
- Definitions of Both Roles
- Key Responsibilities
- Required Skillsets
- Tools and Technologies
- Focus Area: Web vs Applications
- Project Lifecycle
- Career Path
- Salary Comparison
- Industry Demand
- Work Environment
- Education and Certifications
- Conclusion
Definitions of Both Roles
Web Developer vs Software Developer is an important distinction for anyone exploring a career in technology. A Web Developer specializes in creating and maintaining websites and web applications that run on browsers. Their work involves client-side (front-end), server-side (back-end), or both (full-stack) development core roles explored in Web Designing Training, where learners gain hands-on experience with HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and backend technologies like PHP and MySQL. By mastering both visual design and functional logic, developers can build responsive, interactive websites that perform seamlessly across platforms. They focus on accessibility, performance, responsiveness, and SEO to ensure an optimal user experience online. On the other hand, a Software Developer, or Software Developer, builds software programs or mobile applications for devices such as desktops, tablets, or smartphones. Their focus lies in creating standalone or networked applications with rich functionalities, often designed to operate independently of a web browser. Understanding the differences in Web Developer vs Software Developer roles helps individuals choose the path that best aligns with their skills, interests, and career goals.
To Earn Your Web Developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Data Science Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web Developer Courses Today!
Key Responsibilities
As a versatile technology professional, a web and Software Developer plays a key role in creating dynamic digital solutions. They use their knowledge of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and various programming languages like Java, Swift, and C# to design user-friendly interfaces and develop responsive applications for different platforms skills compared in Angular vs React, where developers evaluate how each framework supports cross-platform UI development. Angular’s structured, TypeScript-based approach suits enterprise-grade apps, while React’s flexible component model enables rapid prototyping and dynamic user experiences across web and mobile. Their tasks include implementing responsive design, coding on the server side, maintaining websites, optimizing performance, and conducting rigorous testing across different browsers. In addition to technical work, developers collaborate with teams, gather user requirements, create detailed documentation, and ensure strong application security and performance. By connecting APIs, managing databases, and performing thorough testing, these skilled professionals turn complex technical problems into smooth, user-friendly digital experiences that meet today’s technology needs.
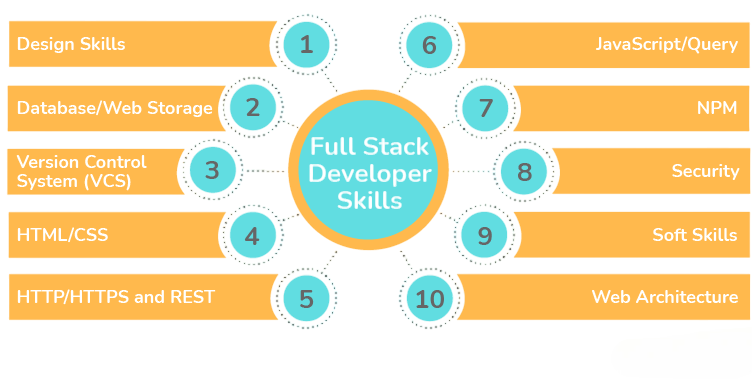
Required Skillsets
Web Developer Skills:
- Proficiency in HTML, CSS, JavaScript
- Frameworks: Angular, React, Vue.js
- Server-side languages like PHP, Node.js, Python
- Knowledge of CMS platforms (WordPress, Joomla)
- SEO fundamentals and web performance optimization
- Understanding of RESTful APIs and AJAX
- Git for version control
Software Developer Skills:
- Strong command of programming languages (Java, C++, C#, Swift, Kotlin)
- Proficiency in integrated development environments (IDEs)
- Familiarity with SDLC and Agile methodologies
- Knowledge of database management (SQL, NoSQL)
- Understanding of security protocols and encryption
- Unit testing and debugging techniques
- Good grasp of UI/UX design for applications
Tools and Technologies
Web Developer Tools:
- Code Editors: VS Code, Sublime Text
- Frameworks/Libraries: React, Angular, Vue.js, Bootstrap
- CMS: WordPress, Drupal
- Version Control: Git, GitHub
- Package Managers: npm, Yarn
- Testing: Jest, Mocha, Selenium
- DevOps Tools: Netlify, Vercel, GitHub Actions
Software Developer Tools:
- IDEs: Android Studio, Xcode, Visual Studio
- Languages: Java, Swift, C#, Kotlin
- Frameworks: .NET, Flutter, React Native
