
- What is a Data Strategy?
- Importance for Enterprises
- Assessing Current Data Capabilities
- Data Governance and Compliance
- Cloud vs On-Premise Considerations
- Choosing the Right Database Types
- Data Integration and Interoperability
- Conclusion
What is a Data Strategy?
A data strategy is a comprehensive plan that defines how an organization will collect, manage, use, and protect its data assets. It acts as a guiding framework that aligns data-related initiatives with the overall business goals, ensuring that data is recognized and utilized as a valuable strategic resource. Having a robust data strategy in place helps organizations maximize the value they can extract from their data while minimizing the risks that come with improper data management, such as security breaches, compliance violations, or poor decision-making. In today’s digital world, businesses generate enormous amounts of data from various sources including customer interactions, financial transactions, supply chain operations, marketing campaigns, and more. Without a clear and well-structured strategy, this data can become fragmented or isolated in separate departments, making it difficult to access or analyze effectively a challenge addressed in Database Developer Training. When data is siloed, its potential to support business growth and innovation is limited, and in some cases, unmanaged data can become a liability by increasing costs or exposing the organization to risks. A strong data strategy provides clarity on how data should be handled throughout its lifecycle, from initial collection and storage to processing, analysis, and eventual archiving or deletion. It ensures that data governance policies, quality standards, and security measures are consistently applied. By doing so, organizations can improve the accuracy, relevance, and timeliness of the information used to drive decision-making. Ultimately, a well-designed data strategy enables companies to become more agile, competitive, and customer-focused by turning raw data into actionable insights that support informed business decisions and long-term success.
Interested in Obtaining Your Database Certificate? View The Database Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Importance for Enterprises
In the digital age, data has evolved from being merely a by-product of business activities to becoming a vital driver of growth and innovation. A well-defined data strategy enables organizations to harness the full potential of their data assets and gain a competitive advantage. One of the key benefits of having a solid data strategy is the ability to make informed, data-driven decisions. By relying on accurate and timely information, businesses can better understand market trends, customer preferences, and operational performance, leading to smarter choices that support long-term success. Additionally, data strategies help improve customer experience by enabling personalization, which can be effectively managed through proper use of Schema in SQL Server. Companies can analyze customer behavior and tailor products, services, and communications to meet individual needs, thereby increasing satisfaction and loyalty. Moreover, a strong data strategy allows organizations to optimize their operations and reduce costs. Through data analysis, inefficiencies can be identified and addressed, supply chains can be streamlined, and resource allocation can be improved. Another important aspect is ensuring regulatory compliance and data security. With increasing regulations around data privacy and protection, a clear strategy ensures that businesses handle data responsibly and avoid legal risks. Furthermore, data strategies foster innovation by helping companies identify new revenue streams and develop novel products or services based on data insights.
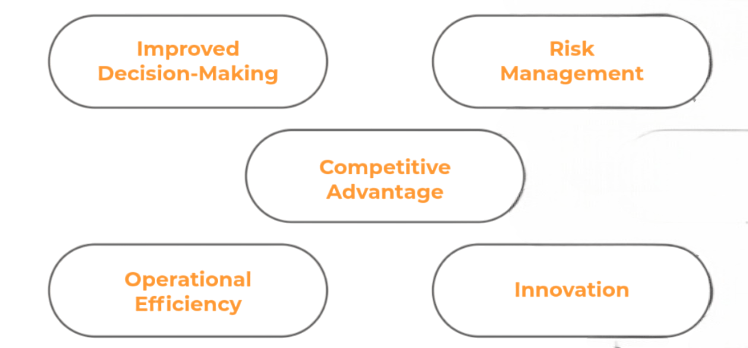
Without a data strategy, enterprises risk becoming overwhelmed by the vast volume of data generated daily. This can lead to inefficiencies, missed opportunities for growth, and increased vulnerability to data breaches and compliance failures. In such a scenario, data may become more of a burden than an asset. Therefore, having a comprehensive and well-executed data strategy is essential for organizations seeking to thrive in today’s fast-paced and data-driven business environment.
Assessing Current Data Capabilities
- Assess Data Quality and Integrity: The first critical aspect is to evaluate the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the organization’s data. High-quality data is essential for making sound decisions and avoiding costly errors caused by inaccurate or inconsistent information.
