- Definition of DBMS
- Types of database management system
- Functions of DBMS
- DBMS vs File System
- Components of DBMS
- Data Independence
- Data Models
- DBMS Examples
- Applications of DBMS
- Conclusion
Definition of DBMS
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that enables users to define, create, maintain, and control access to databases. It acts as an intermediary between end-users and the database, ensuring that data is efficiently stored, retrieved, and managed while maintaining data integrity and security. The primary purpose of a Data Storage Management to provide a systematic and organized way to manage large amounts of data, making it easily accessible for various applications and users. Through Database Training , individuals can learn how to effectively use a DBMS, understand different types of databases it supports (such as relational, NoSQL, and hierarchical), such as relational, hierarchical, network, and object-oriented databases, with relational DBMS (RDBMS) being the most widely used. In an RDBMS, data is organized into tables (relations) consisting of rows and columns, and SQL (Structured Query Language) is typically used for data manipulation. Key functions of a DBMS include data storage, data retrieval, update, and administration. It enforces rules to maintain data consistency, supports concurrent user access while preventing conflicts, and provides backup and recovery mechanisms to protect data retrieval from loss or corruption.A DBMS also offers security features by controlling user permissions and access rights to safeguard sensitive information. Through data abstraction, it hides the complexity of Data Storage Management from users, allowing them to interact with data at a logical level rather than worrying about physical storage details.Examples of popular DBMS software include Oracle Database, MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and IBM Db2.By centralizing data management, a DBMS reduces redundancy, improves data sharing, enhances data integrity, and supports complex queries and reporting. It is a critical component in virtually all modern information systems, from small applications to large enterprise solutions, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on reliable and timely data.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
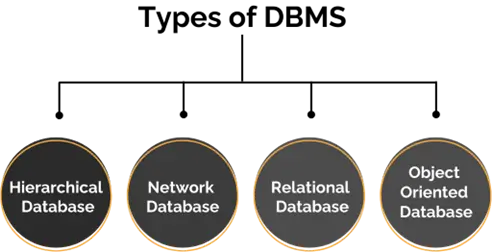
Types of Database Management System
DBMSs can be classified based on the data model they support. The primary types include
- Hierarchical DBMS: Organizes data in a tree-like structure.Data is stored in parent-child relationships.
- Network DBMS: Uses a graph structure to allow multiple parent-child
- Relational DBMS (RDBMS): Stores data in tables (relations). Uses Structured Query Language (SQL) for data manipulation. Most widely used type. In contrast, MongoDB and its Queries .
- Object-Oriented DBMS: Integrates object-oriented programming with database technology.Stores data retrieval in objects as used in object-oriented programming.
- Document-Oriented and NoSQL DBMS: Designed for unstructured and semi-structured data.
Functions of DBMS
- Data Storage Management: Efficient storage and retrieval of data.
- Data Manipulation: Provides query languages like SQL to insert, update, and delete data.
- Data Security and Authorization: Ensures that only authorized users access or modify Database Management
- Data Integrity Management: Maintains consistency and accuracy.
- Concurrency Control: Supports simultaneous data access by multiple users.
- Backup and Recovery: Maintains data safety in case of failures.
- Transaction Management: Ensures ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties.
- Data Dictionary Management: Maintains metadata (data about data).
- Hardware: Physical devices like servers, storage devices, and network infrastructure.
- Software: The DBMS software itself, which includes utilities, query processors, and reporting tools.
- Data: The core component stored data, organized as per a model.
- Database Access Language: Languages like SQL used to interact with the Database Training
- Users: Database Administrator (DBA): Manages the DBMS and ensures its smooth operation.
- Application Programmers: Develop applications that interact with the DBMS.
- End Users: Use applications to access and manipulate data.
- Hierarchical Model: Data is arranged in a tree-like structure.
- Network Model: Allows many-to-many relationships using pointers.
- Relational Model: Uses tables with rows and columns.
- Entity-Relationship (ER) Model: Uses entities and relationships to visually represent data.
- Object-Oriented Model: Integrates database capabilities with object programming languages.
- Oracle Database: Highly scalable RDBMS with robust features.
- MySQL: Open-source and widely used, especially for web applications.
- Microsoft SQL Server: Enterprise-level support and integration with Microsoft tools.
- PostgreSQL: Open-source and feature-rich, supports DBMS vs RDBMS vs NoSQL complex queries.
- MongoDB: NoSQL database used for unstructured and semi-structured data.
- IBM DB2: Optimized for high-volume data transactions.
- SQLite: Lightweight, serverless, ideal for mobile and embedded systems.
- Banking and Finance: Account management, transactions, risk analysis.Fraud detection and audit trails.
- Education: Student records, exam schedules, course materials.Online learning platforms and resource tracking.
- Healthcare: Patient records, treatment history, billing.Integration with diagnostic types of Joins in SQL Server and telemedicine platforms.
- Telecommunication: Call records, billing systems, customer information. Network management and user behavior analytics.
- Retail and E-commerce: Inventory, order tracking, customer profiles. Recommendation systems and dynamic pricing.
- Government: Identity management, tax records, public services. Land records, policy databases, and voting systems.
- Media and Entertainment : Content storage, user analytics, subscription management.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
DBMS vs File System
| Feature | DBMS | File System |
|---|---|---|
| Data Redundancy | Reduced | High |
| Data Access | Complex queries (SQL) | Manual programming required |
| Data Integrity | Enforced by constraints | Needs manual handling |
| Concurrency | Controlled by DBMS | Difficult to manage |
| Security | Role-based, user-defined | Limited |
Components of DBMS
Data Independence
Data independence refers to the ability to change the database management schema at one level without affecting the schema at the next higher level. It ensures that changes in how Data Storage Management is stored or organized do not impact how users access or interact with that data. There are two types: logical data independence, which allows changes to the logical schema (like adding new fields or tables) without affecting application programs; and physical data independence, which allows changes to the physical storage or hardware without impacting the logical structure or user queries. Data independence is crucial for maintaining flexibility, reducing maintenance costs, and enabling the Types of database management system to evolve without disrupting business operations or MongoDB Commands Cheat Sheet . It provides a clear separation between the physical storage of data and the way users view and use the data Integrity.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Data Models

DBMS Examples
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Applications of DBMS
Conclusion
A Database Management System (DBMS) is a vital component in the modern data-driven world. It offers an organized, efficient, and secure way of managing large volumes of data. From handling complex queries to supporting multiple users, DBMS enhances data retrieval accessibility, security, and integrity. Despite some costs and complexities, its benefits in scalability, data consistency, and usability make it indispensable for virtually every industry. As organizations continue to evolve in the digital age, the demand for robust types of database management systems grows. DBMSs are crucial not only for operational efficiency but also for strategic Data Storage Management: Whether managing customer data, financial transactions, or academic records, the DBMS offers unmatched flexibility and control. Database Training equips users with the knowledge and skills to efficiently handle these tasks, ensuring optimal use of the DBMS for secure and organized data storage. Understanding Types of database management system is essential not only for database administrators and developers but also for anyone involved in digital systems. As data continues to grow in volume and importance, DBMS will play an increasingly central role in shaping business intelligence, automation, and innovation.