- Introduction Understanding SQL and NoSQL Databases
- Data Models Relational vs Non Relational Data
- Schema Flexibility and Data Storage
- Query Languages and Interfaces
- Scalability and Performance Considerations
- Transaction Management: ACID vs BASE
- Use Cases Best Suited for SQL
- Use Cases Best Suited for NoSQL
- Cost and Maintenance Factors
- Popular SQL and NoSQL Databases
- Hybrid Approaches and Polyglot Persistence
- Summary and Decision Framework
Introduction Understanding SQL and NoSQL Databases
In the digital age, data has become one of the most valuable assets for organizations across all industries. From customer interactions and financial records to product inventories and user behavior, modern businesses rely heavily on databases to efficiently store, manage, and retrieve vast amounts of information. Database Training emphasizes that the way data is structured and accessed plays a critical role in application performance, scalability, and overall user experience. A well-designed schema and efficient query strategies ensure responsiveness and reliability across diverse workloads. Two major types of databases dominate the data management landscape: SQL (Structured Query Language) and NoSQL (Not Only SQL). SQL databases have been the backbone of enterprise data systems for decades, known for their robustness, consistency, and support for complex queries.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Data Models Relational vs Non Relational Data
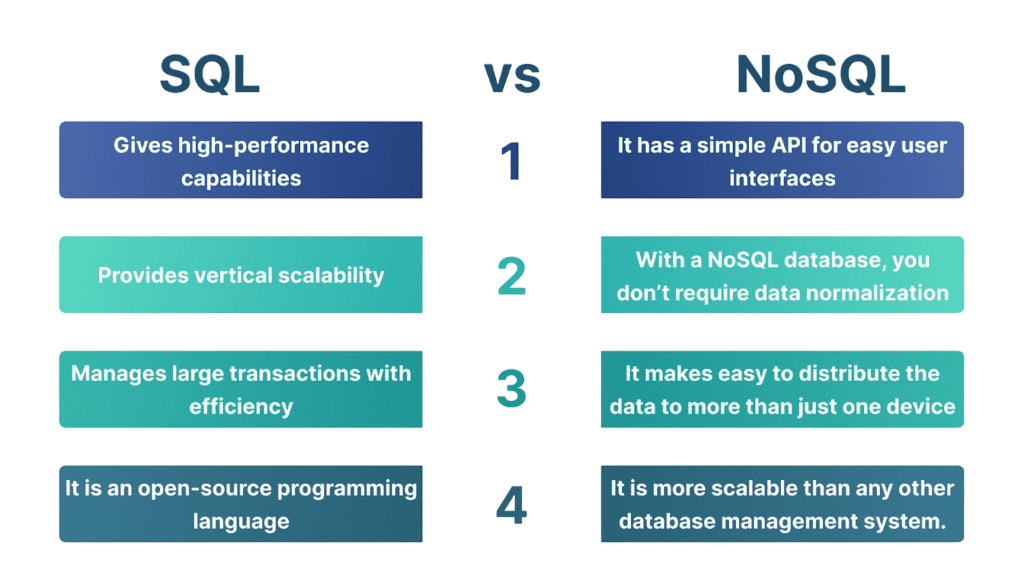
Relational vs Non Relational Data field of database management, two main types stand out: SQL and NoSQL databases. Each has its own way of storing and recovering data. SQL databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle, use a structured model. Here, the data is conducted in tables with set schemas, including rows and columns connected by primary and foreign keys. On the other hand, NoSQL databases provide more flexible data models. MongoDB and its Queries. Document-based systems such as MongoDB store data in documents like JSON. Key-price stores such as Redis allow for quick lookups. Wide-column stores such as Cassandra Group column families. Graphs such as Neo4j represent data using database-connected nodes and edges. This diversity allows organizations to select database solutions that provide scalability, performance, and flexibility in various technology environments that meet their specific data management needs.
Schema Flexibility and Data Storage
- Use rigid schemas requiring precise definitions of columns and data types before insertion.
- Structure enforces data integrity and works best for applications with stable schemas.
- Adding new attributes often requires schema migration, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Feature schema-less or flexible schemas that support varied and evolving data structures.
- Ideal for applications like content management systems, IoT devices, and mobile apps.
- New fields can be added dynamically without disrupting existing records, offering greater flexibility.
SQL Databases:
NoSQL Databases:
Query Languages and Interfaces
Querying and Language Support:
- Leverage Structured Query Language (SQL), a standardized and mature language for data manipulation and retrieval.
- Supports operations like complex joins, aggregations, filtering, and transactions, making it ideal for relational data models.
- Widespread adoption ensures strong tooling, documentation, and developer familiarity.
- Use varied querying methods, often tailored to the data model they support:
- MongoDB: Employs a JSON-like query syntax suitable for document-based models.
- Cassandra: Uses Cassandra Query Language (CQL), similar to SQL but optimized for wide-column stores.
- Neo4j: Implements Cypher, a powerful graph query language designed for traversing relationships.
- Provides expressive and flexible APIs geared towards specific application needs, often sacrificing standardization for agility.
- Structured Data: Best suited for environments with well-defined and consistent data schemas.
- Complex Queries: Supports joins, subqueries, and aggregations for powerful relational operations.
- Transactional Integrity: ACID-compliant systems ideal for banking, accounting, and inventory tracking.
- Data Consistency: Critical for mission-sensitive applications where accuracy is paramount.
- Mature Ecosystems: Enterprises benefit from decades of evolution in tooling, integration, and reliability.
- ERP Systems: Manage interconnected modules like finance, HR, and supply chain with high data consistency.