- Evaluate Existing Data Infrastructure and Tools: Review the current technology landscape, including databases, storage systems, analytics platforms, and software tools. Understanding the strengths and limitations of existing infrastructure helps determine whether upgrades or new investments are necessary.
- Review Data Governance and Management Practices: Examine policies, standards, and procedures that govern how data is collected, stored, secured, and shared, especially when comparing technologies like Cassandra Vs MongoDB.
- Analyze Employee Data Literacy: Assess the data skills and knowledge of employees across departments. Understanding workforce capabilities reveals training needs and helps foster a data-driven culture where staff can confidently use data in their roles.
- Study Data Usage Patterns: Investigate how data is currently utilized within the company. Identifying which departments rely on data and for what purposes uncovers opportunities to enhance data access and promote collaboration.
- Identify Gaps and Opportunities: An honest assessment reveals weaknesses such as siloed data, outdated tools, or limited analytical skills. It also highlights opportunities to leverage data more effectively for business growth and innovation.
- Example Insight: For instance, an organization may find that it collects vast amounts of customer data but lacks advanced analytics capabilities to convert this data into actionable insights, limiting its ability to improve customer experience or drive strategic decisions.
- Defining Policies and Responsibilities: Data governance starts with establishing clear policies that outline how data should be managed. It also defines roles and responsibilities, such as data owners and stewards, to ensure accountability throughout the data lifecycle.
- Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency: A key goal of governance is to maintain high data quality by setting standards and procedures that keep data accurate, consistent, and trustworthy for decision-making.
- Implementing Security Measures: Data governance includes enforcing strict access controls and privacy policies to protect sensitive information from unauthorized use or breaches, a crucial aspect emphasized in Database Online Training.
- Ethical Data Usage: Governance frameworks guide ethical practices, ensuring data is handled responsibly and used only for intended, compliant purposes, thus building organizational integrity.
- Regulatory Compliance: Complying with laws like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is essential.
- Metadata Management and Data Standards: Establishing consistent metadata practices and data standards enables better data cataloging, discoverability, and interoperability across systems.
- Regular Audits and Monitoring: Continuous audits and compliance checks verify adherence to governance policies and identify potential vulnerabilities or gaps. This ongoing oversight strengthens data trust and minimizes risks related to misuse or unauthorized access.
- Relational Databases for Structured Data: Relational databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL are ideal for handling structured data organized into tables with defined schemas. They support complex queries, transactions, and strong consistency, making them suitable for traditional business applications such as finance, HR, and inventory management.
- NoSQL Databases for Unstructured or Semi-Structured Data: NoSQL databases such as MongoDB and Cassandra are designed to handle flexible, schema-less data formats like JSON or XML, highlighting key differences discussed in DBMS vs RDBMS vs NoSQL.
- Time-Series Databases for IoT and Telemetry: Time-series databases specialize in storing and querying data points indexed by time. This makes them perfect for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, monitoring systems, and telemetry data where rapid ingestion and efficient retrieval of time-stamped data are critical.
- Graph Databases for Relationship-Driven Data: Graph databases like Neo4j focus on representing and querying complex relationships between entities. They are particularly useful in social networks, recommendation engines, fraud detection, and network analysis where relationships are as important as the data itself.
- Performance Considerations: Choosing the right database type helps optimize query performance and response times by matching the technology to the specific data and workload characteristics.
- Scalability Needs: Different databases scale differently; relational databases often scale vertically, while many NoSQL and time-series databases support horizontal scaling to handle large, distributed datasets effectively.
