
- Definition of DSA
- Importance in Computer Science
- Types of Data Structures
- Commonly Used Data Structures
- Algorithm Complexity (Time/Space)
- DSA in Real-World Applications
- DSA in Programming Interviews
- DSA vs DBMS vs OOP
- How to Start Learning DSA
- Career Scope with DSA
- Conclusion
Introduction
In the world of computer science and software development, Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) form the bedrock of problem-solving. Whether you’re optimizing search queries, building a new application, or preparing for a technical interview, DSA is an essential part of your toolkit a foundational skill set that complements the structured curriculum offered in Web Developer Training, where learners master HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and full-stack logic. Integrating data structures and algorithms into your development workflow ensures scalable, efficient, and interview-ready web applications. Understanding DSA not only improves your programming efficiency but also enhances your ability to write scalable and optimized code. This guide will explore what DSA means, its components, why it is important, and how it applies to both theoretical and practical computing problems.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Definition of DSA
Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) refers to a combination of two essential concepts. To understand how data is manipulated within these structures, exploring tools like the Python Split Method with Example can offer practical insight into string handling and data segmentation.
- Data Structures are ways to organize and store data efficiently.
- Algorithms are step-by-step procedures or formulas for solving a problem.
Together, DSA is used to efficiently process, retrieve, and store data. For example, an algorithm might sort numbers, and a data structure might be used to store those numbers during the process.
Importance in Computer Science
DSA is crucial in several areas of computing. To build scalable and efficient applications, developers often rely on tools like the Must-Know Top Python Framework’s, which streamline development workflows and enhance algorithmic implementation.
- Efficient Code: Understanding DSA helps create optimized solutions in terms of speed and memory usage.
- Problem Solving: Most real-world problems require breaking down into smaller, manageable problems which are solved using algorithms and data structures.
- Interview Preparation: Most technical interviews for software engineering positions focus heavily on DSA.
- Competitive Programming: DSA is a core part of solving problems quickly under constraints.
Without a solid foundation in DSA, developers may struggle with writing high-performance applications.
Types of Data Structures
Data structures and algorithms are essential for solving computational problems. They provide different ways to organize and process information. Linear data structures, such as arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues, allow for sequential storage and manipulation. This enables efficient data management using methods like Last-In-First-Out and First-In-First-Out. Non-linear structures, including trees and graphs, offer more complex hierarchical and network-based representations, which support intricate data relationships and traversal techniques a foundational concept echoed in Web Developer Training, where learners master both front-end and back-end logic, responsive design, and structured data handling. Understanding these advanced structures equips developers to build scalable, efficient web applications that mirror real-world complexity.
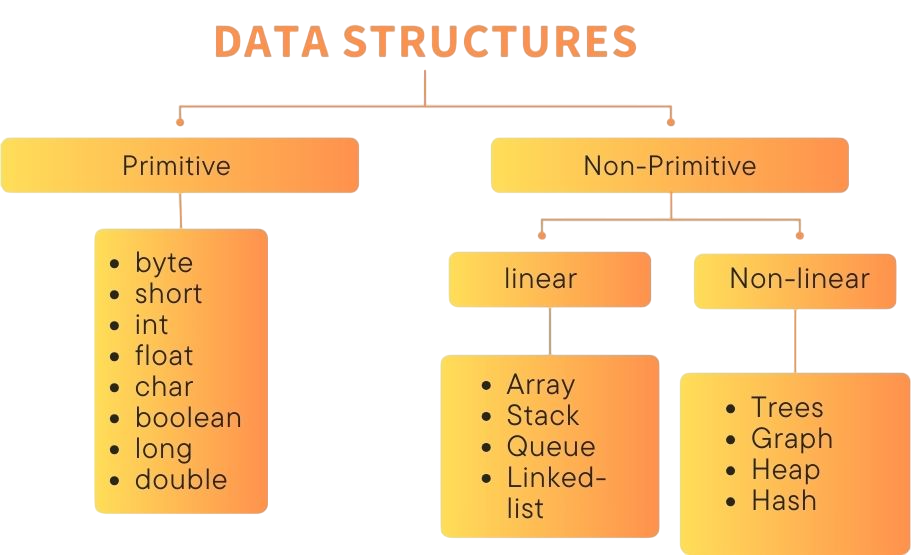
Hash-based structures, like hash tables, allow for quick data retrieval through key-value pair mappings. Algorithms include various problem-solving strategies. These range from basic search and sorting techniques to more complex methods like dynamic programming, greedy algorithms, and recursive approaches. Each type of algorithm addresses specific computational needs and improves performance by choosing the right technique for each challenge. Whether developers use binary search, merge sort, or graph traversal algorithms like BFS and DFS, they can take advantage of these tools to create efficient and scalable solutions in many computational areas.