- CRM Platforms: Track customer interactions, sales pipelines, and support activities with relational integrity.
- E-commerce Platforms: Handle complex product catalogs, transactions, and inventory using relational queries.
- Hotel/Airline Reservation Systems: Coordinate bookings, availability, and customer data with transactional safeguards.
- Unstructured or Semi-Structured Data: Ideal for managing massive volumes of diverse data types (JSON, XML, etc.).
- Rapid Development: Schema flexibility enables faster prototyping and iterative design perfect for agile workflows.
- Horizontal Scalability: Cassandra Keyspace Designed for distributed architectures that scale seamlessly across multiple nodes.
- Schema Flexibility: Supports dynamic attributes, enabling adaptable data models without migration overhead.
- High Throughput & Availability: Optimized for performance under heavy concurrent workloads with built-in fault tolerance.
- Real-Time Analytics: Ingest and analyze streaming data from logs, sensors, or user activity.
- Social Networks: Handle dynamic user profiles, relationships, and content feeds with graph or document stores.
- Recommendation Engines: Store user behavior and preferences to generate personalized suggestions.
- Content Management Systems: Flexibly manage articles, images, and metadata without strict schema constraints.
- IoT Data Ingestion: Capture diverse device telemetry in high volumes from edge networks.
- Chat & Messaging Platforms: Prioritize low-latency delivery and scalability for real-time communication.
- An e-commerce site might use SQL for order and payment management and NoSQL for product recommendations.
- A social app may use PostgreSQL for user profiles and Cassandra for message streams.
SQL Databases:
NoSQL Databases:
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Scalability and Performance Considerations
In the world of database technologies, SQL and NoSQL databases have different scaling methods that serve various organizational needs. Traditional SQL databases usually scale by adding resources to a single server, although some newer versions now allow for more complex horizontal scaling. On the other hand, NoSQL databases are designed for horizontal scaling from the start.
Transaction Management: ACID vs BASE
SQL and NoSQL databases use different transaction models that serve various technological needs. SQL databases follow ACID properties. This means transactions are atomic, so all steps either succeed or fail together. Database Training. They are consistent, which maintains data integrity. They are isolated, preventing interference between simultaneous transactions. They are durable, ensuring that committed data is permanently saved. On the other hand, NoSQL databases use the BASE model. This model focuses on basic availability, recognizes that system states can be soft and evolving, and accepts eventual consistency, meaning data updates may happen gradually. While ACID properties make SQL databases suitable for critical financial systems that need precise data management, the BASE approach fits real-time applications, such as social media platforms and content delivery networks, where immediate availability and flexibility are crucial. This key difference shows how database designs aim to meet specific performance and reliability requirements across different technological environments.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Use Cases Best Suited for SQL
Use Cases of SQL Databases:
Examples of SQL Applications:
Use Cases Best Suited for NoSQL
Use Cases of NoSQL Databases:
Examples of NoSQL Applications:
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Cost and Maintenance Factors
In the changing world of database management, organizations must make important choices between SQL and NoSQL solutions. Traditional SQL databases are powerful, but they often involve high licensing costs from companies like Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server. They also need skilled database administrators to perform well. Apache Cassandra Architecture. These systems generally rely heavily on hardware, which can create infrastructure problems. On the other hand, NoSQL databases provide a more flexible option. Many of these platforms are open-source and cloud-based, which allows for cost-effective scaling and easier management of growing datasets. However, NoSQL solutions come with their own challenges. They may require specialized technical skills and often lack the standardization of traditional SQL environments. This can make long-term system maintenance and integration more complicated.
Popular SQL and NoSQL Databases
In the fast-changing world of database management, organizations have many options in both SQL and NoSQL technologies. Traditional SQL databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and Oracle Database still provide strong, structured data solutions for complex enterprise needs. MongoDB vs SQL. Alongside these, NoSQL databases such as MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, Neo4j, and Couchbase present new ways to store data, meeting various architectural needs from document-based to graph-oriented systems. Modern cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud have made database management easier by offering managed versions of these databases. This significantly lowers operational complexity and maintenance for businesses that need scalable and flexible data infrastructure solutions.
Hybrid Approaches and Polyglot Persistence
Modern applications often blend SQL and NoSQL technologies. This strategy is known as polyglot persistence, where different databases are used for different needs within the same application.
This approach offers flexibility and leverages the strengths of each database type. Challenges include data integration, consistency, and developer expertise across multiple platforms.
Summary and Decision Framework
Choose SQL when your application relies on clearly organized data that must remain consistent at all times. SQL databases are great at handling structured data, which means data stored in tables with clear relationships. For example, banking apps that track accounts, transactions, and customer information depend on SQL’s ability to keep data accurate and reliable. Database Training. When you need to run complex queries to identify patterns or create reports, SQL is effective. Think about inventory management systems or customer relationship management (CRM) tools. These systems need precise, real-time updates and complex joins between data sets; SQL is best suited for this task. It is also a strong option if data integrity is important, like in healthcare or finance, where mistakes can have serious consequences. Choosing SQL creates a solid foundation for applications that need strict consistency and detailed data control. In contrast, NoSQL is built for flexibility and speed. It works well with applications that deal with large amounts of messy, unstructured, or rapidly changing data. Imagine a social media platform that manages millions of posts, photos, and videos each day. This data varies greatly and doesn’t fit neatly into columns and rows. NoSQL databases, such as document stores or key-value pairs, allow developers to store data in more natural ways, like in JSON or XML formats. They are designed to scale quickly across multiple servers, making them ideal for big data projects.This speed and adaptability make NoSQL a great choice for applications that need to grow quickly and manage large, unstructured data.