- Database Tools: SQLite, Firebase, MongoDB
- Version Control: Git, Bitbucket
- CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, Azure DevOps
- Testing Tools: JUnit, XCTest, Espresso
- Junior Web Developer
- Frontend/Backend Developer
- Full-Stack Developer
- Web Architect
- UI/UX Lead
- Web Project Manager
- CTO or Tech Lead
- Junior App Developer
- Software Engineer
- Mobile App Developer (iOS/Android)
- Lead Developer
- Product Manager
- Solutions Architect
- VP of Engineering
- Web Developer: ₹3 LPA (entry) to ₹12+ LPA (senior)
- Software Developer: ₹4.5 LPA (entry) to ₹20+ LPA (senior/mobile lead)
- Web Developer: $55,000 to $115,000
- Software Developer: $65,000 to $140,000
- Web Developer: £28,000 to £65,000
- Software Developer: £32,000 to £75,000
- Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, IT, or related field
- Bootcamps or diploma courses are also accepted if skills are demonstrated
- Meta Front-End Developer (Coursera)
- Google UX Design Certificate
- FreeCodeCamp certifications
- Microsoft Certified: Web Applications Developer
- Android Developer Certification (Google)
- Apple Certified iOS Developer
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate
- Oracle Certified Java Programmer
Would You Like to Know More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Now!
Focus Area: Web vs Applications
Web developers and Software Developers have different but complementary roles in the world of digital technology. Web developers focus on building web-based interfaces that work across different browsers and can be accessed via URLs. They skillfully manage both static and dynamic content while prioritizing front-end performance and search engine optimization core competencies emphasized in Web Designing Training, where learners explore how to balance content rendering strategies with SEO best practices. By mastering techniques like lazy loading, semantic HTML, and responsive design, developers ensure fast load times, improved accessibility, and higher search engine rankings across varied content types. On the other hand, Software Developers create mobile and desktop applications, either native or cross-platform, that handle more complex functions. They pay attention to important technical details like memory management, background processing, and offline access. These developers optimize their applications for specific device hardware and operating systems. Often, they build apps that can run on their own without needing a web browser. While web developers ensure smooth online experiences across various platforms, Software Developers create specialized solutions that integrate closely with hardware, providing strong, independent digital experiences that meet specific user needs and fit various technological settings.
Project Lifecycle
Our project lifecycle follows a clear path for web and app development. It starts with detailed requirement gathering and thorough analysis. We move on to thoughtful UI/UX design and planning, which lays a strong groundwork for development. The process includes solid frontend and backend coding, along with careful unit and integration testing on various platforms. Our developers carry out smooth implementation, launching solutions across web environments and mobile app stores while prioritizing quality core practices outlined in What Is a Web Developer, where learners explore the full lifecycle of web application development. From writing scalable code to deploying across diverse platforms, mastering these workflows ensures high-performance, user-centric digital experiences. After deployment, we offer ongoing maintenance, performance improvement, and targeted SEO enhancements to ensure lasting digital success and client satisfaction. The project lifecycle approach allows us to provide modern technological solutions that meet complex business needs accurately and creatively.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Web Developer? Sign Up For Our Web Developer Courses Today!
Career Path
Web Developer Career Path:
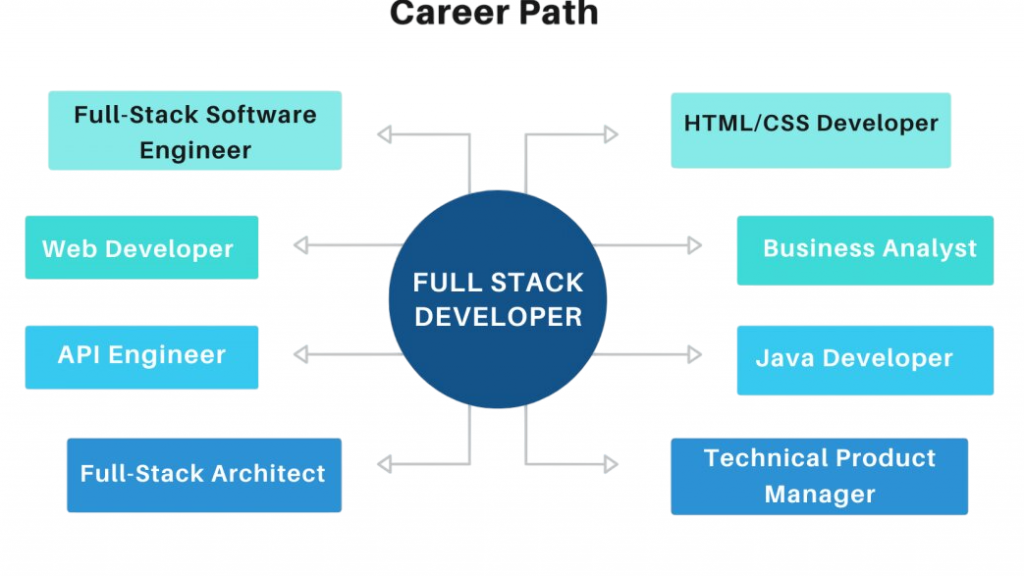
Software Developer Career Path:
Salary Comparison
Note: Salaries vary by country, experience, and company size.
