- Introduction to NoSQL
- History and Evolution
- NoSQL vs. RDBMS
- Types of NoSQL Databases
- NoSQL use cases
- Key-Value Stores
- Document-Oriented Databases
- Column-Family Stores
- Graph Databases
- Future of NoSQL
- Conclusion
Introduction to NoSQL
Understanding NoSQL, or “Not Only SQL”, refers to a broad category of database management systems that diverge from traditional relational database structures. Unlike Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS), which store data in rows and columns, NoSQL databases provide flexible schemas and are designed to handle unstructured, semi-structured, or structured data. This flexibility allows NoSQL databases to scale horizontally, making them highly efficient for managing large volumes of data with high availability and low latency.The term “NoSQL” does not mean the absence of SQL, but rather suggests that these databases do not rely solely on SQL for data management. Many NoSQL systems support a form of querying, although not necessarily SQL itself. The key strengths of NoSQL databases lie in their scalability, performance, and adaptability to various data formats, making them ideal for modern applications such as real-time analytics, IoT, and big data platforms.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Today!
History and Evolution
The evolution of NoSQL Relational Database can be traced back to the early 2000s when the demand for scalable and high-performing data storage systems grew exponentially due to the rise of web applications and cloud computing. Traditional RDBMS technologies, while robust and mature, began to show limitations when dealing with massive datasets and distributed systems.
Key Milestones:- Late 1990s – Early 2000s: The explosive growth of internet companies like Amazon, Google, and Facebook created challenges that relational databases could not handle effectively. These companies started developing their own data storage solutions.
- 2006–2009: The Understanding NoSQL was popularized by Johan Oskarsson in 2009, who organized an event to discuss distributed, open-source databases.
- 2008–2012: This period saw the rise of several major NoSQL databases, including MongoDB, Cassandra, CouchDB, and Redis.
- 2013–Present: NoSQL databases became mainstream, supported by large organizations and cloud providers, with increasing integration into enterprise systems.
- Key-Value Stores
- Document-Oriented Databases
- Column-Family Stores
- Graph Databases
- Real-Time Analytics: Platforms like e-commerce and gaming use NoSQL to process vast amounts of clickstream data and user activity in real time.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Flexible schemas in document-oriented databases allow easy content updates and diverse data formats.
- IoT Applications: NoSQL handles time-series data generated by connected devices efficiently.
- Personalization Engines: NoSQL databases store user profiles, behavior patterns, and preferences to power recommendation engines.
- Mobile Applications: Apps with offline support and rapid synchronization across devices benefit from the performance and schema flexibility of NoSQL.
- Caching systems
- Session storage
- Real-time data ingestion
- Leaderboards in gaming apps
- Time-series data
- Logging and monitoring
- Telecom data
- Financial analytics
- Social networks
- Fraud detection
- Recommendation engines
- Network topology analysis
- Hybrid Databases: As organizations aim for both consistency and scalability, many NoSQL vendors are building hybrid models that support some Understanding NoSQL level of SQL querying and ACID transactions. MongoDB, for example, offers multi-document transactions, bridging the gap between relational and non-relational paradigms.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: NoSQL databases are increasingly being used as backends for AI/ML applications. Their ability to handle varied data formats makes them ideal for feeding large datasets into machine learning pipelines.
- Serverless and Cloud-Native Architectures :Cloud providers offer fully managed NoSQL solutions with pay-as-you-go pricing, auto-scaling, and global replication. This makes it easier for developers to build applications without worrying about infrastructure management.
- Multi-Model Databases: Some modern NoSQL databases, like ArangoDB and OrientDB, support multiple data models (graph + document + key-value) within a single engine, allowing developers to leverage different paradigms without switching databases.
- Improved Tooling and Standards :As adoption grows, so does the ecosystem. Better developer tools, querying languages, visualization platforms, and connectors are making NoSQL more accessible to non-experts.
The NoSQL movement emerged not as a replacement for RDBMS, but as a complement offering tools better suited for specific types of workloads, especially those involving large-scale, distributed, and dynamic data.
NoSQL vs. RDBMS
| Feature | NoSQL | RDBMS |
|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Flexible (document, key-value, column, graph) | Fixed schema (tables, rows) |
| Scalability | Horizontal (adding more servers) | Vertical (upgrading existing hardware) |
| Query Language | Varied (no standard language) | Standardized SQL |
| Transactions | Limited or eventual consistency (BASE) | Strong consistency (ACID) |
| Performance | Optimized for large datasets, high throughput | Optimized for complex queries and joins |
| Use Cases | Big Data, real-time apps, content management | Banking, CRM, ERP, accounting |
RDBMSs are ideal for applications where data integrity and structured querying capabilities are paramount.Types of NoSQL Databases, NoSQL databases, on the other hand, are best suited for environments requiring flexible data models and high-speed data ingestion.
