
- Introduction
- What is Event Handling in React?
- Why is Event Handling Important in React?
- Basic Event Handling in React
- Binding Event Handlers
- Passing Arguments to Event Handlers
- Event Pooling in React
- Common React Event Handling Best Practices
- Functional Components vs Class Components
- Conclusion
Introduction
React is a powerful JavaScript library for building user interfaces, and one of its core features is event handling. Whether you’re creating a simple button click or more complex user interactions, React provides a smooth and consistent way to handle events. Event handling in React is a bit different than in traditional HTML and JavaScript. React uses a synthetic event system, which normalizes events across different browsers. This guide will walk you through the essentials of event handling in React, explain how to handle events in both class and functional components, and give you tips on the best practices.One of the key aspects of creating interactive user interfaces using React is event handling. It involves utilizing React components to respond to user input, such as mouse movement, keystrokes, and clicks. React event handling is a mechanism through which React components can respond to user interactions. It allows developers to create interactive and dynamic user interfaces. React provides an identical user experience on all browsers by covering native browser events with a synthetic event system. The technique through which React components respond to user input, such as clicks, keystrokes, and mouse motion, is referred to as event handling. Developers may create interactive and dynamic user interfaces by building event handlers and linking them to specific elements or components.
Do You Want to Learn More About Business Analyst? Get Info From Our Business Analyst Training Today!
What is Event Handling in React?
In React, event handling refers to the way you interact with user actions such as clicks, key presses, or form submissions. In traditional HTML, events are handled directly on DOM elements, but in React, event handling is abstracted using React Synthetic Events. By providing functions that react to particular events, it enables developers to construct dynamic and responsive interfaces.
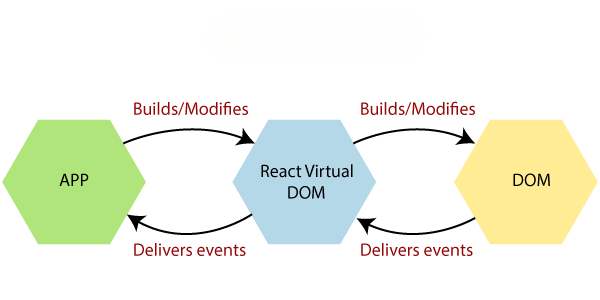
A Synthetic Event is a cross-browser wrapper around the native browser events. React creates these synthetic events to provide a consistent API across browsers and improve performance. It also helps JavaScript handle event delegation efficiently, so you don’t have to attach individual event listeners to every DOM element.
Why is Event Handling Important in React?
Event handling is crucial because it allows you to create interactive applications. In React, every interaction a user has, whether it’s clicking a button, submitting a form, or typing text, triggers an event. Properly handling these events ensures that your application responds appropriately and updates the UI accordingly. React’s event handling is essential for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces. React standardizes events between browsers through a synthetic event system. This means event objects passed to your handlers are React’s SyntheticEvent instances instead of the native browser events. It enables the program to react to keyboard inputs, form submissions, and clicks made by the user.
Some reasons why event handling is essential in React:
- User Interaction: You need event handling to capture and respond to user actions.
- Dynamic UI:React is all about building dynamic UIs, and event handling allows you to update the UI in response to user input.
- State Management: Event handlers typically interact with state, enabling dynamic changes and re-renders.
- import React from ‘react’;
- class MyComponent extends React. Component {
- handleClick = () => {
- alert(‘Button clicked!’);
- };
- render() {
- return (
- onClick={this.handleClick}>Click Me
- );
- }
- }
- import React from ‘react’;
- class HoverComponent extends React. Component {
- handleMouseEnter = () => {
- console.log(‘Mouse entered the component’);
- };
- render() {
- return
- < onMouseEnter={this.handleMouseEnter}>
- Hover over me!
- );
- }
- }
- import React from ‘react’;
- class KeyPressComponent extends React. Component {
- handleKeyPress = (event) => {
- console.log(`You pressed: ${event.key}`);
- };
- render() {
- return (
- type=”text”
- onKeyPress {this.handleKeyPress}
- placeholder “Type something”
- />
- );
- }
- }
- import React from ‘react’;
- class FormComponent extends React. Component {
- handleSubmit = (event) => {
- event.preventDefault(); // Prevents the default form submission
- console.log(‘Form submitted!’);
- };
- render() {
- return (
- input type=”text” placeholder=”Enter your name” />
- button type=”submit”>Submit
- );
- }
- }
- class MyComponent extends React. Component {
- constructor(props) {
- super(props);
- this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this); // Bind in constructor
- }
- handleClick() {
- console.log(this); // ‘this’ refers to the component instance
- }
- render() {
- return button onClick={this.handleClick}>Click Me button>;
- }
- }
- class MyComponent extends React. Component {
- handleClick = () => {
- console.log(this); // ‘this’ refers to the component instance
- };
- render() {
- return button onClick={this.handleClick}>Click Me button>;
- }
- }
- class MyComponent extends React. Component {
- handleClick = (id) => {
- console.log(`Button ${id} clicked`);
- };
- render() {
- return (
- button onClick={() => this.handleClick(1)}>Click Me 1 button>
- button onClick={() => this.handleClick(2)}>Click Me 2 button>
- );
- }
- }
- handleClick = (event) => {
- event.persist(); // Prevents the event object from being pooled
- setTimeout(() => {
- console.log(event.type); // ‘click’ will be accessible here
- }, 1000);
- };
- Use event delegation: Instead of adding event listeners to many child elements, attach listener to a parent component. This improves performance.