India (INR per annum):
United States (USD per annum):
United Kingdom (GBP per annum):
In general, Software Developers tend to earn slightly more, especially those with expertise in mobile development or enterprise software yet backend specialization remains highly valuable, as explored in Become a Backend Developer, where learners master server-side logic, API design, and database architecture. With growing demand across industries like finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, backend developers play a critical role in building scalable, secure systems that power modern applications.
Industry Demand
Web developers face strong demand across various digital fields, including marketing agencies, startups, e-commerce sites, media companies, and educational institutions. The rise of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) has increased their importance, along with steady market opportunities driven by greater SEO and accessibility requirements trends explored in Understanding Render in ReactJS, where developers learn how React’s rendering model supports dynamic, responsive interfaces. By mastering conditional rendering, virtual DOM optimization, and accessibility-aware component design, learners can build PWAs that deliver fast, inclusive user experiences across devices and platforms. Software Developers also see high demand in specific areas like fintech, healthcare, gaming, telecom, and IT consulting. The mobile-first approach has boosted the need for iOS and Android developers, with more focus on cross-platform development using frameworks like Flutter and React Native. While both fields show considerable market potential, mobile application development is growing faster, largely due to the widespread use of smartphones and the increasing demands of the digital ecosystem.
Work Environment
Web developers and Software Developers have different but linked roles in the technology world. Web developers usually work in creative teams. They collaborate closely with designers and marketers and are more likely to work remotely or freelance. Their tasks often include shorter release cycles with agile sprints and require working closely with SEO and UI/UX teams. On the other hand, Software Developers mostly work in software companies, IT departments, or product-based firms roles that increasingly rely on front-end frameworks like React Material UI to build polished, responsive user interfaces. With pre-styled components, theme customization, and accessibility features, Material UI empowers developers to deliver consistent design systems across enterprise-grade applications, streamlining workflows in both startup and corporate environments. They focus on long-term projects that lead to multiple releases. These developers must thoroughly test their applications on various devices and operating systems. They work in teams that include quality assurance, DevOps, and product management specialists. While their methods and work settings vary, both roles are essential for driving innovation and providing high-quality digital solutions.
Education and Certifications
Educational Background:
Web Developer Certifications:
Software Developer Certifications:
Certifications aren’t always mandatory, but they boost credibility especially for beginners.
Conclusion
Web Developer vs Software Developer play critical yet distinct roles in the software industry. The Web Developer focuses on browser-based applications, ensuring responsive design, SEO optimization, and seamless user experience across devices. They are ideal for projects where digital presence and rapid deployment matter most. In contrast, Software Developers specialize in creating software for mobile and desktop platforms. They typically work on more complex, hardware-integrated apps that offer a richer user experience even without an internet connection an advanced capability contrasted in Web Designing Training, where learners focus on building responsive web interfaces while understanding the limitations of browser-based environments. While web design emphasizes accessibility and cross-device compatibility, offline-first and hardware-integrated apps require deeper control over system resources, local storage, and native APIs to deliver seamless functionality in low-connectivity scenarios. In terms of salary, career growth, and demand, Software Developers may have a slight edge due to the explosion of mobile-first businesses and need for custom software. However, Web Development remains a strong, ever-evolving field with ample freelance, remote, and full-time opportunities. Choosing between them depends on your interests, whether you enjoy crafting visual experiences on the web or engineering feature-rich software that interacts with devices and networks, making understanding Web Developer vs Software Developer essential for career planning.





