- What is a Graph Database?
- Key ideas in graph databases include
- Types of Graph Databases
- How Does a Graph Database Work?
- Graph Database Use Case Examples
- Graph Database Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Conclusion
What is a Graph Database?
Graph databases are a specialised kind of database that use graph concepts to constitute, save, and manipulate records. They leverage the energy of nodes, relationships, and residences to seize and navigate the complicated connections among entities. Graph databases are well-suitable for packages including social networks, advice systems, and fraud detection, in which knowledge relationships are essential. These key ideas shape the inspiration of graph databases and allow the representation, storage, querying, and evaluation of linked records in a graph-like structure.A Graph Database is a type of Database Training designed to store, map, and query relationships between data using graph structures. Unlike traditional relational databases that use tables, or document databases that store data in JSON-like formats, graph databases use nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data. Nodes represent entities (such as people, products, or places), while edges represent the relationships or connections between those entities. Both nodes and edges can have properties that provide additional information. This structure makes graph databases especially well-suited for scenarios where relationships are as important as the data itself such as social networks, recommendation systems, fraud detection, and network analysis. One of the key advantages of graph databases is their ability to perform deep, complex queries efficiently, even on highly connected data, without the heavy joins required in relational databases. Popular graph databases include Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, and ArangoDB. With the rise of connected data in modern applications, graph databases offer a powerful way to model and query real-world relationships intuitively and effectively.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Key ideas in graph databases include
- Nodes- Nodes are the essential constructing blocks in the graph database. They constitute entities or items withinside the actual global and incorporate residences that describe them. For example, in a social network, a node may want to constitute someone with residences like name, age, and occupation.
- Relationships- Relationships set up connections among nodes and offer context to the records. They seize the character of institutions among entities. For instance, in a social network, a courting may want to constitute a “friendship” among people, Database Management System with residences including the date the friendship turned into established.
- Properties- Properties are the attributes related to be nodes and relationships. They save extra data about entities and connections. Properties may be used to feature information or metadata to the records version, making it richer and extra expressive.
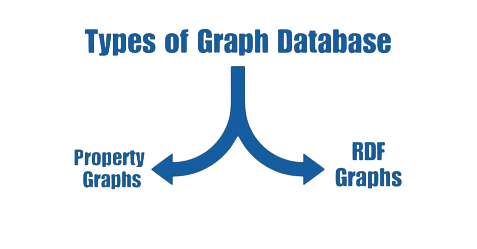
Types of Graph Databases
There are usually styles of graph databases, with every supplying awesome skills suitable to specific records modeling and querying requirements.
Here are the graph database types:
- Property Graph Databases
- Description: They rent a version in which nodes and edges could have related residences as key-fee pairs. Nodes commonly constitute an entity, Self-Join in SQL at a same time as edges depict the relationships among them.
- Examples: Neo4j, ArangoDB, Amazon Neptune, and OrientDB.
- Use Cases: Widely utilized in packages like social networks, advice engines, and fraud detection.
- Description: RDF graph databases, additionally referred to as triple stores, are designed to save, retrieve, and question records withinside the shape of triples, such as subject-predicate-object. These databases are frequently related to the semantic net and related records initiatives.
- Examples: Virtuoso, Jena, Stardog, AllegroGraph.
- Use Cases: RDF graph databases are beneficial in packages like understanding graphs, ontologies, and semantic net projects.
- Relationship Focus– Graph databases constitute and examine relationships among facts factors. They offer a herbal and green manner to version and traverse relationships, allowing effective queries that find significant insights.
- Flexibility in Data Modeling– Graph databases provide flexibility in facts modeling. They permit for dynamic Data warehouses and evolving systems with out the want for predefined schemas. This flexibility is useful whilst facts systems are issue to common adjustments or have various dating styles.
- Efficient Relationship Queries– Graph databases are optimized for dating-primarily based totally queries. Traversing relationships withinside the graph shape is exceedingly green, permitting for immediate and scalable questions that discover connections and styles withinside the facts.
- Complexity in Certain Queries– Graph databases face demanding situations with particular queries that rely upon something apart from relationships. Operations like aggregations, complicated joins, or queries frequently related to tabular information can be much less green than conventional relational databases.
- Learning Curve– Working with graph databases calls for the graph information version and specialised question languages like Cypher or Gremlin. This mastering curve can mission people conversant in relational databases or different database control systems.
- Storage Overhead– Storing relationships explicitly in a graph shape can growth garage overhead in comparison to relational databases. Representing relationships as edges consumes extra garage space, Data Mart vs Data Warehouse which may be a attention for environments with constrained garage capacity.
- Limited Use Cases– While graph databases excel in situations wherein relationships are critical, there can be higher picks for programs that commonly address dependent and tabular data. In such cases, conventional relational databases provide higher overall performance and simplicity.
- Neo4j: One of the most widely used graph databases, known for its powerful Cypher query language and robust community support.
- Amazon Neptune: A fully managed graph database service by AWS that supports both property graphs and RDF graphs.
- ArangoDB: A multi-model database that supports graph, document, and key-value data models, offering flexibility and scalability.
- JanusGraph: An open-source, Database Partitioning Techniques distributed graph database optimized for large-scale graph processing, often used with Apache Cassandra or HBase.
- OrientDB: Combines graph and document database features, allowing complex data relationships with a flexible schema.
- TigerGraph: A high-performance, scalable graph database designed for real-time analytics and deep link analysis.
- Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB (Gremlin API): A globally distributed database service supporting graph data through the Gremlin query language.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
How Does a Graph Database Work?
A graph database works by storing data in the form of nodes, edges, and properties, which collectively form a graph structure that models complex relationships between data entities. Unlike traditional relational databases that use tables and predefined schemas, graph databases focus on the connections between data points, making them especially suited for applications where relationships are central. In a graph database, nodes represent entities such as people, places, products, or concepts. Each node can have associated properties, which are key-value pairs that describe attributes of that entity—like a person’s name, age, or email. The edges represent the relationships between nodes and can also have properties describing the nature of the relationship. For example, in a social network graph, nodes might be users, while edges represent friendships, with properties such as the date the friendship was established. The power of a graph database lies in its ability to efficiently traverse and query these relationships. When you query a graph database, the system quickly navigates from node to node along edges, following paths that satisfy the query’s conditions. This traversal capability allows graph databases to handle complex queries involving multiple degrees of separation or intricate relationship patterns much faster than relational databases, which require costly join operations. Graph Database Training typically use specialized query languages like Cypher (used by Neo4j) or Gremlin to express these traversal queries intuitively. These languages allow developers to specify patterns of nodes and relationships they want to find, making it easier to work with highly connected data. Overall, graph databases excel in scenarios where relationships are critical, such as social networks, recommendation engines, fraud detection, and network analysis. By modeling data as a graph, they provide a flexible, efficient way to represent and analyze interconnected information, helping organizations unlock insights that are difficult to obtain with traditional database models.
Graph Database Advantages
Graph Database Advantages provide numerous benefits that cause them to a sensible desire for coping with and reading complicated and interconnected facts:
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Disadvantages of Graph Databases
While graph databases provide several advantages, there also are a few ability dangers to consider:
Popular Graph Database Platforms point
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Graph databases are a effective and green answer for coping with interconnected information and complicated relationships. By leveraging the inherent graph shape, graph Database Training permit agencies and companies to advantage precious insights, discover hidden patterns, and make information-pushed decisions. The graph version`s inherent flexibility permits clean version to evolving information structures, making it a future-evidence desire for coping with various and dynamic datasets.