- Cost Efficiency: Selecting an appropriate database based on use case helps manage costs by avoiding over-provisioning resources and minimizing maintenance overhead, ensuring the solution aligns with both technical and business requirements.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Database Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Data Governance and Compliance
Cloud vs On-Premise Considerations
Choosing between cloud and on-premise data storage and processing is a critical decision when developing a data strategy. Cloud platforms provide many advantages such as scalability, flexibility, and often lower upfront costs, which make them appealing for a wide range of organizations. Cloud services allow businesses to quickly adjust their storage and computing resources based on demand, avoiding the need for large capital investments in hardware. This elasticity also supports rapid growth and innovation. However, moving to the cloud raises important concerns about data privacy, as sensitive information is stored off-site, potentially exposing it to security risks. There is also the issue of vendor lock-in, where organizations become dependent on a specific cloud provider’s technologies and pricing, making it difficult to switch providers in the future, a challenge that can indirectly impact decisions around data architecture, including understanding the Types of Joins in SQL Server. Additionally, latency or delays in data access can affect performance for certain real-time applications. On the other hand, on-premise solutions give organizations greater control over their data infrastructure. This option is often preferred in industries where data sensitivity and regulatory requirements are high, such as healthcare, finance, and government. Maintaining data on-site can simplify compliance with data residency laws and allow for customized security measures tailored to organizational needs. Despite the benefits, on-premise infrastructure typically requires significant upfront investment, ongoing maintenance, and can be less flexible when scaling resources. Hybrid models, which combine cloud and on-premise components, have grown in popularity. These solutions aim to balance the benefits of both approaches by allowing critical or sensitive data to remain on-premise while taking advantage of cloud resources for less sensitive workloads or peak demand periods. When deciding between these options, organizations should carefully evaluate key factors including cost and total cost of ownership, scalability needs, security and compliance requirements, and how well the solution integrates with existing systems and workflows.
Choosing the Right Database Types
Data Integration and Interoperability
In most organizations, data is stored across multiple systems and platforms, often leading to fragmentation and challenges in gaining a comprehensive view of the business. Integrating this dispersed data and ensuring that various systems can communicate effectively is critical for achieving unified analytics and streamlined operations. Data integration typically involves processes such as extracting data from different sources, transforming it into a consistent format, and loading it into a centralized repository like a data warehouse or data lake. This approach allows organizations to consolidate their data, making it easier to analyze and use for decision-making purposes. Interoperability is closely related and refers to the ability of different systems, applications, and tools to work together seamlessly. Achieving interoperability often requires the use of application programming interfaces (APIs), middleware solutions, or adoption of standardized data formats and protocols, as outlined in the MongoDB Commands Cheat Sheet. These technologies enable data exchange and communication between disparate systems, regardless of the underlying technologies or platforms. When systems are interoperable and data is well integrated, businesses can break down data silos, which are isolated pockets of information inaccessible to other parts of the organization. A well-integrated and interoperable data ecosystem offers several important benefits. It enables cross-functional insights by combining data from various departments such as sales, marketing, finance, and operations, providing a holistic view of business performance. This comprehensive perspective supports real-time decision-making, allowing organizations to respond quickly to market changes or operational issues. Additionally, integration reduces redundancies and inconsistencies in data, improving overall data quality and reliability. Ultimately, a unified data environment empowers businesses to be more agile, efficient, and competitive in their respective industries.
Preparing for a Database Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers
Conclusion
In conclusion, having a comprehensive data strategy is essential for modern enterprises that want to fully harness the power of their data. Data is one of the most valuable assets a company can possess, but without a clear and well-thought-out plan, it can become overwhelming and underutilized. Developing an effective data strategy requires collaboration across multiple departments, including IT, business units, compliance teams, and leadership. Each group brings unique insights and requirements that must be aligned to create a unified approach to data management. Careful planning is necessary to address all aspects of the data lifecycle, from collection and storage to processing, analysis, and security. It is important to establish clear goals, governance policies, and performance metrics to ensure that data initiatives support overall business objectives, a key focus in Database Online Training. Moreover, a data strategy is not a one-time project but an ongoing process that needs regular evaluation and adjustment. As technology evolves and business needs change, organizations must continuously refine their approach to stay competitive. By doing so, they can ensure that data remains accurate, accessible, and secure. When executed effectively, a comprehensive data strategy enables enterprises to turn raw data into meaningful insights that drive better decision-making, improve customer experiences, optimize operations, and foster innovation. Ultimately, a strong data strategy provides a foundation for competitive advantage in today’s data-driven world. It empowers organizations to respond swiftly to market changes, identify new opportunities, and create value that sets them apart from competitors. Investing time and resources into a well-designed data strategy is essential for any enterprise that wants to thrive in the rapidly changing business landscape.


