world projects, developers can leverage this concept to build clean, modular, and well-structured software systems.