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Commonly Used Data Structures
Some data structures are used more frequently due to their versatility. In large-scale data processing, understanding the Hadoop Ecosystem provides insight into how these structures are leveraged across distributed systems to manage and analyze massive datasets efficiently.
- Array: Easy access via index; used everywhere.
- Linked List: Dynamic size; used in queues and stacks.
- Stack and Queue: Useful for undo functionality and scheduling tasks.
- HashMap/Dictionary: Enables fast lookups; commonly used in caching.
- Trees: Represent hierarchical data structures like XML and JSON.
- Graphs: Model relationships in maps, networks, and web pages.
These structures appear in problems ranging from string manipulation to database indexing.
Algorithm Complexity (Time/Space)
Algorithm complexity measures the efficiency of an algorithm.
Time Complexity:
Represents the amount of time taken:
- O(1) – Constant time
- O(n) – Linear time
- O(n log n) – Log-linear time
- O(n²) – Quadratic time
Space Complexity:
Optimizing time and space is essential for writing performant applications. Tools like Lucidchart, Draw.io, or even pen-and-paper can be used to sketch flowcharts easily.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
DSA in Real-World Applications
DSA is not just academic it powers real-world software:
- Search Engines: Use trees, graphs, and hash tables for indexing and retrieval.
- Navigation Systems: Apply graph algorithms to compute shortest paths.
- E-commerce Platforms: Use sorting algorithms to organize and display product listings.
- Operating Systems: Employ queues, trees, and hash maps for scheduling and memory management.
- Social Networks: Use graphs to model relationships and suggest connections.
- Databases: Implement trees (e.g., B-Trees) for indexing and efficient searching.
These examples prove that DSA is behind the scenes in almost every software system.
DSA in Programming Interviews
Most top tech companies (Google, Amazon, Microsoft, etc.) focus heavily on DSA during interviews. To prepare effectively, mastering basics like How to Input a List in Python can help candidates demonstrate practical coding skills alongside algorithmic thinking.
Typical questions include:
- Find the kth smallest element
- Detect a cycle in a graph
- Implement an LRU cache
- Convert an infix expression to postfix
Having solid DSA knowledge gives you an edge in cracking coding interviews and showcasing your problem-solving ability.
DSA vs DBMS vs OOP
These three concepts often overlap but serve different purposes:
| Feature | DSA | DBMS | OOP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Algorithms & Data Management | Data Storage & Retrieval | Design Paradigm |
| Use Case | Problem Solving, Efficiency | Structured Querying | Software Design |
| Example | Sorting, Searching | SQL Queries | Classes, Objects |
| Applications | Coding, OS, AI | Banking Systems, ERP | Applications, Games |
DSA complements both DBMS and OOP, often working alongside them in application development.
How to Start Learning DSA
Starting with DSA may seem overwhelming, but you can follow a structured approach. One effective way to build confidence is by exploring practical projects like How To Make A Chatbot In Python, which combine algorithmic thinking with real-world application.
- Choose a Programming Language: Pick one like Python, Java, or C++ that has strong community support.
- Start with Basic Structures: Learn arrays, strings, stacks, and queues first.
- Move to Intermediate Concepts: Work on trees, recursion, hash maps, and sorting.
- Master Algorithms: Study search, sort, greedy, dynamic programming, and graph algorithms.
Career Scope with DSA
DSA is foundational to many career paths:
- Software Developer: All roles expect strong DSA knowledge for problem-solving.
- Data Scientist: Efficient data handling using appropriate structures.
- AI/ML Engineer: Algorithms for learning, decision-making, and optimization.
- System Architect: Designing scalable, efficient software systems.
- Competitive Programmer: Contests like ACM ICPC and CodeJam require in-depth DSA.
- Startup Engineer: Startups expect developers to build fast and efficiently, which demands DSA knowledge.
Conclusion
Data Structures and Algorithms form the core of effective computing. They allow developers to write better, faster, and scalable code. Whether you’re an aspiring developer, preparing for interviews, or aiming to build cutting-edge applications, mastering DSA is non-negotiable a foundational skill set that complements the structured learning approach in Web Developer Training, where learners gain hands-on experience in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, UX principles, and responsive design. Integrating data structure mastery with design logic empowers developers to build efficient, scalable, and user-centric web applications. By understanding the right structure and algorithm for a problem, you not only solve it but solve it well. The path may seem long, but with consistent practice and curiosity, anyone can become proficient in DSA and open up vast opportunities in the tech world.