- Use arrow functions for binding: If you’re using class components, arrow functions ensure the correct this context.
- Avoid unnecessary re-renders: Make sure to avoid creating new functions inside render methods, which can lead to unnecessary re-renders. Consider using React. memo or useCallback in functional components.
- Use event.preventDefault() and event.stopPropagation() cautiously: These methods prevent the default action and stop event propagation, respectively. Ensure that their use aligns with your application’s requirements.
- In class components, event handlers are often bound in the constructor or as arrow functions.
- In functional components, event handlers are simpler and don’t need manual binding. Functional components also make use of React hooks like useState and useEffect.
- import React, { useState } from ‘react’;
- const MyComponent = () => {
- const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
- const handleClick = () => {
- setCount(count + 1);
- };
- return button onClick={handleClick}>Click Me({count})button>;
- };
Would You Like to Know More About Business Analyst? Sign Up For Our Business Analyst Training Now!
Basic Event Handling in React
React’s event system is quite simple to use. You attach event handlers to elements in your JSX code, just like you Dom would in traditional HTML, but there are some React-specific differences.
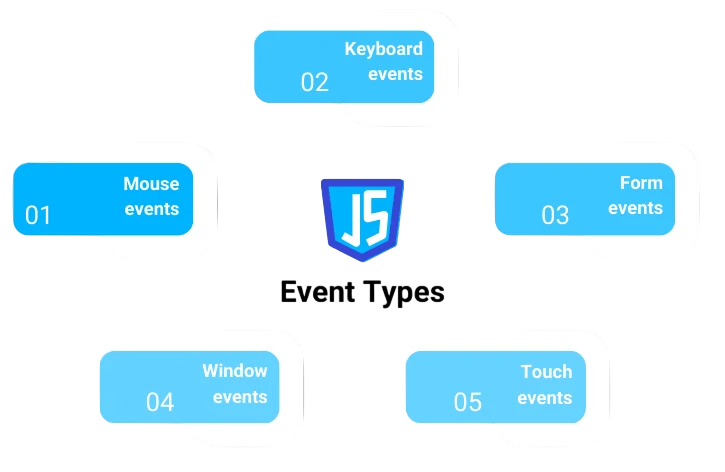
In React, event handlers are written in camelCase syntax, unlike in HTML, where they are written in lowercase (e.g., onclick in HTML in React). React also uses the SyntheticEvent object, which wraps around the browser’s native event object.
In this example, when the button is clicked, it triggers the handleClick method, which displays an alert.
Handling Mouse EventsMouse events like JSX code Click, onMouseEnter, and onMouseLeave are often used for UI interactions such as hovering or clicking.
Example of a mouse hover event handler:React also allows handling keyboard events such as onKeyDown, onKeyPress, and onKeyUp. These are useful for capturing user input or handling form submissions via the keyboard.
Example of a key press event handler:Form events like onSubmit, onChange, and onFocus are crucial when dealing with user input in forms.
Example of a key press event handler:Binding Event Handlers
In React, JSX, especially when using class components, event handlers often need to be bound to the component’s this context. Without binding, this inside the event handler may not refer to the component instance.
Binding in the ConstructorA common approach is to bind event handlers in the constructor of the class component:
You can also use arrow functions to automatically bind this in event handlers:
Arrow functions do not require manual binding because they automatically inherit the context of the enclosing scope.
Looking to Master Business Intelligence? Discover the Business Intelligence Master Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Passing Arguments to Event Handlers
If you want to pass additional arguments to your event handler, you can do so by wrapping the handler in an anonymous function.
Example of passing arguments:
This is useful when you need to pass additional data along with the event.
Event Pooling in React
React’s synthetic events are pooled, which means they are reused for performance optimization. After an event handler is invoked, the event object is cleared and reused for other events. If you need to access the event asynchronously (e.g., inside a setTimeout or promise), you should call event.persist() to prevent it from being released
Example of event persistence:
Common React Event Handling Best Practices
Want to Learn About Business Analyst? Explore Our Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Functional Components vs Class Components
React event handling works similarly in both class components and functional components, but with some key differences:
Example of handling an event in a functional component:
Conclusion
Event handling is a crucial part of building interactive React applications. Understanding how to use React’s onchange synthetic events, bind event handlers, and work with different types of events will help you build responsive UIs. In React, event handling is key to building interactive applications. React provides a consistent and solid API for commanding user interactions, be they button clicks, form submissions, or keystrokes. You can create dynamic, responsive interfaces that improve user experience by being an expert in event handling. Developers can construct dynamic and interactive user interfaces by establishing event handlers and connecting them to particular elements or components. Whether you’re working with class or functional components, React provides a consistent and powerful way to handle user interactions efficiently. By following best practices and leveraging React’s advanced event handling features, you can create highly interactive applications that respond seamlessly to user inputs.