Types of NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases fall into four primary categories:
Each type is tailored to specific use cases and data storage needs.
To Explore Database in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Database Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
NoSQL Use Cases
NoSQL databases have been adopted across industries and applications. Here are a few typical scenarios:
Key-Value Stores
Key-value stores are the simplest type of NoSQL database. Each item in the database is stored as a pair: a unique key and its associated value. This model allows for extremely fast lookups and is ideal for scenarios requiring high-speed read and write operations.
Examples: Redis, Amazon DynamoDB, Riak Use Cases:The key-value model’s simplicity is both its strength and limitation—it performs exceptionally well when accessing data by key but lacks the complex querying capabilities found in other database models.
Document-Oriented Databases
Document databases store data as documents, typically in formats like JSON, BSON, or XML. Each document is self-describing and can contain nested structures such as arrays and sub-documents.
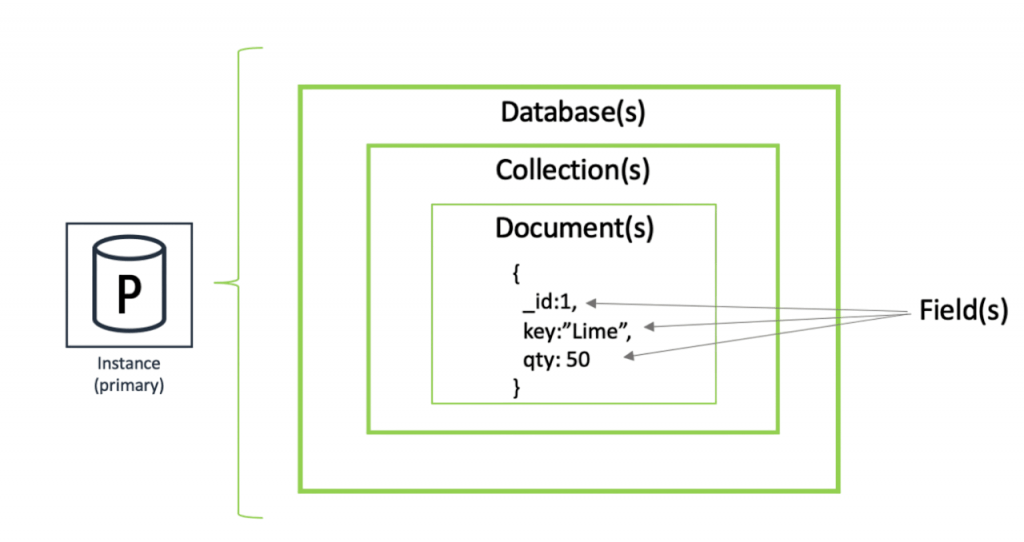
Column-Family Stores
Column-family databases store data in columns rather than rows. This model is suitable for queries that involve reading large amounts of data but only specific columns. Each column family contains rows with keys, and each row can have multiple columns. Examples:Apache Cassandra, HBase, ScyllaDB
Use Cases:Column stores excel in write-heavy workloads and are designed to handle large-scale data with high availability and partition tolerance.
Graph Databases
Graph databases are designed to represent and query relationships among data. They use graph structures with nodes, edges, and properties to model complex, interrelated data.
Examples:Neo4j, Amazon Neptune, OrientDB
Use Cases:Graphs make it easy to traverse relationships and are highly efficient for use cases where connectivity between data points is as important as the data itself.
Want to Learn About Database? Explore Our Database Interview Questions and Answers Featuring the Most Frequently Asked Questions in Job Interviews.
Future of NoSQL
The future of NoSQL looks promising as the demand for scalable and flexible databases continues to rise. Some key trends and developments include:
Conclusion
NoSQL databases represent a significant shift in how data is stored, accessed, and scaled. They have evolved to meet the demands of modern, data-intensive applications that require flexibility, speed, and horizontal scalability. While they may not replace relational databases entirely, Understanding NoSQL systems fill critical gaps where traditional systems fall short.Understanding the various types key-value, document-oriented, column-family, and graph and their use cases helps in selecting the right database for a given application. As digital transformation accelerates and the need for real-time, data-driven decision-making grows, NoSQL will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of Relational Database management.Types of NoSQL Databases ,NoSQL databases have revolutionized how we handle massive, complex, integration and fast-changing data. With various types tailored to different needs key-value, document, column-family, Types of NoSQL Databases semi-structured, Document-Oriented Databases and graph Understanding NoSQL empowers developers to build agile, scalability , and high-performance applications. While challenges exist, the growing ecosystem and evolving best practices ensure NoSQL will remain a vital part of modern data architecture.